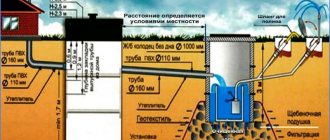
When installing sewer systems, two types of pipes are used - cast iron and plastic. The size of these products is regulated by the Technical Conditions (TU). The standard size, namely diameter, ranges from 50 to 110 mm.
There are products with larger or smaller diameters. From this article you will learn the main parameters that products made of PVC and cast iron have.
They are produced in accordance with TU 2248-022-23208482-02, which allows you to choose an option for any system.
Calculation of wastewater volume
In order for the water drainage system to operate as efficiently as possible, it is necessary to accurately calculate the average amount of precipitation falling in a particular area during the month.
To do this, you can use the formula taken from SNiP 2.04.03-85: Q = q20 x F x Ψ
Here the indicators are the following data:
- Q - average volume of rain or melt water that will need to be drained from the site;
- q20 is the intensity of rain or snow precipitation in a specific region of Russia. The data is recorded in SNiP tables for each specific area;
- F is the total area of all roofs and platforms from which storm or snow wastewater will be drained;
- Ψ is the correction factor, which allows you to achieve the most accurate calculations of the average volume of water for disposal. This indicator completely depends on the type of coating from which the liquid will be drained.
The coefficient indicators are also specified in the tables of SNiP 2.04.03-85 and have the following wording:
- Roofs of any type - coefficient is 1;
- Asphalt platforms and paths - coefficient 0.95;
- For sites and objects made of concrete - the coefficient is 0.85;
- For crushed stone with bitumen admixture - coefficient 0.6;
- And for simple crushed stone in its pure form - 0.4.
Thanks to the use of this formula, it is possible to calculate as accurately as possible the volumes of rain or melted snow water that will “attack” the object in each season.
Table of water pipe diameters
Pipes are qualified according to their external size, which is specified by the manufacturer. To determine the internal diameter, you will need to subtract twice the wall thickness from the external value. However, products made of cast iron and steel are marked by internal diameter, taking into account their throughput. This should be remembered when using products made from different materials in the same system. Let's look at a few examples.
Steel pipe 76x3 means:
- outer diameter of the product 76 mm;
- wall thickness 3 mm;
- the internal passage will be 70 mm.
The calculation was as follows: 76 - (3x2) = 70 mm.
2 example. 1" copper pipe implies an outer thickness of 1 inch, or 25.4 mm.
Fittings are used to join products made of different materials. To connect a metal and plastic pipe, the fittings will have plastic on one side, which will allow for high-quality soldering, and on the other, threads for a reliable threaded connection
To do this, you need to pay attention to the thread size and pitch. When connecting to cast iron, sockets and special seals are used
Plastic can be soldered together, metal can be welded using electric or gas welding.
Steel
Table of sizes of steel pipes
When installed with steel products, their selection is made according to the outer diameter of the pipe of the water supply system. According to the requirements of GOST 10704–91, they are divided into groups:
- large diameter - from 508 mm;
- medium – 114-530 mm;
- small – up to 114 mm.
In home plumbing, the most popular products are those with small sizes. Medium - in the city water supply. Large - for main oil and gas pipelines. The most popular products include:
- ½” - 12.7 mm;
- ¾” - 19.0 mm;
- 1” - 25.4 mm;
- 1½” - 38.1 mm.
Specialists who are involved in laying and repairing water pipes on a daily basis know these values by heart, while others look them up in tables.
Cast iron
Cast Iron Pipe Size Chart
These products are used when laying street water supply networks. Their use indoors is limited. They have long-lasting operation and increased strength. However, they are fragile and are susceptible to impact. Disadvantages include significant weight and high cost. The size of the pipe for such a water supply system is calculated according to the internal throughput of the product.
Plastic
Modern technologies make it possible to produce high-quality plastic that is sufficiently durable, lightweight, does not corrode, and is an environmentally friendly material. Thanks to these characteristics, it displaces metal and cast iron from the construction market; its cost is significantly lower than these materials. The most popular materials are:
Plastic pipe size chart
- polyethylene - is the cheapest option, used for technical water supply in utility rooms;
- polypropylene - requires special equipment for soldering, well suited for cold water supply in the house;
- metal-plastic - one of the highest quality in this segment, used in cold and hot water supply indoors.
The size of these products leaves much to be desired. The problem is that each manufacturer sets its own sizing chart. Therefore, when assembling a plastic water supply system, it is advisable to purchase all components from one manufacturer. Or you will have to take measurements of each product. Despite this, plastic pipelines are distinguished by their performance characteristics and are very popular, especially when laying water distribution indoors.
Determination of nominal diameter
Regardless of the material from which sewer pipes are made and the scope of their purpose, they have the current standard dimensions:
- D – outer diameter;
- d – diameter from the inside;
- S – wall thickness;
- Dy – conditional pass.
The internal diameter sign is placed on the marking of cast iron products, while the external dimensions are most often indicated on plastic products. The external width of the product for all categories remains unchanged, only the wall thickness changes. For example, if a pipe has D = 33.5 mm, then S can vary within 2.8-4 mm. The level of strength of the product and resistance to internal and external pressure depend on the thickness of the walls. Fluid dynamics engineers, for all internal diameters, use one approximate figure of 25 mm and call it the nominal bore.
Conditional diameter is the maximum throughput of the pipeline. The efficiency and performance of the structure directly depends on its size. If you know the dimensions of the internal lumen, you can choose the right connecting elements so that the sewage system has a holistic appearance without the threat of depressurization.
All products of domestic and foreign production have a nominal diameter that is most suitable to the nearest standard according to GOST 28338-89 and GOST 3262-75.
Determination of nominal diameter
In addition to the sewerage capacity, it is also necessary to calculate its angle of inclination. These parameters directly depend on the size of the product and the material it is made of. Formula for calculating the angle of inclination: V× (H / D)½ ≥ K. Where:
V – speed of wastewater movement; H – degree of filling; D – outer diameter; K is the roughness value of the internal walls, for polymers = 0.5.
Pipe diameter with slope
The greater the slope, the higher the waste flow rate. The sewage system is less clogged and is able to serve a larger number of premises.
Some advice from experts:
Despite the fact that the riser is located vertically, it must have the largest diameter, at least 100 mm. This ensures unimpeded drainage of the maximum volume of wastewater. The outlet design should have a minimum number of turns to minimize the likelihood of clogging. Since it is in these places that hardening most often occurs. The recommended slope should not be less than 12 mm per linear meter. This applies to all categories of sewer pipes. If possible, a 90°C turn should be replaced with two 45°C turns, this reduces the likelihood of solid deposits building up inside the structure.
Compliance with generally accepted rules for organizing wastewater disposal guarantees uninterrupted functionality of the system. In modern projects, a hidden type of installation of the structure is increasingly being practiced. This means that if the installation is carried out incorrectly, difficulties will arise during repair work.
How to choose?
When selecting the optimal size of PVC sewer pipes, the main parameter is calculated - the expected volume of wastewater that passes through the pipeline.
In a private household, the amount of liquid drained depends on the number of people living. The more drainage points there are in the house, the wider the receiving drain pipe.
External sewerage cannot be less than 11 cm in diameter. For internal wiring in an apartment, it is enough to choose sewer pipes of small diameter up to 7.5 cm.
When discharging wastewater into a riser, the size of the circle should not be less than the diameter of the common line. For buildings with five floors and below, this figure is 11 cm; if there are more floors, then the diameter reaches 16–20 cm.
Use common sense to select the optimal size of pipes at various drain points.
You should not install a bulky sewer network with high throughput in low-rise buildings and apartments. Efficiency will increase slightly, but the cost and location area will increase significantly.
Corrugated pipes
Sewage pipes are selected according to the following criteria:
- by diameter;
- by wall thickness;
- along the length of the free end.
The internal cross-sectional size or diameter determines the discharge load into the sewer system. Each sewage discharge point requires the use of a diameter of up to 50 mm.
The drain hole under the toilet has a diameter of at least 10 cm, since solid particles go down the drain. In a private house, a pipe with a diameter of 110–200 mm is suitable for installing an external sewer system.
For sewerage coming from a multi-storey building, the cross-sectional diameter must be more than 20 cm. The size of the outlet to the sewer well in the courtyard area can be 30–50 cm.
The thickness of the walls determines the strength class of the structure. The thickness must be selected according to the expected load on the pipeline. Lightweight pipes with walls of 1.2–2.2 mm are suitable for installation in systems with gravity drainage with minimal load in the internal sewer system.
Typically, the diameter of such pipes does not exceed 11 cm. They can be installed to drain sewage from the kitchen and bathroom in apartments and private houses. Pipes must be freely accessible or covered with a box.
Pipes with strength class SN4 are the most common and are used for internal and external sewerage.
The minimum diameter for pipes is 5 cm with walls of 2.6 mm. For a diameter of 11 cm, the thickness is 3.2 mm. Medium-heavy pipes are installed for the common house riser and outlet to the external drain.
Such pipes are also used in external gravity sewerage in private and multi-apartment construction.
The selection of pipe length depends on the length of the pipeline in different sections.
The smallest section for internal sewerage is 30 cm. The length can be easily changed independently depending on the configuration of the pipeline. To get a smooth cut of the required length, all you need to do is use a hacksaw.
For external sewerage with straight sections, pipes with a length of 1.5 to 3 m are often used. The fewer connecting elements in the installation section, the stronger and more rigid the pipeline structure.
When choosing the size of sewer pipes, you can be guided by sanitary standards, which indicate the permissible diameter for various drains:
- Kitchen drain – 32–50 mm.
- The drainage from the bathroom from each point is 50 mm.
- Drain from washing equipment – 25 mm.
- Pipe supply to the riser – 50–75 mm.
- Fecal drainage – 110 mm.
- Central riser – 110–160 mm.
- Output to external drain – 110–160 mm.
- External drain with outlet from the bath – 160–200 mm.
- With outlet from the pool – 20–30 cm.
- City sewer lines – 30–50 cm.
How to install a 110 mm pipe
The laying of sewer pipes is determined according to a certain technology. Compliance with it ensures high-quality functioning of the sewerage system. During installation, certain features should be observed and certain nuances taken into account.
Slope of the sewer system
One of the most important parameters is the slope of sewer pipes. The drainage water should flow away easily and without any obstruction. The natural process of drainage requires the construction of some slope. According to the standard, the slope is 1 cm per 1 m of pipe. To arrange the slope, markings are first made, and then fasteners are installed in accordance with the markings. The marking is done using a level, preferably a laser. First, mark a horizontal line that runs level with the drain hole on the riser. Then it rises by a number that corresponds to the distance from the riser to the original drain point.
Connection process
An important and directly main factor in the quality arrangement of a sewer system is pipe connections. The process itself is simple, but there are some nuances that ensure the reliability and tightness of the joints. Negligence in this matter can lead to the following negative factors:
- leaks;
- unpleasant smell.
In order to prevent the defects listed above when connecting 110 mm pipes, sealing gaskets are used, which are available in several types: single-feather, double-feather and double-feather with a plastic ring. The installation of these gaskets is carried out with some differences, which should also be taken into account. For example, single-feather gaskets are usually installed, but when installing others, it is necessary to use a special lubricant. So, in order to correctly connect 110 mm sewer pipes:
- Insert the gasket into the socket. We make sure that distortions do not form. Also, you should first inspect the gasket so that it does not have any defects.
- As a lubricant, you can use available products: detergent, soap, Vaseline. The main thing is that these products do not negatively affect rubber gaskets and do not change their structure. It is difficult to predict this, so experts recommend using a specialized lubricant that is made on a silicone basis. Silicone itself cannot be used, as it is aggressive to rubber.
- After the seals are installed, all that remains is to connect the products together. During the work, we make sure that the joints are tight.
Sequence of connections
Let us clarify that 100 mm pipes are connected not only to each other. In arranging a sewer system, various fittings are used that allow turning or other bending if necessary. Here is an example of the sequence of connections of the sewer system:
- The drainage system begins with a turntable fitting, to which a flexible corrugated hose is connected on the inside, and a 110 mm pipe on the outside. Many people don't use this element. Then in this case the tightness of this connection cannot be guaranteed.
- Don’t forget, when connecting the product to the fitting, a rubber gasket must be installed. We also monitor the planting depth.
- If it is necessary to arrange a branching sewer system, tee fittings are used. To change the diametrical cross-section in the sewer system, adapter fittings should be purchased.
- The last rule in the connection. All joints must be placed along the flow of water.
Dimensions
Plastic sewer pipe elements are produced in accordance with GOST 51613-2000. The dimensions of PVC pipes are determined by such indicators as length, outer diameter, inner diameter of the socket, bore diameter, wall thickness. The outer diameter assumes the nominal size of the product. The throughput depends on the bore diameter.
The wall thickness determines the strength of the pipeline and what load the pipe structure can withstand.
They are classified according to strength class:
- lightweight SN2 structures with a wall thickness of less than 2.3 mm can withstand loads of up to 630 Pa;
- medium-heavy SN4 with walls from 2.5 to 12.3 mm depending on the diameter, cope with pressure from 600 to 800 Pa;
- heavy SN8 pipes with wall thicknesses from 3.2 to 15.3 mm, varying in diameter, withstand pressures from 800 to 1000 Pa.
The sewer pipeline, capable of withstanding pressure up to 1.6 MPa, is made of unplasticized PVC with a wall thickness of 0.5 to 1.9 cm. It is used for laying to great depths, under highways, in pressure sewer systems.
Sewer pipes are divided depending on the installation location. There are external and internal drainage systems. For the installation of internal sewerage, gray pipes are used. Standard diameter sizes are 32, 40, 50, 75, 110 and 160 mm. The wall thickness is not designed for high loads, varies from 1 to 3.2 mm. The length can be 0.3, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 and 3 meters.
Pipes for external drainage are orange. Depending on the amount of wastewater, diameters of 110, 125, 160, 200, 250, 300, 400 and 500 mm are produced. The wall size starts from 3 mm, the length varies from 1.2 to 3 m. For the arrangement of urban sewer systems, a diameter of 200 mm is used.
Depending on the pressure to which the walls of the pipeline are exposed, pressure and non-pressure sewer systems are distinguished. For internal gravity sewerage, pipes with a wall thickness of 1.8 to 3 mm are used. For street pipelines with free-flow drainage, products are produced with a wall size from 3.2 mm with a diameter of 11 cm to 1.2 cm with an outer diameter of 50 cm.
A pressure sewer system with pumping equipment requires increased strength characteristics. Plastic pressure pipes are made from unplasticized PVC with a greater thickness. The table shows possible wall parameters depending on the pressure tested from 800 Pa to 1.6 MPa.
| Diameter, mm | Wall thickness, mm |
| 90 | 2,2–6,6 |
| 110 | 2,7–8,6 |
| 160 | 4,0–9,5 |
| 225 | 5,5–13,4 |
| 315 | 7,7–18,7 |
| 400 | 9,8–23,7 |
| 500 | 12,3–23,9 |
In addition to smooth-walled PVC pipeline, corrugated pipe is produced. It is distinguished by increased rigidity and different diameters. A gray corrugation of small diameter is used to drain waste from a washing machine, dryer, and dishwasher. Double-layer corrugated pipe structures of large diameter from 11 to 120 cm are used for laying to a depth of up to 15 m with high mechanical stress. The table shows the dimensional form of corrugated pipes.
| Outer diameter, mm | Inner diameter, mm | Corrugation protrusion pitch, mm |
| 110 | 91 | 12,6 |
| 160 | 139 | 12,6 |
| 200 | 176 | 16,5 |
| 250 | 216 | 37 |
| 315 | 271 | 42 |
| 400 | 343 | 49 |
| 500 | 427 | 58 |
| 630 | 535 | 75 |
| 800 | 678 | 89 |
| 1000 | 851 | 98 |
| 1200 | 1030 | 110 |
Shaped elements for internal sewerage from PP
Sewer outlet
| Diameter, mm | Corner | Packaging, pcs. |
| 32 | 45º | 100 |
| 32 | 90º | 100 |
| 40 | 45º | 100 |
| 40 | 90º | 100 |
| 50 | 45º | 100 |
| 50 | 90º | 100 |
| 110 | 15º | 20 |
| 110 | 30º | 20 |
| 110 | 45º | 20 |
| 110 | 67º | 20 |
| 110 | 90º | 20 |
Elbow ABU (WC) eccentric (white)
| Diameter, mm | Corner | Packaging, pcs. |
| 110 | 45º | 16 |
Sewer coupling
| Diameter, mm | Packaging, pcs. | |
| 40 | grey | 50 |
| 50 | grey | 50 |
| 110 | 16 |
Sewer inspection
| Diameter, mm | Packaging, pcs. | |
| 110 | grey | 20 |
Sewer clamp
| Diameter, mm | Packaging, pcs. | |
| 32 | white | 25/750 |
| 40 | grey | 25/500 |
| 50 | grey | 25/500 |
| 110 | grey | 150 |
Sewer tee
| Diameter, mm | Corner | Packaging, pcs. |
| 40/40 | 45º | 50 |
| 40/40 | 90º | 50 |
| 50/50 | 45º | 50 |
| 50/50 | 90º | 50 |
| 110/50 | 45º | 20 |
| 110/50 | 90º | 20 |
| 110/110 | 45º | 20 |
| 110/110 | 90º | 20 |
Sewer reduction
| Diameter, mm | Corner | Packaging, pcs. |
| 50/32 | 180º (white) | 50 |
| 50/32 | 180º (grey) | 50 |
| 50/40 | 180º (grey) | 50 |
| 110/50 | 50 |
Compression air valve
| Diameter, mm | Packaging, pcs. | |
| 50 | grey | 20 |
| 110 | 8 |
Sewer cross
| Diameter, mm | Corner | Packaging, pcs. |
| 505050 | 90 | 20 |
| 1105050 | 90 | 10 |
| 11011050 | 90 | 10 |
| 110110110 | 90 | 10 |
Ventilation fungus
| Diameter, mm | Packaging, pcs. |
| 110 | 9 |
Transition cast iron/plastic
| Diameter, mm |
| 110 |
| 50 |
Expansion coupling
| Diameter, mm | Packaging, pcs. |
| 110 | 10 |
Fastening
| Diameter, mm | Packaging, pcs. |
| 32 | 600 |
| 50 | 600 |
Kinds
There is simply a huge range of sewer pipes on the plumbing market today. There are options from different materials and with different characteristics. This diversity is due to the large number of manufacturers and the great demand for such products.
Cast iron
The most common and widespread is cast iron. Pipes made from it are characterized by high strength, fire resistance and durability (service life 60–80 years), as well as resistance to chemicals and temperature changes. Among the disadvantages of cast iron products are the high price and difficulties with installation due to their heavy weight. Plus, cast iron is characterized by a rough surface, which leads to a layer of fat inside the pipeline and its narrowing.
Methods for connecting cast iron pipes for sewerage
Steel
Steel pipes will cost less than cast iron pipes, but will last much less (maximum 30 years). They are much more susceptible to corrosion than their cast iron counterparts. In private homes, this option is extremely rare. If durability is not so important, then it is better to make the internal sewage system out of plastic.
Methods for connecting steel pipes
PVC pipes
The most common among plastic pipes are products made of PVC (PVC, polyvinyl chloride). They are cheap, light in weight, smooth inside and last about 40 years. Plus PVC pipes are resistant to corrosion and aggressive environments.
Their only serious drawback is the rather low maximum operating temperature. Water heated above +600 C with prolonged exposure gradually destroys polyvinyl chloride. In general, it is recommended to use a PVC pipe when laying an outdoor sewer section, where wastewater from different plumbing fixtures is already mixed and is not so hot.
Methods for connecting PVC pipes
Polypropylene
Compared to PVC, polypropylene is more durable and can easily withstand heat up to +1000C. Pipe products made from it are characterized by increased wear resistance and can last up to 100 years. But they are somewhat more expensive than PVC pipes for internal sewerage.
Methods for connecting polypropylene pipes
Polyethylene
Polyethylene analogues almost completely repeat the characteristics of the polyvinyl chloride version. They are only slightly more resistant to aggressive chemicals, but at the same time they will cost more than PVC pipes. Plus, polyethylene products are softer and are more easily damaged from the inside by abrasive particles (grains of sand or rust contained in wastewater from a private home).
Methods for connecting polyethylene pipes
Asbestos cement
Asbestos cement sewer pipes are usually used to lay the street part of the drainage system. They are distinguished by increased corrosion resistance and low cost. However, they will last a maximum of 25 years. Then the asbestos-cement pipe will definitely have to be replaced due to wear.
Methods for connecting asbestos cement pipes
Ceramics
The most durable, chemical-resistant, smooth and at the same time expensive is ceramics. Pipes for internal sewerage made of this material belong to the premium segment. However, they are quite fragile and difficult to install independently.
Method of connecting ceramic and cast iron pipes
Type of pipes
For properly organized drainage of wastewater, pipes must be stable, durable and smooth on the inside. There are 2 main materials for making such products: metal and plastic. The latter are divided into 3 types:
- PVC – polyvinyl chloride. Durable and UV resistant, but cannot withstand high temperatures of hot water and exposure to aggressive environments. Used for internal and external sewers.
- PET – polyethylene. Operating functionality within temperatures of -40 +40 C°, not recommended for use in a hot water drain system.
- PP – polypropylene. They can last 100 years and are highly resistant to temperature changes and harsh chemicals. Used in domestic wastewater systems.
The cast iron drainage system is an outdated option. Despite the fact that it is durable and strong, it is completely replaced with plastic. This is not due to the disadvantages of metal, but due to the advantages of PVC.
Plastic pipes are also divided according to density and hardness. It depends on which highway they will be used:
- SN-2. Products made of lightweight material are used in areas with minimal load. The installation is carried out shallowly and not under transport roads.
- SN-4. They have a denser material and can be laid under roads with little traffic.
- SN-8. The densest and heaviest products are intended for use under highways and industrial enterprises.
PVC – polyvinyl chloride pipes
It is important to note that a PVC drainage system is not as durable as a cast iron one, but it is more flexible and easy to install. When properly installed, it can last 50 years.
Dimensions of PVC sewer products
When producing rolled pipes, manufacturers use regulatory documents - GOSTs, which regulate the dimensions of the assortment of these products.
Plastic pipes - PVC - PET and PP - differ in characteristics, but their sizes are standardized, so when laying pipelines you can use products from different structural polymers.
The parameters of sewer polyvinyl chloride pipes comply with GOST R 51613-2000 and VSN 48-96. GOST regulates the dimensions of products for pressure pipelines, and construction standards - for non-pressure pipelines.
The sizes of PVC pipes for drainage systems are varied. The number of standard sizes for these products is 13 - their diameters range from 63 to 315 millimeters (for more details: “What sizes of sewer pipes are there and what is best to choose”).
But out of this vast assortment, only a few options are in demand:
- The most famous pressure sewer pipes have a diameter of 75 millimeters. They are used to drain wastewater from bathtubs and showers.
- Classic pipe products with a cross-section of 100 or 110 millimeters are used when installing vertical risers and elements of external sections of discharge mains. But for these purposes you can also choose pipes with a diameter of 150 and 160 millimeters.
- In industrial sewer systems, products with a diameter of 250 and 300 millimeters are used for the installation of central risers and outlet sections. At the same time, the impressive parameters of sewer pipes made of polyvinyl chloride, which have a large diameter, do not prevent them from being installed in the same way as a system of 50 or 75 mm products, namely by joining into a socket.
Carrying out installation
To install the sewer system, a special trench is laid outside the building. Its depth should be below the freezing level of the soil. After this, the pipes are inserted into a special sleeve in the foundation, all components are joined, and then connected to the internal sewerage system. When laying non-pressure pipes, joints are treated with tarred tow or reinforced with rubber rings.
The sewage system is connected to a cesspool, septic tank or concrete overflow well. After checking the connections for leaks, thermal insulation is performed with a special material, then everything is covered with sand, compacting it in layers.
Installation of internal sewerage: after preparatory work and adjustment, a sewer riser is installed, after installing the tee, vertical pipes are inserted, then connections to the plumbing are made.
Pipe dimensions and area of use
There are certain standards according to which the size of a sewer pipe depends on the area of its use. Thus, a pipeline with a diameter of 40–50 mm is installed in kitchen and sink drains, and 75–100 mm in diameter in the sewer leading from the toilet.
Dependence of diameter and area of use
Standard parameters depend on the volume of water that must leave the container in a certain time. For example, in an apartment in a multi-storey building there are standard toilets, from which a large volume of water along with waste must come out in a short period of time. Therefore, in most cases, for toilets, the diameter of plastic or cast iron pipes is chosen to be at least 110 mm.
Table on how to choose the internal diameter for a sewer pipe depending on the use of the outlet:
| For dishwasher, washing machine | 25 mm |
| For connecting pipelines to the drain of a bathroom, shower box, sink, kitchen sink | 32 mm |
| Ensuring the installation of a sewerage system in the premises | 50 mm |
| Installation of pressure pipes for external water supply, sewerage, drainpipes, selection of diameter for the toilet | From 110 to 200 mm |
If you have non-standard parameters of water supply systems, then before installing a sewer system you need to determine the relationship between the amount of wastewater and the rate of its discharge. For this, certain geometric parameters are calculated.
In addition to the fact that the correct diameter allows you to calculate the water drainage rate, pipe cleaning is also carried out taking this parameter into account. For example, the technology of sewer cleaning with Kärcher systems is now very popular, but they are used only on pipes with a diameter of 100 mm or more.
Pipe calculation
To individually select a pipe for installation in houses, cottages or in the country, it is necessary to calculate the permeability. To calculate the useful pipe diameter (internal d), you need to know the following parameters:
- D – outer (external) diameter, mm;
- B – wall thickness, mm;
- m – mass of a linear meter of pipe, g (necessary to take into account the number and type of fastenings if a complete replacement of the pipeline is needed);
- S – cross-sectional area, mm2.
Formulas for calculation:
d = D – 2 b;
S = π/4 (D2 – d2);
V = S * L;
m = ρ * V.
Pipe sizes
Many manufacturers of polyethylene pipes mark most of the required parameters on the communication. But, as a standard, only the outer diameter (D) and wall thickness of the outlet are initially known. The most important parameter is the internal diameter; it is used to connect the pipe to the main and to lay out the sewer system, select additional elements, fittings, etc.
Manufacturer's markings on pipes
Moreover, unlike polypropylene plastic pipes, cast iron sewer lines are initially specified by the manufacturer with a useful internal diameter. Like steel, it is designated DN. It can have different values, in whole numbers, for example, DN 110 or DN 200. This means that this pipe has a nominal water drainage diameter of 110 or 200 millimeters, respectively.
Peculiarities
Pipe structures made of polyvinyl chloride are often used to equip wastewater drains, displacing cast iron and steel ones. Plastic sewer pipes are made from regular and unplasticized PVC. The material contains vinyl chloride and additional additives. High strength properties make it possible to use unplasticized PVC for organizing pressure pipelines.
Sewage pipes are designed for draining wastewater from a water drain, for installing a drainage channel, and installing indoor and outdoor sewage systems. The use of PVC products for sewerage installations is justified due to the technical characteristics of the material. The long service life of sewer pipelines will allow the system to operate for up to 50 years. The tensile strength reaches 50 MPa, so the street section of the sewer can withstand installation to the depth of soil freezing. The pipeline is capable of operating at pressures from 6 to 16 bar.
The use of polyvinyl chloride pipes for sewerage has the following advantages:
- A variety of sizes and shapes of pipes and fittings will allow you to assemble sewer systems of any complexity.
- Smooth internal walls do not allow sewage to settle, preventing the formation of blockages in small diameters and preventing the pipe passage from becoming clogged with sediment.
- The low weight of the products and ease of cutting mean quick and easy installation and dismantling without additional tools.
- Inert to chemicals and corrosive effects.
- Affordable price of pipeline elements.
How are sizes determined?
Any pipe – plastic, cast iron, ceramic and other types – has several parameters that determine its size. These are diameters (through, internal and external) and wall thickness. Diameter is the most important characteristic that helps determine the purpose of communication and its features.
Table: sizes of asbestos-concrete pipes
What tasks can plastic and cast iron sewer pipes perform, based on the diameter size:
- Drain water from toilets and washbasins;
- Used to create a drainage system;
- Organize external and internal sewer systems.
Also, based on these dimensions, it is possible to determine the wall thickness, calculate the throughput of the pipe and determine what type of water supply it is used for. In most cases, the larger the diameter, the thicker the pipe, but there are exceptions. Shaped elements are selected based on DN. External dimensions are very important for installing tees and fittings.
The principle of pipe designation according to GOST
According to GOST, the dimensions in the drawings and calculations are shown as follows:
- dn is the outer diameter, considered nominal, since it does not take into account the deformation coefficient of the pipe under the influence of high or low temperatures;
- en – pipe thickness, also without certain coefficients. Can be calculated without sections, en = outer diameter - inner;
- PO is the maximum deviation, a value that demonstrates the maximum deviation of a certain parameter depending on temperature or other factors;
- SDR – ratio of outer diameter to wall thickness, the value is used for plastic pipes;
- SN is the ring stiffness of the sewer pipe. This indicator is very important for non-pressure internal sewerage and drainage systems. The indicator is measured in kN/m2. In metal-plastic and cast iron it may be absent.
Modern drawings may additionally include various indicators of material strength. Designated by µ, ρ and others.
Large plastic pipes for sewerage
Rules for working with plastic pipes
Despite the apparent simplicity of assembling a sewer system made of plastic materials, there are some nuances that should be taken into account when working. First of all, prepare the tools:
- Hacksaw or pipe cutter.
- Bulgarian.
- Sandpaper for cleaning.
- Lubricant and glue for plastic pipes.
Rules for processing plastic pipes in case of cutting them:
- After cutting the pipe into two parts, it is necessary to ensure that there is a chamfer on the cut for ease of connection.
- The sections are lightly processed with a grinder and cleaned with sandpaper.
- After this, the elements are cleaned of dust, and the ends are treated with a degreaser.
- After the rubber gaskets are installed, apply a thin layer of glue to the end and insert it tightly into the fitting. For reliability when connecting, the elements can be turned a quarter turn.
When installing a sewer drain, it is necessary to carry out the work in such a way as not to return to this procedure for at least ten years. And this is quite possible if you adhere to all the tips and rules given above. Proper pipe laying is the key to the long-term functioning of the sewer system.
How to choose the right PVC sewer pipes: types and size tables
We are glad to welcome you to the pages of our online magazine!
PVC sewer pipes have revolutionized the idea of sewer systems; they have almost completely replaced steel, cast iron and asbestos-cement materials from this area. However, the use of plastic in construction requires knowledge of the physical and operational characteristics of polyvinyl chloride. We suggest you look into this issue.
Advantages and disadvantages of polyvinyl chloride pipes
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a colorless and transparent thermoplastic polymer.
It is characterized by resistance to:
- acid-base environment,
- a large number of solvents,
- fats and mineral oils,
- saline and alcohol solutions.
When used correctly, PVC pipes have a number of advantages:
- The smoothness of the inner surface increases the flow capacity of the pipeline, reducing the coefficient of friction, and prevents the formation of sediment.
- Rigidity and high mechanical strength (tensile strength - 50 MPa) ensure the system operates under internal pressure conditions ranging from 6 to 16 bar and allows the use of plastic pipes even at a depth of 8 meters.
- The material is inert, does not come into contact with the carrier and is not susceptible to bacterial attack, which makes it safe for use in housing and communal services and facilitates cleaning work.
- Corrosion resistance.
- Easy to install. The low specific density of vinyl determines the low weight of products made from it (from 2 kg/lm, parameters may vary depending on the wall thickness). This facilitates transportation, and along with the socket connection method, installation of the pipeline without the involvement of special machinery and equipment.
- Due to the dielectric properties of the material, there is no need to ground the sewer system made of PVC pipes.
- Long service life (up to 50 years).
- Low cost of material and production in comparison with metal, cast iron and concrete analogues.
However, PVC and products made from it have a number of disadvantages:
- With prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation, the material loses strength and elasticity. However, manufacturers solve this problem by adding a special light-absorbing dye to the composition, which creates a kind of filter that limits the affected area to a depth of no more than 0.05 mm,
- Low frost resistance. Already at a temperature of -15⁰C, the PVC material becomes brittle and collapses, which imposes a number of requirements on the external use of PVC pipes: underground laying of the pipeline, or its above-ground insulation.
- Tendency to deform at temperatures above 65⁰C (for some models - 90⁰C). This limits its use in the field of transporting high-temperature media.
Differences from other polymer pipes
In addition to polyvinyl chloride, sewer pipes are also made from other types of polymer: polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polybutylene (PB) or polyamide (PA).
How to choose the right PVC sewer pipes: types and size tables
Advantages and disadvantages of polyvinyl chloride pipes, differences from other polymer pipes. Diameters and sizes of PVC pipes, approximate prices and connection methods. Subtleties of installation and maintenance.