The technical characteristics of HDPE type pipes depend on the physical properties of the structural material used in the manufacturing process of such products. Moreover, in this case, the material is a special type of structural polymers - low-density polyethylene.
Therefore, we invite our readers to study the properties of this material and get acquainted with the technical characteristics and range of HDPE pipes. This information will be of interest to a wide range of visitors to our resource. After all, HDPE pipes are a fairly common component of free-flow and pressure pipelines of industrial and domestic type.
Low pressure polyethylene (HDPE) as a structural material for pipes
Classic polyethylene is produced by polymerization of organic ethylene gas. The molecules of this gas, under certain conditions, are combined into polymer chains. The result is a product with unique characteristics. Low-density polyethylene is produced according to the same scheme, only not under ephemeral “conditions”, but at specific values of pressure (20 atmospheres) and temperature (150 degrees Celsius), maintained in a special pressure chamber.
As a result, under the influence of the specified pressure and temperature, a completely different product is obtained from ethylene molecules, the properties of which determine the following advantages and disadvantages of HDPE type pipes:
- Ability to withstand pressure of tens of atmospheres. The tensile strength of such products is 3-5 MPa.
- Low weight per linear meter of pipe. A cubic meter of HDPE weighs only 900 kilograms.
- Limited operating temperature range. The lower limit is 0°C – at lower temperatures HDPE becomes glassy. The upper limit is 40°C - at higher temperatures the HDPE pipe loses its ring rigidity.
- Relatively low thermal expansion. When heated to the maximum permissible temperature (70°C), any HDPE pipe will increase in size by only three percent.
Of course, such properties of low-density polyethylene limit the use of HDPE pipes.
As a result, products made from this material are used only for laying “cold” water pipelines or “drinking” pipelines. Moreover, these lines are installed either inside the house or in a trench, at depths below the freezing point of the soil.
How are they produced?
HDPE is produced in devices with a pressure below 0.1–2 MPa; temperature 120–150 °C; in the presence of metal halide catalysts (most often a mixture of TiCl4 and R3). Petroleum products are used for the reaction. The degree of crystallization of HDPE is 75–80%.
HDPE products, regardless of size, are made by extrusion, squeezing molten polyethylene through an extruder.
Production technology
First, polymer granules are poured into an extruder and melted while mixing. Then the PE is extruded through the outlet of the extruder, calibrated, and slowly cooled. The finished products are cut and packaged.
HDPE pipes - technical characteristics and operating parameters
According to production standards and construction regulations, HDPE pipes can be used only in four cases, namely:
- For transporting cold (up to 40°C) drinking water;
- For transportation of cold (up to 40°C) process water;
- For transportation of liquid or gaseous media, the temperature does not exceed the same up to 40°C (provided that these media are inert to polyethylene);
- For arranging an insulation layer or a duct for an electrical cable.
Such restrictions on such products are imposed by their technical characteristics - for HDPE pipes there is simply no other application option. After all, as mentioned above, HDPE pipe is capable of maintaining its integrity in the range between zero and 40°C . And if the pipe stays in this temperature range, then the guaranteed service life of the product will be at least 50 years.
In addition to the temperature regime, another parameter affects the operating conditions of the pipes - the type of polymer. After all, the tolerance of internal pressure depends on the type of HDPE.
The characteristics of HDPE pipes in terms of wall resistance are interrelated with the type of structural material in the same way as the characteristics of operating temperature conditions.
Moreover, at the moment, for the manufacture of pipes, such grades as PE 100 (resistance limit - 10 MPa), PE 80 (can be used in systems with pressure up to 75 atmospheres) and PE 63 (limit - 6.3 MPa) are used. Well, such a variety of structural polymers as PE 33, operated at a pressure of less than 3.3 MPa, is practically no longer found in modern water pipelines.
Other operational characteristics of HDPE type pipes depend not on the technical parameters of the product, but on the dimensions of the product range, which determine the throughput, permissible pressure, weight and other qualities of the product.
Therefore, further in the text we will examine the standard sizes of such pipes.
Performance properties of HDPE, their advantages and disadvantages
- HDPE pipes have low thermal conductivity;
- Operating temperature range from -60 to +60 degrees Celsius;
- HDPE is elastic and not subject to cracking;
- Low thermal conductivity in winter prevents freezing;
- transported liquids;
- Polyethylene is lightweight (density 0.93-0.97);
- Physiologically neutral;
- Water resistant;
- Resistant to the negative effects of acidic and alkaline environments, oils and fats;
- Insoluble, but swells to a limited extent in organic solvents.
Due to their high corrosion and chemical resistance, HDPE pipes do not require special coatings to protect them from the aggressive effects of soils. Unlike metal products, they do not require cathodic protection. Since HDPE is environmentally friendly, they do not have a negative impact on soils and the organisms inhabiting them.
The internal surface remains clean, deposits do not accumulate, so the throughput remains unchanged, which ensures high performance of the polyethylene pipeline throughout its entire service life.
HDPE pipes are highly wear-resistant and therefore durable at low cost. The service life is at least 50 years, and the maximum design service life is up to 300 years. Polyethylene products retain their technical characteristics throughout their entire service life.
The ability to thermal expansion limits the use of HDPE pipes for hot water supply and heating systems.
HDPE pipes are resistant to grease-containing and abrasive wastewater and are used for the construction of sewerage systems and collectors. HDPE technical products are used to protect communication cables during underwater and underground installation. Electrical wires are laid in electrical pipelines when laid hidden under concrete and cement. Round and profile HDPE can be used when installing ventilation systems .
Corner connection of HDPE products with markings
Range of HDPE pipes
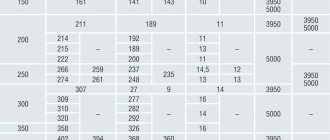
The assortment parameters for polyethylene pipes are specified in a special document - GOST number 18599 of 2001. And the key parameters of the range of such products according to this regulatory document are the wall thickness and diameters of HDPE pipes. Moreover, these indicators are tied to the type of polymer used for the production of pipes and fittings. Thus, the minimum diameter of HDPE pipes made of PE 33 polyethylene is 10 millimeters, and the maximum is 160 millimeters. The wall thickness for PE 33 pipes varies from 2 to 12 millimeters. Such pipes will only survive 3.2 MPa; with a higher load, the product will simply burst .
If the PE 100 grade is used in the production of products, then the cross-sectional dimensions of such products will have completely different dimensions. The minimum diameter, in this case, will be 32 millimeters, and the maximum – one meter. Well, the wall thickness will vary from 1 to 59 millimeters. Through such pipes a liquid or gaseous carrier can be pumped under a pressure of 10 MPa.
Large-sized HDPE pipes of large diameter (up to 1600 millimeters) are made from grades PE 80 and PE 63. Moreover, the minimum diameter of such pipes is only 16 millimeters. The wall thickness of pipes made of PE 80 and PE 63 ranges from 2 to 67 millimeters. Large pipes can pump liquid or gas through themselves under a pressure of 6.3-8 MPa.
The total number of police in the assortment is formed by 34 original products. And this is only based on the diameter of the pipe! Moreover, 15 standard sizes of pipes are produced from PE 33, 30 standard sizes of products from PE 63, 34 products with original diameter dimensions from PE 80, and 26 products from PE 100.
the Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR) coefficient , which is equal to the ratio of the outer diameter of the product to its wall thickness, HDPE pipes are divided into 11 groups. The numerical values of SDR in groups vary from 6 to 41 units. Moreover, each group corresponds to three permissible pressure values, which depend on the specific type of polyethylene.
Thus, with an SDR equal to 41 units (pipe diameters in this case vary from 75 to 1600 millimeters), the permissible pressure for a PE100 pipe is 4 MPa. Well, in the case of a pipe made of PE 63 and SDR21 (diameters, in this case, will range from 40 mm to 1.4 meters), the permissible pressure under these conditions is 5 MPa. As a result, the conclusion suggests itself that even such a technical characteristic as permissible pressure will depend not only on the material of the pipe, but also on its dimensions.
The length of measured sections of HDPE pipes ranges between 5 and 24 meters. However, pipes with a diameter of up to 180 millimeters can also be produced in the form of sections up to 0.5 kilometers long. Of course, in this case the pipe is rolled into a coil.
Options for reliable insulation of polyethylene pipes
- Glass wool is a short-lived but affordable insulation material that requires additional external insulation.
- Basalt insulation is a more functional analogue of the previous material.
- Polystyrene foam - available in shell form, does not require additional insulation, and is suitable for repeated use.
A good option would be to purchase an already insulated HDPE pipe. This is a two-layer structure, where an insulating layer is laid on top of a plastic pipe, covered with an outer shell. However, such products are noticeably more expensive.
Read about Energoflex flexible insulation.
Marking of HDPE pipes type
All of the characteristics mentioned above can be found not only in reference books, but also in special alphanumeric markers applied to the outer surface of the pipe. Accordingly, the ability to read markings facilitates the process of selecting pipes in a warehouse and allows you to avoid errors when assembling the pipeline.
Marking of polyethylene communications is based on displaying the following data on its external side:
- Names of the manufacturing company and designations of the standard to which such products comply. For domestic products, GOST 18599-2001 is used as such a standard
- Names of the material, in international format. That is, immediately after the standard, the product will be marked with the designation of the polyethylene grade: PE100 or PE 80 or PE63.
- The group of numbers following the polymer grade indicates the outer diameter - this value corresponds to the range and is measured in millimeters.
- After the external dimensions, one of the “internal” dimensions is marked on the pipe - the wall thickness of the product, which is measured in millimeters.
- The following symbol informs us about the nominal pressure. Moreover, if the pressure does not go beyond the specified limits, then this product will last in the pipeline for at least half a century.
- In addition to the nominal value, the marking may also indicate the maximum pressure that the HDPE pipe can withstand - the dimensions of this characteristic are indicated in MPa.
- At the very end of the labeling we are informed about the production date and batch number.
In addition to the digital and letter designation, there is also a color marker on the outer surface of the pipe - a blue or yellow stripe. This mark indicates that the pipe belongs to water supply networks (blue stripe) or gas pipelines (yellow stripe).
Application
Depending on the composition, thickness and strength, HDPE pipes are used for the construction of pressure and non-pressure water and gas pipelines, sewers and other systems. To make it easier to determine which pipe is intended for a particular system, a color stripe can be applied to it - blue for water supply and yellow for gas transportation. In addition, every meter, alphanumeric markings are applied to the products, containing a record of their purpose - for drinking or technical purposes.
Technical pipes are most often made:
- Made from second-rate or recycled raw materials, therefore they may be heterogeneous in structure and distribution of properties throughout the entire volume (contain foreign inclusions, voids, minor surface defects). They may also contain foreign toxic substances, so they are not suitable for contact with food.
- Made from technical grade polyethylene, which may contain substances accompanying polymerization reactions (catalysts, esters) and various additives in the form of stabilizers used to make polyethylene stable to various external factors. These substances also make the pipes unsuitable for drinking water supply.
ATTENTION! If the polyethylene pipe is not marked in any way (there are no color or written designations), then it is most likely intended for technical purposes. Such pipes are not suitable for drinking water and the installation of pipelines in which a high pressure of the contents is expected.
Methods for connecting pipes of different diameters
Pipes of different sizes are connected with all kinds of adapter couplings. The easiest way is with socket pipes - elements for them are produced for literally all variants of complex system configurations. Rubber couplings with clamps are sometimes used for sewerage.
The issue of connecting smooth-walled pipes is a little more complicated. Small pipes are connected using compression adapter couplings (collet couplings).
The reduction in diameter is combined with bell-shaped elements and the installation of shut-off valves.
For the installation of large pipelines, transition elements for welding or segment fittings are also available (see photo).
The transition is carried out after the transition from HDPE to metal - there are definitely many transition fittings for metal.
Tips on how to choose
HDPE is the optimal choice for installation in the ground or basements without ultraviolet rays, sudden temperature changes and mechanical vibrations. When choosing the type and size of pipes, they are guided by the purpose and operating conditions. First, the purpose of the pipelines is determined - pressure and non-pressure, sealed or not. Power, telephone or Internet networks are laid in casings made of larger tubes; often these pipelines are not sealed.
The second important factor is the working pressure in the water supply or soil pressure on free-flow networks. The choice of pipe design (smooth-walled, corrugated, double-layer corrugated, bell-shaped) depends on these factors. In addition, the temperature regime is taken into account - overheating of the ground in summer, freezing in winter.
The choice of pipe parameters for sewerage depends on the weight of the overlying soil layer. If the depth is more than 5–6 m or the sewage system is located under a platform for cars, use corrugated two-layer pipes with high ring rigidity. Corrugation is also used for deep laying of water pipes and a large layer of screed over a heated floor system.
When choosing materials in a store, it is better to choose products from well-known brands. Corrugation is definitely better than imported ones. Smooth-walled pipes can also be selected from domestic manufacturers.
In any case, the pipes must be inspected when purchasing to see if there are any cracks, chips, sagging, if they are too soft and if the wall is thin. Receipts and certificates are required for purchase.
Approximate price and best manufacturers
The best domestic ones, “Kazanorgsintez”, “TekhStroyPolymer”, “PolyPlastik”, “BaltEnergosystems”. There are many imported manufacturers, but the quality of imported HDPE pipes is not much higher than domestic ones, but the price is significantly different. The availability and prices of pipes from foreign manufacturers must be determined separately for each region: the range and prices are very different!
Price of popular domestically produced products:
- 1 m of smooth-walled water pipe Ø 32 mm costs from 50 mm, Ø 40 mm - from 70 rubles;
- 1 m of single-layer corrugated pipe Ø 50 mm costs approximately 60 rubles; Ø 63 mm – 90 rubles; Ø 110 mm – 150 rubles;
- bell-shaped HDPE design with a running size of 110 mm and a length of 2 m costs about 300 rubles; corrugated - about 400 rubles.