A single-pipe heating system exists as an alternative to a two-pipe one. Having comparable efficiency, distributing the coolant through a single pipe is a more economical option, since it becomes possible to save on pipes and fittings. To independently calculate and assemble such heating, you should carefully study the principles of operation and methods of installation of its component elements.
Vertical single-pipe heating system
Vertical single-pipe water systems began to be used in the early 50s, and became widespread in the construction of residential multi-story buildings.
They can be made with upper and lower wiring, as well as with “inverted” circulation. Heating devices can be connected to the riser from one side (one-way connection) or from both sides (two-way connection). The connection of a specific device to the riser can be flow-through and with bypass sections (bypasses).
Vertical single-pipe heating systems are recommended for use in systems with a dead-end flow pattern of coolant in pipelines.
Methods for connecting radiators
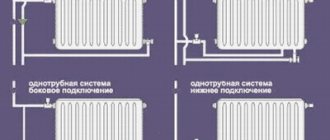
Most models of radiator assemblies allow connection to be made at two of the structurally provided points: at the top and bottom on the sides of the radiator.
There are several main connection types:
- diagonal , when the supply pipe is connected to the upper inlet on one side of the heater, and the outlet pipe is connected to the lower inlet on the opposite side. This is the most effective way;
- lateral , in which the coolant is supplied and discharged through a pair of holes located on one side of the heat exchanger;
- lower , when water enters and leaves the radiator through the lower pair of holes;
- single point connection . It is used only in extreme cases, when it is not possible to route a second pipe to the radiator. For such a connection, there are special injection connection units in which the pipes entering the radiator hole have different lengths.
Water temperature and pressure in the heating system
To determine the temperature indicator, standards are used taking into account seasonal climatic characteristics.
Standard parameters:
- at 0 outside the window, the supply to the radiators is +40 C.. +45 C, in the return flow at least 35 C;
- at -20 – supply to radiators +67 C.. +77 C, return not less than 53 C;
- at -40 – supply to heating devices of the maximum permissible values.
The pressure in the central heating system is also determined individually. If the structures are of the natural circulation type, then the pressure may be slightly higher than static. For one-story buildings with forced circulation, the operating pressure should be in the range of 1.5-2.5 bar; as the number of floors increases, the pressure must be increased so that the coolant circulates normally. Thus, for five-story buildings, the optimal pressure is 4 bar, for 9-story buildings - 7 bar, in high-rise buildings up to 10 bar.
Heating devices
It is obvious that the design of the heating system must include not only a heat source, but also heating devices. Which batteries are best for a budget-conscious homeowner?
First, let's think about the conditions under which the radiator will operate in an autonomous system.
Operating temperature is usually in the range of 50 - 80 degrees. Working pressure does not exceed 2.5 atmospheres. Water hammer is excluded - unless, of course, you fill the circuit by opening the valves sharply and to capacity.
If so, you can safely opt for aluminum sectional radiators - beautiful, cheap and with excellent heat transfer.
Aluminum sectional radiators.
As we have already found out, extreme pressure and high temperature are not expected in the autonomous circuit. If so, you can save on pipes: we will choose inexpensive, lightweight and durable polypropylene.
Since this material has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, we will have to:
- Select pipes with reinforcement. A layer of aluminum foil will noticeably reduce elongation when heated.
- Provide long straight bottling areas with compensators - ring or U-shaped bends.
The U-shaped compensators are clearly visible in the photo.
How to conduct heating yourself using polypropylene?
A low-temperature soldering iron is used to weld pipes with fittings. The melted surfaces are fixed in the working position and after 10 - 40 seconds (depending on the size) they become a single whole.
Important point: aluminum foil must be removed from the welding field by stripping (shaver). It will weaken the connection, and in the future may cause delamination of the pipe.
Cleaning polypropylene with a hand shaver.
What pipe diameters should I choose?
- For bottling a small (no more than 150 m2 per floor) house - with an outer diameter of 25 mm.
- For connections to radiators - with a diameter of 20 mm.
Varieties of single-circuit circuits
With vertical wiring system
In this case, the coolant heated by the boiler rises through a vertically installed riser to the highest point of the heating network (into the attic or under the ceiling of the top floor), from where it then flows down, simultaneously heating the radiators located on each floor of the house.
Features of the design and operation of vertical heating circuits are as follows:
- the coolant can be moved naturally, without the use of electrical equipment;
- all sections of pipes should be laid with a slight slope towards the boiler in order to increase the intensity of water circulation and avoid the formation of air pockets;
- it is difficult to hide pipes in walls, since in this case you are unlikely to be able to maintain the slope;
- The system operates completely autonomously, so even in the event of an emergency power outage, you will not be left without heat.
Scheme of single-circuit heating with vertical wiring
With horizontal wiring system
The vertical riser is not mounted here. The main pipeline is laid along the floor or under it. If you decide to disguise pipes in a concrete screed, take care of their thermal insulation, otherwise quite significant heat losses cannot be avoided.
In addition, it is advisable to observe the slope in this case:
- firstly, the heating network will be able to operate (albeit less efficiently) during a power outage;
- secondly, when filling pipes with liquid, you will avoid the formation of air locks.
Single-circuit connection diagram with horizontal wiring
Additional items
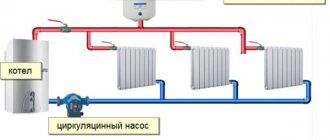
How does a closed heating system work?
In addition to the boiler, pipes and batteries, it contains:
- A circulation pump that drives the coolant.
- Jumper with cold water supply for filling the system with water.
- Drains at the lowest points of the circuit, allowing it to be completely drained.
- Expansion tank. It compensates for the increase in coolant volume as the temperature rises.
- A safety valve that is triggered when the tank is overfilled and the pressure increases above the design pressure.
- Pressure gauge or thermomanometer to monitor system parameters.
- Automatic air vent.
However: the pump, air vent, safety valve and (sometimes) expansion tank are often mounted in the boiler body, effectively turning it into a mini boiler room. Before you go shopping, study the documentation.
Construction of a modern gas boiler.
In addition, optionally the following can be installed:
- Cutting off individual heating devices and sections of the valve circuit.
- Mud trap in front of the pump.
- Throttles or thermostats that regulate the temperature of radiators.
- At the upper points of the circuit there are additional air vents.
How to install heating yourself in a one-story house? According to the author, the best solution would be Leningradka - a single-pipe distribution along the perimeter of the floor with radiators connected parallel to the main bottling. It is absolutely fail-safe and eliminates the possibility of stopping circulation in some part of the circuit due to air congestion.
How to properly install heating on two floors?
There are two possible options here.
- Two rings (one per floor) with a throttle that limits the passage of the shorter circuit.
Leningradka version for two floors.
- Two-pipe scheme with bottlings on the ground floor and in the attic and risers connecting them with heating devices.
How to connect radiators correctly?
For short (no more than 7 sections) heating devices, the traditional side connection is optimal. It is better to connect longer batteries diagonally or from bottom to bottom.
We lay pipes with our own hands
Before carrying out work, it is necessary to draw up a detailed design of the heating system. At this stage, you should choose one of the two schemes described earlier: vertical or horizontal. You should be guided by your preferences and characteristics of the premises.
Then you need to choose the most suitable type of coolant: antifreeze or water. The first, diluted with water, is best used with vertical decoupling so that it does not freeze in the attic during the cold season. The second one can be safely poured into a highway with a horizontal junction.
Let's get started
First, you need to determine what the heating boiler for the Leningrad heating system will be like and where it is best to locate it. Most often, a gas floor heating unit is installed, which is placed in the basement. It is necessary to take care of safety by reliably protecting the surfaces around and covering the floor with sheet iron.
Then you have to think about the chimney. Its type and design features will depend on the type of boiler selected
It is very important that it provides a sufficient level of draft and at the same time does not let smoke in, removing it out
You should start connecting the main main pipe, which has the largest diameter. Experts recommend choosing one of the following options:
- Metal-plastic (26 mm or more)
- Galvanized (22 mm or more)
- Steel (22 mm or more)
You can use polypropylene pipes. However, they have a significantly higher heat exchange with the environment, so they are not suitable in systems with 3 or more radiators. Distributing branches are made from pipes of smaller diameter.
The expansion tank must be securely fixed above the heating boiler. Its height must be at least 3 m from the heating device.
Next, a pipe creeps throughout the house and each of the heating radiators is cut parallel to it. You should try to make as few bends as possible when laying the highway. It is recommended to place batteries under window openings.
The Leningrad heating system must close at the boiler. At the end, it is recommended to place a filter element that will remove various impurities from the coolant. A node is also provided through which the system will be filled with water or emptied.
Despite the simplicity of Leningradka, no one forbids making some modifications to it to simplify operation and maintenance. By installing taps in front of each heating device and thermostats, the following advantages can be achieved:
- The heating will be controlled, allowing the room temperature to be set, and each radiator will be regulated separately
- It becomes possible to heat only living rooms and block the circulation of coolant through radiators in non-residential premises
Home water heating options
In private and multi-apartment buildings, heating can be radiator (collector), baseboard or in the form of underfloor heating. Each system has its own characteristics and advantages.
Warm floor
The design represents heating of the room from the floor, used in any type of room, suitable for rooms with any level of humidity, as well as for placement in open spaces (balcony, loggia, veranda). Features - the use of pipelines with a high degree of thermal conductivity, flexibility, and strength.
The structure is laid out under the screed, the advantages include:
- efficiency when using different floor finishes;
- noticeable reduction in heat costs (up to 50%);
- low cost of construction and the ability to do it yourself;
- application in a combined heating system circuit.
An autonomous water floor does not depend on electricity in any way if it is powered by a gas boiler, so the owner does not have to worry about power outages, plus the threat of a short circuit or fire is minimized.
Baseboard heating
A warm baseboard is a heating element that follows the shape of a building analogue. The operating principle of the device, located around the perimeter of the room, is similar to conventional radiators. The heating of the pipes inside the housing occurs evenly, then the warm air rises up the walls, the room warms up along all planes: wall, floor.
The advantages of the system include:
- Formation of a comfortable temperature. Active circulation of air flows is excluded, which explains the softer and gradual heating of the room. In addition, you can insulate the junction areas between the floor and the wall where mold appears - this is especially true for private houses.
- Easy installation. All structural units are sold ready-made. The arrangement can be single- or double-row, varying in power.
The downside is the location. Placing along the walls along the bottom and the entire perimeter forces you to abandon the usual order of arranging furniture (near the wall).
Radiator heating
Classic scheme with batteries and pipelines. Radiators are connected by tees, which are mounted in the areas of connection with risers and pipes. The principle of the circuit is the connection sequence. You can make a radial design, which increases heating capabilities.
The advantages include: ease of installation, operational efficiency and variety of choice of circuits. Radiator heating can be combined with other types, built on the basis of one- or two-pipe schemes, or become an addition to the perimeter (tee) design.
Connection diagrams for water heated floors
Now let's look at practical diagrams for connecting a heated floor in a house.
Direct connection from the boiler
This scheme is the easiest to install, but has a number of limitations for implementation.
- Firstly, it can only be used in low-temperature boilers with the ability to regulate the coolant temperature. As a consequence, this scheme can only be used when there is no radiator heating, and the heated floor is the only source of heat in the house.
- Secondly, despite the apparent simplicity of installation, the circuit is “capricious” when it comes to connection nuances and requires experience in such work.
This connection diagram is implemented using 3-way or 2-way valves.
3 way valve
The task of a 3-way valve is to mix hot (direct) and cold (reverse) coolant flows. In the diagram you see an option for installing a 3-way valve. Here it plays the role of a thermostat.
A thermostat is a device that ensures a constant temperature, in our case, the coolant.
This scheme has a number of features. Firstly, it does not work in circuits longer than 35-40 meters. Secondly, it is not suitable if you need to separately regulate the temperature of each circuit.
- The first drawback is eliminated by installing temperature sensors with servo drives and thermostatic valves on each circuit.
- The second drawback is eliminated by installing a circulation pump.
2 way valve
An alternative to the 3-way valve is the 2-way valve or feed valve.
Its task is to provide not a constant, but a periodic addition of water. This mixture is ensured by a thermal head with a temperature sensor included in the valve design. Essentially, a 2-way valve either cuts off hot water from the boiler or adds it to the system.
The advantage of this scheme is its simplicity and the impossibility of overheating. The disadvantage is the 200 meter limitation of the heating area. The limitations in installing circulation pumps with the organization of parallel or sequential (popular) type of mixing are solved.
Connection diagram of VTP through a pumping and mixing unit
This circuit is used to simultaneously connect radiators (main heating) and water heated floors (additional heating) to the heating boiler.
To implement this scheme, you will need a collector unit with a pumping and mixing unit. The manifold assembly is sold ready-made and is included in the assembly of the underfloor heating manifold cabinet. The price of the collector unit is 10-20 thousand rubles. Experienced craftsmen assemble the pumping and mixing unit themselves.
The task of the pumping and mixing unit is to provide a high flow rate of the coolant in the system with the possibility of accurate and, most importantly, independent temperature control. Thanks to the pumping and mixing unit, the water-heated floor circuits operate independently from the radiator circuits.
This independence of the circuits ensures guaranteed reliability of operation and quality of connection of the water heated floor system in the house.
Direct connection of the ETP from the heating radiator
Used to connect one thread of underfloor heating in a small room up to 10 square meters. meters.
Connecting the TP through a thermostatic valve is the simplest and at the same time the most controversial connection method. And that's why.
Firstly, this method only works for very small rooms of no more than 10 square meters. meters. Secondly, this scheme does not provide a high coolant velocity and the temperature difference between the coolant inlet and outlet reaches 40-45˚C, instead of the standard 5-10˚C.
To briefly describe the essence of connecting a heated floor through a thermostatic valve, this is another room heating radiator, only laid in the floor. A loop is made in the radiator heating circuit, a tee is installed, a valve is cut in and an air vent is installed.
Adjustment in such a circuit is made through a thermal head with a sensor (surface or submersible) attached to the heating pipe. There are options for adjusting the air temperature in the room.
Hydraulic separator
This circuit is used in combined heating circuits with radiators. In essence, it is a diagram of the hydraulic separation of a radiator heating system and a warm floor system.
If a circulation pump is used in a radiator heating system, then the presence of a second pump in the mixing unit can lead to a conflicting violation of the hydraulic modes.
To operate two pumps in parallel, a hydraulic separator or heat exchanger is installed in the heating system. Example on the diagram.
Vertical single-pipe systems with bottom routing
Such systems are made with U-shaped (diagram a) and T-shaped (diagram b) risers. They can be used in residential buildings with or without attics, with a height of 3 or more floors.
In the first picture (U-shaped riser), radiators 1 and 6 are connected to the riser according to a flow-through circuit. Batteries 2 and 5 are connected through a bypass, offset from the axis of the riser. Heaters 3 and 4 have axial closing (bypass) sections. It is worth noting that the flow of water into the devices is better when using bypass sections offset (from the axis of the risers) (approx. 2 and 5), and at the same time compensation for the thermal expansion of the risers is ensured. Typically, the system uses one (sometimes two) connection option.
Heating devices in flow-through (approx. 1 and 6) single-pipe systems on the lower floors should have more sections compared to devices on the upper floors.
The diagrams also show various options for installing valves to disconnect devices from the system.
In U-shaped systems, the coolant rises through one riser and immediately releases heat to the radiators. Therefore, in the second riser the water temperature will be lower and more sections will be required to obtain the required heat transfer.
In a riser with a T-shaped distribution, the water first rises up, after which it is distributed over two return risers and therefore the decrease in coolant temperature will be more uniform.
Generalization on the topic
Today we can talk about a boom in the construction of individual housing. Many people prefer to solve the problems that owners of a private home have on their own. Practice shows that by doing heating installation yourself, you can save significantly. To avoid mistakes, simpler schemes are chosen. And the easiest system to assemble is a single-pipe heating option for a private home. Leningradka is an effective and economical heating scheme that is easy to assemble and maintain.
In such a system there are absolutely no risers for return flow or intake of water as waste coolant.
In addition, single-pipe systems are much easier to install and require much less materials.
Due to the special design of a single-pipe system, namely the serial connection of radiators, during its operation it is impossible to adjust the heating intensity of each of them without negative consequences for subsequent ones. Thus, if it is hot in the bedroom and it is necessary to reduce the temperature by pressing down the valve on the radiator, the water in the other rooms will also begin to cool.
This heating system requires increased coolant pressure during operation.
If we are talking about installing a single-pipe heating system in a one-story house, then it should have a vertical outlet.
The expansion tank must be installed in the attic, which in this case serves as a technical floor.
When such a system is installed in a multi-storey building, additional tricks are resorted to to ensure the same coolant temperature on all floors. With a vertical spout, water flows down through a single-pipe system and passes sequentially through radiators on all floors, in each of which it releases part of the heat. Therefore, with such a system, additional jumpers are installed on each floor; a larger number of radiator sections are installed on the lower floors than on the upper ones.
Advantages
Today, the single-pipe system is one of the most common, especially in the construction of private houses. Its main shortcomings, characteristic of the Soviet era, were eliminated.
Secondly, a significant advantage of such a system is the saving of materials and a more aesthetic appearance of the finished structure.
Thirdly, there are many technological techniques that will eliminate the problems that occurred ten years ago. When using modern single-pipe heating systems, thermostatic valves, special air vents, radiator regulators, balancing valves, and ball valves are installed. All this makes it possible to achieve a decrease in temperature in previous radiators without lowering it in subsequent ones.
Wiring diagram
In a private house, when installing a single-pipe heating system, the coolant enters the radiators installed in the house sequentially.
Hot water or antifreeze, moving in the direction of movement, entering the first radiator, transfers some heat to it and cools down somewhat, thus, the second and subsequent batteries that are in the chain do not receive such hot water.
The temperature in the room where the last radiator is located will be lower than in the room where the first radiator is located.
To ensure a comfortable, uniform temperature in all rooms, it is necessary to install additional sections in those rooms where the coolant will arrive last.
For balanced operation of the system, additional mechanisms are used on radiators - ball valves, balancing valves, thermostats, etc. These devices allow you to control the temperature in heating appliances.
Features and device
With a horizontal system, there is a need to maintain the movement of coolants forcibly, using a pump. A horizontal system in a one-story building is laid above the floor or hidden in the floor structure. In this case, to prevent heat loss, the pipes must be insulated. In addition, radiators must be installed at one level, the horizontal line is made with a slope towards the movement of the coolant.
In a two-story building, the horizontal system has a vertical riser through which the coolant is supplied to the upper floor.
It cuts in on the ground floor up to the first radiator, if possible. In the gap formed by the riser and the first battery, taps are installed. Thanks to them, you can supply heat and regulate the temperature floor by floor.
Heat source
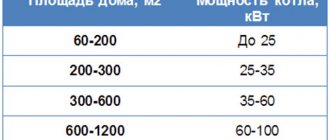
How to heat a room located at a considerable distance from the nearest heating main? Obviously, this requires an autonomous heat source - a water boiler.
When choosing a boiler type, you should pay attention to two of its properties:
- Economical. The lower the price per kilowatt of thermal energy, the lower the operating costs.
- Autonomy of work. Ideally, heating equipment should not require attention to itself.
Let's make the corresponding ratings, and then compare the positions of boilers of different types.
Economical
It seems that the table does not require any comments. Mains gas leads in cheapness of heating by a huge margin.
Autonomy
But for this parameter, the ratings will differ greatly from the previous rating.
- The undisputed leader is electricity. The electric boiler does not require any maintenance in one form or another, nor the removal of combustion products. The owner only needs to set the temperature of the coolant or, if there is an external thermostat, the air temperature in the room.
The electric boiler does not require monitoring or maintenance.
- In second place in terms of ease of use is gas. The design of heating systems with a gas boiler also allows them to operate autonomously for an unlimited time, maintaining the set temperature. The owner will only have to take additional care of installing the air duct leading to the street.
Let us clarify: we are talking about boilers with electronic ignition. Piezo ignition makes the boiler non-volatile, but it has to be ignited manually (in particular, when the igniter goes out).
Wall-mounted gas boiler with electronic ignition.
- The use of diesel fuel also allows the system to operate autonomously for a long time; however, the massive container of solarium and the noise of the burner, not much different from the noise of an airplane on takeoff, make using this heat source less comfortable.
- Pellet boilers with a hopper and automatic fuel supply provide a slightly lower level of automation: the hopper has to be loaded periodically, and the hopper will not save you from cleaning the ash pan.
- Finally, solid fuel boilers require the most attention. Coal and firewood have to be loaded every few hours. The use of gas generators, top combustion boilers and heat accumulators changes the picture for the better, but not so radically.
The conclusions are quite obvious - if you have the opportunity to use main gas, you don’t have to look for other heating options.
When choosing a gas boiler, you should pay attention to a couple more characteristics
- If power outages are not systematic, our choice is a product with forced draft and electronic ignition.
- Condensing boilers are 9 - 11% more economical than convection boilers. They utilize not only the heat of gas combustion, but also the energy released during condensation of combustion products.
Scheme of operation of a condensing boiler.
Thermal calculation
Indoor comfort depends not only on the layout, but also on the amount of thermal energy that the batteries release to the air in the rooms. Therefore, in order not to freeze in winter, you need to make the correct thermal calculations. By the way, this is also indicated by the instructions enshrined in the current SNiP.
Thanks to the correct calculation, you can choose:
- boiler of the required power - a weak one will not be able to heat the house, a powerful one will burn expensive energy resources in vain;
- radiators of the required area - this will help to significantly reduce the cost of their purchase.
Calculations can be made independently (using a special computer program) or contact a specialized engineering company. The second option is more expensive, but this way you will be sure that the data provided to you is correct.
Before installing heating, you need to perform a thermal engineering calculation of the structure
In addition, the engineers of this organization will also prepare a diagram of the heating circuits, drawn on the provided plan of your house (apartment). This will greatly facilitate installation and help you buy the right amount of materials.
Characteristics of the water system
Depending on the main method of heat transfer, convective and radiant heating differ:
- Convective. It involves maintaining the internal air temperature at a higher level than the radiation temperature in the room. Radiation temperature is the average heat index of all surfaces facing the room, calculated relative to the person who is in the center of the room.
- Radiant. Characterized by an excess of radiation-type temperature relative to air temperature. Radiant heating at a slightly lower room temperature is considered optimal for human well-being. For example, in civil buildings it is better to set climate systems to +18..+20 C instead of +22..+24 C.
Diagram of the system of a private house
There are one- and two-pipe water heating systems for country houses and mansions.
Single-pipe is considered simple and does not require significant costs, and is also accessible for installation with your own hands. The circuit represents a pipeline for transferring coolant, to which all the radiators of the building are connected. The coolant goes through a full circle and returns to the boiler for heating, then the heat transport cycle is repeated. The practical scheme has one drawback: in radiators located at the greatest distance from the boiler, the temperature regime will be reduced, but this is an advantage for people who cannot stand the heat.
The two-pipe scheme is characterized by increased complexity for self-installation. It provides for a pair of pipes to be removed from the boiler at once, one of which serves to supply hot coolant to the radiators, and the second to return cooled liquid to the boiler. The advantage is that radiators with a two-pipe design can be placed not sequentially, but in an order convenient for the owner of the house.
To ensure high quality work, experts advise installing a distribution manifold. The unit is needed to regulate the supply of liquid to each radiator and control the temperature of the room.
A bifilar heating system is also found. It is a combination of one- and two-pipe schemes. The circuit is divided into equal parts, equipped with radiators, risers, and branches. The ends are connected in order by one pipe: first the elements of the first and then the second end. The liquid is transported in opposite directions with different levels of heat, which explains the maintenance of the same temperature throughout the heating system.
Diagram of the system of an apartment building
Projects of heating systems powered from a central station are always developed individually, taking into account the housing stock. Typical distributions are single-pipe systems, where there is a heating riser, to which radiators are mounted in parallel, located in each apartment. There could be many risers; they are connected in parallel to the supply line, so they find themselves in approximately the same hydraulic conditions.
The advantage of the design is that even if one battery is turned off in the event of a leak, the heating of other apartments does not change, which is achieved by using a bypass. And the presence of a balancing valve on the batteries makes it possible to reduce the temperature in the room.
Components of a water heating system
The design consists of the following components:
- heat generator (furnace, boiler);
- pipelines;
- radiators;
- circulation pump;
- expansion tank.
If the circulation is natural, then the pump is not used; transportation is carried out due to the natural physical properties of the liquid.
Types of pipe system
In the heating system diagram, the relative position of the coolant supply inlet and the return outlet is of fundamental importance. This depends on the direction of the coolant and the type of pipe system.
Single pipe system
This is a simplified option for arranging heating in a cottage. This option is quite economical, since it requires fewer pipes for wiring and is carried out with less labor for installation work. The system is a chain of radiators connected by one pipe. The coolant heated in the boiler enters each radiator in turn, flowing from one to another. That is, the “return” from one battery becomes the feed for the next, etc.
The single-pipe scheme for connecting heating radiators in a private house has one significant drawback - with it, the radiators heat up unevenly. The first radiator will always be the hottest, and further from battery to battery the temperature will gradually decrease. Therefore, it is impossible to maintain the same temperature in all rooms with single-pipe heating.
Scheme of single-pipe heating of a two-story cottageSource utepleniedoma.com
For certain layout features, a single-pipe system may be quite suitable. So, if in a small house the chain of radiators starts from living rooms and ends with technical rooms, this option may be optimal. But in spacious cottages it is better to install two-pipe heating.
Two-pipe system
A more expensive option to install, but simple and easy to use. In this system, two pipe lines operate simultaneously. The first supplies hot water to each battery. That is, there is one pipe going into each radiator. The coolant, before entering the radiator, regardless of its location in the circuit, does not enter neighboring radiators, but goes directly. The second pipe collects the return from all radiators and delivers it to the heating manifold.
The advantages of the bottom type of wiring are that almost the same temperature is achieved at all heat exchange points. Such a system is better adjustable and ensures uniform heating of the entire building.
Scheme of two-pipe heating of a cottage Source ro.decorexpro.com
Beam (collector) system
The collector circuit is a variant of a two-pipe connection, but with more complex wiring. It is used in cases where it is necessary to hide pipes, for example under a floor covering. In this case, two collectors are installed - for the supply and for the return, and from each radiator one pipe extends into the first collector, and another one into the second.
Some connection schemes use two types of system. The entire house can be heated using the two-pipe principle, but for a separate area, such as a veranda or large living room, a combination of several radiators using the single-pipe principle is used. When developing a two-pipe scheme for connecting heating radiators in a private house, the main thing is not to get confused in the supply and return manifolds.
Radial (collector) heating circuit Source firmacz.ru
How to decorate heating pipes
Heating pipes are an interior element that performs a very useful function, but does not look particularly attractive. Often the pipes in the house are quite “rough”; they take up unnecessary space and create the impression of some kind of incompleteness.
In new houses, the heating system is located so that it is not visible; all this is calculated in advance. However, those who live in old houses have a hard time, because previously they did not think about the design of the room. The owners of these houses and apartments have to decorate the heating pipes if they want to make their home cozy and beautiful. In fact, disguising pipes is not as difficult as some people think. Moreover, after such a “make-up”, a new, full-fledged element of apartment decor will appear in place of the unattractive heating system, creating a beautiful view. The pipes themselves, of course, will also remain, but they will not be visible.
Antifreeze in the heating system
Filling the heating system with antifreeze is recommended only in certain cases, for example, during particularly harsh winters. A special aqueous solution of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol and other glycol-based compounds is used; solutions of inorganic salts.
An advantage is considered to be maintaining the integrity of the entire structure, for example, if the house is used only in the warm season, and there is no way to drain water for the winter. Antifreeze will reduce the risk of rupture of pipelines, radiators, and boiler.
The use of antifreeze also has disadvantages - reduced heat capacity relative to water, so you will have to choose and install powerful radiators, high viscosity, and fluidity. It is unacceptable to use galvanized pipes, as antifreeze can change its chemical properties and lose its qualities.
How the heating system is filled
Before you start filling the heating system with water, you need to determine the volume. It is calculated using the formula: sum up the volume of the boiler, expansion tank, radiators and pipes. The useful volume is indicated in the technical documentation.
Algorithm of actions:
- Start from the bottom point. The top point should be open.
- Connect the electric pump. Pump water through the tap. It is better to open the tap only halfway to eliminate the possibility of water hammer.
- The filling of the system is indicated by gurgling and noise of water movement. You need to finish when liquid flows from the upper open point.
- Now you should bleed the air from the connected consumer devices, boiler, expansion tank, batteries, boilers. Bleeding is carried out using taps and valves with which the units are equipped.
All that remains is to attach the hose to the top point, lower it into a container of water, turn on the pump and fill the system until water flows from the hose without air bubbles. If necessary, loop the system and circulate the coolant several more times to ensure high-quality degassing.
The last step is to pump air behind the expander membrane to ensure the desired level of pressure. This is necessary for the functionality of the circulation pump - it will have to be turned on for testing (without heating).
Pipeline layout in a multi-storey building
As a rule, multi-storey buildings use a single-pipe wiring diagram with top or bottom filling. The location of the forward and return pipes can vary depending on many factors, including even the region where the building is located. For example, the heating scheme in a five-story building will be structurally different from the heating in three-story buildings.
When designing a heating system, all these factors are taken into account, and the most successful scheme is created, allowing all parameters to be maximized. The project may involve various options for bottling the coolant: from bottom to top or vice versa. In individual houses, universal risers are installed, which ensure alternating movement of the coolant.
What circulation will be optimal and why - forced or natural?
When considering this issue, we pay attention to the following circumstances:
- A heating scheme with natural circulation is used in small buildings. Pumping units for such housing are installed when it is necessary to regulate the temperature, both in the whole system and in its individual circuits.
- Random circulation is used involuntarily in the absence of electricity or prolonged interruptions in its supply.
- When operating conditions require increased pressure in the heating system, circulation pumps are used in the systems.
For such purposes, circular units with a wet rotor are currently used. Their selection is made based on the installation features and operating conditions.
Various materials are used as a coolant for the heating system of a private house. This depends on the operating conditions of the building.
For periodically visited buildings, non-freezing liquids (antifreeze, transformer oil) are preferred, which do not lead to pipeline ruptures in extreme cold.
Water can be used in permanent residences.
What is a water heating system
Water heating is considered to be heating using a liquid coolant (water or water-based antifreeze). Heat transfer is carried out through pipelines, convectors, radiators, collectors and a boiler. The main difference between a water system and a steam system is the stability of the liquid’s state of aggregation. This property explains the lower temperature of the coolant and the safety of the water system in relation to other types of heating.
Advantages and disadvantages of a water system
In addition to simplicity and reliability, experts note the following advantages:
- uniform distribution of warm air throughout all rooms;
- when installing one heating boiler, it becomes possible to control processes from one point;
- equipment can be hidden under the decor, leaving only the radiators visible - the heated floor system completely solves the problems of hidden installation;
- the maximum coolant temperature is no more than +95 C, the surface of the radiators is no more than +65 C - this minimizes the risk of burns when briefly touching the elements.
An additional plus is the softness of the heat supplied - the temperature rises gradually. For private houses, the advantage of a water system is that the medium cools down slowly, which means that a comfortable temperature in the room will be maintained even after the heating is turned off.
There are also disadvantages:
- Risk of leakage. The problem can be mitigated by using plastic rather than steel pipes.
- Freezing of water. The situation occurs if the water in the system is not drained for the winter.
There are more advantages, which explains the popularity of designs in private and apartment buildings.
Classification of water heating systems
The classification of heating systems is based on a number of characteristics:
- According to the estimated temperature in the supply line: below +70 C – low temperature, +70..+100 C – medium temperature, from +100 C – high temperature.
- According to the type of arrangement of the supply/return line: with the top distribution when the supply pipe is located above the heating device (HP), with the bottom - if the supply and return pipes are laid below the DP.
- According to the location of the pipes connecting the radiators: vertical with a riser and connecting pipes laid out vertically, and horizontal – with horizontal pipes laid out.
- According to the connecting diagram of pipelines and radiators: two-pipe with parallel connection of batteries, single-pipe with a series connection.
- According to the type of water direction in the supply and return lines: dead-end - when there is oncoming traffic, passing - when the directions of fluid flow coincide.
The method of flow circulation is taken into account: natural is called gravitational, using the force of pumps is called forced.
Circuit mounting options
The main pipeline transporting the coolant can not only have different configurations, called wiring, but also be installed differently.
When choosing an installation option, you should take into account aesthetic, energy and economic feasibility.
The installation of the highway can be done in two ways: open or hidden:
- The open installation method is simpler and cheaper - the circuit is laid in accordance with the selected wiring diagram, and the only additional work required is to secure the pipes to prevent their deformation. In addition, in this case, the main line, in addition to transporting the coolant, also performs a heat transfer function, that is, it additionally heats the premises. At the same time, a pipeline left in sight spoils the interior, it is not protected from external damage and is itself a source of danger: you can get burned on it, flammable materials left nearby can ignite, and if the pipeline ruptures, not only damage to the external and internal decoration of the room, but also there is a risk of injury.
- Installing a pipeline in a hidden way involves laying pipes in channels made in the wall, floor, under the baseboard or behind the suspended ceiling. A simplified option is to make a false wall or use boxes and various pipe covers. Concealed installation ensures safety and looks more aesthetically pleasing.
We recommend that you read: How to choose a needle valve for a pipeline?
Important! Pipes hidden from view increase energy costs. In addition, the labor costs for equipping such a highway and the consumption of materials increase, and when using false walls and overlays, the usable space of the premises decreases.
Features of work on replacing pipes, risers and heating radiators
Dismantling heating risers
Replacing risers
Since heating modernization may affect the systems of other apartments, it is necessary to inform the housing office about the upcoming work. Their employee must shut off the riser in case there is water in the system. When pipe replacement is not an emergency, it must be carried out during the non-heating season.
Before changing heating pipes,
you need to come to an agreement with the neighbors below and above, because if sections of old pipes remain in the ceilings, there will still be a possibility of leakage.
Stages of dismantling work:
- The housing office employee must shut off the risers and drain the water from them.
- The riser is cut off from the upper and lower floors using a grinder.
- Since the new riser pipes are plastic, a thread is made on the riser pipe, it is lubricated, and sealed with fum tape. Then a coupling is screwed on, connecting the plastic and steel pipes.
Installation of heating radiators
The best for central heating are bimetallic or modern cast iron radiators - they have a large enough flow for water, so they rarely become clogged.
Types of radiators
Battery installation features:
- First, the radiator installation locations are marked.
- Brackets must be used to install radiators.
- Installation of the battery must be carried out exclusively according to the level, since if it is skewed, air may collect in it and it will not work well.
- As a rule, radiators are installed under a window to prevent cold air from entering the room.
- The distance between the radiator and the wall should be about 5 cm, the gap to the floor - a maximum of 12 cm, to the window sill - 10 cm.
When replacing pipes and heating radiators, they must be equipped with shut-off valves. This is necessary so that in the event of a radiator leak, this section can be closed, and this will not affect the functioning of the entire heating system.
Connecting pipes to radiators
Heating system diagrams
- A single-pipe system where only hot water flows through the risers. For risers with this system, pipes with a diameter of 32 or 25 mm are used. For pipes supplying coolant to radiators, a diameter of 20 mm can be used.
- A two-pipe system, where hot water is supplied through one pipe (“direct”) and discharged through the second (“reverse”). With this system, the diameter of the pipes is selected depending on the number of radiators: when there are 8 or more batteries, pipes with a diameter of 32 mm are used, when there are fewer batteries, 20 mm. For the riser system, a pipe diameter of 32 mm is also used.
When it is necessary to replace heating pipes, it is important that the diameter of the pipes going to the radiators is not smaller than those that were previously installed. Installation of pipes to radiators:
Installation of pipes to radiators:
- With a single-pipe system, a Mayevsky valve is located in the upper part of the radiator, which is necessary for venting air. The bottom hole is closed with a plug. The surface must be cleared of paint before installing the plugs. Then they install the heating taps using a special wrench - preferably with union nuts. When changing heating pipes ,
the pipeline leading to the radiator is installed after its installation. - With a two-pipe system, grooves are made for the pipes in the floor, the pipes are sheathed with insulation and laid in the grooves. The pipes that go to the radiators are similarly hidden in the walls.
Heating pipes built into the walls
Final stage:
- connecting pipes to risers;
- when replacing heating risers, it is necessary to install a jumper (if the taps on the battery are closed, in the absence of a jumper, the entire heating riser will not work);
- the assembled system must be checked for leaks by testing it under pressure 1.5 times higher than normal.
If the heating system in an apartment is correctly replaced, the problem of heat and leaks will be solved for at least 20 years.
Horizontal heating distribution
In a horizontal heating system, the radiators of each floor are connected to a separate riser. Vertical pipes are missing partially or completely.
Schemes of heating systems with two-pipe horizontal distributions
Schemes of heating systems with single-pipe horizontal distributions
To balance a two-pipe horizontal heating distribution, an adjustable bypass is used, for example, an H-shaped Herz-3000 unit.
Any horizontal scheme can have a parallel or dead-end fluid movement.
The key advantage of horizontal wiring is the ability to implement hidden installation in the structure of walls or floors. For this purpose, metal-polymer pipes are used, which have greater thermal expansion than metal pipes. They are laid using length compensators. At the same time, the problem of air removal arises, which can be solved in one of the following ways:
- installation of Mayevsky crane;
- installation of automatic air vents;
- use of pipes with an oxygen barrier;
- increasing the tightness of the system.
To implement this scheme, it is necessary to organize forced circulation of the coolant.
Heat supply of a multi-storey building
Heating distribution unit for an apartment building
Heating distribution in a multi-storey building is important for the operational parameters of the system. However, in addition to this, the characteristics of the heat supply should be taken into account
An important one is the method of supplying hot water - centralized or autonomous.
In most cases, a connection is made to the central heating system. This allows you to reduce the current costs in the estimate for heating a multi-storey building. But in practice the level of quality of such services remains extremely low. Therefore, if there is a choice, preference is given to autonomous heating of a multi-storey building.
Autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
In modern multi-storey residential buildings, it is possible to organize an independent heat supply system. It can be of two types - apartment-based or communal. In the first case, the autonomous heating system of a multi-storey building is carried out in each apartment separately. To do this, make independent piping and install a boiler (most often a gas one). A common house installation involves the installation of a boiler room, which has special requirements.
The principle of its organization is no different from a similar scheme for a private country house. However, there are a number of important points to consider:
- Installation of several heating boilers. One or more of them must perform a duplicate function. If one boiler fails, another must replace it;
- Installation of a two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building, as the most efficient;
- Drawing up a schedule for scheduled repairs and maintenance work. This is especially true for heating heating equipment and safety groups.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the heating scheme of a particular multi-storey building, it is necessary to organize an apartment-by-apartment heat metering system. To do this, energy meters must be installed on each incoming pipe from the central riser. That is why the Leningrad heating system of a multi-storey building is not suitable for reducing operating costs.