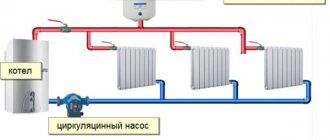
Types of registers for heating systems
Devices are divided into two categories. The technical characteristics of the system as a whole depend on the first. From the second - coolant circulation through the pipeline.
By material: steel, iron, aluminum and cast iron pipes
There are four types, although many other substances and their alloys can be used in production.
Steel
It is used more often than other metals.
This is due to several factors:
- cheapness;
- ease of processing;
- widespread;
- a wide variety of shapes.
Welding technology is used to create it.
Important! Sometimes registers are made of galvanized or stainless steel. It should be borne in mind that both options are expensive, and the first one is also difficult to process.
Smooth
Iron pipes with a high carbon content have this characteristic. To put it simply, the base is steel. To obtain a smooth surface, electric welding is used. They hold much more pressure than regular ones, while being nicer and a little more expensive. Similar registers are described in GOST 10704-91.
Aluminum
It is quite rare because welding requires special equipment that is not easy to find. This is their only disadvantage: the material is cheap, conducts heat well, almost without losing the latter.
Some registers are made from an alloy of steel and aluminum. Bimetallic devices are difficult to obtain, but they have better characteristics than their analogues.
Cast iron
They are almost never used because the registers are bulky and heavy. It is not advisable to create racks specifically for them. In addition, the metal is fragile and is capable of splintering or cracking from impact. Accordingly, you need to purchase protective covers that will reduce thermal conductivity. They are difficult to install, although they are reliable, and operation does not depend on the chemical composition of the pipes.
An almost identical description can be given to copper. It should be noted that it is much more expensive, but it transmits the temperature to the room 3-5 times better. Accordingly, a small harness is required. Among the disadvantages:
- fragility;
- poor compatibility with other metals;
- high requirements for coolant;
- mandatory grounding.
The material should be chosen according to personal preference, but it is also important to carry out calculations. They will help you calculate in advance the required installation dimensions for each type of metal.
By design: sectional, coil
Sectional registers are made from sections of large diameter pipes. They are connected by pipes to admit water. The latter are made of the same metal, and their size must correspond to the supply harness.
It is recommended to install the devices together with a circulation pump, since they create excess hydraulic resistance.
Creating sectional devices is not difficult. A grinder is used to cut out several registers and the connections between them. The system is assembled in one of two ways. In a continuous transition, transitions are made from each edge, and in a stepped transition, alternating. In the latter case, racks in the form of metal plates are placed at parallel sides.
Coil pipes are made from a single section of pipe. It is bent, which makes the creation process difficult. This applies to independent work: such devices are not uncommon in production. To speed up the work, the extreme sides, near the turns, are connected to each other.
For safety, small plates are installed between the bends to support the upper parts.
Sectional ones are slightly better for circulation, and are much easier to manufacture. Coil ones look a little more aesthetically pleasing and go well with a tubular electric heater.
Selecting material for registers
The next parameter that must be taken into account when choosing a register is the material of its manufacture.
It is rare to see heating registers made from a profile pipe - most often steel products with a round cross-section are used for this.
Currently, several materials are used to produce registers - metal, aluminum or bimetallic pipes.
The difference between them lies in the calculated heat transfer and service life:
- Steel heating registers made of profile pipe or round section . They are characterized by ease of manufacture and low cost. Disadvantage: surface rusting. When choosing, special attention should be paid to the quality of welds;
- Aluminum . They are extremely rare, since welding aluminum heating registers requires special equipment. But they have better thermal conductivity. There is virtually no heat loss;
- Bimetallic . They are made from a special type of heating pipes. They have a core made of steel. To increase the heating area, the design has copper or aluminum plate heat exchangers. All bimetallic heating registers are characterized by a small pipe diameter - up to 50 mm. Therefore, they are more often used to organize heat supply in residential buildings and small industrial and commercial premises.
How to calculate heat transfer?
The required amount of material can be calculated based on the temperature parameters that need to be obtained in the room. At the household level, this step is usually skipped - they make heating registers with their own hands “by eye” according to the principle “the more, the better.”
But it is better to make simple calculations of heat transfer, for which you do not need to be a mathematician. All you need is:
- Calculate the area of the room.
- Learn about the heat transfer properties of steel.
- Select the optimal pipe diameter.
The area of a room is calculated by multiplying its length by its width (S = L*W). However, for more accurate calculations, it is recommended to calculate the volumetric parameter by adding the height (H) value to the calculations.
So, the final calculation formula takes the form:
V = L*W*H
For example, you need to calculate V of a room where the length is 5 m, width is 3 m, height is 2.15 m. The volume of the room is obtained: V = 5*3*2.15 = 30.25 m3. Based on this basic value, further calculations should be made to determine the amount of heat, the size and number of heating registers to make with your own hands.
Self-welded heating registers are blocks consisting of six steel pipes with a diameter of over 100 mm. Such batteries, made without proper calculations, can overheat the room being served.
First of all, the required amount of heat per calculated volume of the room is calculated to achieve the required internal temperature (W):
Qп.т = V * k (Tin – Tout),
where V is the volume of the room; k – heat transfer coefficient of the building walls; Tin – temperature inside; Tout – outside temperature.
The amount of heat generated by one register can be calculated using the formula:
Qр = q * L * (1-n),
where: q – heat flow from each horizontal and vertical pipe of the register (approximately 20-30 W/m); L – length of vertical and horizontal pipes of the register (m); n – coefficient of unaccounted heat flows (for metal pipes – 0.1).
The category of unaccounted heat loss also includes the hood in the garage. If the mechanical type is installed, the coefficient n must be increased to at least 0.2.
The number of registers, accordingly, is determined by the formula:
Nр = Qп.т. / Qр
Such a calculation method will most likely be assessed by design specialists as a simplified and crude form. However, this approach still seems to be a more rational action than calculating and making registers with your own hands by eye, without any calculations.
Making heating registers with your own hands
One of the advantages of using registers in heating systems is the possibility of making them yourself. For this, round steel pipes are most often used. Despite the fact that the heat transfer rate of the heating register in this case will not be ideal, the manufacturing process will not require special skills.
To independently produce this heating element, you will need a pipe with a diameter of 40 to 70 mm. A larger cross-section will lead to significant heat losses during coolant circulation. You can make a heating register with your own hands according to the following work plan:
- Calculation of the optimal parameters of the heating device - pipe diameter, total length of the section.
- Drawing up a drawing to calculate the optimal amount of material.
- Carrying out work on making a heating register with your own hands.
- Checking the structure for leaks.
To complete this task, you will need a steel pipe designed to form the main registers and a line of smaller diameter. With its help, the registers will be connected to each other and the heating system. You will also need special end caps for the pipes.
At the first stage, you need to use a grinder to cut the pipes to the required length. It is not recommended to use a welding machine for this, since a weld will form at the ends of the heating register from the round pipe. Then holes are made to connect the pipes. The pipes are welded using a welding machine and the end caps are installed. To ensure the safe operation of a homemade heating register, it is necessary to install an air vent and a drain valve. They are mounted in the upper part of the structure, but on the opposite side relative to the point of connection to the heating.
In some cases, a modernization of the traditional steel or bimetallic heating register circuit is carried out. It consists of installing an electric heating element.
This way you can make an autonomous heat source that will not depend on the operation of water heating. In the event of an accident or technical work, a homemade heating register will generate heat using a heating element. But for this, shut-off valves must be installed during installation so that the coolant circulates only inside the heating device.
When choosing a design and making a heating register, the thickness of the pipe does not matter. The difference in diameters between it and the supply line determines the complete absence of water hammer in the structure.
Types of heating registers
Heat-transfer devices of this type come in several types, depending on their design features, pipe shape and material of manufacture.
Thermal registers of various designs
The design of the heating register can be coil or sectional.
They consist of several parallel pipes connected by arc-shaped pipes, or one pipe bent like a snake. Depending on the characteristics of the room and the required temperature, the device is made with one or more bends.
With this design, all elements of the register participate in the heat exchange process, providing high heating efficiency while saving space. Coils are complex to manufacture, requiring either a welder to assemble the register from individual parts, or a pipe bender to bend a long pipe, which requires certain skills in working with these tools.
Section registers
Registers made in the form of sections are much easier to manufacture, since they represent several identical sections of pipe connected at the edges by connecting pipes. Sections are connected in series or in parallel:
In the first case, connecting pipes are installed either from the left or from the right edge of the sections. The capacity of the connecting pipes is the same as that of the transport pipes. On the opposite edge, instead of a connection, a support is mounted to hold the pipes in the desired position, and the ends of the pipes are closed with plugs. The energy carrier moves along the heat-transfer circuit in the same way as in a coil register - passing through the sections one by one.
Classification by section shape
The snake or sections of heating devices can be made of pipes of various shapes:
| Pipe shape | pros | Minuses |
| Round section | low cost of consumables, availability of fittings and fittings for sale, high throughput, low hydraulic resistance, ease of external cleaning; | complexity of calculating the geometry of holes for connection, large volume of the finished register; |
| Rectangular or square section | simplicity of calculations and installation, ease of external cleaning, compactness; | high price, lower capacity than round pipes, high hydraulic resistance |
| Pipes with fins - heat transfer plates perpendicular to sections | increased heat transfer, compactness; | unpresentable appearance, difficulty of external cleaning, complexity of installation, high price. |
Types of registers by material of manufacture
The material used for the manufacture of pipes also affects the cost, size, efficiency and aesthetics of the register:
| Material | pros | Minuses |
| Carbon steel | low cost, easy installation, | low heat transfer, susceptibility to corrosion, need for coloring |
| Galvanized steel | low cost, corrosion protection | low heat transfer, difficulty of installation due to the impossibility of using electric welding, unaesthetic appearance |
| Stainless steel | resistance to corrosion, ease of installation, coloring is not necessary, but possible | low heat transfer, high cost |
| Copper | high heat transfer, compactness, light weight, plasticity, allowing you to make a register of any shape, corrosion resistance, aesthetics | high price, inapplicability in heating circuits made from alloys incompatible with copper (cast iron, steel, aluminum) due to possible oxidation, Suitable only for clean and chemically neutral coolants, instability to mechanical damage |
| Aluminum | high heat transfer, low weight, | high cost, impossibility of self-production, since welding requires specialized equipment, |
| Cast iron | high heat transfer, durability, resistance to mechanical damage, average price range, chemical inertness | heavy weight, big sizes, complexity of installation, heats up slowly and takes a long time to cool down |
Registers from pipes of various shapes and materials can be made independently or purchased ready-made, then all that remains is to install and connect the device to the thermal circuit.
Installation of registers in the heating system
Correct installation of heating registers can be done in two ways - using threaded connections or using a welding machine. It all depends on the total mass of the structure, its dimensions and the parameters of the heating system.
In general, experts recommend following the same rules as when installing radiators. The difference is only in the size of the structure. If it is necessary to connect the heating register to the gravity system, the required slope must be observed. The heat supply device must be tilted towards the movement of the coolant. There are no such requirements for systems with natural circulation.
To ensure correct installation of heating registers, the following rules must be followed:
- Maintaining minimum distances from walls and window structures. It must be at least 20 cm. This is necessary for carrying out technical or repair measures;
- For threaded connections of the heating register, only paranitic linings or plumbing flax are used;
- All heating registers made of profile or steel pipes must be painted. This is necessary to prevent rust from appearing on their surface.
Despite the fact that the heat transfer rate of the heating register will decrease, the maintenance-free service life of the structure will increase significantly.
Installation is recommended to be carried out outside the heating season. After a trial run of the heating system, you can compare the calculated power of the register with the actual power and, if necessary, make operational changes to the design.
Calculation of water register design
Heating register
To calculate heating registers, you need to determine exactly what requirements they must meet. Perhaps it will just be a homemade radiator for heating, or maybe it will be a clothes dryer. Naturally, the designs will be different. Location of pipe sections in the water heating register:
- vertical;
- horizontal.
The first option is extremely rare; basically, everyone makes water heating registers from several parallel sections that are located in the horizontal plane. To ensure circulation in the register, the horizontal sections are connected to each other by overflow pipes:
- one;
- two.
Register Design Options
Another type of connection of horizontal pipes in a register is made using corner couplings of the same diameter, which are welded to the ends. The rotation is made 180 degrees; for this, two 90-degree corner couplings are welded together. In this case, plugs for heating registers will not be needed. This connection method is best suited for gravity heating systems, where circulation is carried out by gravity.
- above;
- below.
Heating registers of batteries with top supply are much more common than with bottom supply. In this case, the placement of the supply and return pipes can also be different:
- at one end;
- at different ends.
The most advantageous scheme for connecting the heat exchanger to the circuit is considered to be the one in which the supply is carried out from above, and the return flow comes out at the bottom of the opposite end. The GOST for heating registers does not regulate its design, but the technical characteristics of the pipes from which it is made.
What parts does the heating register consist of?
Calculating the power of the heating register consists of selecting the required dimensions of the heat exchanger. This directly affects the amount of coolant in it and the heat exchange area. The larger the register, the larger the room it can heat.
It turns out that you need to determine the diameter of the pipes in such a way that the heat transfer from the heating registers has a sufficient level to heat a room of a certain area. This is if you have the opportunity to choose, but if the register is made from what is available, then you may have to change the design a little.
Each region has its own standards for the amount of energy to heat one meter of space. To calculate registers from smooth pipes for heating, you can take the average value of 100 W. If you are worried that there won’t be enough, then just make a 50% reserve. Now we adjust our register to these requirements. For clarity, let’s take as an example a heating register made of three pipes, each two meters in size. Algorithm of actions:
- determine the area of the room;
- We calculate how much power is needed to heat it;
- We substitute the value into the formula for determining the diameter.
Let's say that we have a room of 50 square meters. It turns out that we will need 500 W of thermal power so that the air temperature is within the limits established by regulatory documents. The formula for calculating the diameter has the following values:
- P – 3.14;
- register length;
- coefficient of thermal conductivity of metal, for steel 11.63;
- difference between supply and return temperatures.
As a standard for calculating the difference in supply and return temperatures, take the value of 80 and 20 degrees, respectively. If you know that the temperature in your circuit will not exceed 65 degrees, then you substitute your value. We will continue the calculation based on average values, that is, the temperature difference is 60 degrees.
Pipe diameter = 500 / (3.14 * 6 (three pipes of 2 meters each) * 11.63 * 60) = 0.038
We got the value in meters, which is 38 mm. It turns out that in order to heat a room of 50 square meters with a register of three horizontal sections of two meters, you need to use pipes with an internal diameter of at least 38 mm. If it turns out that you need to weld a register from existing pipes, then you need to calculate the total length of the segments. To do this, you can calculate this value from an existing formula.
Length of sections = 500 / (3.14*11.63*60*section of our pipes in meters)
For the manufacture of registers, pipes with a diameter of 32 mm are used, let’s say they are in stock. Substituting the value into the calculation, we can calculate that to heat such a room you will need 7.1 meters. This value can be divided into several segments. It turns out that calculating the number of heating registers comes down to finding out the total length of pipes with a given diameter, and then dividing it into convenient segments.
Advantages and disadvantages of heating registers
Homemade steel or aluminum heating registers differ from standard radiators in their size. They consist of several pipes whose diameter exceeds 32 mm. To organize the circulation of the coolant, the pipes are connected to each other by pipes.
What is the reason for the popularity of these heat supply devices? Firstly, the possibility of self-production. You can make bimetallic heating registers, steel or aluminum pipes. Plastic models are much less common, as they do not have the proper performance qualities.
Before connecting heating registers, you should carefully study their “weak” and “strong” sides.
- Long service life . For steel and aluminum models it can reach 25 years. In this case, the probability of breakdown will be minimal;
- Great heat dissipation . This is due to the fact that the power of the heating register exceeds this parameter for classic radiators and batteries. Associated with a large volume of coolant;
- Easy installation and operation . Since anyone who is at least a little familiar with the rules for organizing heat supply can install heating registers correctly, they can be used in buildings of all types. But most often they can be found in the heating system of large industrial, administrative and commercial premises.
But besides this, you need to take into account the possible disadvantages that a heating register made from a smooth steel pipe may have:
- Large volume of coolant . This leads to its rapid cooling;
- Minimum air convection rate . Reduces the efficiency of heat supply;
- Unattractive appearance . Most often this applies to homemade structures.
Correctly calculated heat transfer of a heating register directly depends on its design. Currently, several types of these heat supply devices are used, differing not only in the material used, but also in appearance.
The weight of the register filled with water can be very high. Therefore, you need to think in advance about a reliable system for attaching it to the wall.
Register calculation: main steps
Of course, before you start manufacturing heating devices of this type, you should draw up their detailed drawings. Calculation of heating registers for self-production is usually carried out in two stages:
- the general indicator of the required heat transfer for efficient heating of the building is determined;
- The registers themselves are calculated.
When calculating registers, the following is determined:
- required pipe diameter;
- number of sections;
- step between sections;
- length of segments.
It is believed that the optimal pipe diameter for welding heating registers with your own hands for a utility block or home is 32 mm. If desired, to assemble such devices, you can, of course, take larger material. However, it is still believed that only registers assembled from pipes with a diameter of no more than 80 mm are suitable for installation in a low-rise building.
If the devices are welded from a pipe that is too thick, the return and supply to the heating network of a private residential building will have to be connected to a very powerful boiler, the installation of which will most likely not be economically feasible.
The length of sections when calculating registers is determined, of course, primarily taking into account the layout of a given specific room. In most cases, such devices are welded by hand from pipe sections 1 m long.
The distance between sections in a self-assembled register should be large enough. The further the pipes are spaced from each other, the more efficiently the device will heat the rooms. Most often, when assembling a register, horizontal sections are placed at a distance of 1.5 times the diameter of the pipes used for its manufacture.
Types of heating registers
Initially, you should decide on the type of structure. After all, how to calculate a heating register if its geometric parameters and the principle of coolant circulation are not known? For the manufacture of heating devices, it is recommended to use standard proven circuits.
The determining parameter of choice is the required circulation rate of the coolant in the system and the degree of heat transfer of the register. Based on these requirements, you can choose two types of heating devices:
- Sectional . It consists of two or more large-diameter pipes connected by pipes. The cross-section of the latter must be equal to the same parameter of the supply line. The selection of a heating register of this type is relevant for systems with forced circulation, since the design creates excess hydraulic resistance during the passage of the coolant;
- Serpentine . They consist of one pipe that has bends. Making such homemade heating registers is problematic. To increase the circulation rate, pipes can be connected by pipes. But this is not mandatory, as in the models described above.
Since you can make a heating register with your own hands even at home, they are often made rather than purchased ready-made models. But before this, you must correctly calculate the power of the heating register.
To make registers, you can use pipes of various sections - round, rectangular or square. Preference is given to the first, since for them the friction of water during movement will be minimal.
Advantages of the equipment
The main advantages of this type of heat exchanger can be considered:
- ease of use;
- ease of maintenance (cleaning);
- the presence of a large heat-transfer area with small dimensions;
- high fire safety;
- economical energy consumption in the presence of a heating element;
- Possibility of use as a heated towel rail;
- Wide range of applications - can be installed in warehouses, production workshops, trade pavilions and office buildings, as well as in hospitals and clinics.
conclusions
If you decide to equip your home with this type of heating device, we advise you to carefully understand the features of its operation, as well as study the intricacies of creating and installing registers. Additional reference literature will greatly help you with this.
A heating register of four smooth pipes and a flow diagram of the coolant are shown in the figure below.
We turn on the computer, MS Office and start the calculation in Excel.
Initial data:
There is not a lot of initial data, they are clear and simple.
- Pipe diameter D
in mm is entered
to cell D3: 108,0
- the length of the register (one pipe) L
in m
to cell D4: 1,250
- the number of pipes in register N
in pieces
to cell D5: 4
- the “supply” water temperature tp
in °C
to cell D6: 85
- the return water temperature tо
in °C
to cell D7: 60
Enter the room air temperature t
to cell D8: 18
- Select the type of outer surface of the pipes from the drop-down list
in merged cells C9D9E9: “In theoretical calculation”
- the Stefan-Boltzmann constant C 0
in W/(m 2 * K 4)
to cell D10: 0,00000005669
- the value of free fall acceleration g
in m/s 2
to cell D11: 9,80665
By changing the initial data, you can simulate any “temperature situation” for any standard size of the heating register!
The heat transfer of just a single horizontal pipe can also be easily calculated using this program! To do this, it is enough to indicate the number of pipes in the heating register equal to one (N=1).
Calculation results:
- The degree of emissivity of the radiating surfaces of pipes ε
is automatically determined by the selected type of outer surface
In the database, located on the same sheet with the calculation program, 27 types of external surfaces of pipes and their degree of emissivity are presented for selection. (See the download file at the end of the article.)
- The average temperature of the pipe walls tst
in °C is calculated
in cell D14: =(D6+D7)/2 =72,5
t st =(t p +t o)/2
- temperature difference dt
in °C
in cell D15: =D14-D8 =54,5
dt=t st - t in
- The coefficient of volumetric expansion of air β
in 1/K is determined
in cell D16: =1/(D8+273) =0,003436
β=1/(t in +273)
- the kinematic viscosity of air ν
in m 2 /s
in cell D17: =0.0000000001192*D8^2+0.000000086895*D8+0.000013306 =0,00001491
ν=0.0000000001192*t in 2 +0.000000086895*t in +0.000013306
- Prandtl criterion Pr
is determined
in cell D18: =0.00000073*D8^2-0.00028085*D8+0.70934 =0,7045
Pr=0.00000073*t in 2 -0.00028085*t in +0.70934
- 16.
Calculate the thermal conductivity coefficient of air
λ
in cell D19: =-0.000000022042*D8^2+0.0000793717*D8+0.0243834 =0,02580
λ
=
-0,000000022042*t in 2 +0.0000793717*t in +0.0243834
- A
pipes in m 2 is determined
in cell D20: =PI()*D3/1000*D4*D5 =1,6965
A=π*(D/1000)*L*N
- The heat flux of radiation from the surfaces of the pipes of the heating register Q and
in W is calculated
in cell D21: =D10*D13*D20*((D14+273)^4- (D8+273)^4)*0.93^(D5-1) =444
Q and =C 0 *ε *A*((t st +273) 4 - (t st +273) 4)*0.93 (N-1)
- the heat transfer coefficient for radiation α and
in W/(m 2 *K)
in cell D22: =D21/(D15*D20) =4,8
α and =Q and /(dt*A)
- Grashof criterion Gr
is calculated
in cell D23: =D11*D16*(D3/1000)^3*D15/D17^2 =10410000
Gr=g*β*(D/1000) 3 *dt/ν 2
We find the Nusselt criterion Nu
in cell D24: =0.5*(D23*D18)^0.25 =26,0194
Nu=0.5*(Gr*Pr) 0.25
- the convective component of the heat flow Q k
in W
in cell D25: =D26*D20*D15 =462
Q to =α to *A*dt
- And the heat transfer coefficient during convection α k
in W/(m 2 *K) is determined accordingly
in cell D26: =D24*D19/(D3/1000)*0.93^(D5-1) =5,0
α to =Nu*λ/(D/1000)*0.93 (N-1)
- the total heat flow power of the heating register Q
in W and Kcal/hour, respectively
in cell D27: =(D21+D25)/1000 =0,906
Q=(Q and +Q k)/1000
and in cell D28: =D27*0.85985 =0,779
Q'=Q*0.85985
- the heat transfer coefficient from the surfaces of the heating register to the air α
in W/(m2*K) and Kcal/(hour*m2*K) respectively
in cell D29: =D22+D26 =9,8
α=α and +α to
and in cell D30: =D29*0.85985 =8,4
α'=α*0.85985
This completes the calculation in Excel. Heat transfer from the heating register from the pipes has been found!
The calculations have been repeatedly confirmed by practice!
Registers made of steel with ribs
Before installing registers made of steel pipes with fins, it is recommended to pay main attention to the volume of the pipe. For a private home, craftsmen recommend installations with a volume of 3 or 4 centimeters.
You can use larger diameter pipes for work, but it should not exceed 8 centimeters. The main reason lies in the heating boiler. A device of the type that is installed in everyday life cannot generate a large amount of thermal energy sufficient to warm large areas.
When performing calculations, you need to take into account the length of one register rib and its heat transfer per meter of area. To give an example, a meter-long pipe with an internal cross-section of 60 mm can heat approximately one square meter.
Having calculated the required number of registers, rounding is carried out upward. But, there are certain conditions under which the obtained indicators increase by 20 or even 50 percent. This includes:
- The presence of a large number of openings for windows and doors in the room.
- Small wall thickness.
- Low-quality insulation of the room, or its complete absence.
A simple heating register has less heat transfer than devices with fins. They not only increase heat transfer, but also turn the register into a design - a radiator, which can play an important role in the aesthetic design of the interior.
How to make a homemade register from profile, smooth steel pipes
Welding work, which forms the basis for the manufacture of registers for a heating system, requires a certain number of different tools and materials.
DIY tools and materials
In addition to the welding machine, you will need the following equipment:
- for cutting: grinder, plasma cutter or gas torch (cutter);
- tape measure and pencil;
- hammer and gas wrench;
- building level;
Welding materials:
- electrodes if electric welding is used;
- wire, if gas;
- oxygen and acetylene in cylinders.
Work order: how to weld the structure?
Depending on the type of design chosen (sectional or coil), the assembly of the registers will differ dramatically. The most complex ones are sectional ones, because they have the most joints of elements of different sizes.
Before moving on to assembling the register, you need to make a drawing and understand the dimensions and quantity. They depend on the heat transfer of the pipe. For example, 1 m of pipe with a diameter of 60 mm or a section of 60x60 mm and a thickness of 3 mm is intended to heat 1 m² of heated room area, taking into account that the ceiling height does not exceed 3 m.
The first thing to do is to cut sections from the selected pipe in accordance with the estimated length of the sections. The ends must be ground and cleaned of scale and burrs.
Before assembling the sectional devices, you need to put markings on them along which the jumpers will be installed. Usually this is 10-20 cm from the edges of the sectional pipes. A mark is made right there on the top element where the squeegee for the air vent (Maevsky tap) will be installed. It is located on the opposite side and along the edge of the section and along the outer plane.
- Using a gas torch or a plasma cutter, holes are made in the pipes according to the marks so that the jumper pipe can fit into them.
- The jumpers themselves are cut out from pipes of smaller diameter, 30-50 cm in size.
- Sections of the same length as the pipe jumpers are cut from the metal profile. They will be installed in the form of supports under the section pipes on the opposite side from the installation of the junction element.
- Plugs are cut from sheet metal 3-4 mm thick in the shape of the main pipe (circle or rectangle). In two of them, holes are made for drains, to which the supply and return circuits of the heating system will be connected through shut-off valves.
- First of all, plugs are welded to the sections.
- The leads are welded to the latter.
- Welding of jumpers with pipe sections is carried out.
- Supporting elements made from cut steel profiles are also attached by welding.
- The pipe for installing the Mayevsky tap is welded.
- All seams are cleaned with a grinder and a sanding disc.
It is better to carry out the assembly and welding process on a flat plane, on which two or three wooden blocks are laid (they can be replaced with steel profiles: an angle or a channel). It is on the bars that the pipe sections are laid out parallel to each other, taking into account the distance between the sections. As soon as the structure is assembled with tacks, you can begin welding all the seams, rotating the device so that welding is carried out only in the horizontal plane.
Regarding the installation of registers. Depending on which plane they will be attached to, it is necessary to consider the fasteners. There are several commonly used options.
If the device will rest on a floor base, then legs are installed under it. If it is attached to the wall, then use ordinary brackets with hooks bent upward.
After the register is completely assembled, it must be checked for tightness of the seams. To do this, one of the outlets is closed with a threaded plug, and water is poured through the second. Welding seams are checked. If a leak is detected, the defective area is boiled again and cleaned. After all operations performed, the device is painted.
Making a coil register is much simpler. Firstly, bends are ready-made factory parts that are selected according to the diameter of the pipe section. Secondly, they are cooked together in the same way as with a pipe.
First, connect two branches to each other. The resulting C-shaped fitting is connected in series to the ends of the two pipes, combining them into a single structure. At the two free ends of the register, plugs are installed, in which holes are pre-made, and the bends are welded.
Advantages of steel heating registers and their disadvantages
Steel heating has a number of advantages:
- When working, you can realize any individual drawing.
- Not only water, but also heated steam can serve as a heat carrier.
- Easy to connect to the system.
- Its high heat output makes it an excellent option for installation in a large building.
- Low cost.
There are also disadvantages. These include:
- Low heat transfer rates.
- Fear of corrosion.
- Unpresentable appearance.
- Such products require regular painting.
Combined instruments
Any device can be supplemented with a heating element, this way a combined heating device is obtained. It may not be associated with the system, and can be used separately.
If this is an isolated register with heating only from the heating element, then an expansion tank must be installed in its upper part. Its capacity should not be less than 10% of the capacity of the heating device. For steel registers, closed tanks should be installed.
Such steel structures are a great help in very cold times, when the heating capabilities of the boiler become limited. This option is very practical during the off-season, when it is not advisable to use the network at full capacity. After all, the room at this time only needs a little warming up.
Heat dissipation of registers
The heat transfer of registers made of steel pipes is the transfer of heat energy between the battery and the environment. Heating devices made from smooth pipes are less economically profitable.
The heat output of one meter of these structures is approximately 550 W, for a diameter from 3.2 to 21.9 cm. Welding installation work is recommended to be carried out so that mutual heating of the elements does not occur.
Under such conditions, the heat transfer rate becomes higher. If the register is assembled correctly, it becomes a reliable and durable steel heating device. Optimizing the heat transfer of a steel pipeline is decided at the design stage of its structure. To do this, use the following methods.
- Change of infrared radiation in the direction of increase. This can be done using paint.
- Ribs are installed, which also increases the required design performance.
But, there are cases when these indicators need to be reduced. Such actions are required by sections of the pipeline that pass outside residential premises. In these situations, the line is thermally insulated.
Calculations are carried out in this way: Q = K*F*dT. In this formula, Q denotes the thermal transfer coefficient, K is the thermal conductivity of steel materials, and F shows the length of the pipe taken for calculations. dT in this formula is the sum of the initial and residual temperatures, taking into account the room temperature.
The designation dT is also called temperature difference. You can find out by adding the temperature at the outlet of the boiler equipment with the numbers at its input. The resulting readings are multiplied by 0.5 or divided by two. The room temperature is subtracted from this value.
If the steel heating pipeline is in insulating material, then the resulting number should be multiplied by the efficiency of the insulating material. It shows the percentage of thermal energy of the heating system released during the flow of the coolant.
If you want to design a system competently, then you should not select steel pipe assortment by eye. Correct calculations in this case not only make it possible to reduce the cost of construction work, but also to install a heating system that will work effectively for a long time.
Installation of steel registers
Installation of steel pipe registers is carried out in two ways. The first is threaded connections, and the second is through welding. In this matter, solutions are selected based on the total weight of the structure, its dimensions and characteristics.
The process itself is similar to the work when connecting radiators. The difference lies only in the geometric volumes of the structure. If there is a question of connecting the heating device to gravity networks, then the required slope standards must be observed.
The register must be tilted towards the movement of the coolant. For a pipeline with natural circulation, the described standards are not required.
The rules that are used for the correct connection of structures made of steel pipes are as follows:
- Minimum distances from windows and walls should be maintained. This distance is 20 cm. These indentations are needed for ease of repair maintenance.
- When using threaded connections to connect the device, it is recommended to use only gaskets made of paronite, or flax, which is used in plumbing work.
- Each steel appliance must be painted after installation. Otherwise, rust can form on its surface very quickly. At the same time, the thermal conductivity index is slightly reduced, but its maintenance-free service life is extended.
- All installation work should not be planned for the heating season. After a trial check and comparison of the calculated power of the device, it may be necessary to promptly make changes to the design.