In the event of a power outage, the circulation pump stops, and the flow of water through the pipes of the heating network of a private house stops. The problem can be solved in 3 ways: installing an uninterruptible power supply unit, starting an electric generator, or organizing gravity flow. This means a heating system with natural circulation - convection movement of the coolant without the help of a pump. We'll tell you how to develop and make such a circuit with your own hands.
Schematic diagram of a gravity heating system
The most convenient for consideration is a single-pipe system, using the example of which one can identify almost all the operating issues associated with a gravity heating system. For example, water will be used as a coolant, since in this case the principle of operation of the system is most understandable.
Of course, if constant heating is necessary, other liquids that are not afraid of freezing (antifreeze, etc.) can be poured into the system. The use of antifreeze allows you to avoid defrosting the entire heating system. In addition, after assembling the system, it is advisable to fill it with antifreeze, which will identify all leaky sections of the pipeline.
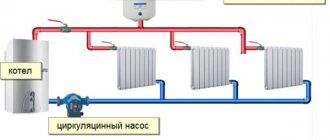
What gravity heating looks like - the diagram is quite simple: a gravity heating system operates on the principle of natural circulation of coolant due to the temperature difference at the inlet and outlet channels of the boiler (for more details: “How does a heating system with natural circulation work - what are the connection diagrams”).
and the system has been in use for a very long time, and its popularity is steadily declining due to its low efficiency, high cost and unjustified consumption of energy resources. Today, such a system can only be used in small houses that do not have electricity, which is quite rare.
Source: teplospec.com
Symptoms and diagnosis
If a characteristic hum appears in the pipes, it is possible:
- a large amount of sediment has accumulated on the pipe walls, which has led to a narrowing of the lumen;
- there is a water leak from the system;
- The system contains devices with too small a diameter.
To determine the cause of the noise more accurately, you should inspect all elements of the heating system and find the location of the leak.
If the pipes look undamaged, no steam or streams of flowing water are visible, you need to pay attention to the connecting elements and shut-off valves, perhaps the leak is occurring here
Sometimes it is difficult to determine the location of the leak, since it is hidden by a layer of insulation. To accurately diagnose the problem, you should call a professional plumber.
If there are no leaks, but the pipes are humming, you need to find the source of the sound. Most likely, this is where the pipe clearance has become too small due to accumulated mineral deposits or debris that has entered the system. Eliminate the problem by flushing the heating system. This is described in detail in the video:
Usually, a good plumber can identify parts of the system that are not properly sized, causing the pipes to hum. This item may need to be replaced or modified. Of course, such work should be carried out as best as possible, in full accordance with technology, so that new reasons for unpleasant noise in pipes do not appear.
Clicking sounds and the characteristic sound of bubbling water can be caused by air trapped in the system. To fix the problem, it is enough to bleed excess air from the radiators, for example, using a Mayevsky tap. Clicking sounds may also indicate the presence of foreign objects or debris in the pipes. In this case, you should clean the system.
If air gets into the heating system, it can cause clicking and bubbling sounds. To bleed air from the system, use the Mayevsky valve
Intermittent crackling, knocking and clicking noises may appear if:
- there are small foreign particles in the pipes;
- system parts are worn out;
- the ventilation valve has broken;
- unstable operation of the system caused expansion of the metal.
To stop the crackling in heating pipes, sometimes it is enough to drain some of the water and debris. In other cases, you will need the help of a professional plumber to repair or replace damaged elements.
Sometimes the cause of noise in the heating system is a heating pipe overgrown with deposits and particles of rust. This pipe should be flushed or replaced.
The breakage of the ventilation valve is often caused by its incorrect installation, for example, when the valve is installed in the wrong direction. Such an error can lead to significant damage to the entire heating system.
The reason for the tapping may also be the condition of the brackets on which the pipes and heating radiators are mounted. A loose bracket moves under the influence of metal expansion and contraction processes, which causes knocking. To stop this unpleasant phenomenon, it is enough to strengthen the old brackets or replace them with new ones. Sometimes special gaskets are installed between the pipe and the bracket.
Operating principle and features of gravity systems
As the name implies, in our case the coolant moves through the pipelines independently, without any external influence, using a pump. A similar circulation method was originally used in all water heating systems. Nowadays, when circulation pumps have appeared, owners of private houses are interested in gravity flow schemes with one goal: to be independent from external sources of electricity.
The independent movement of the coolant is based on the phenomenon of convection. The same medium (in this case, water), which has different temperatures, also differs in specific gravity. In simple words, a cube of cold water weighs more than 1 m3 of hot water due to different densities. Inside the enclosed space of the pipes, this will lead to the fact that the cooling medium will constantly push lighter hot water upward. A typical diagram of such a system is shown in the figure:
Due to the difference in the densities and masses of water, a slight excess pressure arises inside the gravity heating system, overcoming gravity and friction, resulting in natural circulation of the coolant. Hence the second name – gravitational.
Since the amount of excess pressure that occurs is small, favorable conditions must be created for the natural circulation of water in the heating system. The following activities contribute to this:
- the use of pipes of increased diameters designed for slow water flow (0.1-0.3 m/s);
- compliance with the slopes of horizontal highways. The slope is at least 3 mm per 1 m of pipeline;
- significant difference in coolant temperatures in the supply and return lines (at least 25 °C);
- installation at the highest point of the network of an open type expansion tank communicating with the atmosphere;
- installing the boiler in such a way that its return pipe is as low as possible below the level of the heating devices on the first floor.
For reference. In practice, when installing gravity systems with your own hands, main pipelines are laid from pipes with a diameter of at least 50 mm (2 inches), and connections to radiators - 20 mm (3/4 inches).
Homeowners often wonder: is it possible to make a natural circulation system closed by installing a membrane-type expansion tank? The answer is obvious: when expanding, the liquid will have to overcome the resistance of the tank membrane, and the excess pressure in the network is already low. The speed of the coolant will decrease to a minimum, or even to zero. Therefore, schemes using the gravitational principle of operation are always made open.
An important advantage that a gravity heating system provides is independence from electricity, which is very important in areas with unreliable power supply. But you have to pay for this with more expensive installation and large pipes running through all the rooms. The scheme cannot be implemented in private houses of large area and number of floors due to low efficiency and economic infeasibility. Such cottages use a closed-type system with a pump and uninterruptible power supply.
Natural circulation
Approximate diagram of the system
The main issue of the natural circulation system is the issue that determines the force of movement of the coolant to the heating devices and back to the boiler. The force of movement of the heated coolant appears due to the fact that the coolant is heated in a heat generator, whereas in heating devices this coolant cools down and is squeezed out by the heated coolant. In other words, the coolant, which has been heated in a heat generator to a certain temperature, has less mass than the coolant in a cold state.
So, water heated to the required temperature rises in a certain direction in the main riser and is distributed by piping to all heating devices, that is, radiators. After some time, the coolant in the radiators cools down, giving off its heat to the metal, which makes it heavier. Through specially installed return pipes, the cooled coolant is transported back to the heating boiler, where its mass displaces hot water from the heat generator.
This cycle of coolant movement in the heating system will be repeated until the heating boiler is operating, as a result of which the coolant will circulate through the pipe line. Heating systems with natural circulation have different pressure forces, which leads to different rates of circulation and heating of heating devices. The force of movement of the coolant in the heating system depends on the different densities and weights of the cold and hot coolant.
From this we can conclude that the pressure in the heating system and the force of water movement depend on the overall difference between the hot and cold coolant. In other words, the greater this difference, the greater the force of movement of the coolant in the heating system, in which the coolant circulates naturally. Among other things, the pressure in the heating system and the force of movement of the heated coolant depend on the height at which the heating device is located relative to the thermal energy generator.
As a rule, the coolant in a simple water-type heating system heats up to 95 degrees, while the cooled coolant has a temperature of no higher than 70 degrees. From such indicators it is possible to determine the total pressure in the heating system and the force of movement of the coolant to the upper and lower heating devices. In order to visually imagine the distribution between the upper and lower radiators in the heating system, it is necessary to draw some kind of diagram.
In the center we denote the heating boiler, from which there is wiring to the upper and lower radiators, which closes opposite the boiler itself. By drawing a line between the upper and lower heating devices (radiators), we get a temperature difference from 95 to 70 degrees. Next, we will consider the heating process.
System diagram
The heating boiler heats the coolant, in our case water, which, due to the resulting pressure, begins to move from one heating device to another. When the coolant crosses the line we have drawn and goes to the heating devices on the lower floor, its temperature will be significantly lower, and the coolant with a temperature of only 70 degrees will come out of the last radiator. When moving coolant from radiator to radiator, do not forget that part of the temperature is transferred to the pipes themselves, as a result of which the temperature of the coolant is constantly decreasing.
From this we can safely conclude that heating devices that are located above the system separation line will heat up more than those located on the lower floor.
All this leads to the fact that the use of this heating system for two-story houses is irrelevant, because the first floor will be constantly colder than the second. In addition, when using a two-pipe heating circuit, when the radiators are located below the boiler itself or at the same level with it, it is almost impossible to achieve proper coolant circulation without the use of auxiliary mechanisms.
For these obvious reasons, the location of the heating boiler should be such that the heating devices are located at a level above the boiler itself. To do this, heating boilers are placed in a small recess, and the heating system is raised slightly at a certain angle in order to achieve the proper pressure and proper natural circulation of the coolant. Standard single-pipe heating schemes do not have such obvious shortcomings.
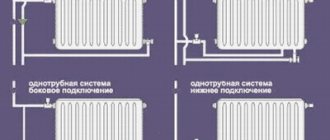
Scheme of a single-pipe heating system
In such schemes, the distribution of hot coolant to radiators and the selection of cooled coolant are carried out through the same pipe. If the wiring is horizontal, then the main line is a closed loop running from the boiler supply pipe to the return pipe. The batteries are connected to it with both connections. An example is the popular single-pipe heating system Leningradka, which can work with natural coolant circulation. Its diagram for a one-story house is shown below:
An indispensable condition for the normal supply of water to the radiators here is the presence of an accelerating manifold loop. An open expansion tank is connected to its top point. The heated water from the boiler rises through the collector, after which, according to the principle of communicating vessels, it flows into all the batteries. If their number does not exceed 5, then the heating will work without problems, this has been tested in practice.
The fact is that each subsequent heating device receives a mixture of hot and cooled coolant from the previous battery. Therefore, its heat transfer decreases if the number of sections is not increased. When the number of radiators exceeds 5, the last of them will be too cold, no matter how many sections you add. If necessary, you need to install a two-pipe gravity system, which will be discussed below.
For a two-story private house with an area of up to 200 m2, a single-pipe heating system with vertical risers and natural circulation is well suited. It makes no sense to install a horizontal Leningrad pipe connected to a vertical collector on each floor, and it will not work well. It is more correct to run the supply line through the attic or under the ceilings of the second floor and lower the risers from it, as shown in the diagram:
The load on the risers is small - there are only 2 heating devices each, so their temperature will be almost the same. To prevent the batteries from depending on each other, you can install jumpers - bypasses - between the supply and return.
Advice. To balance or cut off in gravity systems, it is necessary to use fittings with the least resistance - full bore valves and special thermostatic valves.
Installation of polypropylene pipes
Important! Due to the fact that the strength of polypropylene pipes is not as great as, for example, steel pipes, fastenings during installation should be installed more often, somewhere around every fifty centimeters. So, let's look at the main components of such a heating system
So, let's look at the main components of such a heating system.
- Fasteners necessary to ensure that the entire structure remains motionless.
- AGV, or maybe any other heating boiler.
- An expansion tank is necessary to ensure that water, which expands at high temperatures, cannot damage the entire system.
- Radiators and other heat-releasing elements.
- And, in fact, a pipeline that allows the coolant to circulate between the radiators and the heating device.
Pipeline fastening
For such soldering, special soldering irons are used. They heat the material to two hundred and sixty degrees, after which it becomes a homogeneous monolithic compound. This is explained by the fact that the atoms in it seem to penetrate from one piece of pipe to another. Moreover, such a connection is characterized by strength and tightness.
Video lesson on soldering pipes
Soldering consists of several stages, let's look at them:
- The soldering iron turns on. We wait until the signal indicator on it goes out for the second time.
We cut a piece of pipe according to the dimensions we need; for this we use specialized scissors, which are sold along with a soldering iron.
- We clean the cut ends of the pipes from all excess, in particular, from foil. To do this, you can use a regular knife, or you can use a channel.
- The pipe is inserted into the fitting and held there for some time.
Important! The time that the pipe should spend in the fitting depends entirely on its diameter; a special table should be included with the soldering iron, which indicates all these values. The parts fit neatly together, there should be no distortions.
We hold them like this for some time, while turning the channel is prohibited.
The parts fit neatly together, there should be no distortions. We hold them like this for some time, while turning the channel is prohibited.
Particular attention should be paid to rotary fittings, especially for polypropylene pipes. Be sure to check whether they are positioned correctly, because if the turn is directed in the wrong direction, the entire assembly will have to be completely redone, and the attached part will become completely unusable
The pipes are connected to each other using “Americans” - special devices that can be quickly put on and taken off. They are attached to the ends of the pipes. To prevent deformation from thermal expansion (after all, pipe reinforcement does not completely prevent this, it only reduces it), all pipes should be securely attached to the surface of the walls and ceiling, the spacing, as already mentioned, should be no more than fifty centimeters.
Special devices are also used to attach radiators; they must be included in the kit. It is not advisable to use homemade devices for radiators. The fact is that the factory fasteners were specially designed for the weight of radiators completely filled with coolant, so homemade fasteners may simply not withstand it.
Diagram of a two-pipe system
Here, heat is transferred to the radiators through one pipe, and cooled water is returned through another. This allows more batteries connected to one horizontal branch to operate efficiently. In a one-story house, the supply manifold is placed in the attic or under the ceiling, and the return manifold is above the floor. Acceleration is not required here, the pipe is already raised to a sufficient height, as shown in the image:
As can be seen from the diagram, the optimal solution for good natural circulation is a two-pipe heating system, divided into 2 branches with the same number of radiators on each. Otherwise, due to long slopes, installation of pipelines will be difficult. As for a two-story house, vertical wiring is again appropriate here, but with a division into supply and return lines. How to do this correctly is shown in the diagram:
With a two-pipe system, all batteries receive coolant at the same temperature, this is an important plus. It also becomes easier to carry out automatic control, since the devices do not depend on each other. The disadvantage is the greater consumption of materials for horizontal wiring options, for example, in a two-story building:
For reference. Most homeowners still install a circulation pump on the return manifold to improve the operation of the system. But they put it on the bypass, so that in the event of a power outage, you can always switch to gravity by opening the appropriate tap.
Is it possible to install polypropylene pipes for central heating?
And first of all, we will answer the most important question, is it possible or not. It would seem that the answer is obvious, because polypropylene today is widely used both in the repair of old heating systems and in the installation of heating in new buildings. But in fact, installing polypropylene pipes in central heating systems is a serious miscalculation, which over time can result in big troubles for you. Moreover, even many specialists take such risks, simply for the sake of savings and ease of installation.
What's the matter? Note that the current SNiP allows the installation of polypropylene pipes suitable for such systems on central heating. However, if you think about it, this norm is far from Russian reality. What is the maximum heat resistance of polypropylene? Ninety-five degrees Celsius, beyond that the pipes begin to bend and sag. And the maximum working pressure is twenty-five atmospheres. What happens in centralized heating systems? Yes, it seems that the standard parameters of these pipes are suitable for central heating. After all, the temperature in the networks is limited by current standards, and cannot be higher than the specified ninety-five degrees. And the pressure in the system is usually in the range from four to seven atmospheres.
However, there are several “Buts”. Firstly, for some reason we always forget about force majeure, which is common in our country, that is, unforeseen situations when the standard parameters of the system can be exceeded, and significantly. Let's look at a few possible problems:
- Even in central Russia, severe frosts are not uncommon in winter. The walls of our houses do not always retain heat well enough. And even more so in a high-rise building you need to heat it harder to warm up the top floors. But in severe frosts, sometimes 95 degrees is not enough. And therefore, in order not to listen to residents’ complaints, heating workers sometimes take extreme measures. The nozzle in the elevator unit of the house is dismantled, and the elevator suction is muffled. What does this give? You can simply supply hot water to the system directly from the heating network, and not a mixture of supply and return, as required by regulations. However, at the peak of cold weather, the temperature of such a coolant can reach even one hundred and fifty degrees. What will happen then to your polypropylene pipes?
- Let's not forget about the annual testing of the heating heating main. The pressure in the system is artificially increased to test its strength and to identify the most worn areas of the pipes. All this, of course, is good, but will your reinforced polypropylene withstand such a test? In addition, it is possible that the utility workers are experienced, the shut-off valves are faulty, and the pressure in the system can rise significantly. Although the heating must be turned off during the test;
- Another possible problem is water hammer. As you know, water is almost not compressed, and therefore, when the circuit is quickly filled and circulation is instantly stopped for a few moments, the pressure in the system can reach 25-30 atmospheres, which exceeds the permissible standards even for polypropylene with a reinforcing insert. And the consequences for such pipes are quite predictable.
And one more subtlety. The maximum pressure indicated on such pipes is 25 kgf/cm2. However, this is the maximum permissible pressure at room temperature of plus twenty degrees. But at elevated temperatures, the strength of polypropylene decreases significantly. So, at 90-95 degrees it is only 5-9 kgf/cm2.
Conclusion: is it possible or not to use such pipes in a system to heat your home? The use of polypropylene, of course, is permissible, but only in systems with autonomous heating, that is, when the system has its own heat source and the parameters of the coolant are controlled and known. As you know, the good thing about individual heating is that the pressure and temperature here are completely controlled and constant. Therefore, the possibility of force majeure is reduced to a minimum.
In addition, you can use polypropylene pipes when connecting stoves with heat exchangers or home fireplaces. But the transition to polypropylene here is done outside the heating area, that is, at least 0.5 meters from the outer boundary of the stove or fireplace.
Manufacturing Features
Self-circulation of water has a significant drawback - the lack of pressure in the system. Any deviation from the standards (small slope, violation of the bend radius of the pipe or an excessive number of turns) leads to malfunction. During installation, the following points are taken into account:
- the need to ensure a minimum level of slope;
- material and diameter of the pipes used.
Such standards are specified in the documentation. According to the norm, for every meter of distance a reduction of 10 mm must be observed.
If you do not adhere to this rule, the water circulation will be disrupted. The nearest radiators will warm up, but the heat will not reach the others. In some cases, boiling of the liquid may occur due to lack of water movement.
When installing the system yourself, the material from which the pipes are made is taken into account. It happens as follows:
- 1. Steel. The material is resistant to high pressure and inexpensive. Installation is difficult. Requires the use of a welding machine.
- 2. Metal-plastic. Thanks to the smooth inner surface, dirt does not linger on it. Light weight makes installation easy. However, the service life is only 15 years.
- 3. Polypropylene. The gravity heating system made of polypropylene is characterized by high strength and tightness. Installation is carried out using a soldering iron. The service life is 25 years.
- 4. Copper. The best material to use. Possessing good heat dissipation, it can withstand temperatures up to 500 °C. Operated for 100 years.
Before installation, the required diameter of the pipes used is calculated. First, the amount of thermal energy required to heat the room is calculated. Then 20% is added to the resulting value. Pipe diameters are selected taking this value into account. Some features are taken into account:
- over-diameter leads to unnecessary energy use;
- steel pipes with a diameter less than 50 mm are not installed;
- After each branching, the pipes are narrowed by 1 size.
Source: oventilyacii.ru
I still didn’t understand your numbers, your 0.00000 = 0, in my opinion this is not a slope at all, but a straight horizontal pipe, or not? I have 0.3 and 0.5 degrees. In centimeters it turns out (I specially measured the supply pipe to the garage) for a height difference of 6 meters 6 centimeters. Question: is this enough or should I add more? If added, by how much?
I suggested that you download the distribution kit version 18 from my “Yandex disk” from the same place where the pictures of my SO are now located. After all, downloading (1.35GB) from a source is problematic, I left the computer overnight, and I was able to download from “turbobit” only the second or even the third time. And I suggest you install the same 18 version as mine. True, it is not suitable for (large) commerce, since if it is cracked, it can be tied up. After all, the new one is better than the old one, it seems to work a little faster than the 17th. But if you have a 17th license, then of course, my proposal will not suit you. Having installed the 18th version, I can send you a file at home (137 MB) and you will see everything naturally. After all, everything is made to size there; you can measure anything.
There is a small problem with manufacturers, as I understand, you are in Ukraine, and I am in Russia, and in our stores different manufacturers can sell their products, without duplicating them. Can you make a calculation based on average parameters? Or indicate your preference, and I will try to purchase pipes and fittings from this manufacturer. I indicated about the boiler in the first message of the topic, so as not to search, I will repeat, Gas boiler Proterm 30 TLO power 27 kW.
@Lyko, You are not being imitated as always, thank you again for the history of heating, I really liked it, thanks to you I now know how the heating system of my homeland (five-story building) works. Or maybe she worked, I can’t say for sure, because I haven’t been in the basement since the days of stealing pieces of carbide from plumbers, being, as it now turned out, in a happy childhood.
Why such a garden? I will answer. This “spider” with “crooked legs” was invented by me with the goal of no electricity in CO.
Pumps don’t work without electricity consumption, but why the extra consumption?
It’s better to work hard once, conscientiously, so that later you don’t have to pay off monthly (being retired) extra rubles for kilowatt-hours wasted by the pumps, and saddened by the realization that the money earned by back-breaking labor is being spent for other purposes. And I’ll also add about saving. I’m still confused about the eternal flame (pilot) in a gas boiler after reading a “customer scare” on some website that it eats up 1 cubic meter of gas per day. And it turns out it’s true that he eats it. Well, I, as an old “hardened” designer of cable television networks, and a former antenna operator who graduated from the 11th grade of a school for working youth. I picked up the Internet with Excel and calculated “rubles per month”, according to future tariffs from 07.2015. It turned out as I expected (gas is cheaper than electricity, no matter how you look at it). So from all this “my flood” there is only one conclusion: Savings
, and as a result, respect for the environment. Take care of your Mother nature, as Kasimova’s avatar2 says. But I didn’t save my mother, to my great regret, now it’s too late to repent, and she wanted to live in her own house for a little while...Key phrase. I didn't design the bypasses. The valves on them “supposedly bypasses” are always closed when the radiator is not shut off (working) in the normal position. And I didn’t move it closer to the radiator for the same reason, why heat up an extra long pipe if I intentionally turned it off (for example: “I want it to be a little cooler here”).
The pipes and valves in the risers are the same 32nd everywhere, with the exception of two risers on which one battery hangs, there is a 25th pipe and the corresponding ball valves, of course. I think I wrote this in the first post. I can highlight these (25th) risers in the diagram, for example, in green, to make it clearer.
@Lyko, When designing this “sophisticated miracle” I assumed that it was a spider, but the spider has a classic design, all the pipes come from the expansion tank. But, when drawing the diagram, difficulties arose: 1. Difficulty with placing an “inverted ship mine”, i.e. a tank with a bunch of outlets, in the attic next to the boiler chimney. 2. The difficulty of making such a tank from stainless steel. Therefore, I attached all the outgoing pipes to the accelerating pipe, and attached the thinnest two 25 risers from the very top. Why? I don’t know, it seemed more convenient this way. I will also need to connect one pipe there to the indirect heating boiler, which will lie here in the attic side by side, about a meter or two from the accelerating pipe. In connection with this question. If I connect this pipe to the boiler at the very top of the accelerating pipe (almost under the very bottom of the expansion tank), will it be normal?
Source: www.forumhouse.ru
Step by step guide
Work on installing polypropylene heating begins with bringing the pipes inside the room to “acclimatize” them and eliminate the consequences of expansion or contraction in the heat or severe frost.
The main work when connecting pipes is welding polypropylene (solder). For these purposes, you should choose a soldering iron. The process itself does not take much time and is simple. The main thing is to quickly connect the heated ends of the elements, being careful not to overheat them. The duration of heating depends on the diameter of the pipe. The larger it is, the longer the heating should be. The cross-section of the soldering device nozzle must correspond to the diameter of the pipe.
Pipe soldering technology
Step-by-step instructions for assembling the heating pipeline are as follows
:
- a wiring diagram is drawn up;
- Markings are made on the walls for all areas, following which the elements of the heating system will be laid;
- fittings are selected;
- the time allocated for installation and welding work is determined;
- pipes are marked and cut into sections of a certain length, the cut is made at right angles to the axis;
- to degrease and remove dust microparticles, the ends are wiped with alcohol, the dust is removed with a dry, clean cloth;
- the soldering iron nozzle is degreased, placed in the working position and heated to +265 °C;
- a fitting and a pipe are placed in the nozzle, they are heated together and connected to each other;
- After waiting the necessary time for cooling, the connected section is attached to the wall using clips.
Do-it-yourself polypropylene heating also requires the installation of control equipment, a boiler, heating devices, an expansion tank, and a pump. Their installation is carried out according to the instructions and recommendations of the manufacturer.
Operation of the gravity system
The heating scheme for a private house with natural circulation has a number of advantages:
- there is no need to purchase expensive equipment;
- energy independence (the appropriate boiler unit is selected);
- installation is easy to do with your own hands;
- low maintenance requirements.
Circulation in such a system is ensured due to the fact that the density of the liquid decreases as a result of heating (it becomes lighter), and during cooling the density returns to its original one.
In a gravity-flow design there is practically no pressure - calculations show that per 10 meters of water column pressure the pressure is 1 atmosphere. Thus, the hydrostatic pressure in the heating system of a one-story building will be 0.5-0.7 atm, and in the pipeline of a two-story building it will not exceed 1 atm.
Gravitational circulation occurs due to the expansion and decrease in the density of the heated coolant - it rises along the vertical acceleration section and from the top point moves down through a pipeline mounted with a slope and passing through series-connected heating devices on its way back to the boiler.
An expansion tank is connected to the pipeline with gravity movement of water - a reservoir for “excess” coolant, which is formed due to the thermal expansion of the liquid. A buffer tank (membrane or open) is mounted at the top point of the circuit on the supply pipe.
The gravity heating system can function in combination with:
- With indirect heating water heater. If the boiler is installed in the upper part of the system below the expansion tank, water for domestic hot water will be heated without the use of electrical equipment. If such installation is not possible, the boiler is equipped with a pump and a check valve is installed, which will prevent recirculation of the coolant.
- With heated floor. A circulation pump is installed on the circuit laid in the floor. If there is a temporary power outage, the room will continue to be heated by the wall-mounted radiator.
Features of heating with heated air for industrial and production facilities
The organization of air heating combined with ventilation in private residential buildings differs from the implementation of air heating systems for industrial real estate - warehouses, workshops, hangars, repair shops, etc. These differences are associated with the scale of industrial facilities, the large volume of heated spaces, and increased requirements for functionality and reliability.
Let us list these nuances that our specialists usually encounter at industrial facilities:
- High power of heating equipment, large overall dimensions of air ducts, as a rule, complex geometry of their laying schemes
- More complex design solutions in heating systems
- As a consequence, there is a need for a special operational service of the enterprise responsible for the uninterrupted operation of the heating system
- No high demands on aesthetics. As a result, air ducts and equipment, as a rule, are not covered with suspended ceilings and plasterboard partitions
- More complex installation, including at high altitudes
Types of gravity systems
When planning to install the heating of a private house with natural circulation with your own hands, the schemes are selected in accordance with the planned performance of the system and the characteristics of the building.
Heating circuits with gravity flow of coolant are divided into types according to different parameters:
- according to the characteristics of the expansion tank (open and closed);
- according to the principle of connecting heating radiators (one-pipe and two-pipe).
To determine the best option, it is necessary to make hydraulic calculations taking into account the location and diameter of the pipes, take into account the characteristics of the boiler unit and the thermal needs of the premises. It is better to entrust the calculation to professionals, since even small inaccuracies will negatively affect the efficiency of heating the house.
Pipeline design methods
Heating of a private house with natural circulation can be installed according to two fundamentally different schemes.
They differ in the following features:
- by connecting water heating radiators to main pipes supplying water - there is a single-pipe and two-pipe scheme (the price of the latter option is higher due to the increased consumption of materials, however, it is also more efficient);
- the location of the main water pipelines - they can be located at the top (above the radiators) or at the bottom (along the floor);
- water pipe arrangement scheme - dead-end (water is supplied to each radiator separately and removed from it in the same way) or passing, when the coolant, flowing from the top to the bottom point, passes through all the heating radiators;
- the location of the risers - they can be fixed horizontally and vertically.
When choosing a heating installation circuit diagram, it is necessary to take into account many different factors
Method 1. Single-pipe gravity heating system
Natural heating, made according to a single pipe scheme, can only have upper distribution of main channels. In this case, as the name suggests, a supply line is installed, where the liquid returns after flowing through the heating radiators.
In this case, the natural flow of liquid is organized due to the difference in its temperature and, as a consequence, density.
If a gravity heating system is installed in a two- or three-story house, as the number of floors increases, the area of the heating radiators must be reduced. In this case, despite the decrease in coolant temperature, heating will be uniform.
Pipes in a single-pipe heating system can be installed in two ways:
parallel - part of the water enters the radiator, and the rest of the coolant volume passes further through the main channel (the advantage of this solution is that, using manual or automatic shut-off valves, you can limit the volume of hot water supplied to the heating panel, and thereby reduce the temperature in room);
Parallel house heating scheme
flow-through - in this case, the entire volume of heated water flows through each heating panel in the house (you will not be able to regulate the volume of water supplied to the radiator, or completely shut off its supply, as this will lead to disruption of the entire system).
Flow heating scheme for a cottage
Considering that water supply in a single-pipe system can only be carried out through one channel, the installation of this type of heating is possible only in buildings with an attic floor, where pipes with water heated in the boiler are located.
The disadvantages of a single-pipe scheme include the impossibility of partially starting the system; the advantages are lower cost due to the smaller amount of materials and installation work, as well as aesthetics.
Method 2. Two-pipe gravity heating network
In this case, it is necessary to install two pipelines:
- Incoming. It delivers heated coolant to the batteries. A pipe is extended from the boiler, which enters the expansion tank, which is necessary to create pressure in the line. From it, water lines go to the heating radiators. The volume of the expansion tank used depends on the size of the heating system. In some cases, this device must be equipped with an overflow pipe to remove residual liquid.
- Coming out. Through this pipeline, cooled water is transported to the boiler heat exchanger for heating. The cold main must be laid in the same rooms where the supply channel was installed. This is a more effective scheme, as it makes it possible to better control the temperature in the rooms. Its disadvantages are the high cost of installation and cumbersomeness.
Two-pipe heating system
Closed type
A closed system of pumpless coolant circulation is successfully used for heating one-story and two-story houses. It functions as follows:
- when the coolant expands, excess liquid is forced out of the heating circuit;
- the liquid enters a membrane-type expansion tank - this is a closed container with an elastic membrane that separates the part intended for the coolant and the section of the tank filled with air or nitrogen;
- the heated liquid stretches the membrane, compressing the gas in the second section of the tank; when the coolant cools, the gas expands and pushes the liquid back into the system, as a result of which the water circuit constantly remains full.
Installing a membrane tank in a gravity heating circuit reduces the risk of corrosion of the metal elements of the system. But in Russia, this solution is used relatively rarely, since the cost of a membrane tank is several times higher than the cost of purchasing or independently manufacturing an open-type tank.
Open type
The operating principle is the same as that of the closed version. But in this case, excess coolant is forced into an open tank, which is mounted under the ceiling of the room or in the attic.
An open tank is a tank with a leaky lid, which is equipped with an emergency overflow - a pipe led outside the attic to the street or connected to the sewer.
The disadvantages of an open system include the constant supply of oxygen to the coolant, which accelerates the corrosion of the metal from which the circuit elements are made. Airing of the pipeline also occurs - to avoid this, the radiators are mounted at a slight slope and automatic air vents - Mayevsky taps - are installed in the upper part.
In addition, liquid from an open type tank evaporates and it is necessary to regularly add water so that the open system can function normally. Add water to the tank manually from a bucket, or connect a water pipe with a valve.
The advantages of open-type tanks are their affordable cost and the ability to make a tank of the required dimensions with your own hands.
Single-pipe circuit
A single-pipe heating system with natural circulation is not efficient. It is not suitable for heating the premises of a two-story house and is used in one-story buildings with a small area.
The coolant passes vertically upward through the accelerating section of the pipeline, then enters a pipe that leads to a horizontal pipeline connecting the heating radiators in series. From the outer radiator, the cooled coolant returns directly to the boiler.
With this scheme for connecting heating devices, the temperature of the radiators decreases with distance from the supply riser - this is a serious drawback of the system. To increase efficiency, bypasses are used - they connect the supply pipe with jumpers in the places where the radiators are connected. This contributes to more uniform heating of the rooms.
The advantages of a single-pipe system include a simple design and minimal financial costs for its installation. In addition, there is no need to install pipes under the ceiling, deteriorating the interior of the room.
A single-pipe horizontal scheme, even with accurate calculations, rarely justifies itself, unless we are talking about heating two or three small rooms of a one-story house. In other cases, it is modernized by adding a circulation pump.
Selection of components and manufacturing materials
After the advent of polymer pipes, polypropylene (PP) gravity heating systems became very popular. This material is easy to process; a minimum of equipment is required to connect individual sections.
However, not every type of these pipes is intended for installation as a heating element. Let's consider the main selection criteria:
- Presence of a reinforcing layer
. A polypropylene gravity heating system can be exposed to high temperatures - up to 95°C. To maintain the original shape of the pipe, a rigidity element is required, which is a layer of foil or fiberglass; - Wall thickness
. In a gravity heating system with a closed expansion tank, high pressure can be created. To avoid damage to the main line, polypropylene pipes must be of class PN20 or higher. The thickness of their walls depends on the diameter.
This pipe can be used to equip the accelerating manifold. However, to achieve a temperature difference, it is recommended that the return line be made of steel. In addition to reducing the temperature of the coolant before entering the boiler, this material helps to reduce hydraulic resistance.
Having completed the calculation for a gravity heating system made of polypropylene or steel pipes, you can begin installing it. To achieve optimal efficiency, experts recommend making small but important changes to the standard circuit:
- Highway slope
. The optimal gravitational pressure for the heating system can be achieved by sloping the pipes after the air vent and on the return line behind the last heating device; - Installing a circulation pump on the bypass
. It will help reduce the inertia of the system. The heating time of the coolant can be very long, so the pump can increase the speed of its movement along the line until the desired temperature is reached; - Minimum of turning units in the pipeline
. They create excess hydraulic resistance, which reduces the speed of water movement; - Installation of protective elements
. By installing a check valve for gravity heating, you can prevent water from circulating in the wrong direction. This is especially necessary for a system with overhead wiring and multiple circuits.
Tips on arranging and using a gravity valve for heating when installing heated floors and additional elements can be seen in the video:
The design and construction stage, when the heating scheme of a private house is determined, is a rather crucial moment in the process of thermal insulation. After all, an incorrectly planned system “threatens” your home with a lack of high-quality heat, “oversaturation” of the house with “interior” elements in the form of extra heating radiators, the inability to quickly control the operating mode of the system... and at the same time, you will lose money.
Analyzing the huge number of schemes that are presented on the pages of literature and websites on the topic of insulation and heating, you can get a little lost. Therefore, we will focus on several of the most commonly used schemes, examining their advantages and disadvantages.
As you probably already know, there are two types of schemes:
- heating system diagram with;
- with forced circulation of coolant.
There are also one-pipe and two-pipe heating systems, which can be implemented both in systems with natural circulation and in “forced” ones.
The coolant in such systems can be:
- plain water;
- antifreeze (non-freezing liquid for heating systems)
Two-pipe circuit
Design features of a gravity two-pipe circuit:
- Separate pipes are installed for supply and return;
- the supply pipe is connected to each heating device through a separate inlet outlet;
- The return pipe is connected to each heating device separately.
A two-pipe gravity heating system for a private house differs from a single-pipe one in that all radiators are supplied with coolant that has not had time to cool down, due to which:
- heat in the house is distributed evenly;
- there is no need to increase the number of sections in the radiator in order to improve heating;
- it is easier to regulate the temperature in the system;
- installation of the pipeline requires pipes of a smaller diameter than for a single-pipe circuit;
- there are no strict requirements for maintaining the slope when installing system elements - some deviations from the calculated values are not critical.
A two-pipe heating system with upper and lower wiring is easy to install and efficient; it can be used to heat a two-story house.
Varieties
Let's consider options for heating systems for private and apartment buildings:
• using forced circulation of coolant;
• natural circulation using gravity coolant.
Natural circulation systems have become widespread, mainly due to their strengths:
• functioning of the system with natural circulation, regardless of whether there is voltage in the network or not;
• high rates of inertia of the system, where external factors do not affect the spread of heat
Please note: you should pay special attention to the choice of the diameter of the pipes used for the heating system, given that a larger diameter improves water circulation, but here too you should know when to stop.
Calculation features
Calculating a heating system with natural circulation is much more difficult than preparing a design for a heating system with forced supply of coolant. Since there is no pressure in the circuit, the performance of the system is directly affected by the number of turns of the pipeline and the slope angle of each section. Incorrect calculations or installation errors affect the functionality of the circuit.
When calculating a pumpless circuit, the following is taken into account:
- minimum permissible slope angle;
- pipe material and diameter;
- coolant supply principle;
- type of coolant.
Advantages of using polypropylene in heating systems
There are many such advantages:
- Easy installation. As already mentioned, even one person with a soldering iron can handle it, while installing steel pipes will require a welder.
- Heating with plastic pipes will cost you several times less.
- This material is not subject to corrosion, so it can last up to fifty years.
- Its use has a positive effect on the heat transfer of the system.
- Such pipes do not “overgrow”, that is, salts are not deposited on their inner surface.
- Finally, polypropylene, although flexible, is also very strong, so it can be used under high pressure or temperature.
Pipe selection
The hydraulic resistance of the circuit, its resistance to corrosion, thermal parameters, and installation technology depend on the material of the pipeline. The list of requested materials includes:
- Steel pipes. Affordable, resistant to mechanical stress. Disadvantages: they are installed with welding or a large number of fittings, the pipes are prone to corrosion and overgrowth.
- Metal-plastic pipes. The inner surface is perfectly smooth, which prevents the growth of deposits, corrosion resistance, low weight, resistance to thermal expansion. Disadvantages: high cost, limited service life (about 15 years), the need to use welded fittings or regularly tighten threaded connecting elements.
- Polypropylene pipes. Smooth inside, durable (service life from 25 years), resistant to high temperatures. Disadvantages: high cost, installation using special tools.
- Copper pipes. Maximum heat transfer and durability (over 100 years), stylish appearance. Disadvantages: high cost, need for soldering during installation.
Pipe diameter
To calculate the diameter of the pipes, you need:
- Perform a thermal calculation of the premises and add about 20% to the result.
- Calculate the cross-section of the pipeline based on the ratio of the thermal power and the internal cross-section of the pipe (the values are indicated in the SNiP tables).
- Select the pipe diameter based on the thermal calculations performed and taking into account the pipe material. For steel pipes, the minimum internal cross-sectional size is 50 mm.
To make gravity flow more intense, the following principle is used: the diameter of the supply pipe after each branch should be 1 size smaller than the previous one. The return must be assembled with an extension.
Thus, the calculation allows us to determine the minimum diameter of the supply and return pipes; relative to this value, the parameters of the pipes in different sections of the system are determined according to the prepared diagram for a one-story or two-story house.
Multi-level floor
To zone the space, craftsmen install floors at different levels. They advise installing a podium to separate the kitchen and dining room. This option is considered one of the most practical because, among other things, the owners have additional free space where they can hide something.
It is convenient to use boxes or crates for this. Wicker baskets will look good. But such space can remain free.
However, such a design should not be made if there are small children in the family, since the podium can become an obstacle for him. In addition, various floor coverings can be used.
They will zone the space between the living room and the kitchen and protect the podium from damage. For example, tiles are laid in the kitchen area, and laminate flooring in the dining room. The main thing is to choose colors and textures and combine the finishes correctly.
Date: September 25, 2021
Type of bottling
The natural circulation of water in the heating system depends on the principle of supplying coolant from the boiler to the heating devices. There are different contours with bottom and top filling.
Bottom filling makes it possible to avoid the installation of high vertical pipes - communications are laid at floor level. This option is suitable only for single-pipe circuits and is considered ineffective without installing a circulation pump.
Top filling is the best option, since the distribution pipe of a two-pipe system is located under the ceiling and provides an active supply of heated coolant to each radiator, from which cooled water flows into the return pipe located along the floor. For a single-pipe system, top-type filling is also preferable.
Heating radiators used
The most significant indicator here is the minimum resistance to water flow. And the flow of coolant depends on the width of the radiator lumen, regardless of whether you use pipes made of polypropylene or other materials. However, cast iron radiators are simply ideal in this regard, especially when a single-pipe system is used. They have the least hydraulic resistance.
Aluminum and bimetallic radiators have proven themselves in use, but you need to pay attention to their internal diameter, which should not be less than 3/4”. This will be quite enough to heat a one-story house without using a circulation pump. The use of steel tubular batteries is permitted.
Selection of coolant
The coolant can be water or antifreeze. For a gravity system, it is preferable to use water, since antifreeze has a higher density and less heat transfer; more thermal energy is required to heat it - that is, fuel consumption is higher. If a membrane buffer tank is installed in the system, its volume should be larger than that of the coolant-water tank, since antifreeze expands more strongly.
The use of “anti-freeze” makes sense if the house is heated irregularly in winter with long breaks. In this case, the water would have to be constantly drained to prevent the pipes from bursting when frozen.
The main pros and cons of using air heating technology
The widespread use of air heating technology at various facilities is due to its many advantages. The main ones are:
- High efficiency. In some systems this value can be close to 90%. For comparison, a heating system with coolant has an efficiency of less than 60%
- Possibility to heat a large area, including in the central areas of the premises
- Low installation and operating costs
- Compatibility with the ventilation network. Possibility, subject to connection to a ducted air conditioner, to use the system for cooling in the summer
- The absence of liquid coolant in the air heating system, which eliminates the occurrence of emergency situations (frost, leaks)
- Low level of inertia. Warming up of rooms is carried out very quickly
- The ability to stop the system even in severe frosts without the risk of its failure
But there are obvious disadvantages of these systems, of which we can highlight:
- Warm air tends to rise upward, so for the most efficient and uniform heating, it is advisable to lay a network of air ducts in the lower part of the room or hide them under the floors. Unfortunately, this is often impossible or very difficult to do, especially at industrial sites.
- The use of air heating technology can lead to the rise of all the dust that is present in the house on the floor surface. If you do not clean the premises often, the air will be dusty.
- The complexity of calculations for such a system. In order for air heating to function effectively in a small private house or at a large-scale industrial facility, it is necessary that this system be professionally calculated. These calculations are quite complex and much more complex than the calculations required when organizing a water heating system. They need to take into account many parameters. It is necessary to calculate: heat losses in the premises served, the type and required power of the heat generator, the optimal air flow speed, the air exchange rate, the necessary and sufficient cross-section of air ducts and other specific engineering parameters
Having analyzed the above, it becomes obvious that the air heating system is at the junction of two engineering sections. These sections are heating and ventilation.
Accordingly, the Contractor to whom you entrust the work at your Site must have such specialists or generalists who have experience in calculating, selecting and installing such systems.
It is necessary to take into account that if the air heating system is made with errors, then it will not only fail to cope with its intended purpose - to provide the necessary comfortable temperature in the winter. But it can also be noisy and quite expensive.
When laying air ducts hidden, reworking such a heating system that is not working correctly is a very expensive and problematic undertaking.
If you are looking for a contractor for air heating of your private home or industrial facility, we are happy to offer you our services!
Send a request for a system calculation