Abandoned well: this should not happen
In our country, the conservation and abandonment of wells is regulated by the Gosgortekhnadzor instruction number RD08-347-00. It sets out in detail the rights and obligations of subsoil users, the procedure for drawing up a project, and the conditions for performing work in certain situations.
Based on the provisions of this document, we will talk about how to properly dispose of a well that has exhausted its resource. In addition, we suggest you watch the video in this article.
Purpose of the event
To perform technological plugging, a special solution is used. With its help, the aquifer is isolated. All water wells are gradually losing their original condition. The tightness of their components is compromised, the pipes become corroded, and through holes appear. A leaky pipeline contributes to water pollution and horizon poisoning. The well becomes unusable. These are the main reasons to liquidate or mothball a structure.
The processes under consideration have several common points, but their goals are different. If it is possible to maintain the operational characteristics of water wells, temporary conservation of wells is carried out. In this case, all requirements defined by government services in the regulatory document are observed.
The instructions on the procedure for liquidation and conservation of wells describe the main stages of plugging and arrangement of a borehole. An example of an abandoned structure is the Saratov liquidated facility. The city of Saratov occupies a leading position in the opening of an artesian well. Until 2030, the government has developed several projects in this direction.
The requirements specified in the instructions must also be observed during the liquidation/conservation of an oil and gas field. In the process of drilling and exploitation of the aquifer, the artesian source is subjected to plugging. Since this object belongs to the country's strategic reserves, it is controlled by government agencies.
The project for the development, drilling and operation of the facility is considered by government agencies taking into account current legislation. All accompanying documents are agreed with the relevant authorities. Special equipment is used to preserve wells.
When are these procedures required?
The main goals of the process of abandonment and conservation of wells:
- protection of underground resources from pollution;
- disaster prevention;
- conservation of fauna and flora;
- protection of building structures from destruction.
The issue of mothballing a well may be considered if, during the drilling process, a dangerous gaseous substance has been discovered that requires isolation. To study the condition of the trunk and horizon, a specialist must review the act for opening the hydraulic structure and other documents that allow drilling a well.
If a leak in the facility is detected, the specialist draws up a closure report. A sample act is provided to the owner of the hydraulic structure. There is a list of certain objects that fall under conservation and liquidation:
- a project that has reached the minimum flow rates established in the technical passport;
- a project that has fulfilled its main purpose and is not subject to further operation;
- an object with a destroyed trunk;
- structures that are considered environmentally and technologically unsafe;
- a project that does not involve developing a well to great depth;
- an act on the liquidation of an object located in a restricted water protection zone is drawn up;
- changes in sanitary and environmental standards in this area.
If basic operating standards are not met, the well is closed. The liquidation process depends on the condition of the object and terrain conditions. In this case, there are works that are performed in each case:
- bore drilling;
- removal of a potential source of infection from the walls of the EC;
- disinfection of internal space;
- pumping out water;
- backfilling the filtration zone with gravel or other filter material;
- installation of a cement bridge.
The instructions on the procedure for liquidation and conservation of wells include:
- digging a pit for subsequent pouring of a concrete plug;
- installation of a sign with information about the date of closure of the facility and the employees who carried out the work.
Conservation stages
A hydraulic structure is subject to temporary conservation during construction or operation. The issue of conservation is being considered by experts for a variety of reasons, including:
- inability to drill further due to force majeure;
- lack of finances;
- the preserved object does not comply with the technical conditions and requirements provided for by the project;
- there is no need to operate the structure;
- time factor (winter period).
If the well is being preserved for the winter or for a longer period, then all devices are dismantled. The mothballed facility is put back into operation after it has been inspected by specialists. The owner of the hydraulic structure is provided with an act and subsequent documentation authorizing the use of the well.
There is a certain procedure for preserving wells:
- dismantling equipment that interferes with plugging;
- lowering the tubing to flush the object;
- checking the tightness of the EC;
- filling the barrel with a special compound to prevent pipeline corrosion;
- filling the upper part of the structure with a non-freezing composition.
The instructions on the procedure for liquidation and conservation of wells indicate the mandatory piping of the wellhead and installation of cement bridges. The process in question is considered the surest way to preserve a source of water supply during a long break in use. Self-conservation is not possible, since this project requires compliance with legal regulations. However, the procedure is considered technically complex.
Grouting of objects located in the sandy horizon is allowed. Such structures are not regulated by law, so a liquidation project is not prepared. To self-preserve and abandon wells, you will need to perform the following work:
- dismantling pumping equipment, pipelines and other equipment;
- installation above the mouth of a tripod with a winch;
- lifting and dismantling of casing pipe;
- filling the aquifer zone with gravel and sand;
- filling the remaining EC zone with clay mortar.
A pit is built in the upper part of the structure, and a clay castle is made.
List of works during liquidation
In short, the liquidation of an artesian well is carried out in this order. First, its geophysical condition is studied, water is pumped out and equipment is lifted to the surface.
Please note that any objects or fallen tools that accidentally fell into the well must also be removed. Let us dwell on this issue in more detail, since this information can be useful not only during abandonment, but also during the operation of the well.
Removing Objects from the Wellbore
Anything can get into the wellbore: any part, tool, cable, cable, pump or its motor. Here the question is not even to pull out the fallen object intact, but to somehow remove it at all, albeit in parts.
This is the main difficulty, since the trunk is very long. In addition, the object in it can simply get jammed.
Well inspection video camera
To inspect wells today, special probes equipped with a video camera, or the so-called acoustic borehole television (SAT), are used. A fishing tool is used to remove objects.
If the object is metal and small in size, an electromagnet is used to lift it. But it will not help in every situation. During the excavation process, for example, pipes sometimes break. When removing them, a tool such as a tap is simply irreplaceable - with its help, the pipe can be unscrewed and removed in parts.
Fishing magnet
The list of fishing tools is quite large: this includes a spider, a diverter hook, and a side chisel. A fishing bell, for example, is indispensable when removing a drilling tool that has a cylindrical shape. Its adhesion to the object occurs by screwing, after which it is lifted to the surface.
Oil fields
The industry often mothballs oil wells. This is necessary to protect the source in order to maintain the integrity of the EC during development or after drilling. The issue of conservation is resolved by a specialized government agency. An oil well is not produced at intervals ranging from several weeks to several months.
The process under consideration refers to the sealing of the wellhead during development or after operation of the facility. The manipulation is carried out taking into account the subsequent development and research of the object. The reverse process of exploitation of a mothballed oil well is impossible if it meets the following conditions:
- inability to achieve previously set goals and objectives;
- the project was drawn up for exploration work, but with subsequent planning for the development of an industrial facility;
- during the development process, specialists made mistakes related to the geological soil composition;
- The EC was built in violation of safety standards, which were identified after the work was carried out;
- emergency condition of the object.
To preserve the condition of the trunk, fixation of some elements is required. Preservation and re-preservation of oil wells is carried out using a special resin or cement mortar. An anti-corrosion compound is used to treat the mouth. The gas well conservation project does not involve the use of cement plugs. For such objects, clay of appropriate viscosity is used.
To resume work, completed bridges are dismantled and the shape of the well is restored. A plan for adjusting or altering the structure of the object is drawn up in advance. If a plan to mothball the structure for a longer period has been implemented, permission from the supervisory services is required to resume work.
Compliance
If the fields will be exploited in the near future, then conservation and abandonment of wells is carried out by filling the EC with clay solution. The upper part is filled with oil or diesel fuel (height up to 30 m). Extending the service life is an issue that government agencies decide.
If the facility will remain idle for a long period, a cement bridge is installed to reduce the pressure level. It is installed above the perforated area. The instructions on the procedure for abandonment and conservation of wells indicate that an oil well is filled with a solution, the density of which helps to increase the pressure inside the well.
The top layer of the column is an antifreeze substance. The height of this layer depends on the location of the object:
- in the south the thickness of the layer is 3 m;
- in the north - the permafrost limit.
If the hydrostatic pressure level is less than reservoir pressure, then the conservation project requires flushing work. If the well is closed with a large difference between the considered indicators, and the facility will not be operated for more than a year, then a bridge is installed inside. Its height should be 25 m. Moreover, it should be 30 m above the filtration holes. After removing the swab, you must close the valve.
The work is carried out within the time limits specified in the relevant documentation. To extend the conservation period of a shale oil production facility, coordination with the relevant structures is necessary. Conservation can be stopped if there is an order from the Economic Council. Additionally, the owner of the facility must obtain a corresponding conclusion from the local supervisory authority.
Documentation support
To carry out the work described above, certain regulations are required. If the developed object is not completed, the trunk is preserved before it is transferred to the owner. During development, conservation is carried out in the following cases:
- it is necessary to increase the pressure for subsequent development;
- drop in flow rate;
- the need to transfer the object to another horizon.
To mothball an oil well, a plan is first drawn up taking into account the standards. The result of all actions is recorded in the act. If it is necessary to extend the conservation period, an explanatory note is drawn up. It indicates the duration and reason for the extension.
The procedure for liquidation and conservation of an oil facility:
- flushing the barrel with drilling fluid and water;
- filling the barrel with an antifreeze compound;
- checking for tightness.
The tubing is lowered only by the blowout service. If there are several horizons in the well with different pressures, then they are separated. All hazardous chemicals are isolated. Facilities are inspected twice a year. Upon completion, the prescribed form and journal are filled out, in which the result is recorded.
If there is intercasing pressure at the wellhead, then the object is sent to the background of idle resources. In this case, restoration work is carried out, which is pre-coordinated with the Gostekhnadzor authorities.
What is well plugging?
Water intake equipment loses its quality over time, and the process of aging and wear occurs. This manifests itself in the destruction of equipment, components lose their tightness, and the process of corrosion of casing pipes occurs. There may even be through holes in the pipes. As a rule, this phenomenon is caused by the ingress of wastewater into groundwater. They can make the entire water layer unusable.
Some people believe that mothballing and abandoning a well are the same thing. There are even some common similarities between them, but they are carried out for different purposes. If it is no longer possible to restore a liquidated object, then conservation and re-mothballing of wells is carried out so that they can be used in the future. Thus, it is preserved for a while. A well can be closed only when it has completely lost its operational characteristics.
Self-plugging of a well by backfilling with crushed stone and pouring a liquid solution
There is even a documentary base that provides procedures and rules. In accordance with them, the process of conservation of water wells is carried out. This contains information on how plugging is carried out and how the trunks of a preserved structure are arranged.
Not only a well for water intake can be mothballed, but also objects that are used to study fossil deposits. Artesian springs, which are considered strategic water reserves of the state, must be sealed. That is why the procedure for drilling, equipment, use and conservation is regulated and controlled under the supervision of relevant government bodies.
To plug artesian wells, it is necessary to use special equipment and experienced workers who have the right to perform this type of work.
Why do you need to tamponate?
There are several main reasons why this procedure is carried out:
- to protect against the entry of various types of contaminants into underground water supplies;
- in this way, a humanitarian catastrophe that could be caused by poisoning water from the aquifer is prevented;
- to preserve in their original form the flora and fauna characteristic of a given area;
- wells are also plugged in order to prevent the destruction of constructed premises as a result of disturbances in the structure of the upper layers of the soil.
Scheme of cementing a source with one plug
Offshore wells
Objects that are in the drilling/testing stage are temporarily mothballed for the following reasons:
- the presence of moving ice fields;
- freezing of the water area;
- strong waves.
Mothballing of offshore wells may be carried out due to lack of finance. Completed facilities that cannot be used for a month are subject to conservation. The offshore well must be sealed and there must be no flow of formation fluids.
Conservation of offshore wells is carried out within the period established by the geological service. All actions are formalized by an act of the accepted form. Injection and operational facilities are preserved for 2 years.
If there is hydrogen sulfide in an offshore well, additional measures are provided for anti-corrosion protection of the EC. Cement bridges are installed under the supervision of representatives of the AVO. Conservation of offshore wells involves checking the technical condition of their mouths. Such events are held once a year according to a schedule drawn up by the production department of the association.
If, as a result of the inspection, specialists reveal a leak in the mouth, repair work is carried out. Temporary conservation is carried out if continuation of construction is impossible for more than 5 days. Each temporarily mothballed well is subject to recording. Previously, specialists develop a work plan, which is agreed upon with the relevant authorities. An act is also drawn up for the reactivation of the object.
Structures with exposed layers, but containing fluids, are subject to temporary conservation. In this case, the procedure for the required work and the timing are approved by the geological service in each case individually.
How to equip the trunks and mouth?
If the tests are completed, the barrel is filled with drilling fluid. This technology makes it possible to create 10% more hydrostatic pressure on the formation. Then the cement bridge is poured. Its thickness should be 25 m.
Then the object is washed and the parameters are brought to the set values. A bridge with a capacity of up to 50 m must be installed at the wellhead. The equipment is lifted to the surface, and a special sensor is installed at the wellhead. If all work is completed, the condition of the mouth is examined.
Temporary conservation of objects that do not contain gas and oil involves the following actions:
- filling the interval of the open section of the CSF;
- installation of a bridge with a thickness of more than 25 m;
- The drilling fluid is prepared taking into account the requirements of the hydraulic pump.
Equipped bridges are checked for leaks. When temporarily mothballing an object and leaving the water protection equipment in place after the bridge is installed, it is recommended to raise the drilling machine. Then the sensor is mounted. If the work is completed, the geological service issues a conservation certificate. It specifies a device that will allow you to determine the location of the object.
To re-open a facility, it is recommended to adhere to the plan approved by the government agency. Additionally, it is necessary to obtain permission from the organization that issued the certificate of conservation of the object.
The PDU is installed on the area where the work will be carried out. Then the bridge is drilled and the temperature in the EC is measured. The drilling rig is lowered into the well. Additionally, the pressure is checked.
Expert advice
If the well is located on the Arctic shelf, a project is drawn up, on the basis of which work is carried out to isolate it. All documentation is prepared by the Ministry of Water Resources and Fisheries Supervision. All installation work is controlled by representatives of AVO. All accidents that occur during the liquidation or isolation process are eliminated according to a special plan. If oil comes to the surface, urgent measures are taken to eliminate the contamination.
Offshore objects subject to liquidation are filled with drilling fluid. A cement bridge is installed above the roof at a height of more than 50 m. If the object is in a neglected state, a cement bridge is installed in the last EC.
An offshore oil and gas well requires complete or partial shut-off with a drilling machine. Installation of a cement bridge is allowed. If the object is eliminated due to deformation of the EC, then the bridge is installed in this area. Upon completion of the liquidation, the geological service draws up a certificate indicating the following information:
- location of bridges;
- water parameters;
- equipment and wellhead location;
- EC height;
- liquid composition.
Additionally, a seabed inspection report is issued to identify underwater navigation hazards.
How to tamponate yourself
It is unlikely that you will be able to perform the tampon procedure yourself, since the procedure is quite complicated. But the legislation does not regulate the process of plugging those wells that supply water from sandy layers. Therefore, you can do the work yourself.
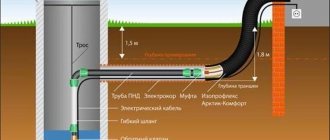
Do-it-yourself tamponing is also carried out according to the rules. First you need to lift the equipment and apparatus. We install a winch on a tripod on top, and with its help we dismantle the casing pipe. Then the aquifer zone must be filled with a mixture of sand and gravel. Then part of the trunk needs to be filled with a clay solution. We make a pit and a clay castle on top.
What documents does a legal entity need when extracting water without a license?
Cases in which legal entities can extract water without a license are stipulated in Article 19 of the Law “On Subsoil”.
Control over wells from which water is extracted without a license is difficult. However, in fact, a legal entity that owns such a well and extracts water from it is required to have at least a passport for the well and a draft sanitary protection zone. If water from a well is used for drinking water supply, the list of documents becomes virtually identical to that given above for the case of water production under a license (with the exception of the license itself).