When setting the goal for an intra-house or apartment heating system to function efficiently, its actual thermal parameters must be extremely close to the calculated values. This can be achieved if the coolant is distributed correctly across the heating circuits, while maintaining stable pressure and temperature parameters.
This problem is especially relevant in developed heating systems that heat objects with a large heating area. To perform this task, a specialized device is integrated into the system - a balancing valve.
What is a balancing valve
To maintain an equal temperature in the radiators, the volume of coolant passing through the device is regulated; the smaller it is, the lower the heat transfer from the battery. In practice, it is possible to regulate the flow using a conventional ball valve, and this is effective if the number of heating elements in the circuit does not exceed one. Otherwise, it is not possible to set the same temperature in different batteries using a ball valve.
Balancing valve
Balancing valve for heating system effectively maintains heat balance by applying automatic or manual adjustment in heating elements. Structurally, this is carried out through a special mechanism that partially closes the passage of the coolant, just like any shut-off and control device, but with the difference that the required volume of the balancer is set manually or automatically using preset adjustment scales.
The balancing valve is installed on the return pipeline. This approach makes it possible to guarantee a constant rate of water circulation in the batteries, even if a common line is used for heating and the DHW circuit. If the balancing scheme provides for the installation of balancers at each radiator, then they are placed at the bottom of the radiator outlet fitting, diagonally with respect to the coolant supply ball valve located in the upper part of the heating device.
How else is a balancing valve used?
In addition to regulating individual branches and risers in the heating system, the device is also used for other purposes. For example, a balance valve is installed in the small circulation circuit of a solid fuel boiler when it is closed to a buffer tank. The point is to maintain the water temperature in the circuit at least 60 ºС and not install a mixing unit for this. But in this case, the flow rate in the boiler circuit should be higher than in the heating circuit. This is what the valve installed on the supply does.
Another installation option is that a balancing valve regulates the supply of coolant to the indirect heating boiler coil. The latter, as a rule, is connected directly from the boiler unit, so it would be correct to limit the amount of coolant for heating the boiler. It must be said that ideally it is better to equip all branches of the system with balance valves, including underfloor heating and hot water circuits. Such measures improve the quality of heating operation and definitely lead to energy savings.
The principle of operation of the balancer in the heating system
Operating principle of the balancer
The principle of operation of the balancing device is that the valve seat is capable of changing the internal passage. Rotating the handle sets the corresponding nut and spindle in motion. When unscrewing, the valve rises to the upper operating position, which ensures maximum fluid flow; when tightening, the spindle presses on the valve seat, lowering it to the lower position, thereby reliably blocking the passage of fluid through the radiator.
The radiator modification, used for mechanical adjustment of the thermal and hydraulic modes of the heating circuits, is made of the following elements:
- The body is made of brass with threaded pipes for installation of intra-house pipelines.
- Molded round seat located inside the body.
- A device for adjusting the cross-section of the coolant passage is a regulating spindle, which rests against the saddle when screwed.
- Rubber sealing ring.
- Protective and safety cap made of metal/plastic.
Functional features of a balancing valve for a heating system
Main balancing valve
The automatic balancing valve for the heating system for the main network differs from the radiator design in dimensions, spindle angle and fitting geometry.
Automatic balancer functions:
- Drainage of water from the heating system;
- connecting sensors to measure coolant parameters;
- installation of a pulse volute tube from a pressure corrector.
The number of turns that the balancer is capable of performing is from 3 to 5; this figure varies among most manufacturers. In order to change the position of the rod, you will need a wrench with a hexagon configuration. The adjustment is carried out based on the pressure difference in the heating network. During the setup process, when the flow rate of circulating water changes, the pressure loss in the pipeline and control valve also changes, which in turn leads to a change in the differential on the balancer.
The pressure drop in the network can be determined independently from the readings of pressure gauges installed on the return/supply of the in-house heating system. For example, with a supply/return pressure of 2.5 / 2.0 bar, the difference will be 2.5 – 2.0 = 0.5 bar. When the valve is automatic, it sets the differential itself according to the algorithm established by the design.
It should also be noted that not all heat supply systems require balancing. For example, if there are up to three short dead-end branches in the in-house wiring, equipped with 2 devices on each, their operation can be configured using ball valves or conventional shut-off and control valves.
Purpose
A balancing valve in a heating system is used to ensure proper distribution of heat transfer. That is, there are times when in one room the batteries are hotter than required, and in another they are much colder than desired. That is, improper distribution of the coolant occurs. This means that adjustment is required to correct this situation.
A balancing valve is a type of shut-off valve through which hydraulic resistance is regulated. This is achieved by changing the cross-sectional diameter of the pipe in a certain area.
Recently, when designing heating (for both multi-apartment and private houses), a balancing valve is immediately added to the system. However, what should owners of ready-made heating systems do?
There are several “symptoms” that indicate the need to install shut-off valves of this type:
- Lack of comfortable temperature even at maximum load.
- Significant fluctuations in room temperature with a constantly equal load in the heating system.
- Difficulties in starting the system - inability to reach rated power.
All this indicates that it is necessary to install a balancing valve and carry out regulation. It will allow you to adjust the flow of coolant to one or another part of the system.
Benefits of use
Installing a balancing valve will help solve the above problems in heating operation.
In addition, the following advantages of using this equipment can be highlighted:
- Reduced costs - that is, owners of private houses note that after balancing the system, the amount of fuel consumed decreases.
- Increasing indoor comfort - you can achieve a more suitable temperature level for each individual room.
- No difficulties during startup - the use of balancing fittings will simplify the startup of the system as much as possible.
Installation
Including equipment in the system
Balancing valves for heating are most often used to adjust two-pipe heating systems.
Read about them in detail here - https://kvarremontnik.ru/dvukhtrubnaya-sistema-otopleniya/
The element is installed using special fittings and adapters. In this case, you should be careful: some taps can be installed on pipes with a certain direction of coolant movement.
On such taps there is a special arrow that shows in which direction the water should move in the pipe. If you install the valve without following this instruction, an attempt to regulate the system with its help may result in breakdown of the element itself and malfunction of the entire heating system.
Regulation
After installing the valve, using special equipment, measurements are taken to determine to what level adjustment is required. Some experts call this method quite labor-intensive.
Important: before carrying out the balancing procedure, you should start the heating system and connect the necessary measuring equipment - this will make it possible to determine the quality of work.
More accurate balancing results can be obtained by dividing the heating system into separate segments and adding balancing fittings to each of them. In this case, the balancing procedure itself will take considerable time - it will be necessary to adjust each individual valve. But the results will be much better.
Types of valves and their design features
All new heating systems using radiator thermostats are considered dynamic. During operation, the thermostat installed on the heating device responds to any slight changes in the temperature conditions inside the room, thus changing the flow of heating water.
This creates a changing or dynamic operating mode in the heating system. It is a prerequisite for the introduction of automatic/dynamic balancing devices.
Classification of balancing valves by parameters:
- Type of coolant working medium: water, steam-water mixture, glycol composition;
- standard coolant parameters for volume flow, T and pressure;
- location points on the heating network: supply, return or bypass;
- purpose and number of floors of the heating facility; residential/public, single-story/multi-story;
- working function: automatic/mechanical.
- Their combination according to connection options is also practiced: threaded or flanged.
A variety of materials can be used to release valves. Static valves are most often made of brass, with a flanged/threaded connection, or cast iron, exclusively with a flanged connection. For dynamic modifications, in addition to brass/cast iron, they also use carbon steel, which is capable of providing the highest quality standard thermal and hydraulic characteristics of the system.
Manual balancers are required in order to adapt the heating network after installation, and automatic balancers change the characteristics of the heating network during the heating period.
When choosing a balancer modification, it is necessary to take into account various parameters:
- Type of heating circuit with natural/forced circulation.
- Thermal and hydraulic parameters of the network.
- installation point in the in-house system.
- adjustment parameters.
Mechanical balancer
Mechanical balancer
The mechanical valve has manual adjustment and works perfectly in a stable heating network. Works well for residential properties with not a very large number of heating devices. It facilitates repair and adjustment work, since when repairing a separate heating section there is no need to turn off the entire system.
Such modifications are very often equipped with measuring nipples capable of measuring the pressure in the system in the area where the valve is located. The main advantage of such regulators is their low price.
Mechanical balancer - the device works effectively in those facilities where the number of radiators is no more than 5 units. With more, the mechanics cannot cope and causes an imbalance in the heat supply circuit. When the thermostat on the 1st battery is closed, the coolant flow on the second increases. Due to this, the temperature of the water in some heating devices may rise to the boiling point, while in others it will remain cold. Only automatic balancers can solve this problem.
Automatic balancer
Automatic balancer
Installation of automatic units is carried out on branches/risers with a significant number of batteries. They differ from mechanical devices in the order of their operation. The balancer is adjusted to the position of the greatest throughput. When the hot water flow rate decreases by the thermostat on one of the batteries, the pressure increases. Then the impulse tube mechanism is activated, which analyzes the magnitude of the pressure drop. This approach allows for fine-tuning of the network.
The main advantages of automatic equalizers:
- The presence of a capillary tube that facilitates instant adjustment;
- the control unit does not change the pressure during operation, thereby preventing hydraulic vibrations in the network from disrupting the set mode;
- if necessary, special temperature independent zones can be installed in the general network;
- the high speed of adjustment of the balancer does not allow thermostats to rearrange their operation, which guarantees balanced operation of the entire intra-house heating system.
Peculiarities
Modern heating systems are characterized by uneven heat distribution across individual rooms. The amount of heat depends on the coolant flow, and the water flow is controlled by the balancing valve. If you do not use this device, the amount of heat received will decrease, moving away from its source. Accordingly, there will be different temperatures at different points in the network.
Previously, in simpler systems, this problem was solved by installing pipes with certain diameters or installing special throttle washers. The latter are characterized by a certain passage size, which ensures the flow of the required volume of water.
The design is a specific valve with which the flow of coolant is regulated. Sometimes, as an addition to this mechanism, two fittings are built in, which measure the pressure in different zones in relation to the control mechanism. Additionally, it connects to a capillary tube to coordinate with other controls.
There are two types of these valves: manual and automatic.
The first type, as you might guess from the name, is controlled manually. The products are inexpensive and therefore are the most common. By changing the pressure difference and water flow, they are able to adjust both individual sections and the entire system. In addition, at control points it will be possible to monitor the indicators of the working environment, and in the event of a breakdown, turn off any fragment and arrange repair work. Unfortunately, the adjustment of such valves is carried out under the condition of a constant flow of coolant. If it changes, the system will not be able to function. Therefore, it is better to install such models in private homes and with a simplified heating system.
Automatic devices are attached to both the inlet and return pipelines. They are connected to each other by a thin tube, thanks to which the valve moves and shuts off the flow of water depending on pressure surges. Such a device is configured once and does not require further adjustment.
Valve models may differ depending on the coolant (steam, water or glycol solution), type of building (private house or ordinary high-rise building), installation location (on the supply or return pipeline), operating environment (at what pressure, temperature and volume of distilled water it operates device). Finally, valves can exhibit other properties, for example, regulate pressure and be equipped with additional devices, such as a measuring diaphragm.
What is the difference between a balancing valve and a regular tap?
Unlike conventional shut-off and control valves, a balancing valve, thanks to the combined action of a membrane and a spring, responds to pressure changes occurring in the installation. It maintains the pressure drop in the dead-end zones of the circuit in accordance with the set value. This regulation is ideal for heating devices that constantly operate at a balanced flow of heating fluid.
This level of control of hydrodynamic modes increases the efficiency of the heating network and reduces the cost of heating services and cannot be ensured by using only conventional ball valves.
The difference between the operation of a balancing valve and standard valves:
- Reduces the cost of operating pumping equipment for coolant circulation.
- Maintains temperature difference - delta T. Pressure independent valves providing the calculated coolant flow through the radiator for full or part load situations. Consequently, the calculated delta T value will be achieved, resulting in increased efficiency of the heat sources or heat exchangers.
- Balances the circulating flow, measures pressure drops in operating condition and blocks violations of the specified hydraulic mode through the radiator.
- Adjusting the flow of heating water depending on the purpose of the objects brings a significant economic effect due to low specific fuel consumption.
- Setting minimum gas flow rates and maintaining a constant temperature in all rooms, including during periods of temporary absence of residents.
Principle of operation
Let's give an example: the radiators in one room are much warmer than necessary, and in another room, one might even say, cold.
This is due precisely to the fact that the coolant is distributed incorrectly. In such cases, adjustments must be made to correct the system's malfunction.
A balancing valve is a subtype of shut-off valve that serves to adjust hydraulic resistance. This is only possible if the diameter of the pipe is slightly changed in the right place.
Today, when a heating plan is created, a balancing valve is installed immediately, without taking into account whether it is required or not. In any case, this will not affect the operation of the system in any way for the worse. But here one question arises: what should owners of houses where the heating is already ready?
Types and installation schemes of balancing valves
Placing balancing valves in the intra-house heating network helps to achieve fine adjustment of the temperature inside the rooms depending on their purpose - in residential rooms it is set higher, and in auxiliary rooms - lower. This motivator increases the comfort of both an apartment and an individual house.
Installation diagrams
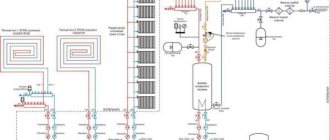
In order to understand the principle of operation and rules for the location of the balancing valve, you need to consider two standard heating schemes:
- From the boiler unit there are 4 heating circuits with different lengths and different numbers of batteries from 3 to 8.
Setting up a system with thermal heads - Also, the heating circuit is only equipped with thermostats.
Setting up a system without thermostatic valves
Since the coolant always passes along a path with minimal hydraulic resistance, in the 1st scheme, a significant part of the thermal energy will be acquired by the first batteries along the flow of water, and those located at the very end of the supply line will receive either a minimal amount of heat or not receive it at all. In practice, situations quite often occur when the temperature difference between these points is 10 degrees or more.
In order to provide heat to remote radiators, balancing valves are installed on the connections to the nearest heating devices from the boiler unit. By partially blocking the passage for the coolant, they reduce the water flow, thus increasing the hydraulic resistance of the above section. Using a similar method, the feed is adjusted in systems where there are five or more dead-end lines.
In the second option, the situation is much more complicated. Installing thermostats on batteries makes it possible to automatically change the volume of water. On remote lines of a heating network with a large number of heating devices equipped with thermostats, balancers are connected to automatic regulators that control the pressure drop.
With the support of a capillary tube, they are connected to the balancer, thereby responding to a decrease/increase in the flow of heating water in the system and, holding the specified medium pressure in the return line. Consequently, the heat will be evenly distributed throughout all rooms, despite the activation of thermostats.
Modifications and manufacturers
Today, the distribution network has a sufficient supply of modern balancing valves, both domestic and foreign. The latter have more functionality and significant cost. The development of the market for such equipment is caused by the EU requirement for the introduction of energy efficient technologies. By the way, it will be said, but in EU countries it is prohibited to put into operation heating systems that are not equipped with valves of this modification.
List and prices of popular models of balancing valves:
- CIM 790, DN15, manufacturer Italy Cimberio, protection against pressure and water hammer, 4500 rub.
- VIR Du15-50, device from Italy, manual type, brass manufacturing with preliminary adjustment and subsequent fixation, 6525 rub.
- USV-I Du 25, manufactured by Danfoss Denmark, with an operating temperature range from -20 to 120 C, RUB 2,768.
- Tadano TR100M-1, produced in Japan, from 15,000 to 100,000 rubles.
- DN 50-300 mm KBCh, produced in Moscow, made of cast iron with a working environment temperature of up to 120 C, from 3460 to 130140 rubles.
- Herz Shtremax-M Du20 (3/4″) Ru10, produced in Austria, brass, temperature up to 110 C, 2561 rub.
How to adjust the balancing valve in a heating system
Setting up a mechanical balancer
Before setting up the balance of the radiator network, you need to study the instructions for the valve, which are included when purchasing it. It indicates an adjustment scheme; if the user installs everything correctly, he can actually reduce the cost of thermal energy. The valve can be adjusted in two ways.
The first way to adjust the valve
This is the simplest and most proven adjustment option, which is recommended by experienced thermal regulators in water heating networks. To do this, you will need to divide the number of valve revolutions by the number of batteries installed in the heating circuit around the perimeter of the room. This technique makes it possible to correctly determine the step of the tuning algorithm. The method consists of closing all the valves in the reverse order - from the outermost to the first battery in relation to the heating source.
For example, for a dead-end circuit with 4 radiators equipped with mechanical balancing valves and a 4.5-turn spindle adjustment:
4.5:4 = 1.1 turns
Opening diagram:
- The first balancing valve is 1.1 turns.
- Second balancing valve – 2.2 turns.
- Third balancing valve – 3.3 turns.
- The fourth balancing valve is 4.5 turns.
The second way to configure the balancer
There is another, very high-quality method of balancing. It runs much faster, and contains the ability to take into account some of the specific location of the battery. The only thing you need to do this is a contact thermometer.
The complete process goes like this:
- Open all the valves and allow the network to enter temperature equilibrium with the operating temperature, for example, 80 C.
- Measure the temperature of all heating devices.
- Eliminate the difference by shutting off the first and middle taps. The end valves are not adjustable.
- Typically, the first valve turns no more than 1.5 revs, and the middle ones - 2.5 revs.
- Allow the system to reach temperature equilibrium for 20 minutes
- Temperatures are measured and valves are adjusted further if necessary.
Existing types and properties
"warm floor"
Balancing devices are divided into groups:
- statistical or manual;
- automatic.
The first group is inexpensive and capable of handling the required tasks. Taking into account the fact that it becomes possible to adjust the necessary areas and complete heating by adjusting the pressure. If necessary, you can eliminate the heat supply to some part of the system so that it can be repaired.
Please note: heating engineers with extensive experience recommend installing manual taps only in private homes or in the case of a single-pipe circuit. All other cases must have automatic devices.
The first setting is the most important, because proper setting will be the key to further stable operation
Then you will no longer need to pay attention to this balancing device