Inside the heated room there should be a constantly comfortable air temperature for a person. For this purpose, a thermal head for a water-heated floor is included in the room heating project.
During operation, the element continuously monitors the temperature of water or antifreeze in the system and adjusts the circulation intensity.
The thermal head and thermal valve are integral parts of the structural unit. The system cannot do without a valve, since it controls the operation of the thermostat and its sensitivity to heat fluctuations in the air outside or in the water inside the circuit. The functions of the unit with thermal units are cutting or mixing.
A thermal head for a water heated floor is extremely necessary, since heated floors are low-temperature systems, and getting too hot water into them will damage the circuit and cause a malfunction.
How to choose a thermal head?
The floor covering heating system has a mixing unit, the most important element responsible for changing the parameters of the heating circuit. This is due to the fact that the moisture from the heating equipment enters the pipeline too hot, sometimes up to 90 degrees Celsius, and inside the screed there can only be a maximum of 40 degrees Celsius.
In order not to overheat the system, a thermal head is installed on the damper, maintaining acceptable parameters of the coolant. The mixer is responsible for bringing together the temperatures of different flows, as a result, antifreeze or water of the required and permissible temperature enters the water circuit.
Return temperature limiter
The Unibox Rtl Oventrop regulator, which limits the degree of heating of the return flow, is used on a small area of underfloor heating < 20 m2. The normalized temperature range is 20-50°C and depends on the indicator set by the thermal head, due to which the degree of permissible heating is maintained automatically.
Regulator for water heated floor Unibox Rtl Oventrop
Such a scheme involves installing the Unibox Rtl Oventrop so that the coolant, when circulating, passes the entire circuit of the heated floor and only then through the Rtl regulator.
The principle of its operation differs from the functioning of the mixing unit, where in order to achieve the required temperature, liquid flows with different degrees of heating are mixed, controlled by a valve.
When using the Rtl regulator, when water enters the heated floor loops, no mixing occurs, that is, when connected to radiator heating, the coolant immediately moves into the heating pipeline. The task of the Rtl valve built into the regulator is to limit the temperature of the liquid flow at the outlet of the water circuit pipes.
Such piping involves supplying hot coolant in portions, so that overheating does not occur. An inertial screed also helps smooth out the temperature.
Design dimensions of Rtl valves
When equipping a water heating circuit system with an Rtl valve, it should be taken into account that the temperature set on the return liquid flow limiter should not be lower than the room air values.
If this requirement is not met, then unstable and incorrect functioning of the Rtl regulator may occur.
Structurally, it consists of a housing, a limit rod stroke limiter, as well as a liquid sensor, thanks to which data on the temperature of the passing flow is transmitted to maintain the set heating value in automatic mode.
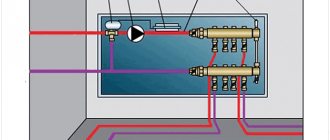
Water heated floor control scheme
The Rtl valve opens only if the maximum value has not been reached. A similar regulator is also used when equipping a combined-type warm water circuit, when the coolant flows in parallel to the radiators and into the system.
A variety of options for connecting a water heating circuit allows you to rationally decide which circuit will be suitable for specific conditions. In country houses, when installing a local boiler with an adjustable temperature of the outlet water flow, there is the possibility of direct connection without additional components designed to reduce the degree of heating of the coolant. [ads-pc-2][ads-mob-2]
Thermal valve for heating system
The thermal head is installed strictly horizontally and contains a specific meter that transmits signals to the electric drive about the closing or opening of the valve. The hydraulic valve has three coolant passages, two of which are used to supply water to the mixer, and the third is responsible for supplying the total flow to the pipeline.
The block is made of stainless steel, since the device has to work in a constantly humid environment and there is a risk of corrosion. In operating mode, the floors sensitively respond to changes in heat in the room, automatically adjusting the heating of the circulating fluid inside.
Three-way valve
According to the design solution, the three-way valve has three holes, two of which serve for the flow of mixed water flows, and the third discharges the coolant into the water circuit system. The piping scheme provides for a branching on the return line, which allows excess cooled coolant to be sent to the water heating device.
Structure of three way thermostatic mixing valve
The three-way valve body is made of corrosion-resistant materials such as bronze. The main part of this device is the thermal head, which is installed on the rod through a special axle box.
During the operation of the heated floor, it reacts to the ambient temperature, changing the location of the axle box and adjusting the degree of heating of the outlet water in accordance with the set values.
To read the temperature, the thermal head is equipped with a sensor that transmits signals to the actuator, which, depending on the values received, closes or opens the valve. It is mounted so that the thermal head is in a horizontal position. When the pipeline length is over 40 meters, a circulation pump is installed to circulate water through the circuits.
How does the thermal head work?
The thermostat consists of a mechanism with thermodynamic parameters based on the elementary physical properties of a substance - expansion at high temperatures. In the body of the thermal head there is a special container with a substance that responds to heating, and under it there is a pusher for the valve rod.
Thermal head for heated floors works as follows:
- Inside the thermostat there is a bellows containing a solid or liquid substance. Its walls are made corrugated, which gives the container the ability to stretch;
- When the degree rises, the bellows expands, the walls stretch and put pressure on the valve stem. The balance of the system is maintained by a spring;
- When the bellows cools, its dimensions are restored and cease to exert pressure on the rod.
Thermal head for heated floors is sold separately or with a valve included. Purchasing a kit is optimal, because in this case the threads and seats of the taps and heads match perfectly.
The complete set is made of different types of valves, therefore they come with straight or angular thermal heads. You can select the desired option based on the configuration of the heating system.
Installing a thermal head on a heating radiator
Connecting a thermostat to a radiator consists of two operations - installing a thermostatic valve and installing a thermal head.
How to install a THERMAL HEAD on a heating radiator with your own hands
Radiator valve installation
Winding flax thread onto the valve outlet threads
Winding flax thread onto the thread of the supply pipe
We coat the winding with sealant
Securing the valve seat
Installing the valve on the pipe
Connecting the valve to the radiator
Valve installed
Installing a thermal head
Install the thermostat as follows:
Set the regulator to the maximum open position
We screw the thermal head onto the valve thread
The thermostat must be installed perpendicular to the radiator
Types of thermal heads
Depending on the substance in the bellows, thermal heads can be gas, liquid or paraffin based. Liquid - inertial, working slower, taking a long time to heat up and cool down, but the most accurate.
Gas ones have a large error and are vulnerable to drafts. Inside the head there is a mnemonic diagram on which zones with temperatures are marked.
The thermal head can be controlled mechanically or electronically. Manual, mechanically controlled, have a radial scale with marks of 2...5 degrees. Turning the knob will increase the distance between the elements and increase the pressure on the rod.
Electronic devices are controlled by a display, and an electric drive presses on the rod. Such equipment is more expensive, but is highly accurate.
The thermostat contacts the surface in several ways, so the thermal head can be a surface-mounted one, with an air sensor, or an immersion type.
The thermostat heats up at the place of fixation, and the overhead and air thermostats are connected to the sensor by a sealed capillary-type tube. The bellows expands from the heating of a canister located remotely - such units are used in heated floors.
Types of temperature sensors
The remote temperature sensor is a gas canister. It is connected to the bellows of the thermal head by a capillary tube. As the temperature rises, the pressure inside the can increases and is transmitted through the bellows to move the rod, which closes the supply of hot water through the valve. When the air temperature decreases, the coolant supply increases.
Instead of a gas valve, a paraffin or liquid thermal valve, which is more inertial, can be used. The signal is sent to a heating element located in a cylinder with a heat-sensitive filler. When heated, the paraffin melts and increases in volume. It presses on the piston and it moves the rod with the valve plate. The coolant temperature control range is within 20-400C.
The temperature of the heating medium is controlled in the mixing unit, consisting of a valve, thermal head and pump. Regulation is carried out continuously, and mixing of flows is carried out inside the valve.
Control can be done manually by turning the thermal head cover with a scale. In position “1” the flows are supplied in equal quantities. The adjustment is rough because the heat consumption for heating is variable. More precise control is provided by a thermal head with a remote sensor for heated floors located inside the return manifold. The method is one of the most effective, although expensive in terms of the equipment used.
Changing operating modes of heated floors
The thermostat is an effective solution for monitoring the water temperature in the heating circuit. This method is inexpensive and accessible to almost every owner. The boiler heats the water to 90 degrees, and water should flow to the floors at a temperature twice as low.
The desired degree can be achieved thanks to the thermostatic head:
- The supply of hot water is short-term - the water fills the pipeline, the supply ends until it cools to an acceptable temperature;
- Constant water supply with the addition of cool coolant from the return pipe.
Periodic short-term supply
With a short-term water supply, the system works in a small space - a bathroom, ceramic floor in the toilet, shower room and other places. At the supply point there is a valve with two strokes, a remote-type floor sensor and a thermal head.
As soon as the circuit is filled with coolant, the sensor is triggered and the flow is blocked by the valve. After some time, the screed will cool down, the valve will open again and hot water will fill the system. This circuit is economical and can replace the mixer unit.
For heated floors, special thermal heads from the RTL series have been developed, without an external sensor. They are installed on the return line to maintain the set water temperature without depending on the heating of the floors. By installing this model of thermostat, the automation changes the threshold heat values (no more than 40 degrees Celsius).
The installation feature is installation in an exclusively horizontal position. Experts from Moscow do not recommend setting the water level in the floors lower than the temperature in the room.
Periodic short-term injections of water into the circuit allow you to maintain stable movement along the coolant circuit without overheating the system.
Constant coolant supply
A constant supply of water requires the installation of a three-way valve in the system, complemented by a floor sensor and a thermal head. Using a tee, a connection is made from the return to the third stroke of the mixing unit. The direct water supply must always be open, so the valve must be installed professionally and correctly.
Experts recommend installing the thermal head on a three-way valve using a locking type axle box. When the sensor heats up, the valve stem moves and a gap is formed inside. This gap receives cool water from the return line.
This sequence of work allows the coolant to stably enter the circuit, while the temperature remains within acceptable limits. Due to the continuity of the flow, the floor covering quickly heats up to 28 degrees Celsius and remains comfortable for the owner, and the circuit does not overheat.
Pipes and screed will last longer due to the absence of excessively high temperatures. The addition of cold coolant is important for heating large rooms where a comfortable temperature is needed.
Two way valve
The wiring diagram for an easy-to-use heated floor with a three-way valve is attractive due to its versatility. But it should be borne in mind that for small heated rooms you can use a cheaper two-way valve, the design of which also includes a thermal head equipped with a sensor. This device supplies cooled coolant constantly, and hot liquid is supplied as needed.
Mixing unit for underfloor heating on a two-way valve
[ads-mob-1][ads-pc-1] A similar scheme with a two-way valve has virtually no risk of system overheating. Since the throughput is less than that of the analogue, temperature control is carried out quite smoothly. It is regulated in accordance with the readings received from the remote sensor, through which hot coolant is supplied from the boiler. The cooled water from the return flows through the balancing valve. Diagram of a unit with a two-way valve
After mixing, the liquid at a set temperature, controlled by a sensor, is supplied to the manifold. Two check valves are additionally installed on the return circuit, preventing the flow from moving in the return direction.
Types and their structure
In a thermostatic distribution valve installed on a heated floor, the heated water is mixed with cooled water from the return pipe. This process is continuous as long as the heating is on.
There are two-way and three-way mixing valves for underfloor heating. They also differ in the method of mixing and the direction of flow.
Two-way
The two-way thermostatic valve is an improved manual type model. It can be hydraulic, pneumatic or electrically driven.
The design is simple, but capable of effectively regulating the temperature level of the coolant in automatic mode. The device is mounted in the heating system, instead of a manual valve.
Main advantages:
- Automatic reduction of liquid temperature level;
- Simplicity of design and low price;
- Easy installation.
Disadvantages - the possibility of installing it on pipelines with a small size. If you use this faucet when installing heating in a room with a large area, the thermostat will function intermittently. A two-way valve is more often used if heated floors act as additional heating.
The valve device is a brass or bronze body, with one or two seats. A double-seated valve can completely shut off the flow of water.
The device is equipped with a thermostatic head with a scale. The head position can be changed manually or automatically. Manual models are simple and inexpensive. More modern devices work automatically.
The two-way valve operates according to the following principle - the coolant from the return line is again supplied to the floor pipes, but before this, a device is activated that opens the supply of heated water. The two flows are mixed inside the housing to the desired degree, then the temperature sensor is triggered and the shutter automatically closes the hole with the hot coolant.
The valve consists of a plunger and a seat. The plunger has a disc, needle and rod shape. It is located perpendicular to the movement of the fluid.
Three-way valve
The operating principle of a three-way thermostatic valve for floor heating is that cooled water from the return line is added to the hot water coming from the boiler.
The valve is designed for heating systems that are installed in large rooms. They have the same advantages as two-way valves. Particularly worth noting is the ease of adjusting the water temperature for heated floors.
But this thermostatic valve also has a minus - if the thermostat is triggered, the valve opens completely, thereby allowing hot coolant to enter the circuits. And this can cause overheating of the heating system, and even rupture of pipes. In addition, it has a lower flow capacity than a two-way valve.
Three-way thermostatic mixing valves are available in brass and bronze. They are equipped with a thermal head or thermostat, and can have an electric drive or a servo drive. The design is a faucet with two inlets and an outlet. Inside the case there is a mixing chamber, on which there is a thermostat with a regulator on which there is a digital panel. A thermal valve is connected in front of the manifold.
Operating principle of three-way thermostatic valve:
- heated water moves through the right and front pipes - if its heating degree meets the required parameters;
- if the temperature of the liquid increases or decreases, the thermostat comes into operation, it sets the rod in motion, as a result, cooled water is mixed with hot water;
- after reaching the set temperature, the front hole opens completely.
It should be said that when the device is turned on, the water flow voltage does not change. This leads to a uniform change in the temperature of the liquid supplied to the line.
Features of Three Way Valve
Mixing fluid flows, which a thermostatic mixing valve allows, makes it possible to direct flows with a stable, standard temperature into the underfloor heating system. This operation is performed automatically. For mixing that takes place inside the device, already cooled liquid from the “return” is added to the hot water.
Description of three way valve
Operation occurs in the following sequence:
Operating principle of three-way valve
- hot water flows to the collector included in the underfloor heating system;
- when passing through the thermo-mixing valve, the degree of heating of the liquid is determined;
- if the water temperature is higher than the set one, then a passage opens into which the cooled liquid enters;
- two flows are mixed inside;
- after reaching the desired value, the cold water passage closes.
Among the disadvantages of three-way valves, there is the possibility of sudden temperature jumps that occur during the start-up of heated water, which negatively affects the condition of the pipeline.
Heat supply and treatment to the floor of a three-way mixer
This faucet, made of brass, has three strokes in its design, which determine the use of different methods of mixing liquid flows, depending on which there are three types of three-way valves.
Overall and installation dimensions of the three-way valve
- Valve with the thermostat function required for heated floors. Such a device not only regulates the intensity of the mixed flows, but also ensures that the system maintains a given temperature. This function is facilitated by the presence of a heat-sensitive element, which, by detecting the degree of heating of both flows entering the tap, changes the cross-section of the holes.
- The three-way thermostatic valve of the second type is distinguished by the fact that it provides regulation of the supply intensity of only the hot flow. The package includes a thermal head with a remote sensor.
- You can also select a mixing valve from the assortment of three-way models that does not automatically maintain the set temperature.
By mixing method
Mixing taps for heated floors, depending on the mixing method, are:
- With a thermostat function - with it it is possible to achieve and maintain the desired degree of heating of the coolant, since the device is able to regulate both flows (heated and cooled). The thermostat in the mixer, reacting to the level of heating of the liquid, opens or closes the hole through which heated or cooled coolant is supplied. In addition, the mechanism is designed in such a way that in the absence of cold water, the automation shuts off the flow of hot water.
- Thermostatic - the device is equipped with a sensitive thermal head that has an external temperature sensor, it is located in each line. The operation of the valve is to determine the water temperature and send a command to the actuator.
Gas or liquid
The effectiveness of a thermostatic valve depends on the properties of the substance in the bellows. Gas-filled thermoelements are more accurate and reliable. They respond faster to temperature changes, but are more difficult to produce and therefore more expensive.
Liquid ones work a little slower, but are easier to manufacture. The advantages of liquid thermoelements also include the high accuracy of transfer of the internal pressure of the bellows to the thermostatic valve stem.
With remote sensor
Thermal valves with a remote sensor are designed for installation in radiators with a bottom connection or located in a niche. The thermostatic head is mounted on the valve using a threaded connection, and the temperature sensor is attached to the wall in any convenient place. The head and sensor are connected to each other by a capillary tube.
Such models maintain temperature more accurately, but are more expensive than others.
Our range
The Santekhkomplekt online store offers a wide range of thermostatic mixers from leading European manufacturers. From us you can buy products from Danfoss (Denmark), Esbe (Sweden) and Giacomini (Italy), known throughout the world for their meticulous attitude to quality.
All products are made from corrosion-resistant alloys that can withstand highly acidic water, which is typical for Moscow. Quality control of the control rod allows the listed manufacturers to achieve its high precision and durability, providing it with stable reliability for many years.