Polypropylene pipes are used to equip water supply systems in residential, industrial and administrative buildings. The material used for the production of plastic water conduits belongs to the group of polyolefins and, like all substances in this category, is an environmentally friendly product. The products are distinguished by impact strength, chemical resistance and mechanical strength in different temperature conditions.
Polypropylene pipes for cold and hot water supply have become popular and widely used due to their advantages.
Polypropylene pipes for cold and hot water supply: scope of application
Plastic composite water supply systems are used as a distribution mechanism in public and residential buildings, and are widely used in the agricultural sector to supply the industry with process and drinking water. In addition, polypropylene pipelines can be used to transport chemically active liquids and compressed air.
The technical characteristics of polymers allow them to be used in almost any industry that requires transportation of air and liquids:
- for cold water and hot water supply;
- for organizing heating systems;
- to ensure the workflow of hydraulic and compressor equipment;
- as ventilation and climate control equipment;
- for the purpose of heating surfaces;
- for organizing sewerage;
- in land reclamation, artificial irrigation, drainage, etc.
The effectiveness of welded joints of plastic pipelines is close in strength to the quality of welding of metal products. This allows us to consider polypropylene one of the most advantageous building materials for the production and use of pipelines.
Ventilation material
Ventilation pipes ensure the flow of fresh air into the room and the removal of exhaust air: their strength in this case is not the main criterion. The main thing is that these products were lightweight, since they are often supported only by partitions or suspended ceilings.
Residential premises are equipped with pipes with a diameter of 100 or 125 mm; industrial systems will require preliminary calculations. The cross-sectional shape of such products can be square, round, oval or rectangular. The installation process uses the socket method, so no welding machine is required.
Advantages and disadvantages of polypropylene pipes
The reliability and durability of polypropylene pipes for cold and hot water supply largely depends on the quality and performance characteristics of the source material, which is characterized by high strength, elasticity and durability.
The main advantages of polymer pipelines:
- When in contact with water, they do not form salt or alkaline deposits that promote corrosion.
- The diameter of plastic pipes remains unchanged throughout the entire service life.
- The product is environmentally friendly, which especially affects the quality of the transported water.
- The material is chemically inert and non-toxic.
- The composite withstands pressure and short-term temperature changes well.
- Eliminates pressure drop due to friction in the pipes (low roughness).
- Low thermal conductivity.
- In operating mode, no condensation forms on the surface of the pipes.
- High sound insulation properties.
- Composite products are made from an opaque material, which inhibits the formation of algae and light-sensitive bacteria during the transportation of liquids.
- When water freezes in polymer pipelines, their structure is not destroyed, but stretches and is restored when defrosted.
- Installation of polypropylene fittings does not require special skills. The use of sleeve welding allows you to create a tight and durable connection in a few minutes.
- Polymer pipes are 9 times lighter than steel water pipelines.
- Low cost and easy to maintain. Plastic does not require additional heat and waterproofing.
Polypropylene pipes are characterized by increased durability and high operating temperature.
Among the disadvantages of polymer pipes, several positions can be distinguished, these are:
- high linear expansion rates;
- impossibility of installation and operation in low temperature conditions;
- low resistance of the material to ultraviolet radiation;
- The use of plastic products in fire extinguishing systems is not permitted.
The deformation and strength characteristics of plastic pipelines largely depend on the temperature of the transported medium. Therefore, the design of pressure polymer networks must be carried out taking into account the operating temperature, technical conditions for performing the work and the planned service life of the structure.
Criterias of choice
The main recommendation when purchasing polypropylene pipes is to select products from one batch of one manufacturer. The composition of the substance may partially change and the quality of pipes in different deliveries will be different. This will affect the butt joints and the durability of the structure. Purchasing pipes from different manufacturers may result in the connecting elements being unsuitable due to size differences. Each manufacturer has its own recipe for the substance; a discrepancy can lead to failure of the entire plumbing system.
You should also pay attention to the following indicators:
- Estimated fluid temperature in the system. For hot water supply, it is better to select reinforced products.
- Estimated pressure. When heated, the material becomes less durable and may burst.
- The diameter must correspond to the area where the pipes are installed.
You should not save if short-term temperature or pressure surges occur in the system, which sometimes happens in centralized systems. In this case, it is better to buy reinforced, expensive polypropylene, which has a longer service life.
In home systems, where the pressure usually does not exceed 1 MPa, you can use ordinary pipes, but follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding what kind of water the product is intended for - hot or cold.
Types of polypropylene pipes
When laying out pipelines for water supply and heating, one of the main factors is the choice of components. Based on their structure and technical characteristics, polymeric materials are divided into several types:
- Single-layer pressure pipe for cold water with an operating temperature of +20°C and an allowed pressure of up to 10 bar.
- Single-layer for hot and cold water supply with maximum pressure up to 20 bar and operating temperature up to +75°C.
- Multilayer, reinforced with perforated aluminum foil, temperature up to +90°C, pressure - 20 bar.
- Multilayer, fiberglass reinforced - up to +90°C, 20-25 bar.
According to the material of manufacture
In accordance with the international standard EN ISO 15874-2013 and Russian GOST 32415-2013, pressure pipes and connecting fittings are made from the following materials:
- PP-N (Type 1 PP-G) - homopolymers;
- PP-V (Type 2 PP-B) - block copolymers;
- PP-R (Type 3 PP-R) - random copolymers;
- PP-RCT (Type 4 PP) are random copolymers with modified crystallinity and high heat resistance.
Fittings of classes 1-4 must be suitable for transporting hot and cold water for 50 years.
By type of reinforcement
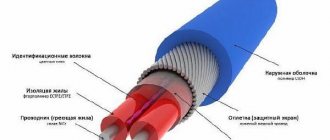
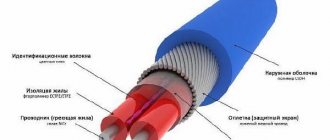
The pipe, whose structure is improved by perforated aluminum foil, consists of three layers. During the manufacturing process, the inside of the pipe is connected to evenly spaced perforated foil and covered with a layer of polymer on top.
Reinforcement reduces the coefficient of thermal expansion of structures.
The outer contour is needed to protect the aluminum perforated layer from damage. The middle part of the foil forms an intra-diffusion barrier to protect against air penetration into closed heating systems.
The low value of thermal linear expansion (less than that of single-layer pipes) makes the product more rigid, which reduces its sagging and allows for a reduction in the volume of fasteners and expansion joints.
Pipes reinforced with fiberglass have the same properties as those with an aluminum layer. The presence of a middle layer gives such reinforcement additional strength and reduces the linear elongation.
Main technical characteristics
Polypropylene is an artificial material with high physical and chemical characteristics, obtained by the polymerization of synthetic substances. Pipes made from such a composite have the following properties:
- density - 0.92 kg/cm³;
- resistance to chemically active liquids;
- bending and tensile-compressive strength;
- high levels of electrical and thermal insulation;
- wear resistance;
- permissible temperature range - -15...+120°С;
- plastic deformation to the conditional yield strength - 50%;
- low linear elongation when heated;
- heat capacity 2.0 kJ/(kg.°C);
- low thermal conductivity.
Product color
There are PPR pipes on the market made from materials of different colors. Is there a difference when choosing? Can we say that a gray pipe is better than a white one?
Experts are divided over this indicator: some believe that shades do not affect anything and that this is just a marketing ploy. However, there are many descriptions of products that differ in color, which present different operational, performance and economic characteristics.
For convenience, the estimates are tabulated:
| Pipe color | Performance properties |
| White | Long service life. The maximum pressure withstand is twenty-five bar. Low cost. Not subject to corrosion. |
| Grey | Ability to withstand elevated temperatures Ability to withstand aggressive environments: acidic and alkaline. Long period of operation. Environmentally friendly. High level of tightness. |
| Black | Immunity to ultraviolet rays. Ability to withstand aggressive environments. Resistance to drying out. Increased strength |
| Green | Cheap option, low operating pressure. Suitable, perhaps, for a country shower and watering the garden. |
Technical requirements according to GOST
According to established norms and standard requirements for the manufacture and use of polypropylene products for plumbing, heating and hot water supply, materials must meet the following characteristics:
- Pipe used to transport liquids must have smooth internal and external surfaces.
- Small longitudinal defects are allowed on the polymer profile: waviness, stripes that do not protrude beyond the limits of permissible deviations.
- The presence of cracks, swelling, chips, cavities, and foreign inclusions on the internal, end and external surfaces is not allowed.
- Changes in yield strength from the original - no more than 20%.
- Vicat creep temperature ≤ +80…+115°С.
- The height of the profile after removing the sprues should be within the range of 0.3-0.5 mm.
- Fitting joints must ensure tightness for 5000-10000 cycles.
The water pipe used must have smooth internal and external surfaces.
Sound absorption
Excellent sound absorption is another reason for purchasing such products, which is simply irreplaceable in cases of transporting water or coolant. Polypropylene is not afraid of temperature fluctuations and pressure changes. Due to their low thermal conductivity, the pipes are characterized by the absence of condensation. The positive aspects of polypropylene products for cold water supply systems include their low weight, which greatly facilitates their transportation and loading and unloading.
To carry out installation work, the participation of two craftsmen and the use of a special soldering iron are required. It is not practical to use additional equipment. The installation of a water supply system equipped with polypropylene cylindrical products proceeds much faster than the installation of a similar structure with metal pipes.
Marking of polypropylene pipes
Technical marking of materials for the consumer is necessary for the correct calculation and selection of the required range of plastic pipes, which depends on the purpose and operating conditions of the product. There is a basic article and several types of additional designations.
The standard designation of a polymer product is as follows:
- the word "pipe";
- abbreviated name of the material;
- SDR is the dimensional ratio of the optimal outer diameter to the wall thickness;
- external profile size;
- wall thickness;
- operating class;
- maximum working pressure;
- standard number.
For example, polypropylene random copolymer SDR 11, external size 20 mm, wall thickness 1.9 mm, class 1, optimal pressure 1.0 MPa:
Pipe PP-R SDR 11-20´ 1.9 class 1/1.0 MPa GOST R 52134-2003.
Marking can also be done indicating the structure of the product, type of material, nominal pressure, category and area of application.
Product structure:
- S—single-layer pipe;
- M - multilayer;
- TI - with thermal insulation;
- PP - standard polypropylene;
- PP-RP - products that can withstand high pressure.
Material type:
- PPB - increased mechanical strength, for hot water in underfloor heating systems;
- PPH - with increased internal diameter (ventilation and cold water supply);
- PPR is a universal pipe with elevated operating temperatures.
Pressure indicator:
- PN 10 - operating pressure 1.0 MPa, temperature - +20...+45°C;
- PN 16 - up to +60°C, 1.6 MPa;
- PN 20 - pressure 2 MPa, temperature - +95°C;
- PN 25 - for heating and hot water supply - 2.5 MPa, +95°C.
Pipe class:
- class 1 - up to 60°C - water supply;
- class 2 - pipelines up to 70°C;
- class 3 - up to 60°C - “warm floor”;
- class 4 - heating, up to 70°C;
- class 5 - up to 90°C, heating;
- class XB - cold water.
Marking of polymer pipes for water supply allows the buyer to quickly determine whether this product is suitable for him or not.
The area of application of the composite is indicated by the color of the product:
- white - water pipes;
- gray - heating system, hot and cold water;
- black - sewerage, drainage systems;
- green - individual water supply within the boundaries of a personal plot.
As additional parameters, depending on the supplier of materials, the pipes may indicate the manufacturer’s trademark, the presence of a certificate, the date of manufacture and the serial number of the batch.
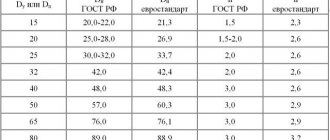
Table of standard sizes of polypropylene pipes
Table of the main parameters of polymer pipes for cold and hot water supply.
| Diameter, mm | Conditional bore, mm | PN10 shell thickness, mm | PN20 shell thickness, mm | Weight of 1 m/p pipe, kg |
| 20 | 15 | 1,9 | 3,4 | 0,106-0,172 |
| 25 | 20 | 2,4 | 4,3 | 0,164-0,226 |
| 32 | 25 | 3,0 | 5,4 | 0,266-0,434 |
| 40 | 32 | 3,7 | 6,7 | 0,412-0,671 |
How to choose a diameter
When choosing pipes, in addition to quality characteristics, you need to take into account the outer and inner diameters of the product, the size of which affects the hydrodynamic properties of the system.
Pipeline capacity depends on many factors, including:
- number of sources;
- purpose of the water supply;
- pressure force;
- maximum load;
- number of branches (consumers);
- distance between the starting and ending connection points.
Connection to the central water supply for individual use is made using pipes Ø 32 mm. For internal networks, profiles with an outer diameter of 16-25 mm are used.
In everyday life, water pipes from 20 to 32 mm are considered the most used.
Popular manufacturers
On the domestic PPR market, water pipes are represented by products of Russian and foreign manufacturers. There is no particular difference between them; the plastic production technology is used in all cases. However, it is extremely important to look at the numbers written on the product label. Manufacturers often add various plasticizers to their plastic to enhance certain characteristics.
Popular manufacturers of polypropylene pipes
Among the popular manufacturers of the pipes in question are:
- Banninger and Rehau (Germany);
- Valtec (Italy);
- Ecoplastic FIBER (Netherlands);
- TEBO and Vesbo (Türkiye);
- BLUE OCEAN (China);
- ProAqua and Politek (Russia)
The quality of these manufacturers is almost the same. But for German pipes you will have to pay a little more due to the brand, and for Chinese ones, on the contrary, a little less. At the same time, Russian analogues also maintain their brand, having a very affordable cost per linear meter.
Which polypropylene pipes are better for water supply?
In order to find out which type of product is most suitable for hot and cold water, you must first choose the manufacturer of the material, read the recommendations and, based on this, make the right choice.
For hot water
When installing hot water supply, it must be taken into account that polypropylene pipes have a relatively high thermal expansion. Thus, with an increase in temperature by 10°C, the length of unreinforced products increases by 1.25 mm/m, and improved ones by an average of 0.32 mm/m.
In this regard, for the equipment of such systems it is necessary to use exclusively reinforced types of propylene pipes.
The temperature of supplied hot water for individual users is within +45…+75°C.
Therefore, to ensure uninterrupted supply, pipes designed for use in this temperature regime are suitable - these are grades PN 20 and PN 25 with an optimal pressure of 2.0-2.5 MPa.
For cold water
Unlike hot water, both single-layer and multi-layer pipes are suitable for cold supply. The main requirement for laying a water pipeline is the pressure of the liquid and the distance to the source.
In terms of price-quality ratio, more suitable materials are single-layer pipes with an operating temperature of up to 20°C and an allowed pressure of up to 10 bar. According to the designation, such pipes belong to service class 1, white or gray, grades PN 10 or PN 16.
Features of the use of polypropylene pipes in the heating system
When determining which brand of pipe can be used for heating, it is necessary to take into account the supply temperature, which depends on the characteristics of the installed heating devices, their technical capabilities, the type of expansion tank and the method of recharging the system.
The higher the water temperature, the shorter the service life of propylene pipes for water supply and heating.
In an apartment, the cross-section of polypropylene water pipes should be equal to the internal diameter of the supply pipelines (risers). It should be taken into account that the wall thickness of polymer pipes is greater than that of steel reinforcement. In a private house, central wiring is carried out with a Ø 32 mm profile, connection to radiators is carried out using pipes with a cross-section of 20-25 mm.
For individual heating, multilayer reinforced products are used, but it must be remembered that for products with aluminum foil, the linear expansion is much greater than for products with a fiberglass layer.
When using a floor heating system in a private house, the pipes are calculated based on the design temperature of the structure, the type of room and the area of the heated area. The heat exchange limit is within the range of +35…+45°C.
Aluminum reinforcement
There are solid and perforated samples of this type. The perforation itself looks like a fine aluminum mesh. The process of extruding polypropylene is accompanied by the ingress of a fluid and viscous substance onto the perforation, which leads to adhesion of the metal and the polymer. Thanks to aluminum reinforcement, a noticeable reduction in the coefficient of thermal expansion is achieved.
However, such engineering systems are installed with some difficulties. When carrying out socket welding, it will be necessary to remove the aluminum shell and the outer polymer layer before starting work. Subsequently, the pipe is cleaned according to the parameter of the inner diameter of the fitting.
As for pipes in which the outer layer does not need to be removed before installation, they have the following disadvantages:
- The fitting can only fix the outer part of the product: usually this is half the wall thickness.
- The welding machine must have a nozzle.
- When the pipe is cut, it must also be terminated.
Installation and wiring - what are the nuances?
The structures of polypropylene pipes are one-piece. They are mounted using diffusion welding. Special fittings are used to install internal outlets. When connecting plastic and metal parts (faucets, mixers), corner joints with pressed-in brass segments are used.
Polymer pipelines are suitable for all types of installation:
- in separate channels and shafts;
- exposed wiring on the surface of the walls;
- closed laying in a layer of cement-sand screed or plaster.
Work order:
- Plastic pipes are cut with special scissors included in the equipment assembly kit.
- Measure the distance with a tape measure and use a pencil or marker to transfer this value to the surface of the product.
- The junction area is thoroughly degreased. Pipe markings that fall within the installation area must also be removed.
- Nozzles are installed on the unit and plugged into the network. The heating temperature regulator is set to 260°C. The heating time of the material is controlled by a burning light bulb. When the operating temperature is reached, the indicator goes out.
- The prepared parts are put on welding attachments. Wait 7 seconds and remove the blanks.
- Quickly, without rotation, the pipe is joined to the fitting and pushed to the specified level.
- Before installation, the finished connection must cool and gain strength (2 minutes).
- It is better to pre-assemble complex components, such as a manifold, branches, and then install the entire set in place.
- When installing water pipelines on walls and ceilings, it is not recommended to use fixed supports.
Reinforcement with fiberglass
The PPR-FB-PPR marking indicates that such a pipe consists of two polypropylene layers separated by a fiberglass gasket. This type of pipe is also called fiberglass.
Fiberglass reinforcement has some advantages:
- There is no need for calibration or cleaning during installation.
- Soldering here is the same as when connecting solid plastic or any polymer-protected pipes. This helps to increase the speed of work and reduce its cost.
- Thanks to fiberglass, delamination of polypropylene pipes is not observed. This is due to the uniformity of its structure, because the central fiberglass layer is literally fused into the polypropylene structure.
- Due to fiberglass, products become more rigid.
The disadvantage of fiberglass-type pipes is that they have greater thermal elongation when compared with pipes with aluminum reinforcement.
What determines the service life
The main quality parameter of composite pressure pipes is their service life, which depends on the characteristics of the source material and the conditions of use - operating temperature and pressure.
Under standard operating requirements, the operating cycle of water pipelines for cold and hot water supply is 25-50 years, respectively.
Standard conditions provide for the use of water supply systems within the boundaries of the recommendations provided by the manufacturer. Exceeding the permissible temperature and pressure leads to softening and rupture of the material structure, which affects the service life of the product.