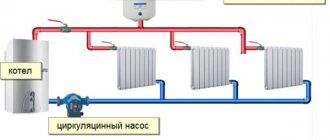
Heating a private home is a key aspect in ensuring comfort in homes. A modern heating system with forced circulation and its circuits can provide excellent conditions in homes, high efficiency at minimal financial costs.
Main nodes:
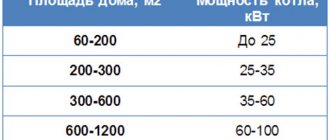
- Boiler . It is selected based on the required power, area of premises, number of storeys in the building, type of fuel, and economic feasibility. The best are models with a closed combustion chamber, which ensures lower fuel consumption. If the unit is also intended to be used to provide hot water supply, then dual-circuit models are selected. The boiler power is calculated taking into account heat loss (20%) and the addition to the hot water circuit (50%) for a standard private house.
- Pump. Provides coolant circulation in the system. Its power must correspond to the expected load. is selected taking into account the type and number of radiators, diameters, length and material of the pipeline, the number of circuits, the number of obstacles - turns, bends (friction and resistance losses).
Important! It is preferable to install the pump on the return circuit, where the coolant flows already cooled. This will increase its service life. For large two-story houses, it is necessary to buy models with ceramic flanges that can withstand high-temperature coolant.
- Expansion tank . A unit designed to stabilize the volume of coolant in the system. The volume is selected in accordance with the power of the boiler and the length of the pipelines.
- Radiators . For small houses, the best option is aluminum and bimetallic, which provide quick heating of the premises and high heat transfer.
- Pipeline . In systems with forced circulation, it is recommended to use pipes of small diameters.
- Measuring instruments. Necessary for monitoring coolant parameters. Installation is expected on the boiler and radiators. If necessary, install an additional pressure gauge to monitor the operation of the circulation pump.
Advantages of forced circulation systems
- High installation performance.
- Pipe laying is possible in any plane and in floors.
- More precise control of coolant parameters.
- The use of pipes of smaller diameter (reducing the cost of purchasing materials).
- A small amount of coolant reduces the time for heating it and energy consumption.
- Possibility of connecting “warm floors” without reconstructing the system.
- The expansion tank can be installed anywhere in the building.
- Unlimited length of pipelines.
- Full automation of the process - using the pump you can regulate the temperature and supply of coolant in the house.
Installation rules
The design of a household circulation pump from any manufacturer provides for its fastening to pipelines or shut-off valves using union nuts (American). This allows it to be quickly dismantled if necessary, for example, for replacement or repair. When installing the pump unit, follow these recommendations:
Place the device on any sections of pipelines - horizontal, vertical or inclined, but with one condition: the rotor axis must be in a horizontal position
That is, installation “head down” or up is unacceptable. Please note that the plastic box with electrical contacts is located on top of the case, otherwise it will be flooded with water in the event of an accident. Yes, and servicing the product will not be easy
This is easy to achieve: unscrew the screws securing the casing and turn it to the desired angle. Remember to follow the flow direction indicated by the arrow on the housing. So that the product can be removed without emptying the system, install shut-off valves before and after it, as shown in the diagrams in the previous section.
A visual aid showing what position the pump unit should be in
Advice. It so happened that the load from the weight of the circulation unit will fall on 1 or 2 ball valves (depending on the orientation of the area in space). Hence the recommendation: do not save money and buy high-quality shut-off valves, whose body will not crack over time from mechanical stress.
Single-pipe
For private buildings, a single-pipe forced circulation heating system is widely used. Modern technical solutions have made it possible to combine all the advantages of the traditional model with the ability to control and adjust operating parameters.
Advantages
- High reliability, long service life.
- Cost-effective, no additional energy costs.
- High hydraulic stability.
- The ability to independently add radiator sections without a negative impact on the entire system (imbalance).
- Possibility of hidden pipe laying.
- Cost reduction up to 40% compared to two-pipe schemes.
Scheme
For multi-story buildings, the diagram looks like this: a vertical pipe on one side approaches the top point of the radiator, and exits from the bottom in the same way. The design contains a bypass - a vertical pipe connected at both ends to the horizontal sections of the main line.
Single-pipe system diagram
Principle of operation
The coolant is forced into the system. The highest temperatures are observed at the beginning of the pipeline, the greatest heat losses are in the most remote section of the network, while 80% of the effective circulation occurs in bypasses rather than radiators.
In old apartment buildings, temperature control was not carried out. The irrationality of electricity consumption was compensated by its low cost.
Operating principle of a single-pipe system
Home automation system
Modern single-pipe systems involve the installation of thermostatic valves on radiator units. The diameters of the liquid passage openings and the valve are structurally made as large as possible to ensure free outflow of liquid (even in cases of contaminated coolant).
Type of thermostat
Radiator temperature adjustment is performed in three options:
- with three-way valve;
- with straight-through valve;
- thermostatic.
When reducing (adding) sections of radiators and removing the thermostat, the system will not be unbalanced.
The valve closes automatically when the room temperature exceeds the set temperature. In this case, the coolant will circulate only through the bypasses. The total water consumption does not change.
Installing a thermostat on a radiator
Economic effect
In the presence of thermostats and overheating of living rooms, the general circulation does not decrease, only the safety valves close. The coolant does not circulate, but there is an increase in losses in the pipes due to the increase in temperature during the reverse cycle. In multi-storey buildings where heating points are built, the DHW heat exchanger is powered from the return pipes of the system.
Important! For safe and efficient operation of a single-pipe system with hidden installation, it is necessary to secure a layer of thermal and waterproofing behind the pipes.
Choosing an installation location
When choosing a “place of residence” for the circulating “engine” of water in the system, it is advisable (for your peace of mind) to take into account the following points:
- If the pump is installed in an old system, it must be flushed.
- The installation location must be accessible - you may need to have access to the pump in the future for maintenance or replacement.
- Mostly they are placed on the return main pipe near the expansion tank. There the coolant temperature is lower, which is safer for the device.
- Modern circulation units for heating systems can withstand high temperatures. Therefore, they can also be installed on the supply pipe of the system. The main thing is to make sure, according to the technical documentation for the device, that it is capable of operating at high temperatures. It is advisable to do this when using devices with a built-in speed control function and when using “night mode”.
- Note! The “wet type” pump can be installed in any way in terms of the direction of the pipeline. But! Its shaft MUST be positioned HORIZONTALLY! And its position should exclude the possibility of water getting into the terminal box.
- Before starting the heating system for the first time after the summer period, it is necessary to check the functionality of the device itself - the engine rotor could be blocked by deposits from the coolant.
Reminder for correct installation and positioning of the device
Two-pipe
This scheme is suitable for heating one-story and two-story houses with a large area. The principle is to install two separate circuits - supply and removal of coolant.
Advantages:
- High-quality space heating.
- Heating uniformity: in the first and last radiator the coolant temperature is almost the same. It depends only on the area of the house, the number of radiator sections and the length of the line.
Flaws:
- Large pipe consumption for the construction of two separate lines to the boiler.
Scheme of a two-pipe heating system
Collector circuit
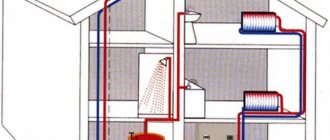
Ensures uniform water temperature in all radiators. It is the most appropriate solution for large two-story houses.
The coolant is supplied and discharged to the radiators of each room via a separate line from the boiler. Pipeline laying - in the floors.
Collector heating circuit
Functional details of the pump
Life is more fun in motion! This is in people... And in heating, a higher speed of movement of the coolant along the circuit allows you to get a number of advantages. Naturally, shortcomings found their place here too. Let's figure it out...
Gravity heating circuits of private houses suffer from this “illness” - uneven heating of various rooms of the house. It is hottest in the rooms that are located closer to the beginning of the coolant movement along the circuit, that is, near the boiler. And distant rooms simply do not warm up, since the coolant, due to the low speed of movement, gave up the “lion’s” part of its heat at the beginning of its journey.
The creation of forced movement of the coolant by a circulation pump contributes to more uniform heating of radiators in all rooms, due to the higher speed of fluid movement.
Open
It is characterized by the fact that the coolant is in contact with the environment in an open type expansion tank. The principle of operation of the system as a whole does not change: the prepared coolant, due to the difference in the densities of the hot and cold layers, enters the pipeline with slopes.
Not used for forced circulation feeds, because The tank itself creates the pressure necessary for coolant circulation in the system.
The main advantage is the absence of a circulation pump in such schemes, which reduces energy consumption.
Scheme of an open two-pipe system
Ensuring uninterrupted operation
The circulation pump is powered from an alternating electric current network (~220V). And this “trait” jeopardizes the functioning of the system in the event of a loss of power supply to the facility. Where to look for a way out and which one?
A saving option may be a circuit using an uninterruptible power supply. It must have a battery capacity reserve to support the operation of the pump (and gas boiler, if necessary) for up to 12 hours in the absence of external power supply, and at the same time produce “alternating” current without distorting its “sine wave”.
Electrical diagram for connecting the UPS to the heating system
UPS, regarding their functionality, can be divided into:
- devices that allow network current (if any) to pass through itself as a “transit” without changing its parameters. If the external power disappears or its parameters do not correspond to the nominal values, the device automatically switches to “offline” mode and switches on the battery;
- devices with a linear-interactive “character of behavior” - they allow you to adjust the parameters (mostly stepwise) of the electric current passing through it from the external network within ±20% of the nominal value;
- units that provide constant power to equipment from a battery(s), which is periodically recharged from an external network. Such devices are capable of operating with input electric current with a wide range of parameters, providing a stable output voltage for consumers. This is the best option for heating equipment equipped with electronics that are sensitive to poor-quality “power,” but it is not cheap to maintain.
The power supply circuit may also include gasoline (diesel) autonomous generators, but in order to “calm the conscience”, eliminate voltage surges and guarantee reliable operation of the electronics, all equipment connections must be made through a reliable stabilizer or UPS.
Closed
A typical forced circulation system in which a pump is used to pump coolant. The expansion tank is a closed membrane type. If there is excess pressure, water flows into an additional tank, and if there is insufficient pressure, it takes the required volume from this tank.
The main advantage is the complete safety of the heating system and the durability of the structures due to the absence of excess pressure inside the system.
Diagram of a closed two-pipe system
Correct installation
To connect the circulation blower to a finished heating system with natural coolant flow, a kind of “transport interchange” is organized: the main pipe and a “detour” through the pump line.
To do this, a check valve (automatic version) or a ball valve of the appropriate size is installed in the section of the main pipe.
The principle of “inserting” (connecting) the pump into the heating system
Two ball valves are installed on the surges welded into the main pipe on both sides of the valve, to which the pump itself is connected through additional pipes and fittings. The valves are designed to shut off the movement of the coolant when servicing or dismantling the pump.
Important point! Before the filter, it is imperative to install a filter for mechanical water purification, since even small particles in the water of the system, if there are enough of them, can damage the pump.
The operation of the unit is checked after it is connected, the entire system is filled with coolant and air pockets are removed from it. Air is released from the blower housing through the central screw located on its cover. Complete removal of air will be confirmed by the appearance of water. Low noise operation and evenly heated all batteries will be evidence of the correct choice of unit parameters.