Copper pipes are used much less frequently than metal-plastic or polypropylene pipes. But thanks to a set of excellent technical characteristics - thermal conductivity, anti-corrosion and biological resistance - they are found in water supply, heating, and air conditioning systems.
Long copper products are expensive, but you can save on installation. For example, soldering copper pipes with a gas torch is available to anyone who wants to independently improve the system or make repairs. We will talk about how solder joints are made and give the rules for their implementation.
Features of the technological process
The technology for soldering copper with a gas torch largely depends on the parameters of the filler material. Depending on the solder, there are two connection methods:
- Low temperature . Used when working with low-melting grades of solders. With their help, they install home water supply and repair pipes of automobile gas cylinder installations. Soldering temperature does not exceed 400 Cº. Connections made using soft solder are prohibited from operating at temperatures above 110 Cº. The technology is not particularly complicated, so if you have the appropriate skills, you can do the soldering yourself.
- High temperature . Hard grades of filler materials are used in the most critical jobs, so they are most often used in mass production. In addition, this method is used when welding air conditioner pipes. They are made from an alloy containing at least 90% copper and additional additives, including silver. Soldering temperature varies between 700-900 Cº.
Some types of solders
Cadmium solders when soldering copper and steel require certain skills to work with them. Because the manufacturability of these materials is lower than that of previous ones.
It should be noted that such a connection is heat-resistant (up to +350 ℃), but not cold-resistant. In addition, a cadmium alloy joint will not be very strong.
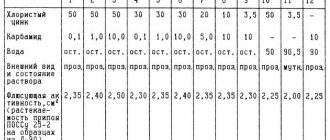
Zinc solder materials are rarely used for soldering copper because the metal itself quickly dissolves into the solder material. This weakens the joint, hence the low tensile strength - up to 15 MPa.
Zinc solders alloyed with silver or copper also have low fluidity. Although these materials are doped with cadmium or tin, they have good fluidity, but the strength of the compound itself decreases greatly.
Copper-phosphorus grades with the addition of silver are a good option for soldering. The connection can withstand high loads, up to 300 MPa, and temperatures up to +800 ℃. But solder metal bonded to copper is not ductile. This means that it has low bending strength.
Silver solder materials have proven themselves well in high-temperature copper soldering conditions. True, they show their qualities if soldering is carried out with acetylene or in special furnaces where corrosive fluxes are used.
Solders with a high silver content are used in the process of joining copper blanks in a vacuum or when heated with argon. If the process is carried out under pressure, then either foil (silver) or silver coating is used for the connection.
Solder materials with a high copper content and a low silver content are used rarely and in exceptional cases. Because it is a refractory alloy that requires high heating temperature.
As for pure lead solders, the connections made with them are not strong enough, but they have high ductility. For example, such joints after soldering can be bent up to an angle of 130°, and in tension they can withstand up to 140 MPa.
Selection and temperature parameters of gas burners
Torches for soldering copper pipes are the main working tool with which they heat the connected sections of pipelines and melt the solder. Power and temperature parameters depend on the type of connection and filler material used. For the simplest work, you can use conventional devices equipped with permanent cylinders with a flammable mixture of propane.
If there is no burner, an industrial hair dryer can be used for installation work. Its temperature is sufficient to work with low-melting tin-based solders.
Let's look at the most common types of burners.
Types
When choosing a burner, you first need to pay attention to the type of power supply. The following types are distinguished:
- Compact disposable cylinder with propane mixture;
- Stationary cylinder with a set of connecting hoses and reducers for working with propane-oxygen composition;
- Power supply system with acetylene-oxygen mixture.
The flame adjustment mechanism is an important part of the device. By controlling the temperature you can work with all types of solders.
Burner auxiliary equipment includes the following components:
- Piece ignition. The convenient feature of compact models greatly simplifies the process of starting the device.
- Flame reflector. Creates a directed flow of the combustible mixture, which allows it to be directed precisely to the heating zone.
- Check valve. Responsible for automatically stopping the gas supply in the absence of flame.
Devices for soldering copper with stationary and removable cylinders
Burners for connecting copper pipes are available not only with disposable cylinders connected directly to the devices. Manufacturers also produce devices with stationary fuel tanks.
Gas burner on a can
Removable disposable cylinders are the most convenient option. The valve on the gas burner handle allows you to regulate the amount of incoming fuel.
The advantages of devices with disposable sealed cylinders include the following advantages:
- Easy transportation.
- The process of use is simple, since the design of the device allows you to take any comfortable position during operation.
- Possibility to connect various nozzles to the handle.
- No need to connect to the electrical power grid.
- High degree of safety, because there are check valves that can shut off the gas in case of emergency situations.
- It is possible to adjust the flame intensity, which allows you to change the heating rate of copper parts and consumables in the form of solder.
- It is possible to obtain good quality seams if all conditions for using the device are met.
Homemade assembly
Having minimal plumbing skills, you can try to make a burner yourself. If you use high-quality materials, the technical characteristics will not be inferior to factory-made products .
The process of assembling a homemade device:
- The handle must be made of a material with low thermal conductivity. Hardwoods are best suited. You can also use the handle from an old burner.
- From steel, 2 mm thick, it is necessary to make a tube with a diameter of 10 mm. Experts recommend using low-alloy steel rather than stainless steel. The finished tube is attached to the handle.
- The body and divider are made of brass. It is necessary to take care of the holes in the divider in advance for the supply of oxygen. When joining the housing to the divider, a small gap should be left near the internal flange.
- To make an injector, it is best to contact a familiar turner, since independent work requires precision and accuracy. A round steel blank is used as a workpiece.
- The connecting gas hose must match the type of mixture used. A regular clamp is used as a fastening element.
The finished product is checked for play and leaks. Particular attention should be paid to the nozzle - it must be screwed onto the tube well. If necessary, you can seal the threads using FUM tape.
The purity of the flame is adjusted by moving the nozzle along the threads of the tube until an even flow without soot is obtained.
Components
Let's look at the basic materials that the soldering process cannot do without.
Filler material
Solder for soldering copper pipes is a material whose parameters determine the connection technology.
Soft compositions have a low melting point. A striking example is the PIC group of solders, which contain tin and lead in various proportions, as well as additives that improve the quality of the seam.
The main difference between hard solders is their high melting point, under the influence of which a high-quality and reliable connection is obtained . Experts recommend using copper-based compounds. This allows you to achieve the best quality. Various additives allow you to regulate the melting temperature. For example, the presence of phosphorus allows you to reduce the melt index to 700-750 Cº.
The following release forms are available:
- wire;
- rods;
- ribbons;
- paste;
- powder.
Flux
The flux is selected based on the parameters of the solder. There are high- and low-temperature compositions. For hard grades of solder, it is recommended to use technical borax.
Soldering flux is applied after mechanical cleaning of pipes, immediately before work . When using the active composition, at the end of the cycle you should wash off its remains to avoid damage to the surface.
Fitting
There are many types of fittings for different purposes and systems. The most popular are:
- coupling;
- corner;
- tee.
Preparing for soldering - what do you need to know about this process?
At the moment, copper can be soldered in two main ways, which differ from each other in heating temperature. The high-temperature method involves increasing the temperature to 900 degrees Celsius; this method has proven itself well in pipelines where the pressure on the walls is maximum. To solder copper pipes using the high-temperature method, you will need special materials, including high-melting flux and hard solder. Ordinary solder will not work here, since only its solid counterpart reaches the required melting point.
Soldering copper
The low-temperature soldering method is much simpler, since the metal is heated only to 500 degrees, although 380 degrees Celsius is usually sufficient. At home, various copper elements are usually welded using this method. To work, we need standard flux, which melts at the specified temperatures, as well as a rod or wire with a diameter of up to 3 mm. If we talk about solder, then it should be soft - a 97 percent alloy of tin with metals, for example, antimony, silver or selenium, is perfect.
In order for the soldered parts to be firmly and firmly bonded to each other, it is necessary to select the appropriate flux. Flux is a special substance that resembles a paste in consistency and contains zinc chloride. This substance is applied in a fairly thick layer to the surface of a pipe or any other copper part. The functions of flux are quite diverse, among the most important are the following:
- Allows solder to spread evenly over the soldering area;
- A kind of indicator that makes it possible to determine the right moment to apply solder and begin the copper soldering process;
- Significantly improves the adhesion of copper and solder;
- Almost completely removes oxygen, which prevents oxidation of metal products.
Soldering is a fairly dangerous process because you have to deal with very high temperatures, even with low-temperature soldering. Therefore, you need to be very careful, while simultaneously observing all safety regulations. All the nuances of the work should be taken into account, because hot metal is just as dangerous to human health as the burner itself. In addition, copper is an excellent conductor of heat, which helps to heat a large area of the pipe, and not just the area directly being soldered.
If it is necessary to weld copper elements that are not built into the pipeline system, it is necessary to prepare for this process in advance. For such cases, special non-flammable supports are provided on which the copper elements can remain for the time required for them to cool completely.
Step-by-step instruction
cutting
Before cutting pipes, it is necessary to mark the locations of the fittings. When cutting, it is best to use a special pipe cutter. In this case, the cut area will be even and smooth, with a minimum number of notches, which will facilitate the process of further preparation.
Chamfering
The pipe cut must be perfectly straight . The slightest deviations will affect the quality of the connection. To remove burrs and prepare the cut, it is recommended to use a bevel remover, or, if it is not available, sandpaper.
Surface preparation
The contact surface must be dry, free of oil, dirt and oxide deposits. This applies not only to pipes, but also to connecting fittings. For mechanical processing uses brushes and pipe cleaners.
Flux coating
Flux is applied to the inner surface of the fitting and the desired part of the pipe. It is important that the composition is evenly distributed over the plane. After this, the elements are joined, leaving a small amount for filler material.
Heating and soldering
The heating indicator is the state of the flux . The appearance of dark shades indicates that the surface has heated to a given temperature. When applying solder, it is necessary to monitor the heating intensity. The molten solder should fill the entire space between the fitting and the pipe. This is achieved due to the capillary effect, in which the liquid adheres to the surface due to the high force of attraction.
The duration of the working cycle should not exceed 5 minutes. Otherwise, the copper pipe will begin to deform from overheating.
Classification of copper products
Copper pipes in Europe are mainly metric; 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 22, 28, 42 and 48 mm are also found in larger diameters, but they can also be inch:
| inches | mm |
| 1/4 | 6.35 x 0.8 |
| 3/8 | 9.52 x 0.8 |
| 1/2 | 12.7 x 0.8 |
| 5/8 | 15.9 x 0.8 |
| 3/4 | 19.1 x 0.8-0.9 |
Copper marking in Russian marks: the letter “M” is used to denote copper. Next are numbers showing the degree of purity in% (00 - highly pure, 0 - pure, 1, 2, 3 - technically pure). The last element of the marking is a letter indicating the method of copper production: (k - cathode, y - cathode remelted, b - oxygen-free, p - deoxidized, f - deoxidized with phosphorus).
| Copper grade | M00 | M0 | M1 | M2 | M3 |
| Purity | 99,99 | 99,95 | 99,90 | 99,70 | 99,50 |
Copper grades M1p, M2p and M3p, with a total impurity content identical to copper grades M, M2 and M3, differ from them in that they are more completely deoxidized and the oxygen content in them is reduced from 0.05 - 0.08% to 0. 01%. Therefore, they additionally contain from 0.002% to 0.012% phosphorus. The M1f copper grade differs from M1r in an even greater amount of phosphorus from 0.012% to 0.04%, for greater deoxidation and, accordingly, a complete absence of oxygen.
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF COPPER ACCORDING TO GOST 859 (%)
| Copper grade | Cu+Ag (%) | Impurities, no more (%) | ||||||||||
| Bi | Sb | As | Fe | Ni | Pb | Sn | S | Zn | O | P | ||
| M1f | 99,90 | 0,001 | 0,002 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,005 | — | 0,04 |
| M1r | 99,90 | 0,001 | 0,002 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,005 | 0,01 | 0,012 |
| M1 | 99,90 | 0,001 | 0,002 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,002 | 0,004 | 0,004 | 0,05 | — |
| M2 | 99,70 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,01 | 0,05 | 0,2 | 0,01 | 0,05 | 0,01 | — | 0,07 | — |
| M3 | 99,50 | 0,003 | 0,05 | 0,01 | 0,05 | 0,02 | 0,05 | 0,05 | 0,01 | — | 0,08 | — |
The use of various grades of copper in plumbing products is determined by GOST 52318, and in Europe - EN 1057. In construction products: GOST 495-92, in Europe - EN 1172. Typically, water pipes contain 99.90 copper and are excellent for home brewing purposes.
Soldering errors
Novice craftsmen who do not have experience connecting copper pipes may make the following mistakes:
- Poor heating . Inexperienced specialists are afraid to overheat copper parts, which leads to weak heating of the surface. The result is a low strength connection that will break under the slightest load.
- Overheating . The opposite situation, which threatens to burn out the flux from the surface. Contact elements without protection will become covered with scale, which will negatively affect the quality of the connection.
To develop the necessary skills, he recommends doing test soldering on unnecessary pipe scraps.
Safety requirements
The technological process takes place at high temperatures, so the worker must have an understanding of the hazardous factors and the basics of safe work performance:
- Work is carried out in rooms with functioning ventilation;
- It is necessary to use personal protective equipment, including goggles, gloves and special clothing made from natural materials;
- Avoid getting flux on exposed skin;
- Checking the quality of soldering and visual inspection is carried out only after the pipes have cooled.