Is it always necessary to insulate pipes in the attic?
If the family has sons and daughters, it is worth making an effort to adapt this part of the house to the needs of the children.
A tent house, a place for witchcraft - all this is an attic. It will be easier for a bachelor, bachelorette, lovers, or young family to manage household chores and take care of their well-being if the attic is turned into a room with a minimal risk of injury. Dust, through cracks, moisture, open pipes interfere more than a low ceiling or poor lighting. The attic can be a mystery room. You can look through an old photo album out of a box, sing your favorite song by turning on karaoke, right here. Or it will become a room in which there is something frightening, the mere thought of it will spoil the mood. The owner chooses what he should be. Hiding the pipes and decorating them is the first thing to do in the attic. More precisely, the first thing to do is take care of thermal insulation.
Any pipe will freeze in winter. By insulating all the pipelines in this part of the house, you can achieve the following goals:
- will extend their service life;
- improve functionality;
- optimize the life support system in the house.
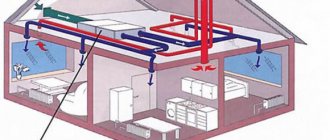
External and internal thermal insulation of ventilation pipes
Insulation of exhaust pipes performs the following functions:
- Provides fire resistance, prevents the spread of fire in case of fire.
- Prevents the formation of condensation on the outer and inner surfaces of the pipe.
- Reduces heat transfer between the external environment and the air in the system.
- Reduces vibration and noise generated during air movement.
Insulation of the ventilation pipe can be done from the inside or outside. With internal thermal insulation, it is necessary to increase its cross-section to maintain the required throughput of the air duct.
External thermal insulation of the air duct
Today, providing sound insulation through thermal insulation material is not relevant, since this problem is often now solved by sound insulation measures at the sound source or by installing mufflers. Therefore, at the moment, the use of external insulation is preferable.
Another circumstance when choosing whether to insulate a ventilation pipe internally is the possibility of the appearance of pockets of bacteria and the appearance of deposits of dirt and dust, due to which the material may begin to lose its properties. With external insulation, these disadvantages are absent. Insulating the outside of the pipe in the event of a fire significantly reduces the risk of fire spreading.
Expanded polystyrene
insulation with polystyrene foam.
A type of polystyrene foam, only with improved characteristics. Differs in the following characteristics:
- Service life up to 5 decades.
- Operating temperatures from -50 to +75.
- During static bending, a high strength limit is observed.
- Over 30 days, the water absorption coefficient is 0.4%.
- Thermal conductivity is at a high level.
The installation rules, advantages and disadvantages largely coincide with the information that has already been provided regarding polystyrene foam.
Installation of thermal insulation on ventilation pipes
Expanded polystyrene insulation
Ventilation pipes insulated with polystyrene foam are less susceptible to corrosion, which significantly increases their service life.
No special skills are required to install polystyrene foam shells. To install it:
- Determine the shell size that is needed.
- Use a saw or knife to cut the shells.
- Place the shell parts on the pipe, offset by a few centimeters from each other, and carefully close the side joints.
Ventilation pipes that are insulated with polystyrene foam shells are quite easy to dismantle in case of an emergency and just as easy to install back.
Polypropylene and polyurethane foam
These materials have significantly lower thermal conductivity and high fire resistance. Ventilation pipes are insulated with polyurethane foam and polypropylene as follows:
- Determine the required size.
- Cut the material into half-cylinders.
- Provide an allowance for the cover layer.
- Install half-cylinders on the ventilation pipes.
- Securely secure the joints using bandages.
PPU (polyurethane foam) shell for pipes
Insulation with foamed polyethylene
A ventilation pipe insulated with this material is the most popular today. Foamed polyethylene is a ready-made shell that completely encloses and insulates the pipes.
To perform thermal insulation of pipes:
- Take measurements of the material.
- Separate the insulating shell along a special seam.
- Attach the casing to the pipe.
- Using mounting tape or glue, secure the joints and seams of the insulating shells.
For square air ducts, foamed polyethylene is produced in rolls (for example, Energoflex Star Duct)
Regardless of how to insulate the exhaust pipe or the location of the thermal insulation material, the main thing is to prevent cold bridges that reduce the effectiveness of insulation and ensure high vapor resistance
To do this, special attention must be paid to the junctions of the ducts with the building structures, where there is the greatest likelihood of cold bridges appearing
Places where pipe insulation is carried out
Thermal insulation is very necessary in areas of greatest contact between warm air and colder air.
If, for example, in a house the ventilation pipe runs partially in the wall, then insulation will be required in the part leading to the deflector. As for private homes, another cold zone will be the attic. The pipes passing there also need to be thermally insulated. Industrial and office buildings typically have a ventilation valve that can be opened and closed to regulate air flow at different temperatures. Such a valve can heat the exhaust air using a built-in heating element, thus reducing the likelihood of condensation. This method is very effective, but expensive to implement.
Materials for insulation of ventilation systems
Thermal insulation of ventilation pipes is made using various materials:
- Mineral fibers. Thermal insulation materials from glass wool or mineral wool are produced in the form of semi-rigid or rigid pipe panels and sections, in the form of a material that can be given the required shape and density by pressing during installation.
- Felt. When installed internally, the rolled felt is protected with fiberglass with surface impregnation. For external use – aluminum reinforced kraft sheet. Pipe sections are used for external cladding with aluminum reinforced protection.
- Elastomer foams are flexible, closed-cell foams. Refers to self-extinguishing materials. This insulation is not susceptible to microorganisms and mold, resistant to vapor permeation and moisture absorption.
- Derivatives of carbohydrate polymerization (polyethylene, polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride). As a rule, they are produced in the form of pipe sections, blocks, plates.
Expanded polystyrene shells
Insulation for domestic premises
Below I will consider their types of insulation for ventilation ducts.
Mineral wool
This is usually called glass fiber wool. Flexible mats of different thicknesses are usually used. Durable, does not rot, does not decompose, and is not afraid of ultraviolet radiation. Cannot be used at high temperatures - for thermal insulation of chimneys with high flue gas temperatures and industrial chimneys.
Mineral wool must be covered on top with a shell - fiberglass, roofing felt, penofol, and insulated from moisture.
This is not the best type of thermal insulation - after a few years the wool cakes, in addition, it absorbs moisture. But with a well-assembled ventilation duct, it can be used indoors, but not for thermal insulation of supply ventilation. A serious drawback is that this is precisely the type of insulation that during installation contaminates everything around with small fragments of glass filaments.
Basalt wool
Basalt (stone wool) is made from basalt melt. This is a higher quality type of mineral thermal insulation, resistant to aggressive environments, high temperatures, ultraviolet radiation, and moisture. Belongs to the group of non-combustible materials.
Basalt wool is produced in the water of mats, slabs, and pipe shells. If the finished products are not covered with a shell, the mats and slabs must be covered additionally. Self-adhesive boards with an adhesive layer are produced. The disadvantage of basalt thermal insulation is that it absorbs moisture.
Foamed polyethylene
Available in the form of sheets up to 10 mm thick, shells and bundles. Shells and sheets may have a foil coating. The cheapest of all types of thermal insulation.
Disadvantages: not available in large thicknesses, burns, is not resistant to high temperatures and ultraviolet radiation. Plastic, durable material. Not as flexible as rubber. Practically does not absorb moisture and does not allow steam to pass through. Very widely used in construction.
Foamed synthetic rubber
A relatively new flexible closed cell foam. Sheets, thin plates, and pipes are produced. Thermal insulation pipes made of rubber are designed for air ducts with an outer diameter of up to 160 mm. Layer thickness – up to 32 mm. There are products with a self-adhesive layer. Operating temperature – from -200 to +175 °C.
Self-extinguishing material. Poorly absorbs water and allows steam to pass through. The big advantage is flexibility. Foamed rubber is very convenient for thermal insulation of non-circular air ducts, fittings, and joints of air duct elements. The disadvantage is that the price is higher than that of mineral wool or polyethylene.
Expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene is the correct name for the granular white foam familiar from childhood. Often called penoplex. There are expanded (foam plastic) and extruded, or extruded - denser and stronger sheets, products (shells) of different colors.
Expanded is called polystyrene foam, extruded - penoplex or expanded polystyrene. Shells are produced for pipelines with a diameter from 32 to 160 mm. The thickness of sheets and shells can reach 100 mm.
Penoplex is a frozen foam made from closed air bubbles with a diameter of 0.1-0.2 mm. Does not absorb water at all and does not allow steam to pass through. Refers to self-extinguishing materials. Density from 25 to 70 kg/m³. For thermal insulation of air ducts, low-density products are used.
Tolerates negative temperatures well and is not resistant to ultraviolet radiation. Very durable - without ultraviolet radiation it can last 50 years or more. Previously, industrial refrigerators and rooms - refrigeration chambers - were insulated with granular polystyrene foam. They have already lasted 60 years, but when disassembling the refrigerators, the foam looks like new. They produce ready-made shells for thermal insulation of pipes of different diameters.
Styrofoam
Polystyrene foam - expanded polystyrene foam - is a familiar white lightweight packaging material made from individual grains. Low density and strength, easily disassembled into grains, can take on a little water. Used for thermal insulation of only well-fixed air ducts.
It is necessary to protect it from ultraviolet radiation, do not touch it - in principle, the thermal insulation will stand for two or more decades. If you have a choice, it is better to choose extruded polystyrene foam - it is denser and does not absorb water at all.
Asbestos boards
Foam asbestos boards have low thermal conductivity and density, can operate at temperatures up to 400 ° C, are resistant to ultraviolet radiation, and do not absorb water.
Previously, due to its natural qualities, asbestos was very popular as a building material. It has now become clear that asbestos is a carcinogen, and its entry into the body is harmful. Therefore, it cannot be used inside buildings; external thermal insulation with asbestos should also be abandoned.
PIR boards
PIR is one of the most promising thermosetting materials. Polyisocyanurate is a polymer material similar in composition to polyurethane. Externally similar to polyurethane.
This is a rigid material with closed cells, low thermal conductivity, does not absorb moisture, and is non-flammable. Its UV resistance is higher than that of polyurethane. Operating temperature range – from -75 to 120 °C. Service life - more than 50 years. Rigid sandwich panels are made from it. In the world it wins approximately 3% of the market for thermal insulation materials.
In our country, PIR thermal insulation is not very widespread yet. They produce slabs with cladding - steel sheet, aluminum foil, fiberglass, kraft paper. Slabs with soft cladding are used like other thermal insulation; air ducts can be installed directly from slabs with hard lining. This type has special tongue and groove or quarter locks (like a tongue and groove board).
Where to choose
It is important to insulate the air ducts, and it is advisable to choose thermal insulation that has no disadvantages, is easy to install, and inexpensive. The most promising material is PIR boards. But they cannot be used to insulate a round air duct.
Mineral wool absorbs moisture and can create additional difficulties, and is also inconvenient to install. Asbestos is carcinogenic - we don’t use it. Foam rubber is quite expensive, you will have to wind several layers. Penofol - you will also need several layers. Penofol or rubber are good for thermal insulation of difficult places - joints, corners.
In practice, the choice comes down to the use of extruded polystyrene foam - in the form of slabs for square air ducts or shells for round ones. Expanded foam has very little strength, so it can only be used where no one will touch it - in the attic or basement.
How to insulate a hood in a private house
Thermal insulation of a hood is no different from ventilation insulation. The air temperature above the stove is not too high, there is no danger of fire or melting of the thermal insulation, and there are no special fire safety requirements for the hood. Therefore, you should not complicate the choice of material - the same polystyrene foam is quite suitable.
Materials
And finally, the cherished question: how to insulate the ventilation pipe? Let's take a short review of modern insulation materials that can be successfully used for ventilation ducts.
Requirements
Let's start by stating our wishes.
- Thermal insulating qualities will, of course, be a priority characteristic of insulation.
- Fire safety. In the event of a fire, the insulated ventilation pipe should not become a conduit for the spread of flame.
- If possible, the price should not be exorbitant.
Mineral wool
Unsurpassed cheapness. Any other insulation will cost more.
Mineral wool 50 millimeters thick is supplied in rolls.
Absolute fire safety.
- Quite labor-intensive installation. The ventilation duct is wrapped in a layer of mineral wool; then it is wrapped in foil (which is only permissible in interior spaces) or protected with galvanization. From the outside, the structure is tightened with bandages.
- The need to protect the respiratory system and eyes when working with the material. Anyone who has ever worked with mineral wool (or glass wool, which differs only in the thickness of the fibers) probably has the most unpleasant memories of it.
- The material cakes over time. Gaps appear in the insulation.
- Humidification leads to loss of thermal insulation qualities.
Some of the shortcomings are devoid of a ready-made solution based on mineral wool - an insulated corrugation for ventilation, which is a two-layer sleeve made of aluminum foil reinforced with steel wire. However, it involves laying ventilation from scratch.
Styrofoam
A ready-made detachable shell made of dense foam plastic (expanded polystyrene) is in many ways more convenient.
The insulation process is not associated with health risks and is relatively simple. How to insulate a ventilation pipe with foam shell? Just put two halves of detachable thermal insulation on the ventilation and squeeze them so that the tongue-and-groove connection is fixed.
The diagram makes the connection method clear.
- The material provides excellent thermal insulation and practically does not change its thermal insulating properties over time, regardless of humidity fluctuations.
- Styrofoam is cheap. It is precisely because of its low cost that it is the main candidate among insulation materials if you are planning to insulate a loggia or the facade of a private house (for more details, see the article How to insulate a loggia and what is required for this).
- Polystyrene foam burns well, releasing toxic combustion products.
- The shell is easy to use only on straight sections of air ducts.
Polyurethane foam, polypropylene foam
The shell can be made not only from polystyrene foam. The other two foam plastics are similar in application to foam insulation.
- Both materials have slightly greater mechanical strength.
- They are more expensive.
- To fix it, you have to apply a bandage. Ordinary knitting wire is often used as it.
Shell made of polyurethane foam.
Foamed polyethylene
This material can be found on sale in the form of split tubes of various diameters. They are put on the ventilation pipe - and, in fact, the thermal insulation work is completed.
The material is cheap and is not afraid of moisture, mechanical impacts of moderate force and rodents.
However, in cases where it is necessary to insulate ventilation in a cold climate zone, you can pay attention to two other types of insulation based on polyethylene foam
- Penofol and its analogues are polyethylene foam coated with a layer of aluminum foil. In our case, it is useful because the insulated pipe will collect less dust: the porous surface of polyethylene foam tends to accumulate dirt.
- Self-adhesive insulation based on the same polyethylene foam is equipped with a sticky layer that simplifies work. If you have ever insulated plastic windows or steel doors with a rubber or foam seal, you have already come across a method for fixing it: simply remove the protective glossy paper and press the material to the surface (see also the article How to insulate windows - getting ready for winter).
The material is very convenient for insulating pipes of square or rectangular cross-section.
The thickness of the insulation can reach 10 millimeters; if necessary, it can be laid on ventilation pipes in several layers.
The right approach to insulation
To answer the question: how to insulate a ventilation pipe in a private house correctly and at the same time economically, you need to understand the reasons for the appearance of condensation. Temperature differences always lead to the appearance of condensation, but the most abundant release of “dew” is observed during the period of active contact between warm and cold air. The closer it can be moved to the outlet of the pipeline, the less potential danger and damage from condensate will be.
The ideal case is considered to be a situation in which the mixing of cold and hot air occurs in a section of the ventilation pipe located outside the building. But this is not always possible to implement in practice.
Therefore, for chimneys and air ducts in an unheated attic, insulation of the ducts is considered mandatory. Thanks to this, it will be possible to remove the “wet” zone - the place where dew is most actively formed - beyond the walls of the building. This solution will help, even with the active appearance of a large amount of condensation, to prevent moisture from penetrating into the walls, causing the appearance of dampness, fungus and other related troubles.
Finding the optimal location
A vertical chimney from a heating stove, fireplace or gas boiler, thanks to the release of hot air, will be completely cleared of moisture during the heating process. Horizontal air ducts, the outlet of which is located in the wall, should initially be installed with a downward slope of at least several degrees. This allows accumulated moisture to drain outside rather than inside the room. Therefore, the most important point before insulating such air ducts is to check whether there is a slope for its removal. Otherwise, even insulated ventilation pipes will become a source of problems in the future, albeit noticeably later than without any thermal insulation at all.
A mandatory place for insulating air duct pipes is an unheated attic space. It is here that the temperature difference during the cold season becomes a source of problems due to the formation of moisture. Condensation on them, regardless of whether plastic or metal pipes are used, forms both inside and outside.
Choosing the best material
In order for the thermal insulation of any plastic, metal and various other ventilation pipes to be quite effective, but also not to hit the budget, you should choose the right insulation. Today there is a fairly wide selection of materials for this, both affordable and quite expensive. The most recommended options are the following types of insulation:
- Mineral wool. An inexpensive fireproof option available at almost any hardware store. The downside of the availability of mineral wool is the complexity of installation and the need for its subsequent protection with foil or galvanization. Afraid of moisture.
- Stone wool. It has the advantages of mineral wool, as well as its disadvantages. Over time, it cakes and loses its thermal insulation properties.
- Polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam. Detachable structures for pipes of a certain diameter. Inexpensive, but providing excellent heat and moisture insulation. The disadvantage of the materials is their high fire hazard and rather low resistance to mechanical damage.
- Foamed polyethylene. Insulation offered in the form of ready-made tubes of different diameters. Inexpensive, has good thermal insulation properties, and is not afraid of moisture. The disadvantage is the need to put a heat insulator on the duct pipe, which is inconvenient or even sometimes impossible.
The choice of how to insulate the ventilation pipe is made by everyone himself. The basic rule that it is recommended to rely on when choosing is to purchase the material that will most fully solve the problem of condensation in a private ventilation network.
Features of thermal insulation
The technology for protecting ventilation pipes from cooling depends on the type of insulation and its performance properties. In this case, it is necessary to follow the sequence of work and carefully perform all operations.
Insulation with mineral wool
It happens as follows:
- the surface of the ventilation pipes is cleaned of dirt and dust;
- a strip of the required size is cut from the roll, which depends on the diameter of the air duct;
- thermal insulation of ventilation pipes made of mineral wool is carried out in one layer, while you need to ensure that the material adheres tightly to the surface;
- The air duct is wrapped with foil insulation over the mineral wool;
- glue the resulting seams with aluminum tape.
- The pipe is wrapped in one layer of mineral wool insulation.
- On top of a layer of cotton wool, wrap the pipe with foil insulation (4 mm thick), which will help retain heat and prevent cold air currents from entering.
Particular attention should be paid to sealing the structure, since mineral wool, when interacting with moisture, deteriorates its thermal insulation properties
Polyethylene foam insulation
This method is one of the most popular because it combines ease of implementation and efficiency. For insulation, foamed polyethylene is used in the form of shells, with which the following actions are carried out:
- measure the insulation of the required size;
- cut the shell along a special seam;
- install the resulting elements around the pipe;
- glue seams and joints using glue or mounting adhesive tape.
For pipes with a square cross-section, it is much more convenient to use polyethylene in rolls.
Polyethylene foam shells
Basalt fiber insulation
With its help you can not only protect air ducts, but also gas pipes. Basalt fiber prevents the occurrence of fires and the spread of fire. How to insulate gas pipes? To do this you need:
- prepare additional wire and aluminum foil;
- wrap the pipe with basalt fiber and then cover it with a layer of foil;
- secure everything with wire, including the longitudinal seam;
- secure the layers of insulation with bandage buckles made of packaging or aluminum tape.
You can also use basalt fiber with a metallized layer to insulate air ducts.
Insulation using basalt fiber
Expanded polystyrene insulation
In this case, the insulation resembles a shell, and the insulation of ventilation pipes is carried out as follows:
- measure out the shell halves of the required size;
- cut polystyrene foam along the marked lines;
- The shell halves are placed on the pipe, shifting them by 20-30 cm.
- close the side connections, ensuring tightness.
Protective shells made of polyurethane foam with foil outer layer
Polypropylene and polyurethane foam insulation are a similar form but have lower thermal conductivity and fire resistance. Fixation of individual parts is carried out using special bandages. Polyurethane foam can also be sprayed onto the pipe surface.
Air duct protection has a significant impact on its service life. By correctly selecting the material for insulating the ventilation pipe, and following the technology for carrying out thermal insulation work, you can ensure the effective functioning of the system for a long time without damage or repair.
Insulation for industrial systems
For insulation of industrial ventilation air ducts, all the materials described earlier in the section on domestic premises and some other products are used.
Polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is polyurethane foam, a very common synthetic elastomer. For thermal insulation of air ducts, solid polyurethane foams are mainly used. They are used to produce all kinds of pierced mats and shells for insulating round pipelines.
Often the shells are covered with a shell made of galvanized steel, fiberglass, polyethylene, or fiberglass. Polyurethane foam is resistant to moisture, has high strength, durability, and is not resistant to ultraviolet radiation. Operating temperature range – from -60 to +80 °C. A good thermal insulator, and also affordable. The method of spraying polyurethane foam onto insulated surfaces is also used. In everyday life, foam is used in aerosol cans; in production, industrial units are used.
In terms of price, this is a relatively inexpensive thermal insulation option. If selected in aerosol packaging, the price increases. Products made from polyurethane foam are also produced for large-diameter pipes.
Thermally insulated air ducts
Installation of air ducts with applied thermal insulation is much faster than traditional assembly with subsequent insulation. But their price is much higher. For insulation, polyurethane foam coated with fiberglass, fiberglass, or polyethylene is usually used.
What is better to choose
The choice of thermal insulation for industrial pipes depends on many conditions:
- Air duct sizes.
- Air duct shapes.
- System locations. In the workshop and ventilation chamber (and now also in the heat recuperator) most of the system is often located, only small pipes for air intake or exhaust are located outside the room. It can be cold in the workshops in winter, down to negative values, so the air ducts in the room require thermal insulation.
- Exhaust gas temperatures and fire requirements.
- It depends on whether a new workshop is being built, an old production facility is being modernized, or thermal insulation of air ducts is simply being installed in an old workshop.
If local suction is insulated in hot shops, then it is often necessary to use mineral and basalt wool - they have the highest operating temperature. The cost of materials is also of considerable importance.
When thermally insulating air ducts in an old production facility, you should take into account the expected service life of the equipment and the building as a whole: if this period is 15-20 years, then perhaps you should not choose modern expensive materials, but make do with more budget-friendly options. It’s a completely different matter when launching new lines or workshops - it makes sense to use ready-made thermal insulation or pipes with a potential service life of 50 years.
Nowadays, ready-made shells with a coating layer are being chosen more and more often. They do not need to be protected from ultraviolet radiation or atmospheric moisture.
Where to insulate
In what places is insulation needed for ventilation pipes?
A simple solution
The simple answer to this question is obvious: where a sharp and significant cooling of the air flow is possible.
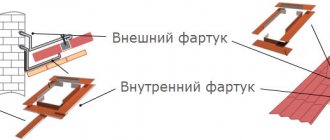
- If the exhaust ventilation is routed through a solid wall, the pipe is passed through a heat-insulated sleeve and insulated right up to the deflector.
- In a private home, insulated ventilation pipes run through the cold attic and are discharged through the gables or roof. Insulation again begins from the point where the ventilation duct noticeably cools (see also the article Insulating the attic - we consider possible options in detail).
Supply ventilation stands apart. Here, the possibility of moisture condensation on the outer walls of the supply ventilation duct depends on its length and location.
If necessary, these pipes can be insulated using the same methods as exhaust pipes, however, the influx of cold air itself can create some discomfort; adjustable fresh air ventilation dampers may even freeze.
One solution to this problem is an insulated ventilation valve. Perhaps in the reader’s imagination a ventilation grille with a layer of thermal insulation appeared? Not so.
The design in the photo bears little resemblance to ventilation blinds.
An insulated ventilation valve is a solution for large premises, primarily for office, warehouse and industrial purposes. It really is an adjustable louvers that allow you to limit the air flow and... if necessary, heat it up using tubular heaters.
Adjustment can be carried out manually - by a system of rods and levers, or using a simple electric drive. The live cross-section of the valve in a fully open state can be up to 3.5 m2, the power of heating elements can be up to 8 kW.
The function of heating elements, however, is not to supply warm air into the room. With a valve area of 3.5 m2, 8 kilowatts of thermal energy is a drop in the ocean. Heating elements only warm up the valve flaps before changing their position to avoid icing and damage.
Difficult decision
In some cases, an accurate calculation is desirable: with a large length of ventilation, the costs of insulation will be significant, and it is better to be sure of their necessity.
The key concept is dew point. This is the temperature at which droplets of condensation begin to form in air with a certain relative humidity.
A simple measurement of the relative humidity in the room and the surface temperature in different parts of the ventilation duct will give the exact boundaries of the zone that needs insulation.
This table will help you determine the area of the duct where condensation will begin to form at the current relative humidity.
How to properly insulate air ducts?
Theoretically, the thermal insulation of air ducts can be both internal and external. However, in practice, only external insulation is used due to the complexity of working with the internal type of insulation.
The quality of the insulating layer depends on its thickness, which correlates with temperature conditions, environmental aggressiveness, humidity and other factors. Calculations must be made by specialists, and the formula for these measurements is given in SNIP 2.04.14-88. It is not recommended to carry out calculations on your own, since the final result will depend on many important factors.
Insulation of ventilation ducts is carried out in accordance with SNiP rules, which require preliminary calculations
The requirements presented in SNIP are regulated for systems used in industrial premises and in private or civil construction projects. The temperature of transported media in the described structures ranges from -180 degrees to +600 degrees.
When using roll insulation, the working diagram will look like this:
- the air channel is wrapped with insulation of the required thickness;
- the insulation layer is attached using flexible wire applied at equal intervals. The self-adhesive insulation layer does not require additional reinforcement.
When insulating large diameter air ducts using mineral wool, additional fastening with pins is required. Metal pins are welded to the air duct, after which it is wrapped with mineral wool. In this case, the mineral wool should be pinned onto the pins. The wound layer of insulation is additionally strengthened by pressure washers, which are placed on each pin. The last step in fixing is to use wire as in the previous step.
If ready-made polystyrene foam shells are used, special attention should be paid to sealing the joints between the two halves of the product. Waterproof glue is applied to the grooves of the shells; it is also recommended to secure the insulation with tape.
Insulating air ducts with mineral wool requires compliance with safety precautions, as this material can be harmful to humans
Condensation is a threat not only to pipes
The main reason for carrying out insulation work on the ventilation line, as a rule, is the appearance of moisture stains on the walls and ceiling. Less often, work is carried out due to loud howling of the wind in the pipe or externally noticeable freezing. These and other factors that destroy individual areas of the building are mistakenly considered the main reason for insulation. In fact, the situation is much more serious.
As mentioned above, moisture in the walls is an excellent environment for the development of fungus and pathogens. But for mold to “appear” on the walls, it takes quite a lot of time and moisture. And until the moment it just “appears” on them, its own “ecosystem” has already formed inside the ventilation system, imperceptibly poisoning the house.
The result of this can be allergies, illnesses caused by unknown causes, and chronic headaches. The pathogens that cause them spread through the air, quietly poisoning it. Therefore, proper ventilation insulation protects not only the walls and ceilings of the house, but also the health of its inhabitants.
Why is ventilation pipes insulated in the attic or above roof level? What insulation is best to use for ventilation? Is it difficult to do this work yourself?
Let's try to figure it out.
Recommendations for installation work
The main emphasis should be on the thickness of the thermal insulation of the air ducts. The thicker it is, the better. But here we must also take into account the price component, because the thicker the insulation, the more expensive it is. Therefore, there are standards according to which the insulation thickness is calculated. The basis for these calculations is thermal conductivity.
If the installation is carried out using shells, then first of all the matching diameters of the air ducts and heat-insulating cylinders are taken into account. The latter consist of several parts that are joined on the air duct using a tongue-and-groove connection. Fastening is done with clamps, wire or tape.
As for roll materials, there are no strict requirements for their installation. The main thing is to prevent the formation of leaks, gaps and cracks, which will subsequently become cold bridges.
Outdoor thermal insulation must be covered with casings made of galvanized metal or aluminum. The latter are not part of the thermal insulation of exhaust ventilation; their main task is to preserve the insulation from mechanical stress and natural loads.
Purpose and types of thermal insulation
Insulation of air ducts allows you to maintain a comfortable microclimate and favorable temperature conditions in the premises, prevents the formation of condensation on the surface of the pipes and prevents their destruction. It also reduces the level of noise and vibration that occurs due to air movement during the operation of the ventilation system.
Depending on the location of the materials in relation to the air ducts, internal and external thermal insulation are distinguished. Insulation from the inside is different:
- the need to use ventilation pipes of larger diameter;
- carrying out additional compaction measures if materials with a loose structure serve as thermal insulation;
- tendency to form bacteria and spread them through the air duct;
- low fire resistance.
Internal insulation of ventilation pipes
Ventilation pipes insulated from the outside do not have these disadvantages. They are easily cleaned of dust and dirt and treated with special compounds that prevent the formation of bacteria. In addition, the cost of external thermal insulation is much cheaper than internal.
External insulation of ventilation pipes
When insulating from the outside, pipes can become a source of noise, but this can be easily avoided by installing special devices as mufflers.
Typically, thermal insulation of gas pipes is carried out externally, taking into account the purpose and material of the structures.
Advantages and disadvantages of ready-made insulated pipes
For those who do not want to do the insulation themselves, there are ready-made insulated pipes with a layer of factory insulation. They have a simple design: a protective layer of basalt fiber is inserted between two channels of different diameters.
Specifications
Such pipes are used in the construction of ventilation systems and chimneys. In the first case, it is necessary to use galvanized products, in the second - stainless steel. Protection from moisture and heat preservation is provided by a layer of mineral wool with the following characteristics:
- flammability - G1 (low flammability).
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.038−0.051 W/(m*K).
- strength - from 5 kPa to 80 kPa.
- water absorption - 2%.
Ready-made insulated pipes
The mineral base prevents the formation of fungus and mold, and the fiber structure is maintained even after a long period of use. The melting point of the insulating liner is 1100 ºС, which indicates the fire safety of the product. The combined composition makes the product absorb internal noise and durable. The disadvantage of this product is the high price.
Why is this necessary?
The key word is condensate. Without insulation, it will inevitably form on the inner surface of the ventilation duct and flow down the inner walls, flowing through leaky joints into the main walls and ceilings. The consequences are obvious: dampening of the walls and ceiling, the appearance of mold and their gradual destruction.
The effect of condensation on the ventilation duct itself depends on what material it is made of:
- Galvanization can be damaged if the protective anti-corrosion layer is damaged. Which, however, is inevitable when cutting sheets.
- PVC and corrugated aluminum pipes tolerate contact with moisture without any consequences.
Another trouble associated with moisture condensation is the gradual freezing of frost on the inner walls of the ventilation duct outside the warm room. Over several weeks of operation in severe frosts, the pipe clearance can decrease from 100 - 150 millimeters to zero.
Where does condensate come from?
There are two reasons for its appearance.
- Human life is associated with excessive air humidification. When washing dishes, cooking, doing laundry, even just breathing, the atmosphere is saturated with water vapor.
- Meteorologists have long used the concept of relative humidity. The higher the air temperature, the more water vapor it can hold. 100 percent relative humidity is the maximum amount of water that can be contained in the air in a vapor state. However, as soon as the temperature changes, with the same amount of steam in the air, the relative humidity will change. With significant cooling, it can exceed 100%, after which excess water will inevitably begin to condense on the surface with a low temperature. In our case, on the inner surface of the ventilation duct.
Consequences of moisture condensation in the ventilation duct.
A special case
In production, there is often a need for forced ventilation with high air flow rates. In particular, to remove harmful volatile production products, sawdust, shavings, etc.
The noise of the air and what it carries becomes a serious problem in some cases. In factory premises, ventilation insulation is often aimed not so much at combating condensation, but at banal sound insulation. The methods, however, are the same.
What could be the consequences if there is no insulation?
Condensation that accumulates inside the hood can negatively affect the condition of the building's floors. In addition, the occurrence of condensation can lead to the following troubles:
- on the street, metal pipes become covered with rust;
- the ventilation duct may lose its tightness;
- the inside of the air duct will decrease in volume over time;
- the quality of air exchange will decrease;
- moisture will penetrate inside the interfloor ceilings, wall structures, etc.
Expert opinion
Konstantin Alexandrovich
If the pipes are not properly insulated, the building will wear out intensively during the cold season. At sub-zero temperatures, the amount of condensation can become significant. That is why experts consider proper insulation of ventilation pipes in an unheated attic and roof a necessary measure.
Conclusion
Which insulation you choose is up to you to decide. The author's sympathies are given to foil materials based on polyethylene foam, but this is more a matter of habit. In the video presented in this article you will find additional information on this topic.
In a private house, the attic can be very warm and used as an additional room. But most often it is used as a storage room. The pipelines that run across its area make it difficult to change its purpose. If you decorate them correctly and sew them up with boxes, you will be able to make this room more cozy and comfortable.