Heating a modern private home depends on many factors. This includes choosing a heating boiler, the presence of underfloor heating systems, and choosing a radiator connection diagram. But the most important factor influencing the energy efficiency of the system is the installation of various heating pipes in a private house, the choice of diameter and installation method.
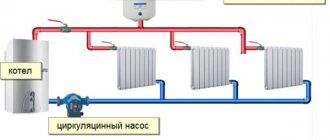
An example of the arrangement of a modern boiler room, in this case using a copper pipe
Recommendations for the selection and installation of pipes
To install the heating of a private house with your own hands, you first need to decide which pipes to choose for this. The modern market offers several types of metal and polymer pipes suitable for heating private homes:
- steel;
- copper;
- stainless steel;
- polypropylene (PPR);
- polyethylene (PEX, PE-RT);
- metal-plastic.
Heating lines made of ordinary “ferrous” metal are considered a relic of the past, since they are most susceptible to corrosion and “overgrowth” of the flow area. In addition, it is not easy to independently install such pipes: you need good welding skills to make a hermetically sealed joint. However, some homeowners still use steel pipes to this day when they install autonomous heating at home.
Copper or stainless steel pipes are an excellent choice, but they are too expensive. These are reliable and durable materials that are not afraid of high pressure and temperature, so if you have the means, these products are definitely recommended for use. Copper is joined by soldering, which also requires some skills, and stainless steel is joined using dismountable or press fittings. Preference should be given to the latter, especially when the installation is hidden.
Heating made from polypropylene will cost you the cheapest. Of all types of PPR pipes, you need to choose those that are reinforced with aluminum foil or fiberglass. The low price of the material is their only advantage, since installing heating from polypropylene pipes is quite a complex and responsible task. And in appearance, polypropylene is inferior to other plastic products.
The joints of PPR pipelines with fittings are made by soldering, and it is not possible to check their quality. When the heating was insufficient during soldering, the connection will certainly leak later, but if it is overheated, the melted polymer will half block the flow area. Moreover, you won’t be able to see this during assembly; flaws will make themselves known later, during operation. The second significant drawback is the large elongation of the material during heating. To avoid “saber” bends, the pipe must be mounted on movable supports, and a gap must be left between the ends of the line and the wall.
It is much easier to make your own heating from polyethylene or metal-plastic pipes. Although the price of these materials is higher than polypropylene. For a beginner, they are the most convenient, since the joints here are made quite simply. Pipelines can be laid in a screed or wall, but with one condition: connections must be made using press fittings, not collapsible ones.
Metal-plastic and polyethylene are used both for open laying of highways and hidden behind any screens, as well as for the installation of water-heated floors. The disadvantage of PEX pipes is that it tends to return to its original state, which can cause the installed heating manifold to appear slightly wavy. PE-RT polyethylene and metal-plastic do not have such a “memory” and easily bend as you need. More information about choosing pipes is described in the video:
Pipes
Most often, metal-plastic pipes are used for arranging heating pipelines. They have a lot of advantages, including excellent ability to withstand heating temperatures, high mechanical strength and long service life. A more traditional material is steel pipes, which are relatively inexpensive, but they have a serious drawback - susceptibility to corrosion, due to which the pipeline will quickly become faulty.
Calculation of the diameter of heating pipes for systems with forced circulation is carried out using special tables that take into account a lot of parameters, including the speed of fluid movement. As a rule, for the type of heating systems under consideration, rather narrow pipes are used, since there is no need to ensure independent movement of the coolant.
Hidden gasket
Hidden installation of heating pipes.
The obvious advantage, compared to the previous method, lies in its aesthetic appeal.
There are practically no restrictions on interior design, since the heating pipes are disguised. Nothing will interfere with the installation of furniture groups or the implementation of any design ideas.
In addition, communications are reliably recorded. As for the disadvantages, they are as follows:
- Labor intensive. For hidden installation of a heating pipeline, a lot of effort has to be made to carry out the work in accordance with established standards. Everything is too complicated and confusing.
- Presence of heat loss. No matter how well the pipes are insulated, some of the heat will still be wasted on warming up the protective structure, which, by the way, simultaneously performs decorative functions.
- High price. More materials are required, which increases the cost.
- Difficult maintenance. Heating communications laid according to a hidden principle are almost impossible to properly repair. Any maintenance costs a lot of money, since in order to gain access to problem areas it is necessary to dismantle decorative and protective structures.
Cost of installation of engineering heating systems
| Installation of heating radiators and pipelines with connection to central heating risers | |
| Steel pipes | 450 rubles per sq.m. heated area (including VAT) |
| Polypropylene pipes | 300 rubles per sq.m. heated area (including VAT) |
| In the groove | plus 50% to the cost |
| Installation of heating / water supply / ventilation pipelines | |
| Diameter up to 32 mm | 150 rubles per linear meter. (VAT included) |
| Diameter from 40 to 100 mm | 180 rubles per linear meter (VAT included) |
| Diameter over 100 mm | 230 rubles per linear meter. (VAT included) |
| In the groove | plus 50% to the cost |
| Installation of a wall-mounted boiler (installation, connection to the chimney, connection to the heating and water supply system) | |
| 1 circuit | 7500 rub (including VAT) |
| 2 circuits | 10,000 rubles (including VAT) |
| Installation of a floor-standing boiler | |
| up to 60 kW | RUB 14,000 (including VAT) |
| over 60 kW | RUB 30,000 (including VAT) |
| Installation of plate heat exchanger | |
| Diameter of pipes up to 50 mm (inclusive) | RUB 35,000 (including VAT) |
| Diameter of pipes up to 150 mm (inclusive) | RUB 50,000 (including VAT) |
| Nozzle diameter over 150 mm | RUB 120,000 (including VAT) |
| Dismantling the plate heat exchanger | |
| Diameter of pipes up to 50 mm (inclusive) | RUB 15,000 (including VAT) |
| Diameter of pipes up to 150 mm (inclusive) | RUB 25,000 (including VAT) |
| Nozzle diameter over 150 mm | RUB 35,000 (including VAT) |
| Installation of a shell-and-tube heat exchanger (water-water heater) | |
| Section diameter up to 114 mm (inclusive) | 17,000 rubles per section (including VAT) |
| Section diameter 168 mm - 273 mm | RUB 32,000 per section (including VAT) |
| Section diameter 325 mm and above | 65,000 rubles per section (including VAT) |
| Dismantling a shell-and-tube heat exchanger (water-water heater) | |
| Section diameter up to 114 mm (inclusive) | RUB 8,000 per section (including VAT) |
| Section diameter 168 mm - 273 mm | 15,000 rubles per section (including VAT) |
| Section diameter 325 mm and above | RUB 25,000 per section (including VAT) |
| Other equipment (pumps, valves, regulators, other equipment) | |
| Installation | by agreement |
| Dismantling | 30-50% of the cost of equipment |
| *Prices do not include the cost of materials and equipment (for work) |
Having finished assembling the components of engineering heating systems, it is necessary to install them in pre-prepared places determined by the project and connect them into a single heating system.
When installing heating pipelines, it is necessary to observe permissible vertical deviations and distances from supporting structures. It is necessary to ensure that the fasteners are not located at the joints of the pipes. Welding of pipes to fasteners is not allowed.
Radiators should be installed level, observing the requirements of the design documentation regarding the number and location of fastening devices. During installation, compliance with the standards for distances from the floor, window sill and wall is required.
Upon completion of installation, engineering heating systems must be flushed with water until mechanical suspensions are completely removed. Dried components and pipes must be painted to avoid corrosion.
The installation of engineering heating systems ends with hydrostatic tests, confirming uniform heating of the radiators and the absence of leaks in pipe connections and heating units.
Complex work on the installation of utility networks requires a responsible approach to quality control of thermal devices and installation materials, technology and accuracy of individual operations. Our company’s experience in organizing and conducting such events will allow you to get the optimal result.
Small sections of pipeline to fittings
The sections extend from the main pipe sections. Must go to the connecting fittings. Proper arrangement of various branches and turns requires both a design and an engineering approach. Pipes are selected based on the joint seams before cutting. It is important that upon completion of the work there are no interference or incursions in the section of the collapsible type connection.
Crimping
The process of pressing the heating system.
Final events. Includes fastening together dismountable joints. In addition, it is necessary to check the finished sections and perform pressure testing of the heating system under a given pressure. All communications through which heating can interact with the atmosphere are blocked. Water is supplied to the pipeline. Pressure control should be done with a pressure gauge.
Water heating devices
The following can serve as heating elements for rooms:
- traditional radiators installed under window openings and near cold walls, for example, on the north side of the building;
- pipe underfloor heating circuits, otherwise heated floors;
- baseboard heaters;
- in-floor convectors.
Water radiator heating is the most reliable and cheapest option among those listed. It is quite possible to install and connect batteries yourself; the main thing is to correctly select the number of sections according to power. Disadvantages are poor heating of the lower zone of the room and the placement of appliances in plain sight, which is not always consistent with the interior design.
All commercially available radiators are divided into 4 groups according to the material of manufacture:
- Aluminum - sectional and monolithic. In fact, they are cast from silumin, an alloy of aluminum and silicon, and are the most efficient in terms of heating speed.
- Bimetallic. A complete analogue of aluminum batteries, only the frame is made of steel pipes inside. Scope of application: multi-apartment high-rise buildings with central heating, where the coolant is supplied at a pressure of over 10 bar.
- Steel panel. Relatively cheap monolithic radiators made from sheets of stamped metal plus additional fins.
- Cast iron sectional. Heavy, heat-intensive and expensive devices with an original design. Due to their considerable weight, some models are equipped with legs - it is unrealistic to hang such an “accordion” on the wall.
In terms of demand, steel appliances occupy a leading position - they are inexpensive, and from the point of view of heat transfer, thin metal is not much inferior to silumin. Next come aluminum, bimetallic and cast iron heaters. Choose which ones you like best.
Watch this video on YouTube
Construction of heated floors
The underfloor heating system consists of the following elements:
- heating circuits made of metal-plastic or polyethylene pipes, filled with cement screed or laid between joists (in a wooden house);
- distribution manifold with flow meters and thermostatic valves to regulate water flow in each loop;
- mixing unit - a circulation pump plus a valve (two- or three-way) that maintains the coolant temperature in the range of 35...55 °C.
The mixing unit and the manifold are connected to the boiler by two lines - supply and return. Water heated to 60...80 degrees is mixed in portions by valve into the circuits as the circulating coolant cools.
Warm floors are the most comfortable and economical heating method, although installation costs are 2-3 times higher than installing a radiator network. The optimal heating option is shown in the photo - floor water circuits + batteries, controlled by thermal heads.
Warm floors at the installation stage - laying out pipes on top of the insulation, attaching a damper strip for subsequent filling with cement-sand mortar
Skirting and in-floor convectors
Both types of heaters are similar in the design of the water heat exchanger - a copper coil with thin plates mounted on it - ribs. In the floor-standing version, the heating part is covered with a decorative casing that looks like a plinth; gaps are left at the top and bottom for the passage of air.
The heat exchanger of the in-floor convector is installed in a housing located below the level of the finished floor. Some models are equipped with low-noise fans that increase the heater's performance. The coolant is supplied through pipes laid hidden under the screed.
The described devices fit well into the design of the room, and underfloor convectors are indispensable near transparent external walls made entirely of glass. But ordinary homeowners are in no hurry to purchase these devices because:
- copper-aluminum convector radiators are not a cheap pleasure;
- to fully heat a cottage located in the middle zone, you will have to install heaters around the perimeter of all rooms;
- in-floor heat exchangers without fans are ineffective;
- the same products with fans emit a quiet monotonous hum.
Baseboard heating device (pictured left) and in-floor convector (right)
Liquid fuel boilers
In terms of the cost of heating equipment and its installation, heating with waste oil or diesel fuel will cost approximately the same as with natural gas. Their efficiency indicators are also similar, although the processing, for obvious reasons, is somewhat inferior. Another thing is that this type of heating can easily be called the dirtiest. Any visit to the boiler room will end with at least the smell of diesel fuel or dirty hands. And the annual cleaning of the unit is a whole event, after which you will be smeared with soot up to your waist.
Using diesel fuel for heating is not the most profitable solution; the price of fuel can hit your pocket hard. Used oil has also risen in price, unless you have some cheap source. This means that it makes sense to install a diesel boiler when there are no other energy sources or, in the future, a main gas supply. The unit easily switches from diesel fuel to gas, but the exhaust furnace will not be able to burn methane.
Features of a water heating system
In the ranking of popular heating models, the first place leader is occupied by an individual hot water heating system. The coolant circulates through a closed pipeline laid from the generation source to the heating radiators. Hot water enters the radiators, which, due to the large heating area, emit thermal energy.
The heating boiler model is selected taking into account the fuel used.
Types of heating systems
Classification of individual heating lines with hot water coolant is made according to the following types:
- Place of laying the supply pipeline: upper and lower wiring. Such schemes are recommended for two- and three-story houses.
- Number of risers. There are one-pipe and two-pipe heating installation schemes.
- Location of risers. The risers can be connected vertically or horizontally.
- Heating network layout diagram. The routing is carried out with direct or dead-end main lines.
The type of heating network is selected taking into account the selected individual system, heating boiler and design features of the residential building.
Basic elements of water heating
An autonomous heating system for a private house or apartment consists of the following main elements:
- Heating boiler. In this device, fuel is converted into thermal energy transmitted by the coolant through pipes.
- Heating pipes. Currently, almost all systems are installed from polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes; metal steel pipelines are practically not used.
- Shut-off valves. Ball valves are installed to shut off the water supply, throttles regulate the heat transfer of heating devices, thermostatic heads maintain a given comfortable temperature in the room, automatic air vents remove excess air from the heating system.
- Safety devices. An expander, a safety valve, and a pressure gauge protect the heating system from emergency situations.
- Heating radiators. Cast iron, steel, aluminum, bimetallic batteries are an integral part of individual heating.
Note: Additionally, automatic devices are installed that maintain the set temperature in the room - programmers that independently regulate the heating boiler switching mode.
Advantages and disadvantages of a water heating system
The main advantages of a water heating system:
- Possibility of adjusting the heating temperature. Wood stoves quickly warm up the air in the room, but, unfortunately, it is impossible to control this process.
- High degree of reliability and ability to operate in automatic mode.
- Economical. Heating residential buildings with electricity is much more expensive for homeowners due to the high cost of energy resources.
- Comfort of use. Unlike steam heating with unregulated heating temperature of heating devices, the water circuit provides more comfortable heating of radiators.
The main disadvantages of water heating:
- Slow heating of heating devices.
- Labor intensive installation.
- Possible freezing of water in pipelines.
- The need to periodically clean heating radiators from solid salt deposits.
How is it built and what does the cost depend on?
The price of the work consists of a set of individual installation operations that are required to be carried out, the complexity of their implementation and the complexity of the heating system itself. The most common factors that influence the estimate are the following:
- Poor insulation
- Architectural features of the Property. Small sections of rooms, a large number of windows, low windows, second light - all this increases the estimate for the installation of water heating
- Configuration of the heating network and the use of non-standard heating equipment in it. For example, heated floor
- Installation of water heating in difficult conditions and additional work - punching holes in thick walls and ceilings, diamond drilling, work at heights or at night
- Fuel used - the price of work on organizing boiler plants operating on different types of fuel can vary significantly
Boiler installation instructions
Strict requirements are put forward only for the installation of gas-powered heaters. But we recommend following these rules when installing any heat generators:
- Equipment with a power of up to 60 kW can be placed in a kitchen with ceilings of 2.5 m (minimum). More powerful units are moved to a technical room - internal, attached or free-standing.
- The requirement for furnace ventilation is threefold air exchange, that is, the amount of supply and exhaust air is equal to three volumes of the room in 1 hour. The kitchen window is equipped with a window.
- When placing a floor-standing boiler, observe the minimum technological passages - 1.25 m in front, 60 cm on the side, 250 mm in the back from the nearest building structure, as shown in the photo.
- The distances from the wall-mounted heat generator to the walls or cabinets are 20 cm on the side, 45 cm on the top, 300 mm on the bottom. Before hanging, a protective sheet of roofing steel is laid on the wooden wall.
- The height of the chimney is 5 m, calculated from the grate or gas burner, not from the ground. The head of the pipe should not fall into the wind support zone of the roof.
- The maximum number of turns of the chimney is 3, the distance from the chimney to combustible structures is 0.5 m.
The heat generator piping depends on the fuel consumed. High efficiency boilers - gas, diesel - are connected to the system directly through shut-off valves. Floor-standing versions are additionally equipped with an external expansion tank and pump.
Typical wiring diagram for a double-circuit wall-mounted heat generator
Solid fuel units must be protected from cold return flow and condensation; accordingly, a small boiler circuit with a three-way mixing valve is provided
Please note: the pump is always installed inside the circuit, on the supply or return line - it makes no difference. Detailed wiring diagrams are shown in the instructions for connecting TT boilers
Watch this video on YouTube
Main types of heating
The difference between all existing systems depends on different criteria. Installation location, heating area, technical features of wiring and installation. In frequent cases, the type of structure is influenced by the method of energy supply and, of course, the total cost of the entire complex responsible for heating a private house. Modern energy-saving technologies offer a wide selection of different heating systems using advanced developments. This article presents popular, common types of heating systems used in almost every home.
Water heating
- Same temperature in all rooms.
- Length of service life.
- Possibility of using different materials of pipes and hardware (polypropylene, metal).
- Quiet operation.
- Fuel saving, easy maintenance.
The individual design elements of this option are an electric, multifunctional or gas boiler. Coal boilers are also used. With their help, water is heated and distributed through pipes (closed circulation) to the batteries. This is how the heat of the heated liquid is transferred to the premises. For ease of use, several subtypes are used. We'll talk about them below.
Air heating
This type of heating was known and used in ancient times. Heated air was supplied into the room using an air duct system, thereby heating it. In its modern version, this is a common method of heating large areas. Until recently, it was used only in production workshops, sports facilities, and public spaces. But the development of modern technologies makes it possible to use the air method in private homes.
Heating and supply of air mass to the premises is carried out by air heaters. In large workshops, these are special installations that provide heating and constant circulation of air at a certain temperature. The local option involves the use of low-power air heating devices. Usually these are heat guns and fan heaters. The devices are quite mobile and use various construction methods (electric heaters, fuel burners, etc.) as the main heater.
The operation of air heating requires strict adherence to fire safety rules and basic hygiene requirements. The second provides for the presence of air purification filters, flow ventilation, air ducts, air curtains and other elements. As well as constant control over the air duct system as a whole.
Heating based on electricity
This type of heating works on the principle of converting electrical energy into heat. The main source of heat is an electric boiler or various heating devices (appliances). Boilers are used in water systems and are considered an environmentally friendly heating method. Individual devices have their own designs:
- Electric convectors.
- Air curtains.
- Oil radiators with heating elements.
- Infrared emitters (UVR), heated floors.
- Fan heaters, heat guns.
The use of different modifications depends on the installation location, heating area, and operating conditions. Electric convectors and oil radiators are well suited for heating apartments or private houses. This applies to UV devices and heated floors. All of the above methods are economical (subject to an affordable price for electricity) and do not require the use of several types of energy resources; only electricity can be used.
Coolant circulation
Depending on the method of moving the coolant through the pipes, home heating can be designed in two ways:
Option with forced coolant circulation
For a heating scheme for a private house with forced circulation, it is necessary to install a circulation pump in the heating system. It ensures the movement of heated liquid through pipes to the radiators. In this case, no tilting of the highways is required. When radiators are installed in the system, it is necessary to install Mayevsky taps on them to displace air pockets. The cooled coolant is supplied through the return circuit back to the boiler room.
The advantages of the option with forced movement of the coolant are:
- High speed of coolant movement. As a result, the liquid in the return circuit practically does not cool down. This allows you to optimize the use of fuel or electricity (depending on the type of boiler)
- Possibility of adjusting the temperature regime of each heating device
- Minimizing the internal cross-section of pipes without reducing the resistance of the medium in the mains
Option with natural coolant circulation
Other names used for this system built on the basis of this option are gravitational, convective. Heating a private house with natural coolant circulation is an economical option
The operating principle is as follows. When heated, the density of water decreases. Therefore, the hot water in the supply circuit is forced upward by the heavier cooled water in the return circuit.
To prevent water hammer due to an increase in volume (and, as a consequence, coolant pressure in the system), an expansion tank is installed in the upper part of the system. As a result, the hotter layers enter the radiators, and the cooled coolant enters the boiler through the return circuit.
In addition to the convection principle, the gravitational principle also works in this heating scheme for a private cottage. To do this, a slight slope is made in the incoming circuit from the riser to the heating devices, increasing the movement of the coolant by gravity. Accordingly, the return circuit provides for a slope in the direction of the boiler.
This method has few advantages:
- Low price
- There is no need for a circulation pump, which requires power supply. This allows for a heating system independent of electricity (provided that an appropriate boiler is used)
The main disadvantages of such a heating system are that a scheme with natural coolant circulation has a low level of comfort and reliability.
Work order
If everything is ready, you can begin installation. Here are its main stages:
Boiler installation
The connection of the heat generator to the gas supply system can only be carried out by an employee of the gas industry, but the user has the right to do everything else independently. First of all, you need to choose the right location for the boiler. It should be located closer to the chimney, so that the length of the pipe connecting them does not exceed 25 cm. The cross-sectional area of the chimney should be no less than that of the boiler smoke exhaust pipe.
The volume of the room must be at least 15 cubic meters. m, and with a boiler power over 75 kW - 0.2 cubic meters. m for every kilowatt.
Heating scheme with gas boiler
The room must have a window, the minimum area of which is determined at the rate of 0.03 square meters. m for each cubic. m volume.
Fresh air must enter the boiler room - directly from the street or through an adjacent room, for example, through the kitchen.
Polymer pipes cannot be connected directly to the boiler. There must be a metal section at least 3 m long between them and the heat generator.
Marking
Before proceeding with the installation of the heating system, you need to mark on the walls the location of fasteners and holes for passing pipes.
It is most convenient to mark the holes for the radiator brackets using a template.
If you intend to use long sectional radiators, then the brackets must be placed not only at the edge, but also in the middle, in order to avoid sagging of the device with its subsequent deformation and depressurization.
Installation of equipment and installation of heating system pipelines
Let's consider the installation of a heating system made of polypropylene pipes. Before hanging the radiator on the wall, you can attach a sheet of foil, which will reduce heat loss by reflecting infrared radiation. Another useful trick is to install a smoothly curved tin canopy over the radiator, which will make it easier for heated air to escape from under the window sill.
The circulation pump is installed on the return line just before the boiler. Here the coolant is the coldest, which means the pump will last longer.
This area is also well suited for a membrane expansion tank. The latter really does not like turbulence, and it is almost never observed just before the circulation pump.
The air vent is installed at the highest point of the circuit.
Complete heating system with piping
Connections in polypropylene and metal-plastic pipelines are made in different ways. Polypropylene parts are welded, for which they need to be heated on a special tool, commonly called a soldering iron or iron.
The holding time is strictly regulated and depends on the diameter of the part and the thickness of its wall. After heating, one of the parts is put on the other and as they cool, they form a durable alloy.
Under no circumstances should polypropylene pipes be butt welded together without using a coupling. Such a connection will not withstand internal pressure and will leak very quickly.
To connect a metal-plastic pipe to a fitting or radiator, you need to attach a fitting to it. There are two types of fittings:
- Crimping: the most affordable, and therefore the most popular option. The part consists of a fitting, a split ring (cracker) and a union nut. The nut is put on the pipe first, then the cracker, after which the fitting is inserted into it. Now the cracker needs to be pushed onto the fitting, followed by the union nut, which is screwed onto the thread on the fitting. You need to tighten the nut until you hear the material creaking four times. Compression fittings have a significant drawback: they have to be tightened from time to time, otherwise they will begin to leak. For this reason, they cannot be walled up in walls.
- Press fittings: more expensive, but also a much more reliable type. The fitting has a sleeve, which is pressed with special pliers around the fitting after the pipe is put on it. With this design, leaks are excluded, so pipes with press fittings can be laid in a hidden way without fear.
Before pulling the pipe through a hole in the wall, wrap the end with plastic wrap to prevent debris from getting inside.
The assembled system must be subjected to pressure testing - crimping. To do this, use a manual or electric crimper. With its help, a pressure of 1.5 - 2 times higher than the nominal pressure is created in the system for several hours.
If the pressure gauge readings did not change during the tests, then there are no leaks.
External gasket technology
Installation of devices. The laying of heating pipelines, carried out in open areas, begins with the installation of all devices that are part of the future system. We are talking about boilers, radiators, pumps and expansion tanks. The list is not final. Sometimes it can increase due to various technical solutions. Given as an example.
Gasket calculation
This event is largely decorative in nature. The main goal is to calculate the location of the pipes in such a way that they do not spoil the overall design of the premises. Therefore, the stage often includes the creation of preliminary design sketches taking into account the heating pipeline.
Selecting a working option
Currently, there are the following three methods of arranging external gaskets:
- Top + bottom. The discharge pipe is mounted at the highest possible height. The lower pipeline is laid almost along the floor surface in the baseboard area. Excellent for natural circulation of working fluid.
- Bottom wiring. Both pipes are installed in the lower part of the rooms. This option is used only with forced circulation of the coolant. The pipeline is almost invisible to the eye, since it is located in the baseboard area and is often decorated to match it.
- Installation on radiators. The discharge pipeline, which has a large cross-section, is stretched between the heating devices directly under the window sills. This is done from one stub to another. The lower pipe is laid in the floor area. As a result, fewer pipes are needed. The system is getting cheaper. It is possible to connect heating devices either in parallel or in series.
The external installation of communications, although simpler, is less attractive from an aesthetic point of view.
Heating system diagrams for a private home
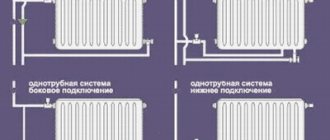
Heating systems sold in private housing construction can be single-pipe or double-pipe. It's easy to distinguish them:
- according to a single-pipe scheme, all radiators are connected to one collector. It is both a supply and a return, passing by all the batteries in the form of a closed ring;
- in a two-pipe scheme, the coolant is supplied to the radiators through one pipe and returned through the other.
Choosing a heating system layout for a private home is not an easy task; consultation with a specialist will certainly not hurt. We will not sin against the truth if we say that the two-pipe scheme is more progressive and reliable than the one-pipe one. Contrary to popular belief about the low installation costs when installing the latter, we note that it is not only more expensive than a two-pipe one, but also more complex. This topic is covered in great detail in the video:
The fact is that in a single-pipe system, the water from radiator to radiator cools more and more, so it is necessary to increase their capacity by adding sections. In addition, the distribution manifold must have a larger diameter than the two-pipe distribution lines. And lastly: automatic control with a single-pipe circuit is difficult due to the mutual influence of the batteries on each other.
In a small house or dacha with up to 5 radiators, you can safely implement a single-pipe horizontal circuit (common name - Leningradka). With a larger number of heating devices, it will not be able to function normally, because the last radiators will be cold.
Another option is to use single-pipe vertical risers in a two-story private house. Such schemes occur quite often and work successfully.
With a two-pipe distribution, the coolant is delivered to all radiators at the same temperature, so there is no need to increase the number of sections. Dividing the lines into supply and return makes it possible to automatically control the operation of the batteries using thermostatic valves.
The diameters of the pipelines are smaller, and the system as a whole is simpler. There are the following types of two-pipe schemes:
dead-end: the pipeline network is divided into branches (arms), through which the coolant moves along the highways towards each other;
associated two-pipe system: here the return manifold is, as it were, a continuation of the supply, and the entire coolant flows in one direction, the circuit forms a ring;
collector (radial). The most expensive wiring method: pipelines from the collector are laid separately to each radiator, the installation method is hidden, in the floor.
If you take horizontal lines of larger diameter and lay them with a slope of 3-5 mm per 1 m, then the system will be able to work due to gravity (by gravity). Then a circulation pump is not needed, the circuit will be non-volatile. To be fair, we note that both single-pipe and two-pipe wiring can function without a pump. If only conditions were created for natural water circulation.
The heating system can be made open by installing an expansion tank at the highest point, communicating with the atmosphere. This solution is used in gravity networks, otherwise it cannot be done there. If you install a membrane-type expansion tank on the return line near the boiler, the system will be closed and operate under excess pressure. This is a more modern option, which finds its application in networks with forced movement of coolant.
It is impossible not to mention the method of heating a house with warm floors. Its disadvantage is that it is expensive, since you will need to lay hundreds of meters of pipes in a screed, resulting in a heating water circuit in each room. The ends of the pipes converge to a distribution manifold with a mixing unit and its own circulation pump. An important advantage is the economical, uniform heating of rooms, which is very comfortable for people. Underfloor heating circuits are clearly recommended for use in any residential buildings.
Reviews about our Company
We only publish real reviews.
Here's what our clients say about us: I express my deep gratitude to Dmitry Saltykov’s team (Dmitry himself, his colleagues Dmitry and Fedor) for the high-quality work on gasification of a country house. Everything is very neat, professional, high quality!!! It is clear that they are real experts in their field. I would like to express special gratitude to Fedor for his approach to business, love for work and, as a result, excellent results!!! Mosoblgaz rated the work on the boiler room as 5+ (without any complaints). I recommend to everyone!!!!
Maria T.
I’m very glad that I called MosInzhGroup when searching. Dmitry Saltykov answered the phone and answered all my questions/doubts very professionally. We signed an agreement and started working. And here the second Dmitry, Dmitry Mironkin, demonstrated how real professionals work. All issues were resolved promptly and competently. Always in touch, will help, give advice. A person with an amazing aura of empathy and responsibility. I recommend this company to everyone.
Anna Baykova
I was satisfied with the result, three employees of the company worked on my project at once - manager Dmitry in the office, engineer Dmitry (also ))) at the site supervised the installation team and since my heating project had not been completed, I also received advice from the designer Alexey. I'm also happy with the installers. I made a boiler room, heating, water and sewerage in a country house of 320 m2. I recommend it.
Anastasia S.
I thank the employees of the Mosinzhgroup company for the quality work carried out on all engineering systems in my house under construction. I myself am not very knowledgeable about this topic, I read a lot on the Internet, and found this company there. I was worried about the quality of the work, because it often happens that they say one thing, and then in reality everything turns out differently. As a result, after much deliberation, I concluded an agreement and did not regret it.
Daniil Z.
You can read full customer reviews about our Company on Yandex Maps.
What kind of heating is there?
Now there are different heating systems by type, purpose and thermal power, the main difference lies in the routing of pipes from the collector:
- single-pipe - all radiators are connected in series, individual ones cannot be disconnected,
- two-pipe - radiators can be turned off independently of each other,
- radial - each radiator is connected to the collector separately, it can be turned off and the heating can be adjusted separately.
The latter option is becoming increasingly popular, as it allows you not only to regulate the temperature in different rooms, but also to save money when installing heat meters.
Single-pipe scheme (“Leningrad”)
Single-pipe heating distribution is an outdated scheme, but sometimes still used. It uses one pipe, forming a ring circuit. Radiators are connected in series to this pipe. Through this pipe the coolant is supplied to the radiators and through it it goes back to the boiler.
The only advantage of the Leningradka is its low price. A significant drawback is the different temperatures of the coolant in the radiators. The radiators furthest from the boiler do not heat up enough. For heating in private houses in today's realities, the Leningrad scheme is practically not used precisely because of this.
Choosing equipment for heating a private house
In places where there are interruptions in the supply of the main type of fuel, it is recommended to install universal heating boilers.
There is a huge range of boilers on the market. There are even hybrid boilers that can operate, for example, on both gas and wood. So, the choice depends purely on your preferences and needs. Of course, boilers with a full range of automation and hybrids will be more expensive. The former will more than pay for themselves with their high efficiency, and the latter – with their versatility.
It is impossible to recommend a specific model, since different devices have different power. Choose the device that is most suitable for your conditions, but try to select the boiler so that its operation is not costly. If you use wood, it is better to choose a wood-burning model. If gas is supplied, then use the gas model.