Calculator for calculating pipe volume in liters
Pipe volume in liters can be calculated using an online calculator in two ways:
- indicating the outer diameter in mm, pipe length in meters and wall thickness in mm. It will be convenient for calculating the volume in liters for those pipes that have the wall thickness indicated in the markings applied to it, for example, polypropylene for soldering and/or for twisting with a fitting.
- indicating the internal diameter in mm and the length of the pipe in meters (linear meters).
When calculating the pipe volume in liters, you need to remember about possible errors, for example, turns, incomplete filling of some pipe sections, etc.
Protecting the inner surface of pipes
Since a variety of substances are transported through pipes - both easily flowing liquids and gases and viscous media with impurities - special requirements must be placed on the inner surface of the tubing. Ensuring the internal smoothness of products, coupled with the use of a protective layer, guarantees long-term uninterrupted operation of the pipeline and the entire enterprise as a whole.
During operation of the pipe under certain conditions, layers of compounds of heavy metals, calcium, paraffins, gypsum, and solidified gas compounds may form on the inside. Naturally, all these deposits impede the normal functioning of the system and, over time, cause the need for repairs.
One way to combat the problem is vitrification of the inner surface of the tubing. In this case, the products are treated from the inside with liquid glass, which significantly increases the throughput of the pipe. It is also possible to process the product with a special varnish, plastic or epoxy resin.
Such processing, together with the fulfillment of the remaining set of requirements for the installation and industrial use of tubing, makes it possible to reduce further costs for unscheduled repairs and replacement of pipeline parts.
How to calculate the volume of a pipe in liters?
To find out the inner diameter of the pipe, knowing the outer diameter, you need to multiply the wall thickness (b) by 2, subtract the result from the outer diameter (D).
You can also use tables, for example, pipes for soldering. In which the wall thickness and its diameters for PN10, PN20 and PN25 are already indicated.
To calculate the volume of a cylinder, use the formula: V = Pi * R² * h = Pi * ( d² / 4 ) * h, where:
- Pi - 3.1415926;
- R – radius of the cylinder;
- d is the diameter of the cylinder, in our case the internal diameter of the pipe;
- h is the height of the cylinder; in the case of calculating the volume of the pipe, replace h with L – the length of the pipe.
Based on this, the formula for calculating the volume of a pipe based on a known internal diameter will take the form:
Important! Before starting calculations using formulas, all dimensions must be converted into a single measure, i.e. - centimeters or decimeters.
An example of calculating pipe volume in liters
D (pipe outer diameter) = 17 mm, b (wall thickness) = 1.3 mm, L (pipe length) = 10 m.
The internal diameter is equal to, d = 17 - (1.3*2) = 14.4 mm
To calculate the pipe volume, convert the values to cm:
- L = 10 m = 1000 cm;
- d = 14.4 mm = 1.44 cm;
- V pipes internally dia. = 3.1415926 * (1.44²/4) * 1000 = 1628.55 cm³
- 1 cm³ = 0.001 liter
- 1 liter = 1000 cm³
Therefore, pipe volume: V in liters = 1628.55 * 0.001 = 1.62855 liters
Source
Calculate the volume of water in a pipe using an online calculator
Pipes are so widely used in the national economy that it is simply impossible to list all the areas of their use. And very often you need to determine the volume of a pipe, for which an online calculator is used. Using this tool, you can quickly and accurately calculate the volume of a single product or an entire pipeline of any length. We suggest you use our free online calculator to determine the volume of water in a pipe.
When calculating, you will find out the volume of water or any other liquid in one meter of pipe, you will also be able to calculate the volume in the entire pipeline and the surface area of the calculated section.
Tubing operation
Tubing is designed for long-term, trouble-free use in pipelines operating under different pressures, with different media and in almost any climate. Therefore, conscientious assembly of the structure, compliance with operating rules and timely implementation of scheduled work are a guarantee of safe and efficient operation of the entire mining complex.
Basic rules that should be followed during the installation and use of structures made from tubing pipes:
- in order not to stain the elements of the future pipeline, before starting work they should be placed on an elevated surface (for example, on a wooden platform);
- before connecting structural elements, it is necessary to clean the thread surfaces of the pipe and coupling using a suitable brush, without damaging the lubricant;
- Safety rings should be placed at the ends of the threads;
- to avoid damage to the surface of the pipes, they are transported using a pipe truck; products cannot be dragged along the ground;
- during and after assembly, the pipes should not sag, so supports, for example, made of wood, are used for installation work;
- When performing installation work, pipes are moved by a crane; they cannot be thrown down;
- during the assembly/disassembly process, a special installation tool is used; disproportionate force must not be applied or hit on the surface of the pipe or coupling;
- You should carefully select and check the cross-sections of the elements of the future pipeline before assembly: pipes that are too narrow will quickly become clogged when moving a viscous medium.
Enter the parameters for calculation into the online calculator
We suggest entering the parameters to calculate the volume in the online calculator.
Why is it necessary to calculate the volume of liquid in the pipe in advance using a calculator, and only then start purchasing? The answer is obvious - in order to determine how much coolant needs to be purchased to fill the heating system of the house. This is especially important for periodically visited houses that remain cold for a long time. The water inside such a heating system will inevitably freeze, bursting conductive elements and radiators. In addition, you need to take into account the points that are listed in the list below.
- Expansion tank capacity. This parameter is always indicated in the passport for this product, but if this option is not available, you can simply fill the container with a certain number of liters of water, and then use this information.
- Capacity of heating elements - heating radiators. Such data can also be obtained from the technical data sheet or instructions for one section. Then, using the design data, multiply the capacity of one section by their total number.
- The amount of liquid inside various components, as well as control and monitoring systems, for example, heat pumps, pressure gauges, and the like. However, this value will be small, no higher than the statistical error, so the data from the third point are usually ignored.
If the water supply or heating system is made of metal products, you need to take into account some of their features. Thus, the water and gas assortment according to GOST 3262-84 is produced in three series:
In this case, the difference lies precisely in the thickness of the walls, which, with the same external size, indicates a decrease in the internal cross-section for different designs. Therefore, when purchasing, you should pay attention to this indicator so that the internal passage is the same along the entire length of the water supply or heating system. The volume of liquid in a pipe can be calculated using a calculator using the following formula:
- V – volume of a meter of pipe, cm 3.
- 100 – length, cm.
- Pi equals 3.14.
- The radius of the internal channel, see here - the cross-sectional area of the internal cavity.
When making calculations, you should not be guided by the certificate data or the seller’s sign. It is advisable to carefully measure the size of the internal hole using a caliper, and when calculating, be guided by these data.
If the design of this measuring device does not allow internal measurements, you can measure the outer diameter and wall thickness. Then the first measurement must be subtracted by twice the second, after which a reliable size of the passage hole must be obtained.
In addition to belonging to the same series, as mentioned above, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of using the source material at minus tolerances, which will naturally affect the cross-section size in the direction of increasing it. If you have the opportunity to use the Internet when purchasing, you can use the built-in software calculator to calculate the volume of water in the pipe online. But at the same time, the initial data must be real. We strongly recommend that you read the instructions before using the calculator, in which case the calculations will be 100% correct.
How to calculate without a calculator
Pipeline transport plays a very important role in Russian conditions. Huge quantities of liquid products are pumped through it. In addition to water, liquefied gas, oil and its products and other liquids, in some cases aggressive, are transported.
The algorithm for calculating the capacity of a pipe is simple - you need to find out the cross-sectional area and multiply it by the length of the product. It is determined by the conditions of its transportation by rail; the base of the car is 11.7 meters, so they are produced with a length of 11.3-11.7 m.
The capacity of such a product is determined by the diameter of the internal space, for example, for a size of 820 x 10 millimeters, we can determine the working diameter by the ratio D = 820 – 10 x 2 = 800 mm. However, it is better to immediately move on to the generally accepted unit - the meter. With an internal diameter of the product of 0.8 meters, the calculation ratio is as follows:
Where:
- V – volume;
- P – pi equal to 3.14;
- r – radius;
- l is its length.
However, it makes no sense to calculate the volume of a single product. It is better to immediately apply this ratio to determine the volume of the entire pipeline.
This indicator is important in order to know the amount of pumped product that will remain in the pipeline upon completion of transportation of the required volume. However, pipelines are not used in one-time pumping mode. They are designed for continuous use.
Using the same method, the volumes of cylindrical containers – tanks, barrels and the like – are calculated.
In pipeline transport for highways, electric welded single or double seam pipes with different wall thicknesses are mostly used. To increase the productivity of the pipeline, products are pumped through it under high pressure - up to 130 atmospheres.
Therefore, sheet metal up to 36 millimeters thick is used for production. The main method of connection in pipelines is electric welding, therefore low-carbon steels, such as 09G2S, 09G2FB and others, are used as the manufacturing material.
The main regulatory document for the production of electrically welded directly seam pipes are GOSTs 10804 and 10805, however, many technical parameters are also used that provide for certain conditions for the manufacture of pipes that will be used in an aggressive environment.
An important area of application for pipes is ventilation systems for industrial and domestic use. To ensure strength indicators, they most often use rectangular boxes, the capacity of which is much easier to calculate.
Box-shaped pipelines for ventilation are made, as a rule, from galvanized steel, which has a long service life. But recently, there has been a tendency to use plastic materials for ventilation systems, the service life of which may exceed that of metal analogues.
The same applies to the use of plastics for pressure and gravity water supply systems.
An accurate determination of the volume of pipes and pipelines from them is available to all Internet users and this allows one to avoid serious mistakes when designing a wide variety of national economic facilities.
Tubing characteristics
As already mentioned, tubing is designed to work in particularly difficult conditions. Therefore, for the entire period of operation of the products, such incidents as the formation of delaminations and cracks or loss of pipe integrity must be excluded. In addition, the well itself must be designed as high quality as possible, which will also extend the uninterrupted service life of the industrial complex.
In accordance with all the features of the use of pipes, we can highlight the main requirements for them:
- lack of tendency to corrosion;
- wear resistance;
- tightness along the entire length of the product;
- smoothness of the inner surface.
Based on the presence of threads, manufactured products are divided into:
- products with smooth ends;
- pipes with external thread.
Pipes of the second type provide better sealing of the pipeline. An anti-corrosion sealing lubricant is applied to the external threads during the manufacturing process. The ends of the pipes are connected with specific wear-resistant couplings. Since, depending on the purpose of the pipeline, the pressure in the pipes can reach 50 MPa, high-reliability trapezoidal threads are applied to connect structural elements.
Pipe volume calculation
To calculate the volume of a pipe, you need to use your school knowledge of geometry. There are several ways: 1. By multiplying the cross-sectional area of the figure by its length in meters, the resulting result will be meters cubed. 2. It is possible to find out the size of the water supply in liters. To do this, the volume is multiplied by 1000 - this is the number of liters of water in 1 cubic meter. 3. The third option is to immediately count in liters. You will need to take measurements in decimeters - the length and area of the figure. This is a more complex and inconvenient method.
To calculate manually - without a calculator, you will need a caliper, a ruler and a calculator. To facilitate the process of determining the size of the pipe volume, you can use an online calculator.
Formula for calculating pipe volume
The process of calculating the volume of the heating system is as follows.
Let's determine the cross-sectional area of the pipe
To find out the exact value, you must first calculate the cross-sectional area. To do this, you should use the formula:
Where R is the radius of the pipe and Pi is 3.14. Since liquid containers are usually round in shape, R is squared.
Let's look at how you can make calculations with a product diameter of 90 mm:
- We determine the radius - 90 / 2 = 45 mm, in terms of 4.5 centimeters.
- We square 4.5, we get 2.025 cm2.
- We substitute the data into the formula - S = 2 x 20.25 = 40.5 cm2.
If the product is profiled, then you need to calculate it using the rectangle formula - S = a x b, where a and b are the size of the sides (length). When determining the cross-sectional size of a profile with side lengths of 40 and 50, you need 40 mm x 50 mm = 2000 mm2 or 20 cm2.
To calculate the cross-section, you need to know the internal diameter of the pipe, which is measured with a caliper, but this is not always possible. If only the outer diameter is known and we do not know the thickness of the walls, then more complex calculations will be required. The standard thickness is 1 or 2 mm; for large diameter products it can reach 5 mm.
Characteristics of tubing
Pipes for a pumping unit must be of high quality to cope with the functionality and high load. There is no damage, loss of integrity, delamination or cracks that could lead to their depressurization. There should be no ruptures or displacements inside the well itself in order to avoid major repairs of the well and equipment for as long as possible. These products can also be used to supply water from an autonomous well. Another application of the tubing pipe is the injection of air to clean the well using the blowing method.
Products of this class are subject to high quality requirements.
Since such parts often come into contact with an aggressive environment outside, there is high pressure inside, so they must be different:
- corrosion resistance;
- wear resistance;
- absolute tightness;
- excellent patency along the trunk (smooth).
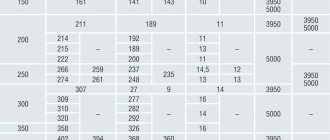
The standard is within 6-10.5 m, at the customer’s request they can be 1 meter longer, that is, 11.5 m. Industrial production of tubing pipes is established in accordance with GOST, where the dimensions are specified and described in tables.
Products of this sample are produced in 2 types:
- with smooth ends;
- with external thread.
Tubing pipes treated at the connections have the greatest protection against depressurization and corrosion. The threads are additionally equipped with a special lubricant to ensure absolute tightness of installation. Visually, they differ in that the ends have coated external threads to connect the ends of two pipes with a special coupling.
Guaranteed tightness of communications under standard load - coupling pipe connection. The usual pressure in the system is within 50 MPa, and a special trapezoidal thread is used.
Geometric parameters of pipes
To determine the volume of a pipe, it is necessary and sufficient to know only two of its indicators: length and internal (actual) diameter. It is important not to confuse the last parameter with the external size, which is given for the correct selection of fittings and connecting elements.
If the wall thickness is unknown, then DN (internal bore diameter) can be used instead of the calculated internal diameter. They are approximately equal, and the DN value is usually indicated on the marking, which is placed on the outside of the product.
Before trying to calculate the volume of any pipe, it is necessary to avoid a common mistake and bring all parameters to a single measurement system. The fact is that the length is usually expressed in meters, and the diameter in millimeters. The relationship of these two units is as follows: 1 m = 1000 mm.
In fact, it is possible to reduce the parameters to intermediate values - centimeters or decimeters. Sometimes this is even convenient, given that in this case the number of decimal places or, conversely, zeros will not be very large.
For pipes not produced in Russia (and not for Russia), the diameter can be expressed in inches. In this case, it is necessary to recalculate, taking into account that 1″ = 25.4 mm.
Types of pipes
Depending on the purpose of application, tubing-73 mm is made of different materials. As a result, price, quality, and service life may vary significantly. In addition, the type of compressor pipe affects the quality of installation and transportation.
Pipes NKT-73
Type of tubing pipes-73 mm (depending on the material):
- Aluminum pipes. Hydrogen sulfide contained in gas and oil has a negative effect on the metal. As a result of corrosion, the service life of equipment is reduced. In such cases, it would be optimal to use aluminum pipes. Due to its properties, this metal is less sensitive to hydrogen sulfide corrosion. In addition, the weight of the NKT-73 5.5 pipe per meter will be significantly less. Accordingly, transportation and installation will be facilitated.
- Tubing pipes with protective coating. In addition to corrosion, high or low temperatures also have a negative effect on metals. Due to the formation of scale, gypsum or salt deposits, the pipes become deformed. To avoid rapid wear, components are added to the 73 mm tubing that protect the metal from harmful effects.
- Fiberglass tubing pipes. This type of pipe is the most modern option. The advantage is that fiberglass is not affected by acids, salts or paraffin deposits. The weight of such a pipe is several times less than the standard weight of a 73 mm tubing pipe.
Aluminum pipes
Depending on the configuration, the following types of pipes are manufactured:
- corrosion-resistant pipes;
- cold-resistant;
- highly sealed;
- pipes with upset ends (with external thread);
- with seal unit;
- pipes with increased ductility.
Formula for a single pipe
From a geometry standpoint, the pipe is a straight circular cylinder.
The volume of such an object is equal to the cross-sectional area multiplied by the length:
The cross-sectional area of a pipe shaped like a circle with a known diameter is calculated using the formula:
S = π * d 2 / 4
The final formula for the volume of a pipe with a known internal diameter and length will be as follows:
V = π * l * d 2 / 4
If the unit of measurement for the length and diameter of the pipe is another value (dm, cm or mm), then the volume will be expressed in dm 3, cm 3 or mm 3, respectively.
Also, I wanted to show you a simple way to measure the outer diameter of a pipe (D) without a caliper. D = L / π , where L is the circumference:
To correctly calculate the volume of pipes, you need to substitute two parameters into a simple formula: length and internal diameter. The more accurately they are measured or calculated, the more accurate the result will be.
Release and marking of tubing pipes
Tubing is the main load-bearing element of pipelines in various industries. Due to their purpose and increased performance requirements, these products must meet the necessary safety standards and be labeled accordingly.
To ensure the strength of the product, it, together with connecting couplings, is made of durable steel grades D, E, K, L, M. Such grades of steel tubing pipes are more expensive than lower-quality analogues, but their use helps to provide the necessary for long pipelines operating in different climatic conditions .
The production of such pipes in Russia is carried out in accordance with GOST 633-80, which provides for the production of the following types of pump and compressor pipes:
- Standard tubing produced with couplings for connection.
- NKM is a brand of products for creating pipeline sections with increased tightness.
- NKT-V – pipes with threads placed outside.
- NKB is a type of pump and compressor pipes without couplings.
Production is allowed in accordance with specifications (technical conditions), with the following characteristics of tubing pipes:
- Particular resistance to low temperatures, allowing the use of products in the regions of the Far North (TU 14-3-1282-84 and TU 14-3-1588-88).
- Increased resistance to corrosive environments with a high content of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and acid fumes of various natures (TU 14-161-150-94 and TU 14-161-173-97).
- Improved ductility - such products are equipped with one or more plastic connecting elements (TU 14-3-1722-91).
As for the marking of products, which is an indispensable condition for the production of tubing, according to the rules, it, in the form of a mark, should be located near the end of the product, in place of the coupling.
It is typical for tubing pipes that such a mark contains information:
- About the date of manufacture of the product (year and month).
- About the wall thickness and diameter of the tubing pipe (both parameters are presented in millimeters).
- About the grade of steel from which the product is made (indicated by one of the letters indicated above).
- Trademark of the manufacturer.
Applied examples of calculations
Specific examples will provide significant assistance in understanding the principles of calculations and the sequence of actions when performing calculations, which interested visitors should familiarize themselves with.
Task #1 – calculating the volume of required coolant
For a country house of temporary residence, you need to calculate the volume of purchased propylene glycol - a coolant that does not solidify at temperatures down to -30°C. The heating system consists of a 60 liter jacketed stove, four aluminum radiators of 8 sections each and 90 meters of PN25 pipe (20 x 3.4).
The volume of liquid in the pipe must be calculated in liters. To do this, you need to take the decimeter as a unit of measurement. The formulas for converting from standard length values are as follows: 1 m = 10 dm and 1 mm = 0.01 dm.
Obtaining the result using the experimental method
In practice, problematic situations arise when the hydraulic system has a complex structure or some of its fragments are laid in a secret way. In this case, it becomes impossible to determine the geometry of its parts and calculate the total volume. Then the only way out is to conduct an experiment.
It is necessary to drain all the liquid, take some kind of measuring container (for example, a bucket) and fill the system to the desired level. Filling occurs through the highest point: an open-type expansion tank or an upper drain valve. At the same time, all other valves must be open to avoid the formation of air locks.
If the water movement along the circuit is carried out by a pump, then you need to let it run for an hour or two without heating the coolant. This will help expel any remaining air pockets. After this, you need to add liquid to the circuit again.
This method can also be used for individual parts of the heating circuit, for example, a heated floor. To do this, you need to disconnect it from the system and “spill” it in the same way.
conclusions
Despite the fact that the network offers us a huge selection of software products for calculating the coolant volume, there are GOST tables for determining the internal volume of pipes, you need to know the principles of “manual” calculations.
They are necessary for those who independently construct and repair communications, and for those who use the services of design and construction organizations. Useful information will help you determine the material consumption before installing the system, accurately calculate the estimate and get an idea of upcoming operating payments.
Would you like to talk about how you calculated the volume of coolant for an autonomous heating system in a country house or country house? Do you have information that might be useful to site visitors? Please write comments, post photos related to the topic of the article, and ask questions in the block below.
Source