Here you will learn:
- Operating principle of closed type heating
- Advantages and disadvantages of a closed heating system
- Protecting the system from air
- Differences between open and closed heating systems
- Components of a closed heating circuit
- Heating system performance
As you know, any heating system in a private home has an expansion tank. This is a container that contains some coolant removal. This tank is necessary to compensate for thermal expansion under various operating conditions. By design, expansion tanks are of open and closed type, respectively, and heating systems are called open and closed.
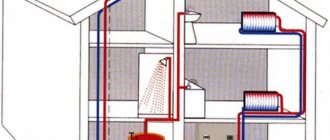
Closed two-pipe heating system
In recent years, a closed heating scheme has become increasingly popular. Firstly, it is automated and works without human intervention for a long time. Secondly, it can use any type of coolant, including antifreeze (it evaporates from open tanks). Thirdly, the pressure is maintained constant, which allows the use of any household appliances in a private home. There are several more advantages that relate to wiring and operation:
- There is no direct contact of the coolant with air, therefore, there is no (or almost no) unbound oxygen, which is a powerful oxidizing agent. This means that the heating elements will not oxidize, which will increase their service life.
- A closed-type expansion tank is placed anywhere, usually close to the boiler (wall-mounted gas boilers come immediately with expansion tanks). An open-type tank should be located in the attic, and this means additional pipes, as well as insulation measures so that heat does not “leak” through the roof.
- The closed type system has automatic air vents, so there is no airing.
In general, a closed heating system is considered more convenient. Its main drawback is its energy dependence. The movement of the coolant is ensured by a circulation pump (forced circulation), and it does not work without electricity. It is possible to organize natural circulation in closed systems, but it is difficult - it requires regulating the flow using the thickness of the pipes. This is a rather complicated calculation, which is why it is often believed that a closed heating system only works with a pump.
To reduce energy dependence and increase heating reliability, install uninterruptible power supplies with batteries and/or small generators that will provide emergency power supply.
Classification of heating systems
To properly fill a water heating system.
you need to know what type it is. There is a classification of systems according to the method of pipe routing: from the top, from the bottom, horizontal, vertical or combined. According to the method of connecting devices using pipes, systems are divided into: single-pipe and double-pipe. Also, water can circulate in the system naturally or forcefully (if a pump is used). Based on the scale of operation, local and central heating systems are distinguished. As the water moves in the pipes, there are dead-end and passing pipes. All these types are used in mixed order in everyday life.
Scheme
The scheme of a closed heating system can be one-pipe or two-pipe. The choice depends on the conditions of use and performance requirements.
A single-pipe closed heating system is suitable for small buildings. It can be installed in a two-story house, and each floor should have no more than 5 radiators. The single-pipe scheme (Leningrad) has a significant drawback - the radiators are connected in series, and the further the heating device is located from the boiler, the lower the temperature of the coolant that passes through it. The radiators closing the chain should be heating devices with an increased heat transfer area compared to the first ones.
Scheme of a two-pipe heating system
The two-pipe scheme of a closed heating system is more efficient, since it allows the coolant of the same temperature to be delivered to all radiators. This option is suitable for large houses, including several floors.
Water or coolant, select the optimal filling system
Antifreeze for heating system
The optimal composition of the liquid should be determined by the parameters of the heating system. Often the heating system is filled with water, as it has a number of significant advantages. The determining factor is the affordable cost - they often use simple tap water. However, this is fundamentally wrong. A large number of metal elements and alkali will contribute to the formation of build-up on the inner walls of pipes and radiators. This leads to a decrease in the bore diameter and an increase in hydraulic losses in certain sections of the pipeline.
But how to properly fill a closed heating system with water to avoid such troubles? Experts recommend using distilled water. It is maximally purified from impurities, which has a positive effect on its physical and operational properties.
Energy intensity. Water accumulates heat well in order to subsequently transfer it to the room; Minimum viscosity index
This is important for closed heating systems with forced circulation and affects the power of the centrifugal pump; As the pressure in the pipes increases, the boiling point shifts upward. Those
in fact, the process of transition from liquid to gaseous state occurs at a temperature of 110°C. This makes it possible to use high-temperature heating modes.
But if there is a possibility of exposure to negative temperatures, then water as a liquid for filling heating systems is unacceptable. In this case, you should use antifreezes with a crystallization threshold significantly lower than 0°C. The best option is solutions of propylene glycol or glycerin with special additives. They belong to the class of harmless substances and are used in the food industry. Solutions based on ethylene glycol have the best technical qualities. Until recently, they were used to fill closed heating systems. However, they are extremely harmful to humans. Therefore, despite all their positive qualities, the use of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze is not recommended.
But what can you fill the heating system with - water or antifreeze? If there is no chance of exposure to low temperatures, water is the best choice. Otherwise, it is recommended to use special coolant solutions.
Automotive antifreeze cannot be poured into the heating system. This will not only lead to boiler breakdown and failure of radiators, but will also be hazardous to health.
Hydraulic calculation for a closed system
In order not to make a mistake with the selection of pipes according to the diameter and pump power, a hydraulic calculation of the system is necessary.
Effective operation of the entire system is impossible without taking into account the main 4 points:
- Determining the amount of coolant that needs to be supplied to heating devices in order to ensure a given heat balance in the house, regardless of the outside temperature.
- Maximum reduction in operating costs.
- Reducing financial investments to a minimum, depending on the selected pipeline diameter.
- Stable and silent operation of the system.
Hydraulic calculations will help solve these problems, allowing you to select the optimal pipe diameters taking into account economically justified flow rates of the coolant, determine the hydraulic pressure losses in individual sections, link and balance the branches of the system. This is a complex and time-consuming, but necessary design stage.
Rules for calculating coolant flow
Calculations are possible if a thermal engineering calculation is available and after selecting radiators by power. Thermal engineering calculations must contain reasonable data on the volume of thermal energy, loads, and heat losses. If this data is not available, then the radiator power is taken based on the area of the room, but the calculation results will be less accurate.
The three-dimensional diagram is easy to use. All elements on it are assigned designations, which include markings and numbers in order
They start with a diagram. It is better to perform it in an axonometric projection and plot all the known parameters. Coolant flow is determined by the formula:
G =860q/∆t kg/h,
where q is the radiator power kW, ∆t is the temperature difference between the return and supply lines. Having determined this value, the cross-section of the pipes is determined using the Shevelev tables.
To use these tables, the calculation result must be converted into liters per second using the formula: GV = G /3600ρ. Here GV denotes the coolant flow rate in l/sec, ρ is the density of water equal to 0.983 kg/l at a temperature of 60 degrees C. From the tables you can simply select the pipe cross-section without performing a full calculation.
The Shevelev tables greatly simplify the calculation. Here are the diameters of plastic and steel pipes, which can be determined by knowing the speed of the coolant and its flow rate
The calculation sequence is easier to understand using a simple diagram that includes a boiler and 10 radiators. The diagram must be divided into sections where the cross-section of the pipes and the coolant flow rate are constant values.
The first section is the line running from the boiler to the first radiator. The second is the section between the first and second radiators. The third and subsequent sections are distinguished in the same way.
The temperature from the first to the last device gradually decreases. If in the first section the thermal energy is 10 kW, then when the first radiator passes, the coolant gives it a certain amount of heat and the lost heat decreases by 1 kW, etc.
The coolant flow can be calculated using the formula:
Q=(3.6xQuch)/(сх(tr-to))
Here Qch is the thermal load of the area, c is the specific heat capacity of water, which has a constant value of 4.2 kJ/kg x s, tr is the temperature of the hot coolant at the inlet, to is the temperature of the cooled coolant at the outlet.
The optimal speed of movement of hot coolant through the pipeline is from 0.2 to 0.7 m/s. If the value is lower, air pockets will appear in the system. This parameter is affected by the material of the product and the roughness inside the pipe.
In both open and closed heating circuits, pipes made of black and stainless steel, copper, polypropylene, polyethylene of various modifications, polybutylene, etc. are used.
When the coolant velocity is within the recommended limits, 0.2-0.7 m/s, pressure losses from 45 to 280 Pa/m will be observed in the polymer pipeline, and from 48 to 480 Pa/m in steel pipes.
The internal diameter of the pipes in the section (din) is determined based on the magnitude of the heat flow and the temperature difference at the inlet and outlet (∆tco = 20 degrees C for a 2-pipe heating scheme) or coolant flow. There is a special table for this:
Using this table, knowing the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet, as well as the flow rate, it is easy to determine the internal diameter of the pipe
To select a circuit, you should consider one- and 2-pipe circuits separately. In the first case, the riser with the largest amount of equipment is calculated, and in the second, the loaded circuit is calculated. The length of the site is taken from a plan drawn to scale.
Carrying out accurate hydraulic calculations can only be done by a specialist of the appropriate profile. There are special programs that allow you to perform all the calculations regarding thermal and hydraulic characteristics, which you can use when designing a heating system for your home.
Selection of circulation pump
The purpose of the calculation is to obtain the pressure that the pump must develop to move water through the system. To do this, use the formula:
P = Rl + Z
Wherein:
- P is the pressure loss in the pipeline in Pa;
- R—specific frictional resistance in Pa/m;
- l is the length of the pipe at the design section in m;
- Z—pressure loss in “narrow” sections in Pa.
These calculations are simplified by the same Shevelev tables, from which you can find the value of friction resistance, only 1000i will have to be recalculated for a specific pipe length. So, if the inner diameter of the pipe is 15 mm, the length of the section is 5 m, and 1000i = 28.8, then Rl = 28.8 x 5/1000 = 0.144 Bar. Having found the Rl values for each section, they are summed up.
The value of pressure loss Z for both the boiler and radiators is in the passport. For other resistances, experts advise taking 20% of Rl, followed by summing the results for individual sections and multiplying by a factor of 1.3. The result will be the desired pump pressure. For single- and 2-pipe systems the calculation is the same.
The pump is installed so that its shaft is in a horizontal position, otherwise the formation of air pockets cannot be avoided. They mount it on American ones so that, if necessary, it can be easily removed
In the case when the pump is selected based on an existing boiler, the formula is used: Q=N/(t2-t1), where N is the power of the heating unit in W, t2 and t1 are the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the boiler and at the return, respectively.
How to calculate an expansion tank?
The calculation comes down to determining the amount by which the volume of the coolant will increase during its heating from the average room temperature of + 20 degrees C to the operating temperature - from 50 to 80 degrees. These calculations are not easy, but there is another way to solve the problem: professionals advise choosing a tank with a volume equal to 1/10 of the total amount of liquid in the system.
The expansion tank is a very important element of the system. The excess coolant it takes in during its expansion saves the line and taps from bursting
You can find out this data from the equipment passports, which indicate the capacity of the boiler water jacket and 1 radiator section. Then the cross-sectional area of pipes of different diameters is calculated and multiplied by the corresponding length.
The results are summed up, data from passports are added to them and 10% is taken from the total. If the entire system holds 200 liters of coolant, then an expansion tank with a volume of 20 liters is needed.
Image gallery
Photo from
A simplified version of tank selection
Membraneless expansion tanks
Expansion tanks with membrane
Expansion tanks for large systems
Main types of coolants
Heating system.
The operating principle of the heating system is that the coolant moves from the heat source to the end point through pipes, heating them. The type and design of the heating equipment determines the type of coolant used, which can be liquids and gases.
The most popular liquid coolants are:
- Water is the most accessible and cheapest resource. According to statistics, about 70% of heating systems use water, which has a high density and heat capacity. In addition, this type of coolant has gained such popularity due to its properties, such as low viscosity, high heat transfer coefficient, and easy temperature control. The main disadvantage is the ability to freeze at zero temperatures. If water freezes in the heating system, this will lead to rupture of pipes and failure of all equipment.
- Antifreeze - this type of coolant is not as widespread as water, and its use is 5%. It is used for heating administrative buildings and residential buildings where the heating system does not allow the use of water due to the increased risk of corrosion. The main advantage of antifreeze is freezing in frosts of 60 - 70 degrees.
The following gases are used as coolant:
- Water vapor is mainly used in industrial buildings, since its use is prohibited in residential and public buildings. Water vapor maintains the temperature of heating devices at 100 degrees; according to sanitary standards, this figure should not exceed 80 degrees.
- Flue gases are toxic, so recently they have been used only for heating water and in order to save electricity to produce a heat source.
- Air is characterized by low heat capacity, so moving it through the heating system requires large energy costs. It is most cost-effective to use air as a coolant, provided that it simultaneously performs two functions: heating and ventilation.
Currently, organic liquids are being introduced as a coolant, which have excellent freezing properties and low viscosity. However, they have not yet become widespread due to their high cost and scarcity.
Installation features
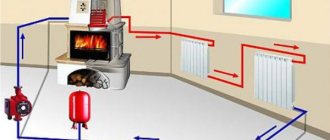
Solid fuel units, double-circuit and single-circuit, are prone to the formation of condensation in the combustion chamber, which causes corrosion and damages the metal. In order to avoid this effect, a mixing unit is added to the piping circuit, which includes a three-way valve and a bypass. Thanks to the valve, the coolant circulates through a small circuit until it heats up to the required temperature, after which access to the boiler for coolant from the heating circuit opens. Solid fuel boilers with this type of piping are safe to use and last as long as possible.
Heating unit piping
The closed-type heating system is designed to operate in autonomous mode and use temperature sensors to maintain a comfortable microclimate. This is taken into account when choosing the type of boiler - it is recommended to use an automated unit. Gas and electric boilers are equipped with automatic equipment; if a solid fuel boiler is connected to the heating system, it is better to choose a long-burning unit, pyrolysis or pellet.
Security group
The coolant supply pipeline at the boiler outlet is equipped with a safety group, which is responsible for monitoring the operation of the heat generator. It includes a pressure gauge (measures pressure), an automatic air vent (for bleeding gases), and a safety valve (discharges excess coolant at high pressure). A security group (SG) can be purchased ready-made or installed on the collector with appropriate devices purchased separately.
Attention! It is prohibited to install shut-off valves between the safety group and the boiler pipe.
Expansion tank
Closed-type heating involves the installation of a device to compensate for the increase in the volume of the heated coolant. A membrane expansion tank is a sealed container with an elastic internal partition of a pear-shaped or disk shape. The heated coolant, having increased in volume, stretches the membrane and fills part of the reservoir. As it cools, the volume of the liquid decreases, and the membrane tends to take its previous shape, displacing the coolant from the container. Due to this, a certain level of pressure is maintained in the system.
Operating principle of a membrane expansion tank
The volume of the membrane tank is calculated specifically for each system. It must be at least 10% of the total coolant volume in the circuit (boiler capacity, all heating devices and pipes), if we are talking about water, or 15% if antifreeze is selected as the coolant.
Circulation pump
Water circulation is ensured by a special pump, the selection of which takes into account the thermal power, the heated area, the length of the pipeline, the layout of the autonomous system, the diameter of the pipes and a number of other factors.
It is recommended to choose a wet-type circulation pump, where the coolant passes through the rotor - with such a device, the heating system is much less noisy during operation. Installation of the system involves installing a pump in the return pipeline.
Correctly installed circulation pump
If the system is designed for operation with natural and forced circulation, depending on the availability of power supply, it is necessary to provide a bypass through which the coolant will bypass the pump.
Pressing the heating system
Pressing the heating system
Before filling the heating system with coolant, it is necessary to check the tightness of all joints and connections. To do this, pressing is performed - creating excess pressure in the pipes, i.e. a situation of destabilization of the system is artificially created.
This can be done in two ways - using air injection or coolant. This must be done before the heating system of the double-circuit boiler is filled. This procedure can be carried out using a mechanical (electric) pump or by connecting the water supply. The last option is not recommended, since it will be very difficult to control the process. The order of execution is as follows:
- Preliminary visual inspection of joints and connecting nodes;
- Connecting the mechanism to the inlet pipe of the system;
- Creation of excess pressure, the value of which should exceed the norm by 1.5 times.
The condition of the heating elements must be checked. If a leak occurs, the process stops immediately and can only begin when the defect is repaired.
Selection of expansion tank
The expansion tank in closed systems is a container with high sealing performance, which is divided in the horizontal plane by a special membrane. In the upper part of such a container there may be an inert gas, which increases the performance characteristics of the device.
The operating principle of this device is based on the temperature of the coolant. That is, while this indicator is low, the container will be empty. After the coolant is heated to a high temperature, the excess formed as a result of thermal expansion is removed into the container. In this case, the membrane rises and the inert gas is compressed.
The expansion tank for such a heating system must be sealed and equipped with a pressure gauge
The process described above, as a rule, is recorded on a measuring device (pressure gauge) and can serve as a signal to reduce the intensity of heating of the coolant. Some types of such tanks are equipped with a safety valve, which is necessary to relieve excess gas.
The coolant in such a container gradually cools and the pressure of the inert gas acting on it gradually squeezes the coolant back into the structure. After removing the cooled coolant from the tank, the pressure on the measuring device is equalized.
Membranes for such devices are divided into two types depending on their shape:
- disc-shaped;
- pear-shaped.
The process of starting an open gravity heating system
In modern houses, open heating systems are quite rare; such technologies have long been considered a relic of the past. But they still exist, so you should consider how they need to be filled with water. In any such heating system there is an expansion tank at its highest point; it is designed to accumulate water after increasing its volume in the system with increased pressure during rising temperatures. The tank is an open container with or without a lid. The system is filled with water through the tank. Large volumes of liquid, of course, will be quite problematic to fill in small containers, especially at the highest point.
It would be most rational to use a regular household vibration pump. To do this, prepare a capacious container and fill it with water. Pre-prepared hoses are attached to the pump with clamps. This pump has a submersible type of structure. The hose through which water will be drawn must be lowered into a prepared tank of water. The hose from which the water will be released is immersed in the expansion tank. Turn on the pump, the pressure in the system should be from one and a half to two atmospheres. When lowering, add water to the prepared tank and lower the hose into it. When the heating complex is filled, water will be visible at the bottom of the expansion tank, the system can be considered full.
Installation diagram of a water heating system.
Excess air will come out of the pipes during the first fire through the expander. It should be noted that during the heating season, when the system maintains a constantly high temperature, water will gradually evaporate from the expander. It is necessary to recharge by adding water to the expander to the required level. You should also monitor the temperature on a thermometer attached to the heating boiler. When its level reaches above 80°C, the water will soon begin to boil and splash out. In this case, it is necessary to block the access of oxygen to the firebox to reduce the intensity of combustion.
Types of heating systems
Regardless of which heating structure is used, the principle of operation remains the same - the coolant is heated in the boiler to the required temperature and circulates through the pipeline to the heating devices, gradually cooling. After the coolant gives up its heat, it returns back to the boiler and the process repeats.
As a rule, two substances act as a coolant:
- water;
- antifreeze.
There are two main types of heating systems, which are classified according to the design of the expansion tank. An expansion tank is a device that compensates for the thermal expansion of the coolant when it is heated.
The heating system can be closed or open. Let's look at these two types in more detail:
- Open. In this design, the expansion tank is leaky. Therefore, when laying such communications in a private house, any suitable container can be used as a tank. However, there is one very important rule that should be followed when installing an open heating structure - the expansion tank must be located above other elements of the system.
- Closed. In a closed heating communication, the tank is sealed. Thanks to this, such a container can be mounted anywhere in the system.
In a closed system, the expansion tank must be large, but it can be located anywhere
Helpful information! Thanks to the high sealing performance of such a system, it becomes possible to increase the pressure. Contact of the working environment with oxygen is also excluded. As a result, the corrosive effect is reduced and the service life of heating equipment is increased.
In some cases, heating tanks are connected to the boiler (the so-called built-in tank). Tanks for closed structures are mainly of the membrane type.
Filling the system from below
So, let's get back to pumping fluid into the system. We use a container of suitable volume (a 200-liter plastic barrel works well). We lower a pump into it, creating the pressure required for pumping liquid no higher than 1.5 atm (typical value in the range of 1-1.2 atm). Such pressure requires the pump to create a pressure of 15 m (for the submersible “Malysh” it reaches 40 m).
Having filled the barrel with water, we start the pump, monitoring the liquid level, which should be located above its inlet pipe to prevent “airing”. The level drops - add water. Antifreeze should be pumped from a smaller container (bucket) so as not to immerse the submersible pump housing in the liquid (and then wash it) - just immerse the inlet pipe. You will have to add antifreeze frequently, turning off the pump periodically.
Filling the system is carried out with Mayevsky taps open on installed heating radiators with substitute containers for collecting water. When liquid comes out of all air vents, close the taps and continue the injection process.
We control the pressure using a pressure gauge (a boiler gauge will do). When its value exceeds the hydrostatic pressure, equal to the pressure in the liquid column height from the bottom to the top point of the system (a height of 5 m gives a static pressure of 0.5 atm), we continue to fill the system, monitoring with a pressure gauge the moment the pressure reaches the required value.
Pumping antifreeze with the “Malysh” pump.
Having filled the system, turn off the pump, open the air valves (the pressure will inevitably drop), and then pump up the water. We repeat the process several times, displacing air bubbles.
We complete the filling by inspecting the system for leaks. After the pump is turned off, the liquid in the hose connected to the outlet pipe is under pressure. If antifreeze was pumped in, first disconnect the hose from the pump inlet pipe and drain the liquid into a container, being careful not to drench the mechanism body.
Filling the system
For home craftsmen setting up autonomous heating with their own hands, it is important to figure out in advance how to properly fill the heating system in a private home in order to prevent the formation of air pockets.
To start heating for the first time in a private house, it is advisable to invite a specialist who will check the correctness of the circuit and the quality of installation of the elements, and control the operation of the boiler. But in the future, after maintenance work, the heating system will again need to be filled with coolant, so you need to know how to do this without errors.
Heating system filling pump
Note! It is recommended to fill a closed heating system with an assistant. One person will fill the circuit with water or antifreeze, and the second will monitor the release of air from the pipes.
Filling with water
At the top point of a properly installed heating system there is an automatic air vent. Before filling the circuit with water, the valve must be fully opened to allow the displaced air to escape through it.
The return pipeline is installed at a slope and a drain valve is installed at the lowest point, which allows the coolant to be removed from the system. Nearby, just below the boiler unit, there should be a pipe with a check valve, which serves to fill the heating system.
A water supply pipe can be connected to the pipe; in this case, to fill the heating system with water, just turn the valve. In the absence of a stationary pipe, the pipe is connected to the water supply using a flexible hose. Filling a closed heating system with water requires that the water be supplied at a pressure slightly higher than the design operating pressure.
Checking the battery after filling with water
The supply of water to the system is completed when all heating devices and pipes are filled - coolant begins to flow from the upper air valve
. At the final stage of filling, close the upper air valve and open the Mayevsky valves on all batteries one by one to eliminate air bubbles. Water injection stops when all air has been removed from the system and the pressure gauge on the safety group shows the design pressure (1.5 atm or more, depending on the characteristics of the boiler).
If a closed heating system uses a double-circuit boiler with a water make-up module, the procedure involves connecting the filling hose to a special tap for pumping coolant, which is part of the module.
If we are talking about a system with a gas boiler and a water circuit, it is important to know how to start the unit
. The front cover is removed from the boiler to provide access to the circulation pump. After filling the system with your own hands and checking it for leaks, turn on the unit, setting the operating mode. From the pumping circulation pump, which begins to gurgle, lightly unscrew the cap with a screwdriver so that the air comes out and water begins to drip. Then the lid is screwed back on and after 3-4 minutes the operation is repeated two or three times at short intervals. The unit will become quieter and the burner will ignite. Check the pressure gauge and briefly open the supply valve to create the design pressure.
Filling with antifreeze
The use of non-freezing liquid as a coolant has its own characteristics. Let's figure out how to fill a closed-type heating system with antifreeze, given that it cannot be filled through an expansion tank or supplied from a water supply.
Filling with antifreeze
The system is filled as follows
:
- Option 1. Non-freezing liquid is pumped with a manual pressure test pump, which will provide the required pressure.
- Option 2. An electric pump is used that is capable of pumping liquids with different densities.
- Option 3. Filling is done through a hose, the lower end of which is connected to the non-return valve, and the upper end is raised above the top point of the system (to the attic, roof, second floor). Upon completion of the work, the remaining coolant is drained from the hose into a substitute container.
Types of closed heating system diagrams
The main advantage of natural circulation schemes is their independence from the availability of electricity, but they have a limitation: the length of the circuit must be no more than 30 meters, otherwise the system will be inoperable. There is one more nuance - with natural circulation, even in a closed system, you need to install a drain valve at the top point, with the help of which you can remove air that has entered, for example, when adding coolant.
System with natural circulation of a one-story house. Single-pipe circuit, top wiring
In a forced circulation circuit, pressure is created by a circulation pump. Some boilers have it built in, some don't. Some long circuits require the installation of two pumps. Then it is not necessary to observe slopes; the most important thing is not to make the sections slope in the other direction, which will negatively affect the performance of the heating and may even require rework.
On the one hand, the use of circulation pumps is a disadvantage, since its performance depends on the availability of electricity, but on the other hand, it is a big plus:
- allows you to use pipes of a smaller cross-section and radiators of a smaller volume, which means you spend less money on purchasing materials;
- increase the speed of movement of the coolant, and therefore reduce its inertia and increase the level of comfort;
- less coolant, less fuel is wasted on heating it - money is saved.
Reduced volumes of pipes and radiators mean a decrease in the volume of the system, which again makes it possible to reduce the heating inertia of the coolant - it heats up faster, and the heating is more efficient. A smaller volume of coolant means a smaller volume of the expansion tank, and there is no need to look for a place to install it. Modern boilers have built-in membrane tanks (for example, wall-mounted gas boilers), and the heating efficiency using them is very high due to the fact that a powerful pump is installed (it is also built-in).
It is better to connect the pump with a bypass - to be able to repair/replace it without destroying the system
When choosing a pump, remember that there is a direct relationship between its power and heating efficiency. Therefore, choose one that is low noise, powerful and reliable.
It is worth noting that it is easy to make a closed one from an open system - you just need to change the expansion tank - install a membrane type and the system will be operational. To make it more efficient, you will need to install a pump. Moreover, modern pumps can be installed in both supply and return. Previously, they were installed on the return line because the coolant temperatures there are lower. But modern pumps use heat-resistant materials; the temperatures of heating systems are not so critical for them
Just when buying, pay attention to the operating temperature range, or put it in the return line - only so that it “presses” into the boiler. In this case, the pump power may be small, since open systems use larger pipe diameters than closed ones, and the hydraulic resistance of the system is small
There are many nuances and features in heating a private home, and it’s not easy to figure it out. But once you set a goal, you can do everything yourself - create a workable good project, select the right equipment and install everything yourself. And closed systems in this sense are no exception.
Features and Benefits
Heating systems differ in the configuration of the expansion tank - a special container that compensates for the thermal expansion of the coolant. An open tank is installed in a gravity system - the liquid moves through the pipes without installing a circulation pump for heating. The coolant moves due to the natural circulation of the medium, which changes density when heated and under the influence of gravity.
A feature of a closed system is the use of a closed expansion tank, which is a sealed container equipped with an elastic membrane inside. This ensures efficient operation under pressure and eliminates contact of liquid with air.
Internal structure of closed expansion tanks
With forced circulation
A closed-type heating system in a private house may include a circulation pump that forces the coolant to actively move, maximally warming up all heating devices or the heated floor circuit.
A closed heating system with forced circulation has a number of advantages
:
- Heating of a liquid under pressure occurs faster;
- the risk of airing of the pipeline and radiators is reduced;
- evaporation of the coolant (which is especially important when using antifreeze) and the penetration of oxygen into the liquid, which provokes corrosion of the metal elements of the system, are prevented;
- due to the installation of the membrane tank below next to the boiler, and not at the top point of the circuit, as in open systems, installation and maintenance are simplified;
- the movement of liquid under low pressure simplifies the calculation and installation of the pipeline - unlike a gravity system, in this option there are no strict requirements for the angle of inclination of the pipes and pipes of smaller diameter can be used;
- there is no need to use large-diameter pipes and install them in an open manner in order to have access to any part of the system to eliminate air pockets.
An example with an induction boiler.
The heating system of a private house with a circulation pump and a membrane expansion tank provides better heating of the premises compared to gravity. But it has one significant drawback - energy dependence. The operation of the pump requires electricity, so this option is not suitable for buildings in remote areas with insufficient power supply or its complete absence.
With natural circulation
The gravity heating system is energy independent, and this is its advantage. Typically this is a heating system with a solid fuel boiler or stove; liquid fuel units are less commonly used.
Heating without a pump is suitable for a home with a relatively small area; it is important to correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes for each part of the system and design their installation scheme, observing the optimal angle of inclination of the pipeline sections. It is necessary to reduce the risk of airing and ensure efficient movement of the coolant.
A circulation pump can be added to a closed heating system with natural circulation at any time, increasing its efficiency. This is the best option for areas where there are problems with power supply. In this case, if there is a temporary lack of electricity, the house will not be left without heat - a closed-type system in a private house will work like a gravitational one.
Natural circulation
Note! The use of a membrane tank in a gravity system negatively affects its functioning, since the liquid in a closed heating system needs to overcome the resistance of the membrane in a sealed container. For gravity systems, an open tank is preferred, and a circulation pump is usually added to a circuit with a membrane expansion tank.
Filling technology where to supply coolant
The necessary means are a container and a pump that creates the required pressure of the coolant liquid. Submersible type “Gnome” or “Kid” are quite suitable (popular with gardeners who use them for watering areas located above the levels of reservoirs). There is evidence of successful filling of closed systems using hand pumps - from those used for spraying protective solutions on garden crops, to specialized hand pumps used for pumping motor fuels or liquid chemicals from drums. Any heating circuit can be successfully filled by monitoring the pressure using a pressure gauge.
Filling the system with antifreeze using a submersible vibration pump.
The first step is to select the fluid entry point. If the pressure created by the pump raises the liquid to the top of the system, it should be connected at the lowest point of the boiler room - the coolant make-up pipe, cut into the “return” in front of the boiler. In addition to the make-up inlet, a structurally separate drain outlet is required (two different system components). The first is equipped with a valve (ball valve) and a check valve, the second - only with a valve (ball valve). If the lowest point of the system is the water drain fitting from the boiler, then you can drain/fill the system with water through it. Since a check valve is not installed behind the boiler drain (behind the drain at all), any shutdown of the pump will cause the pumped liquid to leak out - you need to quickly turn off the tap in front of the fitting.
Design of a typical drain/recharge unit.
Choosing the right boiler for a closed system
A closed heating system can operate in autonomous mode. Experts recommend installing automatic boilers that operate according to the parameters set after installation. In this case, no intervention from the owners is required, which is very convenient.
The main types of boilers, depending on the fuel on which they operate:
- gas;
- electrical;
- liquid fuel;
- on solid fuel.
The most suitable option for closed heating communications are boilers that use gas as fuel. When installing a gas boiler for a closed heating structure, it is possible to connect a room thermostat to the system. This device allows you to set the required temperature in heated rooms, and the temperature accuracy is very high (up to one degree).
Some types of boilers can be connected to special weather sensors, which are installed outside the building and transmit weather information. According to their readings, the boiler regulates the power and heating rate of the coolant.
A closed system for heating a house can be organized with any type of boiler, including electric
It is also worth saying a few words about models that operate on electrical energy. There are three types of such boilers:
- conventional boilers that include a tubular electric heater (TEH);
- induction;
- electrode.
The last two types are considered more compact and profitable from a financial point of view. In addition, they have a lower coefficient of inertia, which is also an undeniable advantage.
The most versatile boilers today are those that use solid or liquid materials as fuel.
Note! When installing a device that operates by burning liquid fuel, it is necessary to arrange a separate room (taking into account fire safety rules). Solid fuel appliances are allowed to be installed in the house.
Solid fuel boilers have the ability to organize automatic control of the combustion process, however, due to the specifics of the fuel, the efficiency of such an automatic system will be lower.
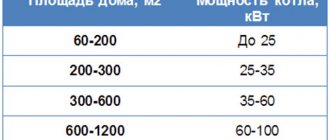
Calculating the power of this device is quite simple, but there are some nuances here too. Experts advise choosing a boiler based on the following calculation: 100 watts of power are required per 1 m² of area. It is advisable to select a boiler with a slightly higher power. This is due to the fact that there are abnormally cold winters. The power reserve should be approximately 30–50%.
When filling with coolant
There are only two known situations that require this technological operation:
- putting heating into operation (at the beginning of the heating season);
- restart after repair work.
Typically, coolant water is drained in late spring for two reasons:
- Water inevitably becomes contaminated with corrosion products (inside radiators, metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes are not susceptible to it). If you leave old water for the new season, you risk breaking the circulation pump with solid contaminants.
- Flooded systems in country houses that have not been started can “defrost” during a sudden cold snap - such cases are not uncommon. In this sense, antifreeze coolant is preferable. The high-quality composition has high anti-corrosion properties, increasing the drain interval to 5-6 years. There are known cases of uninterrupted heating operation with the same volume of antifreeze for 15-17 years. It is recommended to drain low-quality antifreeze after 2-3 years.
Pumping antifreeze into the heating system.
System pressure and make-up
Stable operating pressure is the key to efficient operation of the heating system. Let's figure out why the pressure in the heating system drops. This is due to a decrease in the volume of coolant, which is caused by inevitable leaks in components and connections, release of liquid from air vents during manual de-aeration of radiators, etc.
An automatic make-up valve connected to the water supply will protect you from falling pressure below the required values. In small systems, a mechanical valve is installed, but in this case the consumer needs to regularly check the pressure gauge readings and add the required volume of coolant manually.
Conclusion. The ability to correctly fill a closed-type heating system will allow you to properly prepare it for the heating season and start it up after repair or maintenance work.
Video on the topic:
Features of starting a closed heating system with distilled water
Filling a closed heating system with water has the following features:
It will be much easier to provide the heating circuit with the necessary pressure if the living space has access to a central water supply. In this situation, to pressurize the heating system, it is enough to fill it with water through a jumper that removes the water supply, while carefully monitoring the increase in pressure on the pressure gauge. After completing such an event, unnecessary water can be removed using any of the valves or by means of an air vent.
Many people wonder whether special preparation of water for the heating system should be carried out or whether it is possible to limit it to water from the nearest body of water. At the same time, some argue that distilled water in the heating system will have a beneficial effect on the service life of the equipment and will not allow it to fail prematurely. But it is much more important to understand how to prepare water for heating if a special non-freezing liquid like ethylene glycol is added to it and how to subsequently fill the heating circuit with such coolant.
For these purposes, it is customary to use a special pump that serves to fill the system with water, and it can be controlled either automatically or manually. This pump is connected using a valve, and after ensuring the required pressure, the valve is closed. There are situations when such equipment is not at hand. As an option, it is possible to connect a standard garden hose to the discharge valve, the second end of which should be raised to a height of 15 meters and the circuit should be filled with water using a funnel. This method will be especially relevant if there are tall trees near the building being developed.
Another option for filling the heating system is to use an expansion tank, which performs the function of containing excess coolant caused by its expansion during the heating process.
Such a tank looks like a reservoir, which is divided in half by a special membrane made of elastic rubber. One part of the container is intended for water, and the other for air. The design of any expansion tank also includes a nipple, with which it becomes possible to establish the required pressure inside the unit by removing excess air. If the pressure is insufficient, then this parameter can be compensated by pumping air into the system using usually a bicycle pump.
The whole process is not particularly difficult:
First, air is eliminated from the expansion tank, for which you need to unscrew the nipple. Ready-made tanks go on sale with slightly excess pressure, which is equal to 1.5 atmospheres; then the heating circuit is filled with water. In this case, the expansion tank must be mounted so that it is positioned with the thread upwards
It is important to remember that it is not advisable to fill the tank completely with water. It would be more correct if the total volume of air in this device is approximately one tenth of the total volume of water, otherwise the tank will not cope with its main function and will not be able to accommodate excess heated coolant; after this, air is pumped into the system through the nipple, which, as mentioned above, can be done using a regular bicycle pump
The pressure must be monitored using a pressure gauge.
All of these actions will allow you to carefully fill the heating system with water and ensure stable and high-quality operation of the entire circuit. If necessary, you can always turn to specialists for help, who always have in stock various photos of devices necessary for such work that can help with connection.
Filling the heating system with water in the video:
Protecting the system from air
Theoretically, air should not enter a closed heating system, but in fact it is still present there. Its accumulation is observed when pipes and batteries are filled with water. The second reason may be depressurization of joints.
As a result of the appearance of air pockets, the heat transfer of the system decreases. To combat this phenomenon, the system includes special valves and air bleed valves.
If air does not accumulate in the system, the air vent float blocks the exhaust valve. When an air lock accumulates in the float chamber, the float stops holding the outlet valve, causing air to escape outside the device
To minimize the likelihood of air pockets, certain rules must be followed when filling a closed system:
- Supply water from the bottom to the top. To do this, lay the pipes so that the water and the released air move in the same direction.
- Leave the air vent valves open and the water drain valves closed. Thus, with a gradual rise in coolant, air will escape through open air vents.
- Close the vent valve as soon as water starts flowing through it. Continue the process smoothly until the circuit is completely filled with coolant.
- Start the pump.
If the heating circuit has aluminum radiators, then air vents are required on each one. Aluminum, in contact with the coolant, provokes a chemical reaction accompanied by the release of oxygen. In partially bimetallic radiators the problem is the same, but much less air is produced.
An automatic air vent is installed at the top point. This requirement is explained by the fact that air bubbles in liquid substances always rush upward through the pipe, where they are collected by a device for removing air
In 100% bimetallic radiators, the coolant does not come into contact with aluminum, but professionals insist on the presence of an air vent in this case too. The specific design of steel panel radiators is already equipped with air bleed valves during the production process.
On old cast iron radiators, air is removed using a ball valve; other devices are ineffective here.
Critical points in the heating circuit are pipe bends and the highest points of the system, so air exhaust devices are installed in these places. In a closed circuit, Mayevsky valves or automatic float valves are used, which allow air to be vented without human intervention.
The body of this device contains a polypropylene float connected through a rocker arm to a spool. As the float chamber fills with air, the float lowers and, upon reaching the bottom position, opens the valve through which the air escapes.
Water enters the volume freed from gas, the float rushes up and closes the spool. To prevent debris from getting inside the latter, it is covered with a protective cap.
The body of both manual and automatic air vents is made of high-quality material that is not susceptible to corrosion. To remove the air lock, turn the cone counterclockwise and release the air until the hissing stops.
There are modifications where this process takes place differently, but the principle is the same: the float is in the lower position - gas is released; the float is raised - the valve is closed, air accumulates. The cycle repeats automatically and does not require human presence.
Closed heating system. How to fill with water correctly
Nowadays, many owners of apartments and private houses choose closed heating systems. A closed system is a circuit within which the movement of the coolant is carried out using the movement of the coolant - a pump, that is, forced. A special feature is a membrane-type expansion tank. Essential elements. boiler, tank - membrane, radiators, pump, pipes, also fittings, fasteners and filtering equipment. But very often, buyers of such “closed heating” soon wonder how to fill it and how to close the heating pipes. Below we will tell you how to properly fill a closed heating system with water.
The heating system is filled through the boiler power supply. This is done using an electric pump, as well as a manual crimping machine. The system is filled with prepared network water or antifreeze made using a special method - it is a non-freezing coolant. At this time, air is released throughout the entire internal part of the system (faucets, radiators, vents, etc.). When the required pressure has been achieved, the system can be put into operation. Sometimes there are difficulties in creating ideal pressure. Closing the heating pipes will largely depend on individual wishes, the design solution of the room and the location of the pipes themselves in the apartment, their number and size.
Difficulties often arise when filling with water. If the system is closed, then the expansion membrane tank (pressure inside the tank up to 6 bar) and the safety valve up to 3 bar must also be closed. Special valves must be installed to bleed air in accumulation areas, as well as a valve for feeding and filling pipes and heating equipment. The sequence of actions when filling a closed system is as follows:
Unscrew the screw located on the pump. Use a screwdriver to unscrew the pump system shaft. Tighten the screw tightly. Open the make-up screw. Fill the system until the pressure reaches approximately 0.5 bar. (you can start from 0.3 bar). Be sure to check if there are any leaks during this procedure! Raise the operating pressure in the system to 2 bar. Make sure that there are no leaks anywhere. Bleed the air in absolutely all internal places of the system. The next step is to increase the pressure in the system to about one and a half bar. This will be the most optimal pressure for a closed heating system. If the system undergoes cooling or heating, then the fluctuations should not be significant (from 0.1 bar to 0.5 bar). Watch the range of fluctuations! Sudden changes threaten to break all equipment, pipes and fittings!
There is no water level in such closed systems. The presence or absence of water is controlled using pressure. At normal levels, it should be between one and two bars.
A closed heating system is easy to operate, less susceptible to corrosion and destruction, and is easy to replenish and, if necessary, drain. If you have any questions or find malfunctions in the operation of the heating system (freezing, leaking, etc.), then immediately contact support!
Heating boilers are one of the main types of heating equipment and are devices for heating the coolants entering the heating system to a certain temperature. The coolant passes through a closed circle of the heating system.
Before you start looking for contractors to improve your own balcony, answer yourself one question: what do I want to get as a result of glazing? Perhaps you just want to use this room for drying.
Such cast iron radiators, which are familiar to the majority of the population and were installed many years ago, can no longer fully cope with the functions assigned to them for heating rooms and have a rather unattractive appearance.
Solid fuel heating boilers are devices that heat a room using solid fuels (for example, wood, coke, briquettes or coal). Typically, such boilers are universal, as they can work on anyone.
Operating principle of closed type heating
What does a closed heating circuit look like? The main design feature, which determines the name of such a system, is its tightness.
A closed-type heating system, the diagram of which includes elements, some of which are used in other types of heating, looks like this:
- boiler;
- air valve;
- thermostat;
- heating appliances;
- expansion tank;
- balancing valve;
- ball valve;
- pump and filter;
- pressure gauge;
- safety valve.
This is what closed-type heating looks like, the diagram and principle of operation of which is quite simple: the liquid circulating in the system is heated in the boiler and enters the pipeline. When expanding, excess liquid enters the tank, and when the temperature drops, it returns back, which makes it possible to maintain the internal pressure in the system at a given level (pro
What to do if the pressure in the system drops and increases
If you notice a decrease in pressure, the first thing you need to do is turn off the pump. And then act based on the pressure gauge readings:
- If the static pressure also drops, there is a leak somewhere. It is necessary to inspect all the elements and eliminate it. Please note that even a very small hole (less than a millimeter) can be the cause, so it can be difficult to find the damage. If the pipeline is long, you can localize the leak area by disconnecting the branches one by one. As soon as the fall has stopped, the area is determined - depressurization on the one that was just turned off.
- If the pressure is stable when the pump is turned off, the pump has failed and needs to be repaired or replaced.
An increase in pressure is observed less frequently, but it also happens. It is usually caused by an increase in temperature in the system, and it rises due to insufficient coolant circulation. But why the coolant circulates poorly needs to be understood.
- First, we check the functionality of the pump. Let's turn it off and watch. If the pressure continues to rise, the problem is not with the pump. If it stabilizes, it’s his fault.
- We clean filters and dirt traps.
- If the pressure still rises, an air lock may have formed - bleed the air in the system.
- If this does not help, we check the condition of the shut-off valves - maybe someone accidentally or intentionally closed it, blocking the flow of coolant.
- Another reason is that due to a breakdown or failure of the automation system, the system is under constant recharge.
Using this algorithm, you can independently determine the cause of the abnormal condition of the heating system and eliminate it.
Security group for a closed system
Security group for a closed system
Safety group for a closed system The safety group is installed on the supply pipeline at the outlet. The main function of this element is to control the operation of the entire system, as well as adjust its parameters. Its kit includes a pressure gauge, air vent and safety valves.
Using a pressure gauge, you can measure and control pressure. The pressure should vary between 1.5-3 bar depending on the size of the house (for two-story buildings this is a maximum of 2 bar).
If the device shows a deviation from the norm, then it is necessary to look for the reasons for this behavior of the equipment:
- A sharp decrease in pressure, you need to look for a leak in the system, and also add coolant.
- If the pressure becomes high, then pay attention to the operating mode of the boiler - it can greatly heat the coolant.
There may also be problems with the operation of the circulation pump, the safety valve (its function is to remove excess coolant at elevated pressure) - or you need to check the correctness of the pressure gauge readings. The problem most often occurs in the safety valve - it is connected to a pipe through which excess liquid is discharged into the sewer. This is why it is necessary to monitor that the valve operates, but if the water is released too often, then there is a malfunction somewhere in the system.
The safety group also includes an automatic air vent that releases excess air that enters the equipment. Its main function is to prevent the formation of air pockets.