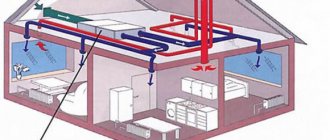
Register constructs
Each individual register is welded from one or more pipes located vertically or horizontally.
Material with a diameter of 32–200 mm (usually 32–80 mm) is used. The choice of register cross-section size is limited by the boiler power - water in wide volumetric tanks is not heated to the required level. The length and number of pipes depends on the parameters of a particular room: area, insulation, and the presence of other heat-releasing elements in the room. In order for the heat transfer from the panel to be maximum, the distance between the two pipes during welding is made 5 cm greater than their diameter. This increases the area from which heat is radiated into space. At a smaller distance, a register made of smooth pipes will waste heat on heating itself, and at a larger distance, there will be air “holes” in the created thermal “wall”, and the efficiency will decrease. The pipes are connected to each other by welding (less often by a threaded connection) with thin transverse tubes - pipes. There are various designs of this type of heat-transfer elements: heating registers made of smooth pipes (round or profile) and finned pipes. The last option is a heating element on which perpendicular metal plates are welded at high frequency. This was done to increase the heat transfer area and increase the efficiency of the device. The appearance of the finned pipe leaves much to be desired; it is more often used for heating non-residential premises. In apartments, they prefer to replace the finned structure with a more “civilized” option.
Horizontal register. In shape, horizontal registers are S-shaped (serpentine) and sectional, which are several parallel pipes forming one section. Essentially a single-pipe S-shaped system is heating from pipes without batteries. If the pipeline is installed with a slight slope of 0.05%, then a pump is not required for the system, the water circulates naturally. When using a horizontal register, any connection is possible - top, diagonal, bottom or side.
Vertical option. Registers and vertical radiators are a series of vertically welded thin tubes. In this design, pipes of large diameters are not appropriate, since they are often installed where space is limited - for example, when replacing batteries with registers as a result of connecting a loggia. A circulation pump is required to move the liquid vertically. The main advantage of these samples compared to horizontal ones is the aesthetic appearance. A carefully welded vertical heating radiator can decorate a room on its own or with the use of decorative elements.
Useful tips
If the heating system of the house was assembled taking into account the use of forced movement of the coolant, that is, a circulation pump is installed in it, then the home-made device can be installed as desired (vertically or horizontally).
If the coolant in the heating system moves according to natural laws, then the battery must be mounted only horizontally. In this case, there is no need to install an air vent on it (Maevsky tap).
It is impossible to make a high-quality radiator from pipes if you have the skills to operate a welding machine at the beginner level. The seams must be welded well; the safe operation of the device and the entire heating system depends on this.
Registers from a profile pipe
The profile pipe in cross-section forms a shape other than a circle: square, rectangle or oval. You can make registers from any type of profile. Although the products are more compact and more attractive in appearance than analogues made from round pipes, the manufacturing process is somewhat more complicated. For this you will need:
- rectangular pipe with a cross-section of 60*80 mm (or another type of profile);
- inch pipe for jumpers with a cross section of 25*25 mm;
- plugs for profile pipes;
- Mayevsky tap to eliminate airiness in the system;
- grinder, hacksaw;
- welding machine.
The sequence of actions in the manufacture of a three-pipe sectional register from a rectangular profile is as follows.
The rectangular pipe is cut into pieces of the required size in the required quantities.
Markings are made on the cut metal pieces to cut out holes into which jumper pipes are subsequently welded. The holes are cut out.
For jumpers, 4 inch pipes (25*25 mm) are used.
The plugs for the profile pipe are cut from sheet metal 3 mm thick. The dimensions of the rectangular plugs around the perimeter are 1.5 mm smaller on each side than the cross-section of the profile pipe - to fill the space with a welding seam.
The pipes are laid out horizontally, and jumpers are placed strictly along the holes.
The jumper pipes are “caught” point by point by welding: 3 points are made so that during further work there are no kinks or distortions.
WATCH THE VIDEO
The product is installed vertically. All jumpers are welded with a full weld.
Build process
First of all, you need to prepare, i.e. purchase all necessary materials. We cut a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm into two halves 80 cm long; for this you can use a grinder.
Next, we cut 2 pieces of 100 mm length from pipes with a diameter of 25 mm, and 4 pancakes are cut from a steel sheet for an outer diameter of pipes of 100 mm.
Then two holes with a diameter of 25 mm are cut out in 100 mm pipes - their location from the edges should be at a distance of 50 mm on diametrically opposite sides.
After this, you can assemble the structure. First, pancakes cut from sheet iron are welded. Then two 100 mm pipes are connected to each other with a 25 mm pipe, exactly along the cut holes.
The second piece of 25 mm pipe is welded on the opposite side; it will serve as a reinforcing element, after which two bends are welded: top and bottom.
Installation methods
A homemade heating battery is assembled from individual pipes using welding or threading. The first option is preferable and stronger than the second; the welds can withstand a pressure of 13 atmospheres. Heating registers are assembled into finished products and then connected to the heating circuit. The device is mounted on the wall with brackets; for installation on the floor, supports are welded from below. The process of assembling a sectional product occurs in several stages:
- Cut the required number of pipes of the required sizes.
- Markings are made on the workpieces, marking the places where the pipes are connected.
- Connect pipes and pipes.
- Weld the plugs and install the drain valve.
- The product is connected to the heating system.
Advice. The pipes are located closer to the edges of the register - the circulation of the coolant in this case will be more intense.
"Samovar" for heating. In some cases, a homemade register is supplemented with a heating element and an expansion tank - you get an independent heating device, called a samovar. It is not connected to the general heating system; it heats the room autonomously from a 220 V network. The heating element’s sufficient power is 1.5 kW, which is slightly more powerful than a kettle. For convenience, a thermostat is connected to the electric heating element. You can make a samovar with your own hands from round or profile pipes; the models can be stationary or portable, used for heating an unheated shed, pantry, or garage. In these cases, it is better to use antifreeze or oil as a coolant rather than water.
Checking the device
The homemade radiator is ready. As you can see, it is not very difficult to make. All that remains is to check it for the tightness of the welded joints. To do this, one of the drains is closed with a plug, and water is poured into the battery through the second.
Now you need to examine the weld seams. If there are no wet smudges, then all the work was carried out efficiently. If stains do appear, you will have to mark the leaks with a marker, drain the water from the radiator and re-steam the seam.
Answers from experts
Tori:
plastic pipes and aluminum radiators.
LegendaSporta:
polypropylene.
mu.rza:
we bought polypropylene ones. each has its pros and cons. Read this, a very informative article about pipes
Vladislav Ushkalov:
Igor Shkurny:
Polypropylene... have less trouble with it... unless of course you have a soldering iron!!!!
Lizard:
I bought a house with completely defrosted metal pipes and cast iron radiators. I chose, consulted, changed to polypropylene and aluminum batteries. I bought one cast iron. and what? It was she who cracked in the very cold (there was no heating, and there was antifreeze in the pipes, but it did not help). I also changed it to aluminum. Further, in the well next to the house there is water supply for five houses, each has its own valve, the pipes are all iron. They rusted like hell. When it burst again, I raised a fuss, collected money from the people, and the local master replaced the filling of the well with polypropylene again. Now we are all calm. So polypropylene is perhaps more reliable. Some people claim that pipes made of polyethylene (very dense) are even more reliable and are not afraid of frost at all, but I don’t know.
Floors:
Iron pipes are 3-5 times cheaper and much more reliable than propylene and plastic. The disadvantage is corrosion of the metal from the inside, which cannot be gotten rid of in any way, but if the water is not drained from the system, then after cutting a 20-year-old pipe, it is as good as new inside (I myself have cut old heating pipes more than once - there is almost zero corrosion inside. And heating devices are more aesthetically pleasing than aluminum and bimetal. USSR cast iron is no longer in fashion, and the material consumption is appalling)))
Sergey Rudin:
Look here: agrosad m /catalog/tverdotoplivnie_kotli_1
Solo:
In a private house AOGV. ) There seem to be no other options.
Andrey:
rephrase the question. A radiator heating system is one thing, but pipes and radiators are a completely separate issue.
Alexander Bonn:
Gas boiler, steel radiators, welded pipe. Energy consumption: 10 sq. m = 1 kW. For a private house, warm floors (1st floor) and radiators are combined. But there must be an emergency heating system (electric or solid fuel).
Alasseia:
question about heating a spherical house in a vacuum, no information about the source of energy supply, no information about the house itself, what would I recommend - a project for heating your bungalow completed by a specialist
F F:
Boilers, boiler equipment. Heating 2 x storey house. : // forum .domostroy /#gazosnabjenie-vodoprovod-otoplenie-konditsionirovanie Gas wall-mounted boiler Heating, plumbing, sewerage for a house or cottage. Heating 2 x storey house.
Which radiators or pipes are better? - it is necessary to rely on the volume of coolant for the correct operation of the boiler! example - 70 sq. wooden house, - they wanted a fan system with aluminum. heating radiators, after calculating the amount of coolant, we chose a register system of pipes.
For a brick house, combine heated floors (1st floor) and radiators, a fan distribution system, and metal-plastic in a screed. Alexander Bonn +++
alexm66:
The question is very general: which is better, a foreign car or a VAZ - for which there is money and opportunity. I think the main criterion is the reliability of the equipment, and a competent installer will be able to make a workable system out of it, but an illiterate one will ruin any “luxury” equipment.
Best answers
drinker in the thorn bush:
If it is done aesthetically, it is better to use steel registers. If the registers are already mounted, close them behind decorative grilles.
Tech Box:
Smooth pipe circuit for good circulation and large volume of coolant.
Guy from the Future...:
The thermal conductivity of steel is 5 times less than that of aluminum. This means that with the same surface area of the device, the heat transfer of a steel device will be lower than that of aluminum. That is, you will have to make it 5 times larger in size..
Alexander:
The advantage of a smooth register with a large open surface area is that it remains efficient at low coolant temperatures, which cannot be said about modern aluminum ones at temperatures of 40 and below. The disadvantage of a register that has a high heat capacity is that this heat capacity prevents precise regulation. Now it remains to understand the wood-fired boiler and what fraction of the day the return temperature can be no higher than 40C or you have an automated pelletizer with a bunker for several days.
ip:
The best option for hydraulics together with registers is cast iron radiators. They have a slightly larger surface area relative to their volumes and linear dimensions compared to registers. If you need to heat a room without windows and without furniture along the walls, then registers will be good, and if there are windows , then you should put cast iron under them and it will block the heat loss of the room together with a DN50 pipe around the perimeter. The calculation of cast iron comes down to a set of sections in the ratio of two sections per linear meter of street wall for the first floor and one and a half for the second when the first one is heated. Good luck.
Anatoly Bananan:
I think that aluminum heating radiators teplofresh/catalog/alyuminievye-radiatory-otopleniya are best suited for a private home. There are two types of such radiators - cast and extruded. Extrusion radiators are more suitable for heating systems that use antifreeze liquid, since these radiators are more durable and are made of aluminum of fairly high purity.
Marya Lamyr:
I think that decorative stainless steel mesh will suit you perfectly, it is both beautiful and durable! By the way, decorvesta is a good store with similar products!
Pavel Mokov:
The thermal conductivity of steel is less than that of aluminum, so it’s better to take an aluminum radiator, look here tallosplav /catalog/alyuminievye_radiatory/.
Sectional registers made of smooth pipes
Sectional registers are in very good demand among owners of private houses. Such devices consist of pipes that are interconnected and closed with plugs. The energy carrier passes through the top pipe, enters the next one, and ultimately ends up in the discharge line. To increase heat transfer, they try to make transitions between sections as close to the edge as possible. Interpipe plugs can be elliptical or flat. The inlet pipe can be made with a flange, thread or welding.
The design of sectional registers includes a threaded fitting, to which a special vent is attached to remove air from the system. Pipes for sections can have different diameters (from 25 mm to 40 cm), so choosing the appropriate option is not difficult. Transition pipes usually have a smaller diameter. In addition, one of the most important operating conditions for such installations is the pressure in the system not exceeding 1 MPa.
Advantages and disadvantages of devices
Homemade metal or aluminum devices differ from conventional radiators in their dimensions. They consist of some pipes whose diameter exceeds 32 mm. To organize the circulation of the coolant, the pipes are connected to each other by pipes.
What is the reason for the popularity of these heat supply devices? First of all, the prospect of independent production. You can make bimetallic devices, metal or aluminum pipes.
Before connecting the heating registers, you should carefully study all their sides.
Advantages:
- Long service life. For metal and aluminum modifications it can reach 25 years. In this case, the possibility of breakdown will be minimal.
- Significant heat dissipation. This is due to the fact that the power of the devices exceeds this parameter of traditional radiators and batteries. Due to the large size of the coolant.
- Easy installation and operation. Since anyone who is at least a little familiar with the instructions for organizing heat supply can correctly identify the devices, they can be used in buildings of all types. But most often they can be found in the heating system of industrial, administrative and commercial premises.
Read also: Inhabited sandblasting chamber
But, in addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the possible disadvantages that a register made of a smooth metal pipe may have:
- Large coolant size. This leads to its rapid cooling.
- Lowest rate of air convection. Reduces the efficiency of heat supply.
- Unsightly appearance. Most often this applies to homemade systems.
Correctly calculated heating heat transfer directly depends on the design of the device. Currently, a number of types of these heat supply devices are used, differing not only in the production material used, but also in appearance.
Design characteristics
Radiators made of smooth steel pipes are most often used. Welding of smooth pipes can be registered and serpentine. Registered ones can have 2 types of pipe connections - column and thread. Column - connecting each pipe to each other on both sides using jumpers. When connecting “thread”, the jumpers are installed alternately, first on one side, then on the other. This ensures a consistent connection, and the coolant flows around all the pipes one by one.
The heater radiator can be welded not only from round, but also from square pipes. They are not much different, but they are more difficult to work with and have higher hydraulic resistance. Although such radiators are much more compact.
In this case, the contact area of the metal with the air is much larger, which increases heat transfer. Such heating registers do not look very presentable, but they heat the room well, despite the temperature outside the window.
Production of seamless hot-deformed thin-walled pipes
Products are made from a blank (various metals are used) - a rod. It is a monolithic cylinder. First of all, it is placed in an oven, where it is heated to a temperature at which the metal recrystallizes.
After this, using a piercing press using ductile metal, a sleeve is formed (the cylinder is hollow inside). At this stage, the difference from the future pipe is the irregularity of shape and size.
After this, the workpiece is processed on rollers, acquiring the desired shape and wall thickness. The mandrel remains inside the pipe throughout all these stages. The cooled, calibrated pipe is cut into pieces and packaged.
Pipes and a radiator in the heating system of a private house...
From the wording of the question it is not entirely clear whether the private house is yours or belongs to the customer...
If we assume that the house belongs to the customer of the work, then in order to avoid claims on his part, everything should be done in accordance with the project (contract).
If you equip your home with a heating system, then its elements should be chosen taking into account durability and ease of maintenance, naturally taking into account the “price of the issue” available to you personally. Usually everything works out when the work is carried out according to a ready-made project that suits everyone.
Now, in order. And so the pipes:
“...which pipes to choose: steel or ferrous metal?” There are only two types of ferrous metal - steel and cast iron. Cast iron differs from steel only in the percentage of carbon in the alloy and usually in the presence of certain alloying additives. Pipes for heat, water and gas supply systems previously (in the last century) were produced only from steel of various grades. This was due to their relatively low cost and the ability to quickly install systems. However, this is where the advantages of steel pipes ended. The main disadvantage of steel pipes is their poor resistance to corrosion and, as a result, low durability. Therefore, if you want to leave a legacy of a reliably operating heating system, then I do not recommend using ferrous metal pipes.
Currently, polymer and metal-polymer pipes are produced for use in heat-water-gas supply systems. Their structural difference is the reinforcing layer. Some use fiberglass, others use metal (usually aluminum).
Their main advantage is the impossibility of recycling the material under natural conditions. It is this quality that determines their exceptionally high resistance to corrosion destruction. In addition, polymer pipes have many other advantages over steel ones. When operated under certified conditions, the service life of polymer pipes is at least 50 years.
In accordance with modern design standards, pipelines of all systems must be laid covertly. In interior design, pipelines of engineering systems are not used. Pipelines of engineering systems are fixed to elements of load-bearing structures of buildings, in specially equipped channels, behind decorative lining. As a last resort, pipes are laid in special plastic boxes.
And now about: “which radiator is better to buy for a private house, the area of the house is approximately 60 square meters?”
Let me assume that you need a heating device for your home, and not a source of thermal energy. If this is the case, then it is usually chosen according to two parameters - the required power and as an element of the interior of the room, naturally, based on financial capabilities. The power of a heating device for a “regular” living space made of stone-reinforced concrete structures with “standard” thermal insulation is selected at the rate of 1 kW per 10 sq.m. area. But it is far from a fact that the temperature in the room after such a “selection” will be comfortable. Typically, one heating device is installed in each room. In large rooms and taking into account the requirements of space-planning solutions, several heating devices can be installed. If a decision is made to use radiators of standard designs as heating devices, then most likely they will need to be covered with decorative grilles, which will inevitably reduce their efficiency.
Today, in terms of design and technical characteristics, the most efficient heating device is the fan coil. None of the radiators can compare with it in terms of operating efficiency and heat transfer.
Fan coil units are currently produced in a fairly large number of models, differing significantly in a number of capacities and appearance. All of them fit easily and naturally into any interior.
That’s basically all about which pipes and radiator are better in the heating system of a private house...
If you have any questions, I will answer them in personal correspondence. Good luck!
Steel pipe
Alliance-Metal offers prices for steel pipes and other products below market prices. This is a rapidly growing company that has proven itself to be a reliable supplier of profile and steel pipes for general and special purposes. Many companies with which we cooperate are our regular customers.
Prices for profile and steel pipes
The classification of pipes is made according to their main characteristics:
according to the material of manufacture:
- non-metallic pipes: made of non-metallic materials (concrete, asbestos-cement), polymer (plastic);
- metal pipes: cast iron, steel, non-ferrous metals, alloys;
pipes differ in the homogeneity of the material in their cross section:
- multilayer pipes - in particular, plastic-metal-plastic - metal-plastic pipes.
- single-layer pipes;
According to the cross-sectional shape of the pipe, there are:
- conventional (with an annular section);
- profile (profile pipe rectangular, square, flat-oval and oval).
The scope of application of profile pipes is somewhat different from the scope of application of round pipes. Profile pipes are used as a supporting element in construction and mechanical engineering, and are also successfully used in agriculture and in interior decoration. Prices for profile pipes can significantly reduce the cost of construction work. Savings on construction compared to the cost of work using traditional materials can reach tens of percent.
In addition to the fact that the prices for profile pipes make these products economically profitable, they have important consumer qualities. Construction time, as well as its price, when using profile pipes, is significantly reduced. As a result, profile pipe allows achieving high manufacturability and reliability in the construction of buildings and structures.
by purpose:
- pipes for special purposes;
- general purpose pipes;
They differ according to the production method:
- hot-deformed seamless (seamless pipe) and cold-deformed pipes;
- welded - spiral-seam and straight-seam pipes;
- cast iron pipes;
Hot-deformed seamless steel pipe in accordance with GOST 8732-78 is manufactured with a diameter of 20-550 millimeters.
Seamless steel pipe (GOST 8734-75) cold-deformed:
- thin-walled seamless steel pipes - wall thickness 0.6 - 20 mm, diameter 5 -250 mm;
- extra-thin-walled seamless steel pipes – wall thickness 0.3 - 6 mm, diameter 5 -250 mm;
- extra-thick-walled steel pipes - wall thickness 2 - 12 mm, diameter 6 - 70 mm.
- thick-walled steel pipes – wall thickness 1.6 -24 mm, diameter 6 -250 mm;
Hot-deformed steel pipe, seamless, corrosion-resistant GOST 9940-81
Manufactured with a diameter of 76 - 325, wall thickness 3.5 -28 mm.
Seamless hot-deformed steel pipes are made from steels: 45, 35, 20, 10, 10G2, 20Х, 40Х, 15ХМ, 15Х5, 12Х8, etc.
Seamless steel pipes are intended for pipelines, structures, boiler plants, machine parts and other technical purposes.
The price for seamless steel pipe is indicated in the price list.
Electric welded straight-seam pipe GOST 10705-80
Straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes with a diameter of 10 – 530 mm from carbon and low-alloy steel are produced in accordance with GOST 10705-80. A straight-seam pipe is made from rolled sheets by welding a straight joint.
Welded steel water and gas pipes (VGP) GOST 3262-75
This group includes both galvanized and non-galvanized welded steel pipes for water and gas pipelines, as well as for parts of heating systems of buildings and structures.
Shaped products and pipes can be of two types according to the thickness of the insulation: 1 - standard, 2 - reinforced.
For the manufacture of insulated pipes, steel pipes up to 12 m long, with a diameter of 57-1020 mm are used, meeting the requirements of GOST 8731, GOST 8733, GOST 10705, GOST 20295, GOST 550, PB 03-75 and SNiP 2.04.07, as well as the regulatory requirements of the manufacturer .
The price for welded steel pipe is indicated in the price list.
You can also buy wire and other rolled metal products from the Alliance Metal company.
If you need competent specialist advice, call us at:
Main selection criteria
Any specialist has a whole arsenal of tools that help him make the right choice. Each type of pipe has both positive and negative characteristics. Therefore, taking them into account, it is not difficult to find the optimal solution. Much also depends on knowing what heating systems exist and what engineering conditions must be met
Here is a list of basic initial data that must be taken into account when choosing heating pipes:
- Availability of forced or gravity heating system
- Laying method - internal or external
- Complex or simple system configuration.
- System pressure power
- Maximum water temperature
Below is a list of existing options. It will help you decide correctly which pipes to choose.
Heating based on polypropylene
If you decide to make a heating system or any other system from polypropylene pipes, the master will need additional equipment in addition to plastic hoses.
In particular, you will need the following material, equipment, and tools:
- pipe shears or pipe cutter;
- soldering plumbing machine;
- foil remover;
- sealing tape (fluoroplastic);
- sharp knife;
- degreaser (for example, Tangit wipes);
- required range of fittings;
- tape measure and marker;
- fasteners, screws and dowels.
You should pay attention to the main material - PP pipes, from which it is supposed to create a heating system. Because a heating system made of polypropylene pipes can be assembled using materials of different classes.
The heating system of a residential building, mounted on the basis of polypropylene pipes, is already a familiar way of everyday life. Practicality and simple manufacturing have made polypropylene extremely popular
The specific choice of assembly depends on the planned operating conditions.
How to make registers from round pipes with your own hands
This option has become the most widespread of all the above-mentioned designs for several reasons: manufacturing does not require specific skills, round pipes are commercially available, and the design of the product is simple. Required materials and tools:
- round pipes of the required diameter (40–70 mm);
- pipes Ø 25 mm;
- end caps;
- drain valve;
- grinder, hacksaw;
- welding machine;
- measuring tool.
Standard four-chamber radiator
If you plan to manufacture an autonomous “samovar”, then you will additionally need to purchase a heating element and an expansion tank. The work flow diagram for manufacturing and connecting the device is as follows:
- Selecting a model suitable for a particular case: horizontal or vertical heating radiators.
- Determining dimensions, drawing up a diagram.
- Purchase of materials.
- Welding the product (or less commonly, assembly with a threaded connection).
- Checking for leaks.
- Connection to the heating circuit system.
Below are recommendations for making registers from round pipes yourself.
Any plumber or person who has the skill of assembling pipes or wiring according to a sample or diagram can install the product.
To manufacture registers, no drawings are required; a simple diagram or drawing is sufficient, giving an idea of what kind of design should be obtained at the output.
It is important not to give in to the temptation to “weld the pipe thicker.” The larger the diameter of the pipes, the larger the volume of water will have to be heated, and this is an additional load on the boiler plus an unjustified increase in the heating bill
The optimal nominal pipe diameter is Ø 32 mm.
Heat transfer can be increased by increasing the distance between the pipes - add 5 cm to the pipe diameter.
The most reliable connection is welding. If a thread is used, then plumbing flax or UNITEC adhesive-sealant, which is specially designed for threaded connections in plumbing systems, is used as a gasket.
How to calculate heat transfer?
The required amount of material can be calculated based on the temperature parameters that need to be obtained in the room. At the household level, this step is usually skipped - they make heating registers with their own hands “by eye” according to the principle “the more, the better.”
But it is better to make simple calculations of heat transfer, for which you do not need to be a mathematician. All you need is:
- Calculate the area of the room.
- Learn about the heat transfer properties of steel.
- Select the optimal pipe diameter.
The area of a room is calculated by multiplying its length by its width (S = L*W). However, for more accurate calculations, it is recommended to calculate the volumetric parameter by adding the height (H) value to the calculations.
So, the final calculation formula takes the form:
V = L*W*H
For example, you need to calculate V of a room where the length is 5 m, width is 3 m, height is 2.15 m. The volume of the room is obtained: V = 5*3*2.15 = 30.25 m 3 . Based on this basic value, further calculations should be made to determine the amount of heat, the size and number of heating registers to make with your own hands.
First of all, the required amount of heat per calculated volume of the room is calculated to achieve the required internal temperature (W):
Qп.т = V * k (Tin – Tout),
where V is the volume of the room; k – heat transfer coefficient of the building walls; Tin – temperature inside; Tout – outside temperature.
The amount of heat generated by one register can be calculated using the formula:
Qр = q * L * (1-n),
where: q – heat flow from each horizontal and vertical pipe of the register (approximately 20-30 W/m); L – length of vertical and horizontal pipes of the register (m); n – coefficient of unaccounted heat flows (for metal pipes – 0.1).
The category of unaccounted heat loss also includes the hood in the garage. If the mechanical type is installed, the coefficient n must be increased to at least 0.2.
The number of registers, accordingly, is determined by the formula:
Nр = Qп.т. / Qр
Such a calculation method will most likely be assessed by design specialists as a simplified and crude form. However, this approach still seems to be a more rational action than calculating and making registers with your own hands by eye, without any calculations.
Types of registers to install
The most commonly used products are cast iron, steel and aluminum. The most common are aluminum. Their advantages are the following:
- resistant to corrosion;
- have minimal weight;
- long period of use;
- there are no connections or joints from welding;
- high heat transfer.
Monolithic casting is used in the manufacture of aluminum registers. Such products are most often installed in residential and office premises. If you need heating in production, it is better to install registers made of steel or cast iron, as they are more durable. Heating systems can be either stationary, in which the coolant is heated using a boiler, or mobile. Such registers have special protection against accidental electric shock. Steel heating registers are not characterized by high heat transfer, but they benefit significantly due to their budget cost, ease of processing and large selection of sizes.
Stainless steel registers are also used, but they have low heat transfer, so their manufacture requires a lot of pipes, which is quite expensive. In heating systems, where all wiring is made of copper pipes, registers made of a similar material are installed. They have the highest heat transfer. It is 4 times higher than steel. Copper has high ductility, so it is easy to bend in the right places. Welding is only required at the points where different parts join. Copper registers have quite significant disadvantages - they are high cost and the need to comply with the conditions of use. In order for copper registers to last a long time, the following conditions must be met:
- there should be no solid particles in the coolant;
- there should be no other metals incompatible with copper in the system;
- to avoid corrosion, grounding is installed in the system;
- Since the metal is very soft, special protection is needed for the registers.
Cast iron registers are massive and heavy, so you need to install strong stands under them. Cast iron is a very brittle metal and can be damaged by a strong impact. Because of this, cast iron registers need protection in the form of casings, which significantly reduces heat transfer and increases their price. Installing them is quite difficult. Cast iron is a chemically neutral material, and it does not care what kind of coolant is in the radiator.
The most affordable and reliable material for registers is steel.
Calculation of parameters and drawing
The first stage of making a heating register with your own hands is design. It is clear that it will not be possible to make a heating register normally by eye. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out a number of additional calculations, based on which it will be possible to select the optimal heat exchanger. When making heating registers, many factors need to be taken into account:
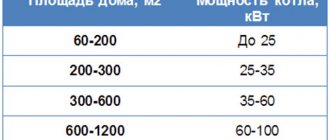
Before you make heating registers with your own hands, you need to understand that this is a heating device, which means it must warm up a certain room. Its heat transfer must correspond to the situation; do not install a heat exchanger covering the entire wall in a small room. One meter should account for from 100 to 200 kilowatts, depending on the region. There is a formula for calculating the heat transfer of heating registers. It includes the following values:
- heat exchanger length in meters;
- internal section in meters;
- metal thermal conductivity coefficient;
- delta of supply and return temperatures;
- number "P".
To determine heat transfer, you need to multiply all the components of the calculation. Of course, from this formula you can separately determine each of the above values. So, knowing the square footage of the room, you can determine what dimensions the structure should have. Often, homemade heating registers are made from scrap materials, so it is not possible to select some parameters. It is necessary to adjust the entire structure to the existing characteristics, while not forgetting about the functionality of the heat exchanger.
When calculating the length of the heat exchanger, you need to remember that the resulting value indicates the total length of the pipes.
For example, according to the formula we got a value of five meters. This means that both one five-meter pipe around the perimeter and several sections, the sum of the lengths of which will be the same five meters, are suitable for heating. The point is to maintain the heat exchange area.
There are two methods for placing main (thick) pipes:
In principle, there is no difference in manufacturing. If you take a horizontal structure and rotate it 90 degrees clockwise, you get a vertical heat exchanger. This will make a difference when installing on a circuit.
That's the whole difference between vertical and horizontal register
In addition, the heating registers are secured with special jumpers. There may be one or two such jumpers. Also, the connection of horizontal sections can be carried out using couplings of the same diameter, which are welded into the end. These are the so-called serpentine registers. You can choose any method of assembling a heating register from pipes with your own hands, the main thing is that you have enough skills to perform it.
Do you want to learn more about heating elements for heating radiators, features of selection and operation?
Reviews about infrared heating can be read here.
In order not to complicate the register manufacturing process, we will use a scheme for connecting horizontal sections with two pipes. Heating register, drawing:
Heating register drawing
For work we will need:
- three identical pieces of pipe;
- four connecting pipes;
- six plugs.
The distance between the heating register pipes may be larger, but not smaller. Moreover, if pipes of large diameter are used, the distance between them is determined by the formula: diameter x 1.5. This distance is optimal. The next stage is welding.
Practical heating registers: what to choose for your home and apartment
On the market, everyone can choose heating registers for installation in an apartment or private house. On sale there are designs made of metal horizontally located pipes connected to each other by special jumpers, due to which water moves through the heating device. Modern registers have higher heat output than traditional Soviet batteries. The most popular aluminum registers have the best technical characteristics. Homemade batteries are used in small apartments or rooms, ensuring proper heating of the available space.
Error correction
Sometimes, incorrect measurements of a room lead to incorrect calculations. The installed heating radiator does not work efficiently and the room is cool. You should not immediately rush and make a new device, spending both time and money. There is a way to increase thermal output.
To do this, it is necessary to increase the heating area. The only option in this case is to weld ribs made of a metal sheet 1.0-2.0 mm thick to the pipe structure. The shape of the ribs can be different, the main thing is their area.
Therefore, for example, rectangular pieces with a length greater than the height of the radiator and a width of 100-150 mm are cut out of a sheet of iron. Semicircles with a diameter of 100 mm are cut into them on one side. On each piece of sheet there are two semicircles, the distance between which is determined by the gap between the two pipes in the battery.
The finished forms are welded to the heating structure. The more there are, the higher the heat transfer of the device.
Material of manufacture
If you make a selection depending on the material of manufacture, then the registers can be classified into the following categories:
- Steel;
- Aluminum;
- Cast iron.
Which heating registers are best to choose? Steel registers became the most common. Their connection to the heating system is carried out by threading or welding. Such devices have good heat transfer and reasonable cost.
Aluminum registers are much lighter than steel registers. In addition, they are resistant to corrosion, are made without connecting seams and have good heat dissipation. The main disadvantage of such devices is their very high price.
Registers made of cast iron are connected to the heating system using a flange connection. They are quite easy to install and inexpensive. The disadvantages of cast iron products include low inertia, which significantly reduces the heating time of the registers.
Calculation of the number of ribs
Heating registers must be calculated before purchasing them. The diameter of the pipes is very important: experts believe that pipes with a cross-sectional diameter in the range from 3 cm to 8 cm are suitable for a private house. This decision is determined by the fact that a conventional heating boiler is not capable of producing a larger amount of heat, so too large surfaces will not warm up completely .
When making calculations, you need to pay attention to the length of one register rib and the heat transfer per meter of this length. For example, a meter-long pipe with a 6-centimeter cross-section can heat one square meter of area
When calculating the required number of edges, the result must be rounded up. The calculation of the number of heating registers must also take into account the characteristics of the building. For example, if a building has a large number of windows and doors, or if the walls are thin and poorly insulated, then the number of registers can be increased by 20-50%.
Basic heating register calculation
If the level of heat transfer of a purchased battery can be found out from its passport, then in the case of homemade heaters you have to calculate everything yourself. Otherwise, it will not be possible to heat the room effectively and evenly.
Calculating the required radiator power to heat a room
For calculations, they use formulas that may be simple, but require certain mathematical skills. Another option is online calculators, of which there are now more than enough on the Internet. Strictly speaking, the topic is quite extensive and deserves a separate article, so we will use simple calculation methods. In any case, this issue should be given close attention, otherwise your family will complain that the radiators do not heat well and the room is cold.
A simplified method for calculating the required thermal energy is to calculate the heating area and then multiply by 100. Why is this so? Because for comfortable living per square meter you need 100 W of heat. To be more precise in the calculations, let’s take into account the number of window openings and walls:
- A room with one window and one external wall – 100 W per 1 m² of area.
- A room with one window and two external walls - 120 W per 1 m².
- A room with two windows and two external walls - 130 W per 1 m².
Important! The calculations are suitable for rooms with ceilings of no more than 3 meters, when the house is located in a moderate climate in the middle zone. If the building is located in the northern regions, then the result must be multiplied by a factor of 1.2-2.0, and if in southern latitudes - by 0.7-0.8.
Simple calculation of the thermal power of a radiator made of steel pipes
Knowing what to strive for, all that remains is to choose the design of the heating device that would satisfy your needs. How to do this?
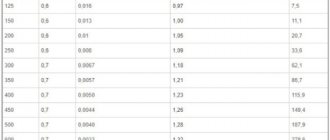
There is an elementary solution - use a table. It already calculates the heat transfer rates of rolled pipes. The values take into account the temperature regime, in which the supply temperature of the coolant is +90℃, and the return temperature is +20℃.
So, the table below allows you to find out the thermal power of one linear meter of register pipe per square meter of heated area.
External section of the pipe, mm
Heated room area, m²
Which metal is better
To begin with, we note that structures of this kind can be intended both for heat transfer, performing the function of radiators, and for heat intake, when a tubular register is mounted directly in the combustion chamber of a boiler or furnace.
Plus, in some models, instead of a coolant liquid, heated gas is used, for example, a radiator chimney pipe.
- Steel pipes for heating radiators are deservedly considered leaders in this market sector. Of course, the heat transfer of steel is not as high as that of aluminum or copper; it is susceptible to corrosion and requires regular maintenance. But these shortcomings are more than compensated for by the affordable price, as well as a wide range of types and sizes. In addition, it is much easier to weld ordinary ferrous metal than non-ferrous metal.
- Stainless steel is used extremely rarely for such structures. Apart from the fact that its cost, to put it mildly, is far from budget, argon welding is used for soldering stainless steel, and not every professional welder can work with it.
Important: in this case there is simply no point in using galvanized iron. Thin zinc coating simply burns out during the welding process.
As a result, the already weak weld is further affected by corrosion.
The use of copper tubular registers is justified only in the case of copper wiring throughout the house. The heat transfer of copper is four times higher than that of ferrous metals, so here we can talk about heating with pipes without radiators, or rather with a minimum number of radiators. But, firstly, the price of copper is incredibly high, and secondly, this metal is very demanding in terms of operating conditions.
Copper heating wiring.
- Copper systems require a finely purified coolant that does not have solid abrasive inclusions.
- In such systems, fittings must be copper or compatible metals such as bronze, nickel, chrome or brass. Moreover, it is strictly forbidden to combine aluminum with copper.
- Copper pipelines necessarily require high-quality grounding, as there is a danger of electrochemical corrosion.
- Copper is a soft material, so the system needs additional protection; naturally, casings and shields also cost money.
The cast iron radiator heating pipes shown in the photo are still used in industrial buildings and technical rooms. But the weight of such a design is much higher than that of a household cast-iron battery. Considering the unesthetic appearance and rather low efficiency, they are not popular.
Tubular cast iron batteries.
Tip: cast iron tubular registers are ideally suited for installation in the combustion chamber. Optimal heat capacity, low price and unpretentiousness in terms of coolant make them leaders in this area.
Advantages of homemade radiators
The main advantages of do-it-yourself radiators:
- An opportunity to express yourself, your imagination and give the room an interesting look.
- Independent assessment of heat loss or heat transfer, drawing up an individual installation plan, according to the characteristics and purposes of operation of the residential premises.
- Use of available materials, spare parts and equipment.
In order to make a battery with your own hands, you will need:
- welding machine (not necessarily powerful);
- electrodes;
- sheet of stainless steel of special strength (from 3 mm), size 100x500 mm;
- steel pipes: grade VGP Du-25, 20 cm long; length 2 m, diameter 100x3 mm;
- squeegee brand Du-25, length 100mm x 2 pcs.;
- plug brand DN -25 x 1 pc.;
- grinder with a circle for metal (grinding machine).
Making a register yourself
Homemade heating registers are quite simple, and no special skills are required in their manufacture. All you need is experience with a welding machine and the availability of basic parts for manufacturing.
When creating registers with your own hands, the following algorithm is used:
- First, pipes of appropriate diameters are prepared and the blanks are cut;
- The internal space of the pipe is cleaned to reduce the resistance to the energy carrier;
- It is necessary to weld plugs at the ends. Some plugs must be provided with holes;
- It is now possible to connect large diameter horizontal pipes with smaller vertical pipes;
- At this stage, taps are installed that will allow air accumulated in the system to be removed;
- The last step is to clean all the seams and paint the surface of the register with oil paint.
Heating registers made from a profile pipe will have all the necessary parameters. When assembling portable structures, it is necessary to install a heating element with a power of 1.5-6 W, which can be connected to an outlet. By connecting registers to heating boilers, you can increase the performance of the system by installing a circulation pump.
Selecting a heating device configuration
Homemade radiator designs are mainly made on the basis of metal pipes with a diameter of 80 - 150 mm.
Design features are limited to two versions:
- Lattice.
- Snake.
The lattice design of the heating battery differs from the “snake” in a slightly different circuit design, and, depending on the variations in such batteries, the distribution of the coolant may be different.
Coil structures actually have a monotonous design, implying strictly sequential movement of the coolant.
Lattice registers are constructed according to different schematics:
- with one or two jumpers and one-way power supply;
- with one or two jumpers and versatile power supply;
- parallel connection of pipes;
- sequential connection of pipes.
The number of pipes in one assembly can range from two to four or more. Rarely, there is also the practice of making single-pipe registers.
A coil assembly usually contains at least two pipes connected on one side by a blind jumper and on the other by a through jumper, which are made from two pipe bends (2x45º). It should be noted that the design of heating registers in the form of a coil is used much less frequently than “grid” designs.
Both manufacturing options - lattice and coil - can be made not only on the basis of classic round pipes, but also on the basis of profile pipes.
Profile pipes seem to be a somewhat specific material, since they require a slightly different approach when assembling heating radiators. However, registers made from a profile pipe are more compact and take up less usable space, and this factor is also important.