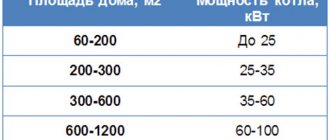
Installation of a ventilation system in a residential building or garage is the main condition for creating a comfortable microclimate. The best way to stabilize indoor humidity is air circulation. To organize supply ventilation, it is necessary to correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes.
Before you begin choosing the material of ventilation pipes and their diameter, you should find out the selection criteria. It is best to focus on regulatory documents. According to them, the main indicator of a properly designed and installed ventilation system is the air exchange rate. In addition, sanitary standards should be taken into account for residential buildings.
According to this parameter, the calculated rate of air flow into the room depends on its intended purpose.
- Residential building. The optimal volume of air flow is 3 m³/hour per 1 m², regardless of the number of people staying in it. According to sanitary standards, 60 m³/hour is required for one permanent resident, and 20 for a temporary resident.
- Utility room (garage). For an average garage area, it is necessary to provide an air flow of 180 m³/hour.
Natural ventilation is used as the basis, without installing auxiliary devices. There is a calculation system that, due to its complexity, is difficult to apply in practice for a private house, apartment or garage. It’s easier to use simple ratios of the area of the room to the cross-section of the ventilation hole:
- Residential building - per 1 m² of area, 5.4 cm² of ventilation pipe cross-section is required.
- Garage - per 1 m² 17.6 cm² section.
Those.
for a room with an area of 30 m², a pipe with a cross-section of 162 cm², or a diameter of 14 cm, is selected. The same technique is applicable for calculating ventilation in a garage. It must be remembered that for complete air exchange, 2 pipes are installed - an input pipe is installed in the lower part of the room for air flow, and an outlet pipe is installed in the upper part. This is just one of the few indicators that must be taken into account when calculating the ventilation system. In addition, the length of the air ducts, the possibility of forced influx of air masses, etc. are taken into account. Therefore, a full calculation of the system is possible only by professionals.
As a rule, when designing a ventilation system on their own, people do not like to complicate the task too much and select the dimensions at what is called randomness. Usually, the diameter with a margin does not particularly affect the operation of the ventilation, but this approach does not suit engineers. It’s a good idea to know how to choose the right ventilation pipes.
Pipes for ventilation
What should the ventilation pipe be like?
Ventilation, compared to other systems, for example, water supply, will not experience significant loads during operation, which means there is no need for a significant thickness of metal. Therefore, the first requirement for a metal air duct can be called a small wall thickness.
The second important parameter is corrosion resistance. Still, the level of humidity in the air passing through the channels is quite high, so that the metal should not become covered with a layer of rust after 6-12 months.
Galvanized pipes are used for ventilation
Well, the most important characteristic can be considered the diameter; the efficiency of the ventilation system directly depends on this. A 120 mm ventilation pipe has a cross-sectional area of 113.04 cm 2, a diameter of, for example, 75 mm is only 44.15 cm 2. It is clear that if the cross-sectional areas differ by a factor of 2.56, then they will be able to pass different volumes of air per unit time (at the same flow rate).
No. 3. Plastic pipes for ventilation
Plastic ventilation pipes have replaced galvanized ones from residential premises and are already actively used in some industrial buildings. Such air ducts are made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyurethane and polypropylene , and the last two types have not become widespread. When people talk about plastic ventilation pipes, they usually mean PVC products.
Main advantages:
- price. Plastic pipes cost much less than metal ones;
- light weight, ease of cutting, easy technology for assembling and fastening pipes allow us to talk about maximum ease of installation;
- resistance to corrosion and rotting;
- smooth walls allow air flows to pass as freely as possible;
- excellent noise insulation, which is important;
- durability;
- nice appearance, so if you can’t hide pipes behind walls or ceilings, they won’t spoil the picture;
- in terms of the range of possible sizes, plastic pipes are, of course, inferior to metal ones, but in the vast majority of cases the existing choice will be enough to equip even the most complex ventilation system. Plastic pipes are available in lengths from 3 to 12 m, cross section from 16 to 1600 mm.
The main disadvantage of the material is its inability to withstand high temperatures. PVC retains its original performance qualities at temperatures not exceeding +800C. If we talk about ordinary home ventilation, then such temperatures never exist there. If we are talking about removing hot air, for example, from a fireplace or in a production environment, then you will have to make a choice in favor of a metal analogue.
A few opponents of plastic pipes blame the products for their low strength. It would be foolish to argue with the fact that plastic is softer than metal, but ventilation pipes, as a rule, are installed in a hidden manner, so the impact on them from the outside is minimal, which means that less strength cannot in any way affect durability.
Normative base
The main indicator that is used when selecting the diameter of the air duct can be considered the air flow per unit of time. SNiP 41-01-2003 contains the basic requirements for the ventilation system, both in terms of productivity and in terms of geometric dimensions.
For example, according to this standard for a residential premises, the air flow should be (per 1 person):
- for rooms with an area of more than 20 m 2 - either 30 m 3 / hour, or at least 0.35 air exchanges, calculated based on the entire volume of the apartment. Finally, the calculations take the larger value;
- if the area of the room does not exceed 20 m2, then the air exchange can simply be taken based on the average value of 3 m3 / hour per 1 m2 area.
Standard air exchange values
That is, through a medium-sized room (19-20 m2) ventilation should provide circulation of about 60 m3 per hour. A small standard size, for example, a 75 mm ventilation pipe, simply will not cope with this task.
Note! Theoretically, it is possible to increase the volume of supplied air even through a small cross-section; simply install a powerful fan. But this will lead to a large increase in air flow speed. It is unlikely that the apartment needs drafts and howling wind in the ventilation.
The same standard (SNiP 41-01-2003) also contains some requirements regarding pipeline dimensions.
As for profile air ducts, you need to navigate along the larger side:
- for sizes up to 250 mm, the wall thickness should be 0.5 mm;
- with an increase in size to 1250 - 2000 mm, the wall thickness increases to 0.9 mm;
- if the size of the larger side exceeds 2000 mm, then an additional calculation is needed to justify the thickness of the metal.
System construction process
The installation of exhaust ventilation in the kitchen or bathroom begins with marking out the entire system. After this, materials are selected and calculated. Never rush into calculations. Everything needs to be done carefully and calmly.
When designing, remember that ventilation is important for its functionality with the ability to make maximum use of all conditions in each room. If you make a mistake, you will have to use mechanical air blowers, which will significantly increase the cost of the system.
For normal operation of a gravity-type system, it is desirable that the air ducts have as few turns as possible. It is recommended to install turbine deflectors on exhaust pipes rising above the roof - they will increase the outflow
Installation steps:
- Ventilation design.
- Purchase of equipment: sewer pipes, installation products, fasteners, fittings, mounting metal tapes.
- Installation of brackets and clamps at the locations of ventilation communications.
- A ventilation riser is assembled from large pipes.
- Assembly and installation of air ducts.
- Connecting all branches to each other.
- Sealing of connections. There is no particular need for this, but it won’t hurt.
- Installation of fans and valves, if provided.
- Installation of ventilation dampers.
The end of all types of installation work is testing the system for operability. All actions consist of checking traction. To do this, you need to attach a piece of paper or a napkin to the exhaust ducts.
Design or development of a circuit
Creating a ventilation project begins with basic calculations and collection of information, then:
- Calculate the air exchange rate throughout the entire house. This indicator depends on the volume of all premises, their purpose and the number of residents. In living rooms, the air should be completely changed once every 1 hour, and in technical rooms (toilet/bath) - at least 3 times every 1 hour. By adding up the resulting figures, we obtain a performance indicator, taking into account which the diameter and height of the ventilation equipment will be selected.
- Draw a diagram of the movement of air flows. Immediately estimate the position of the intake and supply channels.
- Draw a diagram of the air ducts. For now, ignore the detailing, stick to the rules and try to fit the system in without complicating the design. This is the most difficult stage of the work. Hiding ventilation from bulky plastic pipes is not so easy.
The sketches are ready. Take some time to think about what devices you will have installed in the system and where they will be located.
Detailing and assembly of the system
Having resolved all the issues regarding the diagram and given it its final form, it’s time to move on to detailing.
First, calculations are also carried out, system components and equipment are selected and the budget is reduced, then:
- The cross-section and area of the air ducts are calculated. The maximum speed of quiet air movement is taken into account - otherwise there will be a hum in the house.
- All dimensions are transferred to the diagram.
- Detailing. A list of all necessary elements is compiled, indicating the sections.
- The total cost of the ventilation system components is calculated. Reduce your desires to your available budget. At this stage, you will have to change the components several times, abandoning the desired in favor of the real.
- The final project is drawn. Do not forget about the passage of ventilation channels through the roof, ceiling, walls, insulating and consumable materials, ventilation grilles, fasteners and all other little things that will ultimately add up to a decent amount.
All that remains is to find, buy and install. Not much has been written, but it will take a lot of nerves, time and effort to implement the plan. Having installed the entire system, one cannot yet say that everything is ready.
Air ducts from sewer pipes are assembled in accordance with the drawn up project. PP pipes and fittings are connected by butt soldering, PVC by cold welding
The ventilation system made from plastic sewer pipes still needs to be tested and modified during operation. Achieving coordinated operation of each element of the system is also not so easy. If the natural ventilation option is not effective enough, it is worth upgrading by installing exhaust valves or their supply counterparts.
Air duct selection
When determining the cross-sectional dimensions, the speed of air movement must also be taken into account. The ventilation duct located in the apartment should not be a source of constant noise, and the speed of air flow entering the apartment (applies to both supply and exhaust ducts) should not cause discomfort.
For this reason, for different sections of the ventilation system, their own recommended air speed indicators are introduced, which greatly affects air exchange. For example, a ventilation pipe with a diameter of 200 mm at an air speed of 1.0 m/s can provide air exchange at a level of 113 m 3 / hour. When the speed increases to 1.5 m/s, the air exchange will increase 1.5 times - up to 169.5 m 3 / hour.
Dependence of air exchange on air flow speed and diameter
In this case, much depends on the method of air circulation (natural or forced). Thus, for systems with natural circulation, the maximum air flow speed can reach up to 2 m/s (in mines); in air ducts in apartments, the air flow moves at a lower speed.
But if the ventilation pipe in a private house is supplemented with a duct fan, then the flow rate increases.
Since the spread of fan power is quite large, you have to rely on the recommended values for different parts of the system:
- at the level of the supply grille, the speed should not exceed 1 - 3 m/s;
- exhaust grille – 1.5 – 3.0 m/s;
- air distributor – 1.5 – 2.0 m/s;
- side channel – 4.0 – 5.0 m/s;
- main ventilation duct – 6.0 – 8.0 m/s.
Approximate speed values in different sections of the ventilation system
The procedure for selecting the cross-section of the air duct
The instructions for independently selecting a section consist of just a few points:
- first you need to decide on the rate of air exchange in the room;
- then, having specified a certain speed of air movement, the area of the ventilation duct is calculated. The calculation is carried out according to the formula
In order to determine the diameter of the ventilation pipe, a formula is used.
- Since when selecting a standard size it was necessary to round the result obtained, you need to check how much the air flow speed has changed. You just need to derive expressions for determining speed from the previous formulas
where a and b are the dimensions of the rectangular section, m.
As for air exchange, you can use 2 approaches to determine it, but when the calculations are done by yourself, they are often simply set at a rate of 30 m 3 / hour per person. In general, the following options are possible:
- taking into account the frequency of air replacement in the room, in this case the amount of air exchange is determined by the formula
where V is the volume of the room, m 3 /hour;
n is the rate of air exchange rate (as a rule, for residential buildings it is taken within 1-3).
- taking into account the air exchange rate per 1 person in the building (the amount of air exchange in this case is discussed at the beginning of the article).
An example of duct sizing
Suppose you need to select the dimensions of the ventilation duct to provide exhaust hood in a room measuring 4x5x3 m. Only one person is planned to be in the room for a long time.
The calculation is carried out in the following sequence:
- air exchange is determined - in our case, you can set the value to 60 m 3 / hour (at the rate of 3.0 m 3 / hour for every 1.0 m 2 area);
- the speed of air movement in the channel is assumed - you can stop at a value of 1.0 m/s;
- the cross-sectional area is determined to be A = 60/(3600∙1.0) = 166.67 cm 2 ;
- the appropriate standard size is selected. In our case, you can choose either a round air duct of 140 mm (sectional area 154 cm2), or a rectangular section of 100x200 mm (area 200 cm2);
Air exchange depending on speed and diameter for profile pipes
- speed is checked. For a round channel it will be v = 60/(3600∙0.0154) = 1.08 m/s, and for a rectangular section – v = 60/(3600∙0.0200) = 0.83 m/s. Both values are within acceptable limits, so the deciding factor in the choice may be the price and method of pipe installation.
Video description
How to properly make ventilation for a private home in the following video:
The ventilation duct looks appropriate in the bathroom interior Source roomester.ru
- Just care . Surface dirt can be easily cleaned. Since PVC air ducts undergo antistatic treatment, dust does not stick to the surface.
- Ease of use . The noise produced by the system with PVC pipes does not exceed acceptable sanitary standards. The products fit well into the interior and are not hazardous to health.
The main disadvantage of PVC pipes is their low melting point, which prevents them from being installed in a sauna or bathhouse (they are replaced with metal ones).
Sandwich pipe
Sandwich pipes are a convenient substitute for sections of conventional ductwork that run from the outside or through the attic and require additional insulation. A sandwich pipe looks like a double-circuit product made of nested pipes of different diameters, between which a layer of heat-insulating material is placed. Stainless or galvanized steel is used for pipes; basalt wool is most often used as insulation.
Sandwich pipes are also used in the construction of chimneys; they have a reputation for quality and functionality. The design of the material causes its disadvantages - heavy weight and high cost.
Galvanized sandwich pipe Source proventilyaciyu.ru
Summarizing
The key to high-quality ventilation can be called a correctly designed ventilation system design. A significant role in this is played not only by the location of the air ducts, but also by their calculation (meaning the selection of cross-sectional dimensions). The recommendations proposed in the article will help you avoid typical beginner mistakes, and the ventilation of your apartment will always work stably.
The video in this article shows an example of an already installed ventilation system made of rectangular pipes.
The hood has become almost a mandatory element of equipment for a home or professional kitchen. The favorable microclimate in the food preparation area and neighboring rooms created during its operation has long been appreciated by housewives and cooks. The quality of operation of the entire air exhaust system depends on the correct choice of equipment, pipes for ventilation in the kitchen, and the material for its manufacture.
Natural ventilation of sewerage facilities
Ensuring spontaneous air circulation in the ventilation system of drainage systems is ensured by the generation of heat in the mass of sewered products through the natural processes of their decomposition.
In this case, the generated gases have a higher temperature and rise upward, providing circulation and their release into the environment.
But they have one unpleasant feature - flammability.
Therefore, wastewater storage and accumulation facilities are flammable, and in large quantities can be explosive. Cesspools are especially dangerous in this regard.
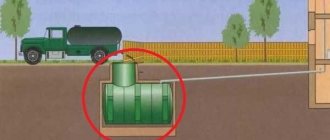
Therefore, the presence of ventilation in such facilities is mandatory. Currently, the main material for ventilation devices is plastic pipes with a diameter of 100-110 millimeters. The pipe from under the cesspool cover is brought out at a distance of 4-5 meters to a ventilated place.
To increase the efficiency of the extraction process, a deflector is installed on it. In addition to protecting the upper end of the pipe from clogging with leaves and other debris, this device actively enhances the air flow, although active exhaust through the deflectors only works in windy weather.
In windless regions, it is advisable to use low-power axial fans for exhaust to ensure forced removal of gases from the sewer system.
In the same way, external ventilation is arranged in filter wells and septic tanks.
To eliminate strong odors in the cesspool itself, you can use chemicals.
Functions, types, selection of exhaust device
The importance of a hood in a food preparation area is obvious, because its main tasks are:
- removal from the working area of air contaminated with combustion products, smoke, fumes, odors;
- reduction of humidity and air temperature near the stove for more comfortable work;
- providing conditions that prevent the appearance and proliferation of unwanted microorganisms;
- increasing the durability of kitchen furniture, household appliances and interior items, on which soot, grease and dirt will not settle;
- ensuring an influx of clean air instead of exhaust air containing pollutants;
- creating comfortable conditions for working in professional kitchens and favorable living conditions in private properties near the kitchen premises.
The hood, connecting the air duct pipes to the ventilation shaft, helps remove contaminated air to the outside.
The following types of hoods are installed in kitchens: flat, inclined, built-in, T-shaped, island, corner, dome, telescopic.
To remove the entire volume of contaminated air, the dimensions of the hood must be the same or larger than those of the hob. The minimum productivity (m3/hour) of exhaust equipment should be at least 10 times the volume of the kitchen space.
Recommended hood installation height:
- above the gas stove – 0.75-0.85 m;
- above an induction or electric stove – 0.65-0.75 m.
Ventilation installation: an alternative to air ducts
The ventilation system is an important condition for creating comfortable conditions in a country house. Depending on the design of the house, it can have a rather complex device, additional functions and a decent price. The last point brings to life an understandable desire to save money by replacing some of the air ducts with sewer pipes. To understand whether such a decision will lead to the expected result, the following facts should be considered:
- Size difference . The dimensions and cross-sections of sewer and ventilation pipes most often do not match, so it will not be possible to assemble a combined system. There is a chance if the installation is carried out from scratch.
- Environmental friendliness of the material . For ventilation products, plastic is used that does not impair the quality of incoming air. Sewage pipes are not environmentally friendly, which is explained by the specific application. Taking these features into account, sewer elements in the ventilation system can only be used in the exhaust part.
One way to disguise a ventilation pipe from a hood Source folksland.net
- Feature of the material . During production, air ducts are treated with antistatic agents, so the surface of the products remains clean. Unlike sewer analogues, dirt will inevitably accumulate on the outer walls of which, and accumulations of dust will form inside and all kinds of microorganisms will feel comfortable. Wiping off dust from the surface weekly is not a difficult task; the question is what to do with the internal contents.
- Weight . Sewage pipes are much heavier than air ducts; When installing suspended ventilation, they will require reinforced fastening.
- Appearance . The design of sewer elements loses in presentability. It is much easier to select suitable ventilation pipes for the design of the room.
The above facts cast doubt on the advisability of using sewer pipes for organizing home ventilation. A compromise that has a right to exist is their use in non-residential premises (for example, a garage) or for arranging a hood.
Correctly selected elements of the ventilation system will fit into any interior Source bouw.ru
Choosing a pipe for the exhaust system
For the productivity and reliability of the entire structure for removing contaminated air, the choice of pipe for ventilation is of great importance. Let's consider the main criteria.
Material of pipes used
Corrugated aluminum pipes are the cheapest and easiest to install option for organizing the removal of polluted air from the hood. The base of the pipe is metal rings. They are covered in several layers of laminated foil. Initially, the rings are pressed against each other, the upper shell is folded into an “accordion”. During installation, the corrugation can extend several times and bend at the required angle. Therefore, it is easily laid in cramped conditions and hard-to-reach places.
An incompletely stretched corrugated pipe becomes a source of characteristic noise in the exhaust system due to the increased resistance of the uneven internal surface to the air flow. Additional pipe kinks also increase the noise level.
Corrugated pipes for ventilation can withstand significant heat (up to +250°C), have significant strength, are resistant to aggressive environments, can be extended if necessary (metal tape is used for connection), and can last up to 50 years.
Plastic exhaust systems have a number of advantages that make them leaders in consumer demand:
- The low weight allows one person to install the entire system, does not require additional fasteners or supporting elements, and eliminates additional load on the suspended modules of kitchen furniture.
- High resistance to many chemical compounds and moisture.
- Excellent tightness of air ducts with high strength of the mounted structure.
- UV resistance.
- Simplicity and ease of maintenance, availability and low cost of necessary detergents.
- Ability to operate the system over a wide range of temperatures.
- Creating good sound insulation that does not interfere with the comfortable stay in a room with an exhaust system.
- Durability.
- An impressive range of plastic exhaust duct elements of various shapes and sizes, from various materials: polypropylene, polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride.
- Aesthetic, strict appearance of the assembled system.
- Ease of installation allows you to assemble reliable exhaust structures from standard shaped parts.
- Plastic elements of pipelines are not subject to corrosion, their material is environmentally friendly.
- The smooth inner surface of the pipes does not allow dirt and grease to accumulate.
- Exhaust systems with plastic pipes (especially round sections) are almost silent, compared to air ducts made of other materials.
Pipe material
The ventilation system actively participates in regulating the microclimate of a country house, supplying clean air into the room and removing used air. The choice of pipe material is made based on the parameters of the system and its operating conditions. There are several types of pipes.
Metal pipes fit perfectly into the kitchen interior Source yandex.ru
Shape and dimensions of the pipe section
Corrugated pipes have a round cross-section, plastic pipes have a round or rectangular cross-section. Pipelines made from round pipes have less resistance, which is why they are popular. Rectangular pipes look more aesthetically pleasing, are easier to assemble and can be placed close to the wall.
The most commonly used pipes are:
- Round, diameter (mm): 100, 120 – the diameter of the ventilation pipe for the hood usually indicated in the instructions; 125 and 150 are also often used by users.
- Rectangular ventilation pipes for exhaust hoods have the following dimensions, height x width (mm): 55x110, 60x122, 60x204.
Important! For effective air removal, the cross-sectional size of the ventilation pipe must match the area of the hood outlet pipe or be larger (then a connection through a transition element will be required).
Calculator of the required ventilation capacity for a kitchen hood
If you need to calculate ventilation for residential premises, use the online air exchange performance calculator.
Using the Software
Calculations using formulas and tables may seem too complicated for people who do not have experience in designing ventilation systems. A good solution in this situation would be to use special programs that not only simplify the process, but also take into account additional parameters that are difficult to take into account in manual calculations.
Many similar programs can be found in the public domain. For example, the Vent-Calc program. It not only selects the required diameter of the ventilation pipe, but also generates a complete image of the network, close to reality, along with all the main aerodynamic characteristics.
Several parameters are used in the calculations: temperature, air flow, speed.
Using the program you can make the following calculations:
- hydraulic calculation of the air duct;
- calculation and selection of ventilation system elements: branches, extensions, outlets;
- selection of the air duct cross-section for natural ventilation, taking into account the resistance to air flow;
- calculation of the thermal power of the air heater;
- other.
Similar programs include:
- CADvent;
- Ventmaster.
Important installation features
Errors during the assembly and installation of the supply and exhaust piping can negate previous efforts to correctly select the hood, calculate the required cross-section of the pipes used, and select the necessary transition and connecting elements. In order for the exhaust system to work correctly, you should pay attention to the following points of its installation:
- The assembled pipeline structure should not have any deflections. If a corrugated pipe is installed, its stretch should be maximum.
- The entire exhaust system must be grounded to remove static electricity.
- To avoid damaging the air vent when passing through walls, special adapters and sleeves are used.
- The places of all connections (between pipes, pipes and hoods, pipes and ventilation shaft adapter) must be treated with sealant.
- Bends of the corrugated pipe to radii that are smaller than the diameter of the corrugation used will reduce the pressure and, therefore, the efficiency of the air exhaust system.
- The optimal exhaust system pipeline has a minimum of bends and turns, its length is up to 3 m, and the bend angles are obtuse.
- If the corrugated air duct is long, it must be secured with clamps every 1-1.5 m to prevent possible swinging when the hood is running.
- To connect the pipeline to the cavity of the ventilation shaft, use a special frame with a grille for supply ventilation, a flange for attaching the pipe and a check valve. When the hood is operating, the valve is closed and prevents contaminated air from entering the room. When the hood is not working, the valve is open - free air circulation occurs.
Turning the pipe at an acute angle or 90° will invariably reduce the performance of the entire system by 10%. Several such kinks will make its operation ineffective, although the exhaust equipment will work with overload. If it is impossible to change the pipe route, it is advisable to increase its cross-section and exhaust power.
Recommendations for setting up the system
The normal operation of the system under construction and the thoughtful purchase of materials for its assembly should be preceded by a well-made project.
Even at the design stage, it is necessary to decide whether the ventilation scheme will include equipment that stimulates its movement, purifies and heats the flow from the street
In order for the result to meet expectations and the system to cope with its responsibilities, the following must be taken into account:
- When designing a project, try to reduce the number of sharp turns and bends in the ventilation duct. The smoother the ventilation channel is, the more intense the air circulation will become.
- The following recommendation directly follows from the previous recommendation. The shorter the air path from inlet to outlet, the more effective ventilation will be.
- When thinking about and creating a project, stick to uncomplicated and simple schemes. Convenience in planning will lead to a decrease in efficiency.
When constructing a ventilation system from plastic pipes, pay attention to the height of the structure itself. If the air outlet pipe rises to a height of less than 5 meters from the lower level, then natural ventilation will not work. In this case, it will have to be reinforced with fans.
Masking of exhaust system elements
Even a carefully installed exhaust vent pipe may not fit into the design concept of the room or may attract too much attention to itself. If the pipeline was assembled from galvanized elements or aluminum corrugation, it will fit perfectly with the overall high-tech style. In all other cases, the structure must be masked or decorated. Often a method of camouflage is used:
- Ceilings (stretch, suspended). They can also hide elements of other utilities.
- A special box made of plastic or plasterboard.
- Installation of pipelines in wall-hung kitchen furniture.
- Special false panels covering passing communications. They are installed or mounted on hanging cabinets and decorated to match the kitchen facade or the decoration of adjacent walls.
A properly installed exhaust system made from well-chosen components is the key to comfortable and safe cooking.
Ventilation in the basement of a private house
Vents and vents should be installed in unused basements. Ideally, at opposite ends of the base. If there are partitions, there should be vents in them. The vents should have a diameter of 12 cm and be located under the ceiling. It is advisable to protect them with bars that prevent the entry of mice and rats.
In basements that are intensively used and where people are often present, it is worth installing ventilation the same as in the residential area, but with minor adjustments to the functional purpose of the premises. So, ventilation for a gym in the basement will be different from a wine room, and a cinema room in the basement needs to be ventilated a little differently than a dressing room or sauna.