The main function performed by the heating network is to maintain a comfortable temperature inside the premises it serves. Installation of heating systems is a complex and multi-stage task. Its successful solution should be based on professional design and knowledge of the intricacies of work production that are not noticeable at first glance.
What are heating systems
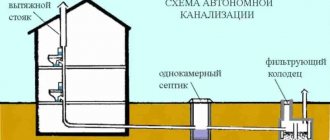
Heating networks include all engineering networks and communications designed to convert various types of energy carriers into thermal energy. In this case, both individual heating for individual residential buildings and centralized heating can be organized to serve neighborhoods and areas in large populated areas.
Each heating system must include:
- Heat source
- Design for transporting coolant
- Circulation and expansion devices
- Automation and Security Tools
Zoning
In order for your stay in the house to be comfortable and cozy, and the consumption of thermal energy to be economical, it is necessary to correctly distribute heat throughout the rooms. In this case, the following rules can be taken as a basis:
- The average comfortable temperature in the premises should not exceed 240C.
- In the bedroom, comfort is felt at a temperature of 220C -250C.
- For the bathroom and toilet, the figures drop to 210C. The same indicator is set for guest rooms.
- In the kitchen, dining room and work areas, you can reduce the temperature to 18-22 degrees.
- For a comfortable stay in the hallway, garage and passage area, you can set the temperature within 120C.
Types of heating systems
All heating systems can be classified according to a number of characteristics.
Fuel used
Depending on the type of energy carrier used, heat sources can be:
- Gas
- Solid fuel
- Liquid fuel
- Electric
- Geothermal
Installation of heating for cottages with boilers burning liquid fuel is extremely rare. Usually only in cases where all other fuel sources are unavailable and delivery is too expensive.
Electric heating equipment is easy to install and very convenient to use. But the cost of such heat is higher than when burning gas or solid fuel. Making changes to this situation, it is quite likely that the use of flat Tesla induction coils, which have recently begun to appear on the Russian market, can provide a solution.
Type of coolant
Depending on the type of coolant used, individual heating systems can be:
- Mermen
- Steam
- Electrical
- Gas
- Air
In our country, the most common heating schemes are those using liquid coolant. They are followed in approximately equal shares by electric and gas. Steam is used only in industrial enterprises, and the installation of air heating as the main one can only be found in the southern regions.
Type of circulation
The movement of heated water in heating systems can be organized in two ways:
- Naturally
- Forcibly
The main advantage of the first type is its complete independence from the stability of the power supply. In them, the coolant moves through the pipeline due to the ability of the liquid to rise upward when heated, and to fall down when cooled. But low stability of operation, the need to increase pipe diameters, the difficulty of adjusting the temperature and the use of radiators with a large internal volume make the use of such heating systems unpopular.
The forced movement of the coolant is carried out thanks to the operation of electrically driven circulation pumps. This allows you to significantly increase reliability, comfort of use and reduce operating costs.
Calculation of heating systems
Before starting the installation of the heating system, it is necessary to complete the calculation stage.
Calculation of heat losses
The main calculation required for this is thermal engineering. The result is the determination of heat losses in the rooms and the building as a whole. It is these heat losses that the heating system will have to restore and its power must be sufficient for this.
Thermal engineering calculations are carried out taking into account the five coldest winter days. These data can be found in SNiP “Climatology”.
We can say with confidence that only a qualified heating engineer with a special technical education can accurately calculate the heat losses of a building.
If we talk about small-sized cottages with standard architecture, then the installation of a heating system can be performed on the basis of a simplified calculation based on aggregated indicators.
With conventional glazing of a building without wide large stained glass windows, a room height of up to 3.2 m and normally insulated walls, approximately 1 kW of thermal energy will be required to provide heat to 10 m2. These aggregated data are slightly larger than the real ones that would be obtained as a result of thermal engineering calculations. The rooms served will definitely be warm. In addition, it is not at all difficult to reduce the amount of heat supplied if necessary.
The disadvantage of this approach is the unreasonable reserve of power of all equipment, which leads to an increase in the cost of heating systems. The boiler and radiators will cost about 10% more.
Based on the calculation of heat losses, equipment is selected:
- Boiler
- Radiators, convectors, heated floors
Hydraulic calculation
Its main goal is to determine the minimum permissible cross-section of pipes and reduce the cost of purchasing materials. The diameters of pipelines for the installation of heating systems are determined based on the results of hydraulic calculations. Also, on its basis, the selection of pumping equipment is made.
Pipe laying methods
Pipe laying is done in two ways: open and closed. In the second case, the process takes more time, money and effort than the first.
However, with the closed method, you can avoid using additional space, because the pipes will be built into the walls.
The disadvantages of this option include the following: you do not have open access to the pipes. That is, in the event of any breakdown, you will not have the opportunity to immediately identify the problem area and will have to break the wall.
The open method is characterized by the ease of laying and installing pipes, the ability to carry out inspections if necessary, and then eliminate problem areas. But the obvious disadvantage is considered to be the reduction of space and the unaesthetic appearance of bare pipes.
Selection of materials
Before starting installation work, you must carefully consider the choice of equipment.
Pipes
Installation of heating systems is carried out using the following types of pipes:
- Cross-linked polyethylene (both for radiator networks and water heated floors)
- Metal-plastic
- Polypropylene reinforced with glass fiber or aluminum
- Cink Steel
- Copper
- Brass
- Stainless steel
Non-reinforced polypropylene pipes have a maximum heating temperature of 60˚C and therefore heating systems cannot be installed from them.
Black or galvanized steel pipes have excellent strength and are resistant to high temperatures from superheated water. However, they are susceptible to rust and are more difficult to install. The prices for these materials make it advisable to use them for piping furnace and boiler rooms.
Plastic pipes of small sections are durable, easy to install, but have limitations on operating temperature and pressure. Laying heating pipeline systems made of plastic is not practiced in areas where emergency operating conditions are possible. For example, at the outlet of hot water solid fuel boilers and drainage discharge lines in furnace boilers.
Copper, brass, and stainless steel pipes are rarely used due to the high cost of the material and the need to use special tools when performing installation work.
Today, installation of heating using pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene (for hidden installation) or pipes made of reinforced polypropylene (for open installation) is the most optimal option. For piping boiler equipment, it is advisable to use copper or reinforced polypropylene.
Heating devices
The choice of the type of heating radiators depends, first of all, on the efficiency of their heat transfer, the pressure of water heating systems, the coolant used, the requirements for their appearance, and cost.
Depending on the material of manufacture and design features, radiators are of the following types:
- Steel panel
- Steel tubular
- Bimetallic sectional
- Aluminum sectional
- Cast iron
In closed circuits, the flow of oxygen into the water is minimal and heating systems can be installed with any type of radiator. The limitation is imposed by the coolant used.
The best results in the mid-price segment are shown by steel panel radiators. When using bimetallic sectional radiators, you must remember that the coolant (if it is not water) can corrode the gaskets between the sections and the radiator will leak.
Heating system installation
It is recommended to perform installation work in the following sequence.
Boiler room arrangement
It is recommended to begin installation of the heating system with work in the combustion room. Performed:
- Boiler installation
- Connecting chimneys
- Placement of additional equipment
- Wiring of all used boiler equipment
After this, connections are made to an external gas pipeline (if gas is used). The connection is carried out by a representative of the local gas service.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account:
- A pump to create coolant circulation is installed on the line returning it to the boiler. In this case, its working life increases significantly
- It is necessary to connect a hot water drain line to the return and supply circuits of heating systems to remove coolant in the event of repairs or accidents
- Each piece of equipment when installing heating systems must have a separate shut-off valve to enable its emergency shutdown
Placement of heating devices
Initially, the locations of radiators and convectors are marked. The possibility of using in-floor convectors should be ensured by the design of the floor, in which special niches are made for them.
Side plugs are installed on the radiators, all connecting fittings and end fittings are screwed in for connection to the pipeline.
Radiators are installed in such a way that the distance to the finished floor mark should not be less than 150 mm, and to the window sill 100 mm.
Installation of heating pipeline systems
There are several pipeline laying schemes. In modern houses, you can increasingly see radial (collector) piping, in which each radiator or convector has its own connection to the distribution manifold.
Heating installation can be carried out using a two-pipe wiring diagram. Its main disadvantage is the large number of pipe joints, which reduces reliability. That is why it is optimal to install two-pipe wiring in an open design.
The laying of pipelines is carried out according to a pre-developed scheme or on the basis of a project.
Installation of a heating system made of polyethylene pipes is carried out using tension press fittings, crimp or tension rings. PVC pipes are assembled more easily by soldering using a special welding machine. All threaded fittings are connected in the traditional way by packing on ordinary brushed flax (tow) and sanitary silicone.
Connecting heating devices
At this stage, pipelines are connected to radiators, convectors, and heated floors. All connections are made with standard fittings.
Connection to radiators can be bottom, side or diagonal. From the point of view of aesthetics, the bottom connection is optimal, from the point of view of the efficiency of heating systems - diagonal. Which connection to choose is determined individually in each case.
Hydraulic tests
At the final stage, hydraulic tests are carried out. The installed circuits are filled with water and left under pressure. The pressure should not drop during the entire hydraulic test. If this happens, the location of the leak is sought and its cause is eliminated. After this, the tests are repeated until the pressure is constant.
Recommendations and tips
In conclusion, I would like to give a few recommendations that may be useful.
- Installation of piping systems should be carried out taking into account the fact that tension fittings cannot be laid in the floor and walls. If this occurs, a small amount of free space must be left to accommodate the connections.
- Radiators should be within 70% of the window width. Panel radiators can ensure that this condition is met. Changing the thickness of the device allows you to change its overall dimensions, and choosing the best option is not difficult
- Installation of smoke removal systems should not pass through rooms with long-term occupancy. With an external chimney, it should be taken into account that the distance from it to the windows of residential premises must be at least 800 mm
- When using non-freezing antifreeze liquids as a coolant, sectional radiators cannot be installed. After a certain time, nipple connections may leak
- Using a room thermostat with an on-timer allows you to save up to 40% of the energy spent on heating
There are still a huge number of subtleties and nuances. If you do not have experience, knowledge, or working skills, then it is better to entrust the installation of heating systems to a trusted Contractor. The usual cost of work is estimated at 30-40% of the price of equipment and materials.
The best option is to conclude an Agreement with a company that will carry out all the work on a turnkey basis - develop a scheme or carry out a project, complete the equipment and install it. Practice shows that the installation of turnkey heating systems helps the Customer save significantly. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that all materials and work are provided with a Guarantee.
Read other articles on this topic
| Features of heating a country house with electricity | Do-it-yourself heating of a private house made of polypropylene |
| Heating distribution for a two-story house | Country house heating system |
| Basic rules for the location of radiators when heating a private house | Heating a private house with underfloor heating |
| Heating diagram for a two-story house | Heating and water supply of a country house: description of installation technology |
| Infrared heating of houses | How to save on heating a country house |
| How to heat your home without gas | Installation of a heating system in a private house |
| The best heating for a private home | Water heating in a private house |
| How to heat a private house | Heating system for a private house with natural circulation |
| Heating a private house with a heat pump - pros and cons | How is pressure testing of a heating system performed? |
| Heating options for a frame house | Autonomous heating of a private house |
| Thermal trace - purpose, classification, use cases | Combined heating system for a private house |
| Gas consumption for heating a private house - consumption calculation | Heating a private house with electricity |
| Heating the house with liquefied gas | Heating project for a private house |
| Heating a private house with forced circulation | Heating system for a private house using a warm baseboard |
| Heating wiring diagrams from a boiler in a private house | Heating your home is the most economical way |
| Heating a private house with convectors | Collector heating system for a private house |
| Heating a private house from metal-plastic pipes | About heating schemes for a private house with a gas boiler |
Services on this topic
| Heating design | Turnkey solid fuel heating |
| Turnkey gas heating | Turnkey heating |
| Heating in a turnkey wooden house | Turnkey water heated floor |
| Installation of water heated floor | Heating a two-story house |
| Heating installation in a cottage | Heating a country house: options and prices |
| Heating installation | Heating installation in a private house |
| Installation of plumbing and heating engineering systems | Diesel heating of a country house |
| Autonomous heating on a turnkey basis | Air heating of a country house |
| Prices for heating installation in a private house | Design and installation of heating systems |
| Water heating in a private house | Electric heating of a country house: options and prices |
| Heating in a townhouse | Gas heating design |
| Heating design cost | Heating calculator for a private house |
| Installation of water heated floors in a private house | Price for installing a water heated floor |
| Installation of water heated floors on a wooden floor |
Heat loss calculation
At this stage, all external walls and corners are taken into account, since large heat losses are observed in these places. The calculation takes into account the thickness of the walls and the thermal resistance of the material from which they are made.
Each element of the house fencing has its own heat loss values. For example, at a temperature of -300C, up to 135 W per 1 m2 goes through a double-glazed window. At the same temperature levels, heat losses through solid double wooden doors amount to up to 234 W per 1 m2. Through the attic floor at -30 degrees, up to 35 W of heat per square meter is lost. 1 m2 of wooden floor above the basement deprives the room of 26 W of thermal energy.