For the comfort of residents, an efficient, working heating system is necessary. The heat supply must provide space heating in all weather conditions. When designing, each heating system diagram for a two-story private house must be calculated and the most profitable option for each specific case must be adopted.
Important! The heating system must not only be of high quality. Proper design can reduce heat consumption costs by up to 40%. At the design stage, the cost of installation work, maintenance, use of a boiler that runs on different types of fuel, etc. should be taken into account.
High-quality heating systems can operate with high efficiency for several decades without repairs or additional maintenance.
Important! Proper heating design and installation will ensure a comfortable temperature level in any home.
What to consider when choosing a heating system
In addition to climatic conditions, when choosing a scheme and system, it is necessary to take into account:
- the presence and type of material from which the external walls are made, the presence of insulation;
- type and quality of glazing, number of windows;
- area and volume of heated premises.
Temperature indicators for high-quality heating:
- For living rooms +22°С.
- Bathrooms +24°C.
- For coolant within +60..80°C with radiators.
- When heating with heated floors, the indicator is +30..35°C.
Hydraulics and balancing
If the heated area of the building does not exceed 200 sq.m, the coolant flow is distributed naturally. In a hydraulic calculation for a two-pipe dead-end heating system, the pressure loss in each of the branches is calculated.
Balancing is necessary to connect the branches to each other in such a way that the pressure loss in all branches is the same. Installing balancing valve branches in the mains simplifies the process. This allows you to avoid situations where the coolant, moving along the path of least resistance, will circulate only along a branch with low pressure.
Main components of the heating system
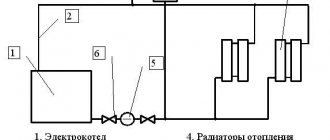
A boiler in which the coolant is heated. Located below the level of the radiator and pipelines. After determining the optimal location of the boiler, it is necessary to outline the installation location of the radiators, the laying of pipelines and the source of water supply to the system.
Pipeline. Steel and plastic pipes can be used. Metal pipes are characterized by high thermal conductivity and high resistance to mechanical stress. Disadvantages include susceptibility to corrosion.
Polyvinyl chloride pipelines have a number of advantages: light weight, quick installation, long service life, corrosion resistance. Due to the low temperature, heat losses in pipelines are reduced.
Important! Antifreeze cannot be used as a coolant in metal pipes.
Radiators – for heat transfer. Used from different materials:
- cast iron;
- aluminum;
- bimetallic.
Aluminum ones are designed for pressure up to 18 atmospheres. The main advantage is high heat transfer. It is not recommended to drain the coolant from the network for a long time due to the susceptibility of the material to corrosion.
Heating system controls
Bimetallic. Used at high pressures up to 40 atmospheres. Characterized by high heat transfer and durability.
Steel. Designed to operate at pressures up to 8 atmospheres. Like aluminum, they are susceptible to corrosion.
Cast iron is a classic type of radiator. They have a high heat transfer coefficient. Advantages: slow cooling, corrosion resistance.
As well as other components of the system:
- Circulation pump (in case of artificial circulation) for forced water supply into the system.
- Expansion tank - to remove excess coolant pressure.
- Thermostatic and safety valve.
- Shut-off valves.
- Instrumentation devices.
Is a gravity single-pipe system of a two-story house profitable?
Intending to install this cheap scheme, the homeowner is very mistaken. A gravity-flow system (in common parlance, “gravity flow”) will cost two to three times more than one equipped with a circulation pump. Natural circulation requires:
- thick pipes to minimize hydraulic resistance to the coolant;
- sufficiency of slopes of main pipes;
- the location of the heating boiler below the level of the heating devices in the pit in the kitchen/basement, shown in the figure below.
Gravity heating of a 2-story house has a standard drawback - the radiators on the second floor warm up better than the first. Installation of bypasses and control devices increases the cost of the system.
Selecting a heating system
According to the type of coolant for two-story houses, heating is divided into:
- Air. A gas furnace acts as a heat source. The main disadvantage is the constant drop in oxygen levels in the rooms. This type is used in two-story houses without permanent residence.
- Combined.
- Steam. The coolant is water vapor. Due to the complexity of implementation, it is practically not used.
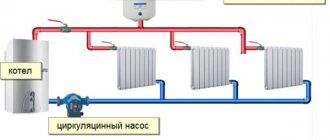
- Vodyanoe. The most appropriate type of heating system in which the coolant is heated water. There are several schemes: with artificial and natural circulation. The types are discussed below.
How does a properly assembled circuit work?
When implementing the classic one-pipe scheme (“Leningrad”), when a main pipe is laid under the radiators, the situation is different. The moving coolant, encountering the first tee on its way, is distributed into two flows in accordance with the values of the hydraulic resistance of the direct path and the side outlet of the tee. Due to the greater hydraulic resistance of the side outlet, a small part of the total coolant flow flows into the radiator (the usual “flow coefficient” is 0.2-0.3). This small part cools down inside the battery by several degrees, as shown in the figure below, mixing at the outlet with the main uncooled flow. Its resulting temperature turns out to be higher than when the entire volume of liquid is passed through the heating device.
Distribution of the coolant in the radiator piping of the “Leningrad” scheme.
When moving along the contour, the temperature of the liquid still decreases, but to a lesser extent, to a temperature of no longer 35 °C, but approximately 45 °C, i.e. The batteries in the chain are more evenly heated. Experts express the opinion that the single-pipe scheme (“Leningradka”) allows for uniform heating of up to 10-11 radiators in the circuit (ten sections in each device).
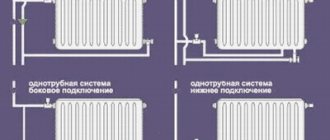
Single-pipe
This circuit is designed so that water is supplied to the radiators sequentially from block to block.
Advantages:
- Low cost of materials and installation work.
- Durability.
- Easy to install.
Flaws:
- Inability to carry out repairs on individual elements without shutting down the entire system.
- Inability to adjust network parameters.
Vertical wiring diagram of a single-pipe heating system
Types of connection
Horizontal wiring is implemented for low- or one-story houses using a dead-end scheme, direct-flow or with a collector.
Vertical wiring with a circulation pump is considered the most effective. All radiators are connected to a vertical riser, which works well in multi-story buildings.
Two-pipe
It is considered more universal. The device involves two circuits: forward (supply) and reverse (return of coolant to the boiler).
Each radiator block has 2 pipes: one brings water in, the other drains it.
For two-story houses, it is recommended to connect the supply circuit at the top point, and the return line at the bottom - to ensure optimal pressure in the pipeline.
Pipes are usually installed in walls so as not to spoil the appearance of the room.
Advantages:
- High efficiency.
- Possibility of adjusting parameters using valves installed on radiators. If necessary, you can exclude the element from the system or reduce the coolant supply to it.
- Possibility of repairing each unit without negatively affecting other heating elements.
Flaws:
- High cost of materials.
Scheme of a two-pipe heating system
Common installation mistakes
Above are “Leningrad” diagrams of horizontal single-pipe floor circuits with radiators connected to a common main line by two tees. Only part of the total volume of coolant circulating through the circuit flows through each device. You may encounter an erroneous connection without a main pipe (see the outline of the first floor in the figure below).
Types of connection of radiators in horizontal single-pipe circuits.
This method of connecting heating radiators is extremely cheap. Each radiator has one fitting for connecting a DN20 or DN25 metal-plastic pipe and a section of pipe between adjacent devices. Can't think of anything cheaper. But the price to pay for the cheapness is poor performance of half the radiators. The first of them (in the direction of the coolant movement) is heated to a temperature of 55 ° C, and the last one at N = 6-8 is heated to only 35 ° C, since the coolant, passing through the radiators, intensively cools down in them.
Gravity system with natural circulation
The coolant moves through the system by gravity.
Principle of operation
When the coolant is heated, it stratifies: the lower layer with a higher density pushes more heated water into the system. The difference in densities ensures natural circulation of liquid through pipelines.
Device
An expansion tank is installed at the top point of the system, which ensures the expansion of water in the system, discharges liquid and recharges the system.
The boiler must be installed in basements or basements. It should be remembered that the level of the return pipes must be laid below the boiler.
Horizontal sections of pipelines are laid with a slope - at the upper connection points of radiators and from the lower ones on the way to the boiler.
Important! To ensure high efficiency, it is necessary to use pipes with a large nominal bore, which ensures a low resistance coefficient of the internal surfaces of the pipes.
Scheme of a gravity heating system
Advantages:
- Autonomy. This circuit can operate without the use of electricity. The best option for remote areas where there are interruptions in the supply of electricity.
- Long service life. Due to the low pressure in the system, the equipment is less susceptible to wear.
- Quiet, because the presence of a circulation pump is not provided.
Flaws:
- High consumption of materials. High costs, because Large diameter pipes are used.
- Labor-intensive installation process. Difficulty in ensuring the correct slope.
- They are used in houses with a total pipeline area of no more than 150 m2.
- Long process of heating rooms.
- Difficulty in removing oxygen from the coolant. Can be eliminated by designing the correct pipe slope to allow bubbles to flow naturally through the expansion tank into the air.
Features of a dead-end highway: what is it?
The dead-end heating system is a two-pipe circuit. A single-pipe line is closed. A dead-end system is caused by the movement of coolant from the radiator and back. This scheme involves directing the liquid through the supply pipes in one direction until it enters the battery. There the coolant gives off heat and moves into the return pipeline back to the boiler.
Dead-end circuits can also occur with a single-pipe system. But this option is expensive and difficult to implement.
Most often, a dead-end circuit is used for forced movement of coolant, since in this case a smaller pipe diameter is used. But more and more often there are systems with natural circulation of liquid and the use of overhead wiring. Dead-end systems are considered the simplest and most economical to implement and use.
Types of two-pipe systems:
- Passing;
- Radial.
When evaluating hydraulics, such options are considered better than a dead-end system. The parallel movement of the coolant implies its direction in one direction after leaving the radiator. Good balance of the network is maintained by maintaining the same distance between the inlet and return pipelines.
The beam (collector) system is the easiest to use and regulate. But its arrangement will be the most expensive. But this option can fit perfectly into a cottage with a large area.
Scheme with heated floor
The water supply occurs through a collector, the second serves for the return flow of the coolant.
Main components (basic version):
- Manifold cabinets. To ensure proper fluid flow. Installed in a location accessible for maintenance.
- Instrumentation and automation devices: thermometers and pressure gauges.
- Shut-off valves, compression fittings, adapters.
- Pipeline.
- Warm floor system.
The only drawback is that in the usual scheme it is impossible to control the temperature of the coolant; adjustment must be provided.
To increase efficiency, the circuit is supplemented with the following elements:
- Circulation pump. Used when it is necessary to increase the pressure. Installation is provided on the return circuit.
- Three-way mixer.
- Clan for liquid discharge.
- Pumping and mixing unit. Used to: reduce the temperature in the system, return cooled liquid back to the system. installed behind the water supply manifold.
Important! Instead of shut-off valves, it is possible to use mixers (thermostatic). Thus, the water supply is carried out without jerking.
Connection diagram for a water heated floor to a boiler
Which system is better
For high-quality heating of two-story houses, both single-circuit and double-circuit connections can be used.
The economic and technical effect of heating two-story small houses with a short pipeline length is observed with the introduction of single-pipe systems.
For two-story houses with a large area, the use of two-pipe heating systems with forced circulation is recommended. The pump load depends on two parameters: the diameter of the pipes and the area of the heated premises.
Recommendations for operating the heating network:
- Pumps are selected from ceramic parts with a mechanical adjustment system, which are silent in operation and durable.
- Connections and fittings must be properly protected from liquid leaks.
- Fittings should be selected depending on the material and diameter of the pipes.
- Radiators should be installed under window openings to reduce heat loss. The number of radiator sections depends on the area and type of heated room. The temperature level for residential rooms is higher than for non-residential ones (for the kitchen the number of sections should be reduced, since heating elements - gas and electric stoves - are expected to operate in the room). To reduce losses, it is recommended to install thermostats on each radiator block to constantly adjust the parameters of the heating network.
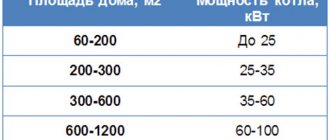
- The boiler power is selected based on the area of the rooms, the length of the main sections, the number of windows, the climatic conditions of the region, the presence of insulation of the external walls of the building, etc.
- For systems with antifreeze as a coolant, due to physical characteristics, the number of radiators in the network must be increased.
Heating system of a two-story house with heated floors
pros
Single-pipe systems also have advantages, which determines their popularity. The most important advantage is the low cost of installation due to the reduction in the number of pipes and time.
Important! This scheme is suitable for houses of different heights and with different layouts. Regardless of the architectural features of the house, it will completely cover all rooms.
During installation, it is allowed to lay the deck chair in the floor screed. For underfloor heating systems, a single-pipe design is the ideal choice. The pipeline can also be laid on the floor surface. In this case, it is necessary that the sun lounger goes as low as possible.
conclusions
Heating is the main condition for comfort in the house during the cold period. Correct selection of equipment will not only improve the quality of the network, but also reduce fuel consumption for heating the house. For two-story residential buildings, the heating system is selected based on the parameters of the buildings themselves.
Errors in the design and installation of equipment should be avoided, because they lead to improper circulation of coolant in pipelines and incorrect temperature conditions.
When designing the system, the climatic region should also be taken into account, because for cold regions, the coolant flow increases to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house.
Advantages and disadvantages
A two-pipe system requires more materials and more work.
The advantages of a dead-end heating system for a private house include:
- simple installation and operation;
- the versatility of the system, since it is used to heat one-story and two-story buildings;
- the ability to replace the battery while the system is running;
- vertical and horizontal types of heating are attractive in terms of cost, which is why they are popular among cottage owners.
The disadvantages of a dead-end system include prolonged heating of radiators, the need to lay a long line and a large amount of installation work.