Polypropylene pipes are used for installing engineering systems in apartment buildings and private buildings. On their basis, pipelines for water supply, heating, sewerage and ventilation are laid out. On the building materials market you can find many varieties of PP pipes, which differ in type, presence/absence of reinforcement, outer diameter (section) and wall thickness.
The choice of a specific size of PP pipe depends on the physical properties of the engineering system indicated in the design documentation.
Classification of polypropylene pipes according to the composition of raw materials
Based on the type of raw materials used, polypropylene products are divided into 4 types:
- PPR or PPRC. The base is a static polypropylene copolymer (or random copolymer). The substance has a molecular structure in the form of crystals. The main features are the ability to withstand temperatures from -180 to +1400°C and resistance to pressure. PPR pipes are characterized by a wide range of applications: for water supply, heating, sewerage - the highest quality and most durable pipes of this type today are German aquatherm GmbH - the official representative of which in Russia is the Agpipe Group of Companies (agpipe.ru).
- PPH. During production, various modifiers (nucleators, antistatic agents, etc.) are introduced into the polymer to improve certain properties of the finished product. This type is used when laying cold water supply, ventilation and drainage networks. Low resistance to heat imposes restrictions on the use when laying systems that pass liquids at elevated temperatures.
- PPB. To manufacture this type of product, a block copolymer is used, the structure of which is based on a combination of homopolymer micromolecules. Each block has an individual structure and composition. This structure gives the final product high resistance to impact loads. The PPB type is used when creating underfloor heating or cold water supply.
- PPs. The basis of this type is polyphenyl sulfide. Raw materials give the final product excellent technical characteristics, which include strength, wear resistance, ability to withstand elevated temperatures, and load. The properties are due to the special structure of the molecules. Used in ventilation and heating networks, hot and cold water supply systems.
Polypropylene pipes can be reinforced with various materials. Multi-layering increases resistance to pressure and temperature.
The following can act as reinforcement:
- fiberglass;
- layer of aluminum (external reinforcement);
- perforated aluminum foil (internal reinforcement);
- composite (layers of fiber or glass fiber).
For hot water supply and heating systems, only multilayer products can be used.
Use of reinforcement
Reinforcement is one of the ways to give pipes special mechanical properties.
Reinforcement is as follows:
- Aluminum foil layer. It can be either external or located internally.
- Fiberglass layer. As a rule, it has an internal location.
Thanks to the reinforcement, the pipes are more durable, and the amount of their thermal expansion becomes smaller.
Experts recommend paying attention first of all to the fiberglass reinforcement layer. This type of pipe never loses its mechanical strength and does not delaminate, and its installation does not require stripping
This type of pipe never loses its mechanical strength and does not delaminate, and its installation does not require stripping.
Pressure classification
Polypropylene pipes vary in resistance to the pressure of the medium flowing through it.
Classification of polypropylene pipes.
According to this parameter, there is the following classification of products:
- N10 or PN10. This type is suitable for creating heating systems or water heated floors, where the heating temperature of the liquid is not higher than +45°C and the load on the walls does not exceed 10 atm.
- N16 or PN16. The products are operated at a temperature of the passing medium of no more than +60°C and loads on the walls up to 16 atm. This type of pipe is rare due to low demand.
- N20 or PN20. The products can be operated at pressures up to 20 atm. and temperatures up to +80°C. Heating and plumbing systems are installed from them.
- N25 or PN25. This type can withstand wall loads of up to 25 atm. and temperatures up to +95°C. Increased strength characteristics are due to the presence of an additional foil layer. Products are used in systems in which the flowing liquid is characterized by high temperature and pressure.
What are the influence of pipe parameters?
The design values of the engineering system and the parameters of polypropylene pipes are mutually dependent.
The diameter of the pipeline affects the throughput and flow of water. We are talking about the internal cross-section, since the amount of water that can pass through the pipes in a certain period of time depends on it.
The physical properties of the working medium are the initial value for calculating the design parameters of the pipeline. The water capacity of the system, as well as the temperature and speed of water movement, determine the choice of polypropylene products.
To maintain the required speed, pressure and water flow, PP pipes of a certain size are selected.
How to choose the right line size
To select the dimensions of pipes for highways, a special formula is used. In this case, the geometric characteristics directly depend on the speed of passage of the medium through the networks and the volume of its consumption. The formula for calculating the diameter is as follows:
D=√(4-Q-(1000/π*V),
where Q is the average flow rate of the medium, l/s; π is the number Pi (is 3.14); V is the speed of fluid passage through the system, m/s.
Water main.
This formula is used in the construction of a private house. Products measuring 20 mm are suitable for water supply.
If the calculation is carried out for a multi-story building, then there are features. When determining the parameter, the number of apartments and entrances, the number of storeys of the building, etc. are taken into account. The more sources of consumption, the greater the fluid consumption and, accordingly, the larger the diameter of the pipes for arranging the main line.
In most cases, they focus on the following dimensions:
- D= 25 - installation of risers in 5-story buildings;
- D=20 - for water supply and indoor wiring;
- D=32 - installation of risers of high-rise buildings.
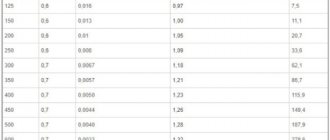
The ratio of the bore diameters of pipes made of different materials. Sample Pivot Table
Very often, installers and mechanics confuse pipe diameters. I had to see how a mechanic from the housing office insisted that during the alteration the diameter of the pipes in the central heating should not be narrowed, while demanding that everything be passed through as 25 metal (34), but the installers understood this as 25 polypropylene.
Do not forget that in pipes it is the internal diameter that is important, because it determines their throughput.
Below is an approximate summary table of pipes of different diameters and different materials. The most common materials and diameters are taken.
How to use the table: on the left, the vertical column shows the internal diameter, for example, we find 15.6 mm, this internal diameter corresponds to a regular steel pipe 12. PN10 polypropylene with a diameter of 20 mm, 20 mm metal-plastic and 18 mm copper.
By the way, an ordinary pipe in 34 corresponds to polypropylene PN20 with a diameter of 32 mm, which is considered to be inch.
Polypropylene and metal-plastic pipes using information about Wavin pipes from 20 to 40 mm in diameter
Copper pipes were used according to GOST 2005, up to 15mm diameter the wall thickness was 0.8mm, up to 28mm the wall thickness was 1mm, over 28 -1.2mm
The steel pipes used are old GOST from 1975.
Uponor-PEX polyethylene pipes with pressure up to 10 bar for heating and plumbing.
Pipes that are very similar in internal diameter are combined under the closest value.
Perhaps such a table will be useful in calculations.
How much heat should the pipeline supply?
Let's take a closer look at the example of how much heat is usually supplied through pipes, and select the optimal pipeline diameters.
There is a house with an area of 250 sq. m., which is well insulated (as required by the SNiP standard), so it loses heat in the winter by 1 kW per 10 sq. m. To heat the entire house, 25 kW of energy is required (maximum power). For the first floor - 15 kW. For the second floor - 10 kW.
Our heating scheme is two-pipe. One pipe supplies hot coolant, and the other pipe cools it to the boiler. Radiators are connected in parallel between the pipes.
On each floor, the pipes branch into two wings with the same thermal power, for the first floor - 7.5 kW, for the second floor - 5 kW.
So, 25 kW comes from the boiler to the interfloor branch. Therefore, we will need main pipes with an internal diameter of at least 26.6 mm so that the speed does not exceed 0.6 m/s. A 40mm polypropylene pipe is suitable.
From the interfloor branching - along the first floor to the branching on the wings - 15 kW is supplied. Here, according to the table, for a speed of less than 0.6 m/s, a diameter of 21.2 mm is suitable, therefore, we use a pipe with an outer diameter of 32 mm.
7.5 kW goes to the wing of the 1st floor - an internal diameter of 16.6 mm is suitable, - polypropylene with an outer diameter of 25 mm.
For each radiator, the power of which does not exceed 2 kW, you can make an outlet with a pipe with an outer diameter of 16 mm, but since this installation is not technologically advanced, the pipes are not popular; a 20 mm pipe with an inner diameter of 13.2 mm is more often installed.
Accordingly, we use a 32mm pipe on the second floor before branching, a 25mm pipe on the wing, and we also connect the radiators on the second floor with a 20mm pipe.
Laying plumbing and heating
The dimensions of polypropylene pipes for water supply are smaller. With a diameter of 16 to 110 millimeters, their length varies greatly, but most often it is 5 meters.
When choosing products for plumbing and heating, in addition to their sizes, you should pay attention to:
- Operating temperature . The most in demand are PPR products that, according to manufacturers, can withstand temperatures of 95 degrees or more. PPR pipe sizes vary in the range of 16–110 millimeters. They are selected depending on the pressure that will be exerted on them (about
Ventilation systems
Polypropylene pipes must ensure the inflow and outflow of air masses, which means they do not require special strength. When laying ventilation, low weight is of great importance, since the installation of pipelines is most often carried out on decorative partitions or on top of suspended ceiling structures, and not on load-bearing walls.
The dimensions of polypropylene pipes for ventilation depend on the type of room where they are planned to be installed. In most cases, standard five-meter products are used. The products that I use when laying ventilation systems can have a cross-section of square, rectangular, oval or other shape.
In living rooms, as a rule, pipes with a diameter of 100 to 125 millimeters are laid; they are connected without welding. One product is inserted into the socket of the previous one (about
Practical recommendations
The wrong choice of product diameters is fraught with many troubles: leaks (due to hydrodynamic shocks or excess pressure in the line), increased consumption of electricity (fuel) due to low efficiency of the system, and a number of others. Therefore, you should not install it according to the principle “like a neighbor (godfather, brother-in-law).”
If the circuit consists of dissimilar pipes, then special calculations will have to be made for each section (line) of the route. Separately - for plastic, metal (steel, copper), apply different coefficients and so on.
Only a specialist can solve such a problem. In such situations, you should not do the calculations yourself, as the error can be quite significant. The services of a professional will cost much less than the subsequent alteration of communications, and even during the heating season.
All devices (expansion tank, battery, etc.) of the circuit are connected using pipes of the same cross-section.
To avoid the formation of air jams (in case of some errors in the calculations), so-called air vents should be installed on each line.
What else to consider when choosing fittings
Connecting pipeline parts are selected taking into account the type of designed engineering system. When purchasing fittings, you must take into account the following nuances:
- For PP water supply, the elements are white or gray.
- Installation work is carried out using special pipe cutters and soldering irons specifically for PP pipes.
- For communications made of polypropylene, it is necessary to purchase connecting parts from the same material. They cannot be replaced with PVC fittings.
It is recommended to buy polypropylene pipes and fittings from well-known manufacturers. In addition, the brands’ products are distinguished by their neat appearance, large assortment, and availability of all standard sizes.
Fittings for pp pipes
You should also pay attention to the SDR indicator, which characterizes the cross-country ability of products. Parts with a high value of this characteristic have good maneuverability and relatively thin walls.
Pipeline products with a small SDR have low permeability, but are characterized by increased strength and density.