A constant supply of hot water to a multi-apartment high-rise building can be carried out using two methods using different operating principles:
- In the first case, the hot water supply of an apartment building takes water from the cold water supply (cold water supply) pipeline, then the water is heated by an autonomous heat generator: an apartment boiler, a gas water heater or boiler, a heat exchanger that uses the heat of a local firehouse or thermal power plant;
- In the second case, the hot water supply scheme of an apartment building takes hot water directly from the heating main, and this principle is used in the residential sector much more often - in 90% of cases of organizing hot water supply in a residential building.
Important: the advantage of the second option of a water supply system for a residential building is better water quality, which is regulated by GOST R 51232-98. Also, when hot water is taken from a centralized heating main, the temperature and pressure of the liquid are quite stable and do not deviate from the specified parameters: the pressure in the pipeline of the hot water supply system is maintained at the level of the cold water supply, and the temperature is stabilized in the common heat generator.
Let us consider the water supply of an apartment building according to the second option in more detail, since this is the scheme that is most often used both in urban areas and in country houses, including country houses or garden houses.
What elements does the water supply scheme of an apartment building include?
The water metering unit, which organizes the supply of water to the house, is responsible for several functions:
- It takes into account the consumption of cold water supply, that is, it acts as a water meter;
- It can shut off the supply of cold water to the house in emergency situations or when it is necessary to repair components and parts, as well as to eliminate leaks;
- Serves as a filter for coarse water purification: any hot water supply scheme for an apartment building should contain such a mud filter.
The device itself consists of the following components:
- A set of shut-off valves (taps, valves and valves) at the inlet and outlet of the device. Standardly these are gate valves, ball valves, valves;
- Mechanical water meter, which is installed on one of the risers;
- Mud filter (filter for coarse water purification from large solid particles). This could be a metal mesh in the housing, or a container in which solid debris settles to the bottom;
- Pressure gauge or adapter for inserting a pressure gauge into a water supply circuit;
- Bypass (bypass from a section of pipe), which serves to turn off the water meter during repairs or for data verification. The bypass is equipped with shut-off valves in the form of a ball valve or valve.
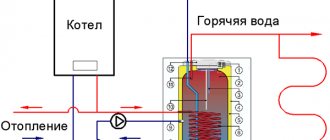
Heating point
It is also an elevator unit that performs the following functions:
- Ensures full and continuous operation of the heating system in an apartment building, and also regulates its parameters;
- It delivers hot water to the house, that is, it provides hot water supply (hot water supply). The coolant itself in the heating system enters the hot water supply system of the apartment building directly from the centralized heating main;
- The heating point can switch the hot water supply between return and supply. This may be necessary during severe frosts, since at this time the temperature of the coolant on the supply pipe can rise to 130-150 0 C, and this despite the fact that the standard supply temperature should not exceed 750 C.
The main element of a heating point is a water-jet elevator, where hot water from the working fluid supply pipeline circuit in the house is mixed in a mixing chamber with the return coolant by injection through a special nozzle. Thus, the elevator allows a larger volume of low-temperature coolant to pass through the heating circuit, and, since injection is carried out through a nozzle, the supply volume is small.
Adapters for connecting DHW can be inserted between the valves at the inlet of the route and the heating station - this is the most common connection scheme. The number of inserts is two or four (one or two each on the supply and return). Two inserts are typical for old houses; in new buildings, four adapters are practiced.
On the cold water supply route, a dead-end tie-in scheme with two connections is usually used: the water metering unit is connected to the bottling, and the bottling itself is connected to the risers through which pipes are routed to apartments. Water will move in such a cold water supply system only during disassembly, that is, when opening any mixers, taps, valves or valves.
Disadvantages of this connection:
- If there is no water supply to a particular riser for a long time, the water will remain cold for a long time when drained;
- Heated towel rails embedded in the DHW inlets from the boiler rooms, which simultaneously heat the bathroom or toilet, will only be hot when the DHW is drawn from a specific riser in the apartment. That is, they will almost always be cold, which will cause the appearance of moisture on the walls, mold or fungal diseases of the building materials of the room.
A heating station with four hot water connections in the house makes the circulation of hot water continuous, and this happens through two bottlings and risers connected to each other by jumpers.
Important: if mechanical water meters are installed on the hot water taps, then the water supply consumption will be taken into account without taking into account the water temperature, which is incorrect, since you will have to overpay for hot water that was not used.
Hot water supply can operate in three ways:
- From the supply pipe to the return pipe to the boiler room. Such a hot water system is effective only in the warm season when the heating system is turned off;
- From supply pipe to supply pipe. Such a connection will bring maximum benefits in the demi-season - autumn and spring, when the coolant temperature is low and far from maximum;
- From the return pipe to the return pipe. This DHW scheme is most efficient in extreme cold, when the temperature at the supply pipe rises to ≥ 75 0 C.
For continuous movement of water, a pressure difference is required between the starting and ending points of insertion into one circuit, and this difference is ensured by limiting the flow. This limiter is a special retaining washer - a steel pancake with a hole in the middle. Thus, the water that is transported from the inlet to the elevator encounters an obstacle in the form of a washer body, and this obstacle is regulated by a rotation that opens or closes the retaining hole.
But too much restriction of the movement of water in the pipeline route will disrupt the operation of the heat station, so the retaining washer should have a diameter 1 mm larger than the diameter of the heat station nozzle. This size is calculated by representatives of the heat supplier so that the temperature at the return heating pipe of the elevator unit lies within the standard temperature limits.
Background
Dead-end cold and hot water supply systems are typical for buildings built by Stalin and Khrushchev. In a dead-end system, the bottling flows into risers, and each riser ends with a water supply on the top floor with a cistern and mixers connected to it. Water in such a system begins to move only at the moment when one of the residents opens the taps.
Black pipes - tie-ins of a dead-end hot water system into the supply and return of the heating network
For cold water this is quite acceptable, but in hot water it has a couple of unpleasant consequences:
- If in your part of the house (along a riser or in a group of risers) no one has used hot water for a long time, it cools down in the pipes. Yes, yes, despite the thermal insulation of the bottlings: insulation slows down cooling, but does not stop it completely.
As a result, in order for hot water to come out of the tap, you are forced to drain cold water for several minutes: its volume with a DHW filling diameter of 80-100 mm can amount to tens of liters;
Do you want to wash your face? Drain the cooled water in the pipes!
Please note: this situation is especially bad for the owners of water meters installed in the apartment. They drain cold water and pay for hot water: there are no temperature sensors on mechanical metering devices.
A mechanical device takes into account water flow without recording its temperature
- Heated towel rails were installed everywhere in Khrushchev-era bathrooms. They are connected to the gap in the hot water supply, between the riser and the taps, and heat up only when water is consumed in that particular apartment.
Khrushchev: the dismantled heated towel rail was installed between the water supply and the riser
Since hot water is rarely used for more than an hour a day, these appliances sit cold most of the day and night. Hence the musty smell of towels, cold and dampness in the bathroom, and often fungus on the walls.
Mold is one of the consequences of cold in the bathroom
A revolution in the design of domestic hot water systems took place on January 1, 1977, when SNiP II-34-76 was released. Paragraph 2.8 directly stated that hot water supply must now be designed with continuous circulation of water through ring jumpers and risers.
The document has now been canceled, but there are current reissues of it.
What the circulation of water in the water supply system does is quite obvious: from now on, the water in the hot water supply and in the risers has become hot around the clock. To heat the water flowing from the tap, it is enough to drain the few liters of water that are in the water supply.
Heated towel rails migrated from the supply to the riser and began to heat constantly - as long as circulation was maintained in the risers. As we will find out later, it is possible that this circulation may stop.
In new houses, dryers are connected not to the inlets, but to the risers
Features of hot water supply and calculation of the volume of hot water
Calculation of the amount of hot water in the system depends on technical and operational factors:
- Estimated hot water temperature;
- Number of residents in an apartment building;
- The parameters that plumbing fixtures can withstand and the frequency of their operation in the overall water supply scheme;
- the number of plumbing fixtures that are connected to the hot water supply.
- A family of four uses a 140 liter bathtub. The bathtub fills in 10 minutes, the bathroom has a shower with a water consumption of 30 liters.
- Within 10 minutes, the water heating device must heat it to the design temperature of 170 liters.
These theoretical calculations work based on average water consumption by residents.
Connection diagram for DHW recirculation: how to make it yourself
There are at least several popular strapping options that have emerged due to fundamental differences in the design, layout and configuration of houses.
Therefore, before starting work, it is necessary not only to select a specific solution (taking into account the type, volume and features of the heating element), but also to draw up a drawing with installation points for all elements - pump, consumption devices, etc.
In practice, there are 4 types of connections that are most in demand - we will consider each.
Through an indirect heating boiler
At its core, it is a reservoir with a coil connected to the boiler in such a way that the coolant moves in a closed circuit and in no case mixes with household liquid. For this purpose, it has five pipes:
- straight, from container to spiral;
- reverse, providing return movement;
- cold make-up;
- supplying the flow to the point of consumption;
- reverse, leading to the tank.
Attention, for successful circulation of hot water, the scheme also provides for installing the pump strictly on the return pipe. Such an engineering move will prevent overheating of the elements, and therefore helps maintain normal operation. It is important that all installed heated towel rails will be constantly hot, and this is the key to a healthy and comfortable microclimate in the bathroom, as well as the absence of mold and mildew.
Through a storage boiler
This is already a tank with thermally insulated walls, which receives the required volume of liquid from the boiler - 100-1000 liters, depending on the number of residents in the building and their needs.
Its contour is a loop, with a forward feed and a return line. The latter is connected to the make-up pipe, and so that its entry point is behind the shut-off valve assembly. It also houses a pump equipped with control devices.
This solution has two important features:
- The medium that is in the tank has one temperature, and the other that runs along the replenishment line has a second temperature, due to the cooled “return” and/or the effect of mixing layers.
- Heating is carried out solely by adding flow after spending part of the reserves.
When idle, the media cools down very quickly. Therefore, a hot water recirculation system with a storage tank is relevant only for those houses where water consumption is constant and quite high, that is, for multi-storey buildings, but not for country houses.
Using a double-circuit gas boiler
This option is usually chosen when there are a small number of end-use points and when only one type is intended to be used at a time, for example, exclusively washbasins. In such cases, a medium-power flow heater capable of providing up to 20 l/min is also quite suitable. It will turn out to be quite simple (and therefore reliable and durable) and economical.
To install it, you only need to organize the supply of cold liquid to the tank and ensure that the flow of the required temperature is output. Keep in mind that during the run through the pipes the medium may cool down somewhat. Because of this feature, the option is poorly suited for buildings of large area and number of floors.
Installation of a gas boiler with built-in boiler
When you need to organize the circulation of hot water in a private house, a scheme with an integrated heating element is better suited than with a remote double-circuit one. Why? For three reasons at once:
SF-mix manual up to 0.8 m3/h
AMETHYST - 02 M up to 2 cubic meters/day.
Aeration unit AS-1054 VO-90
- heating is more stable;
- It’s more convenient to use plumbing – you can turn on all the appliances and open every tap;
- It is not difficult to create a supply of 40-60 liters of well-warm liquid (albeit gradually cooling).
But there are also disadvantages, and these are:
- large dimensions - a set of equipment and space takes up a fair amount of space and weighs a fair amount, which is not always convenient;
- high cost – implementation of such a solution is relatively expensive;
- serious associated costs - to ensure and maintain the required fluid temperature, you have to spend a lot of fuel.
In practice, these disadvantages outweigh the advantages, so this option is being implemented less and less.
Breakdowns in the hot or cold water distribution system
You can fix the following emergency situations with your own hands:
The valve or faucet is leaking. This happens most often due to wear of the oil seal or seal. To eliminate the malfunction, it is necessary to open the valve completely and with force so that the raised oil seal stops the leak. This technique will help for a while; in the future, the valve must be rebuilt and worn parts replaced.
Noise and vibration of a valve or faucet when opening in a hot water supply system (less often cold). The cause of noise is most often wear, deformation or crushing of the gasket in the gearbox of the mechanism. Noises appear if the tap is not opened all the way. This fault can cause a series of water hammers in the pipes, so its elimination is of utmost importance. The faucet valve is capable of closing the valve seat in the faucet or valve body in a few milliseconds, if it is not a ball valve, but a screw valve. Why is the risk of water hammer higher in hot water supply systems? Because in hot water pipes the operating pressure is higher.
How to fix the problem:
- Shut off the water at the inlet;
- Unscrew the valve housing of the noisy faucet;
- Replace the gasket, but before installing, chamfer the new gasket so that the valve does not vibrate when opening under high pressure.
The heated towel rail does not heat up. The cause of the breakdown may be the presence of air in the water supply system with constant coolant circulation. Typically, air accumulates in a pipe jumper, which is installed between adjacent risers, after an emergency or scheduled drain of water. The problem is eliminated by bleeding the air plugs. To do this you need:
- Vent the air at the highest point of the system - on the top floor;
- Shut off the hot water supply riser located in the apartment (the riser is closed in the basement of the house);
- Open all hot water taps in the apartment;
- After bleeding air through taps and mixers, you need to close them. And open the shut-off valve on the riser.
Hidden faults
At the end of the heating season, the pressure difference between the heating main pipes may not be maintained, and because of this, heated towel rails connected directly to the hot water supply will be cold. This is not a cause for concern - you need to bleed off the air, which equalizes the pressure, and the heating will be restored.
Heating systems with natural circulation
The natural circulation heating system became widespread in the pre-war period due to its efficiency, simplicity and reliability. Most often, this type of heating system is used in dachas, as well as in country houses due to frequent power outages at such facilities. Such systems are conventionally divided into two types - with bottom and top water supply. To determine the choice of the type of heating system, it is necessary to consider their differences, characteristics and scope of application.
Schematic diagram of heating with natural coolant circulation
Heating systems with natural circulation
Ready-made solutions to issues with hot water supply and hot water in housing and communal services
We restore hot water supply in accordance with GOST, SNiP for apartment buildings in Perm and the Perm region.
Water supply cold water supply, hot water supply: Audit. Analysis. Conclusions Recommendations.
6 years for a legal entity, this means that the work will be completed on time, and the guarantee will be fulfilled.
- Boiling water from the tap?
- Frequent burns with hot water?
- Are you running hot water for a long time?
- Slightly warm water?
- In the morning, hot water from the tap is cold?
- Does the hot water temperature change frequently?
- Bad hot water?
We have ready-made solutions to these issues.
We will help you. Call!
Causes of problems with hot water supply
- poor circulation;
- pipeline clogging;
- narrowing the diameter of the pipeline;
- incorrect calculation of hydraulics of metering devices;
- adjustment of equipment settings in the control unit;
- automatic temperature control does not work;
- heat exchanger clogged
- +100 more reasons.
Call us. We will determine the reason.
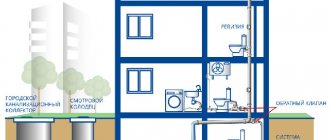
How is the supply of communal hot water arranged in an apartment building?
The principle of operation of hot water supply: Hot water is supplied to apartment buildings according to two schemes:
- Cold water flows to the central heating point - the central heating point. There it is heated to the required temperature of 65-75 C, after which it is distributed to apartment buildings.
- Cold water enters the ITP - an individual heating point of an apartment building. Heat exchangers are installed at the heating point. Cold water is heated in heat exchangers to the required temperature of 63 - 75 C, after which it is distributed among the apartments.
Installation process
Now let's see how to recirculate DHW (hot water) in the house. We remind you that all work must be carried out at the construction stage or at the stage of major renovation of the building, in parallel with the installation of the boiler. We also need to assemble and place the outline correctly, so let's decide what we need for this.
Tools and materials
So, you will need:
- welding machine of suitable performance and configuration;
- grinder, jigsaw or other appropriate tool for cutting pipes;
- fasteners, adapters, fittings;
- plumbing winding;
- Unipak sealant or similar thread paste.
To place the load-bearing elements, it is also worth arming yourself with an impact drill, a hammer drill, and a set of drills.
Equipment
When choosing a DHW scheme with recirculation for a private home, remember that in any case you will need:
- pipes - of different sections and made of various materials, from copper to plastic, depending on the purpose and characteristics of the line;
- three-way and ball valves, valves, reversing valves and other shut-off valves;
- medium or low power pump.
High pump performance is not even desirable, because it needs to provide only a small pressure - to move the flow along the line, but not to make it run quickly. Well, the nature of the execution of communications may require additional work, for example, soldering brass connections.
Installation algorithm
The answer to the question of how to circulate hot water (DHW) in a private home is quite simple. This problem must be solved step by step - in the following order:
- mark the supporting surfaces (usually walls) according to the drawing;
- install brackets, clamps, clips and other load-bearing elements;
- cut pipes along the entire length of the future communication;
- organize the line by sequentially connecting all the necessary adapters and fittings;
- connect the pump, mixers and similar units, as well as shut-off valves;
- provide outlets for the outflow of used liquid.
If a more complex circuit is planned, deviations from the given algorithm are acceptable, but in practice they will turn out to be insignificant and will consist of adding some additional elements, for example, distributors, and flow control and metering devices.
What should the temperature of the hot water in the tap be?
Standard hot water temperature:
According to SanPiN 2.1.4.2496-09 Hygienic requirements for ensuring the safety of hot water supply systems:
The temperature of hot water in water supply areas (washbasins, sinks, showers), regardless of the heat supply system used (from the central heating substation or from the heat exchangers in the heating substation) must be no lower than 60°C and no higher than 75°C.
Important : Do not allow the hot water temperature to fall below 60 °C. If you deviate from this temperature, there is a risk of contamination of hot water with highly contagious infectious pathogens of viral and bacterial origin, which can multiply at temperatures below 60 degrees, including Legionella Pneumophila.
Operation and mode of operation
Operation of hot water supply lines with circulation requires periodic checking of the condition of pumping equipment, removal of air pockets and other necessary actions. However, if the line installation was done correctly, there will be no problems with air locks and pipelines.
In my house
The domestic hot water supply system of a private house is entirely under the control of its owner. This allows him to carry out repairs without regard to the management company or the HOA, but creates additional worries.
The main task is to monitor the condition of the circulation pump , since its failure will cause the hot water supply to stop.
In addition, you have to take care of the performance of boiler equipment and other elements of the water supply system.
In an apartment building
No action is required from the subscriber. All concerns about the condition of the systems and the operation of the pumps are carried out by the specialists of the management company.
Residents of apartment buildings must promptly notify the company of any problems that arise, follow the rules for operating water supply systems, and not install unauthorized elements in the hot water supply lines.
Problems with dead-end hot water supply
- Why does cold water flow from the tap instead of hot water in the morning?
- Why does it take so long to run hot water?
One of the reasons for this problem is dead-end hot water supply. During periods of no water supply, hot water remains motionless in the pipeline. Being in the pipe for a long time without moving, hot water cools down. The water temperature can drop to ambient temperature, in the basement it is 10-15 C. To get hot water, the consumer has to pass the entire volume of water in the pipe and wait for heated water from the heat exchanger.
Solution to this issue:
- Device for forced circulation and recirculation of hot water.
- Reducing heat loss from the hot water pipeline by insulating the pipes.
What it is?
It is impossible to organize continuous heating of water using conventional methods, so a simple and effective method is used - the hot water supply line is looped and the circulation process is started.
The flow leaves the boiler, passes in a circle and returns to the heating container.
All that remains is to adjust the speed of movement to ensure the supply of water at the standard temperature for all subscribers of the line.
Used for movement
circulation pumps
, although in small systems natural circulation is possible.
How can you raise the temperature of hot water?
Raise the hot water temperature by 5 - 10 degrees:
Add a number of plates or section to the heat exchanger.
This option is available:
- If you have your own ITP.
- If you have a first heating circuit of 150/70.
- A plate or shell-and-tube heat exchanger is available.
To do this, it is necessary to make changes to the design documentation. Coordinate the project with RSO, the resource supply organization.
What is the water cycle?
The water cycle on Earth is a natural process, which is a continuous exchange of water between the atmosphere, lithosphere and the World Ocean. During this exchange, the water mass changes its state of aggregation: from liquid or solid it turns into gaseous, and vice versa. During its movement, it takes and transfers a huge amount of organic compounds and mineral elements necessary to support life on the planet.
The largest volume of water mass is concentrated in the oceans (97.5%), so most of the natural liquid contains salt. The remaining 2.5% are fresh sources, of which:
- glaciers and eternal snow – 68.9%;
- groundwater (including moisture in soils of marshy areas and permafrost zones) – 30.8%;
- rivers and lakes – 0.3%.
Water is in continuous movement, and its volume on the planet is a constant value. However, its presence in various states of aggregation changes during the history of the Earth. Many centuries ago, there were much fewer water sources on the planet, since the bulk of the water mass was concentrated in glaciers. Even 20 thousand years ago, along the ice sheet that divided the Bering Strait, it was possible to freely move from Alaska to Asia.
Very hot water! What to do?
If you have overheating of your hot water supply, resulting in a burn with hot water, it means that your home is not configured to operate a shell-and-tube boiler or plate heat exchanger. The heating system is designed in such a way that in cold weather the temperature of the coolant can reach more than 130 ° C (water in the pipes does not boil due to pressure). Accordingly, with low water consumption, the water in the heat exchanger heats up above the standard 75 °C.
To solve problems associated with overheating of hot water, it is necessary to introduce a system of automatic control of the DHW temperature. Automatic hot water supply prevents the water temperature from rising above the parameter you set, and at night reduces overall heat consumption to save energy. An adjustable valve is installed on the coolant pipeline to limit it. In this way, quantitative regulation of hot water occurs.
Private sector
What hot water supply schemes with circulation are used in cottages?
Actually, there are only two basic diagrams: with circulation through the water heater (for this it must be equipped with an additional pipe for connecting the DHW return) and with a thermal mixer. The water is driven by a small-sized pump with a wet rotor.
Closed circuit with circulation pump and boiler with three outlets
Pump for heating and hot water needs with a wet rotor
A three-way thermostatic valve allows you to implement recirculation even if in your home an electric boiler or an indirect boiler with two pipes (DHW and make-up) is responsible for heating the water.
Scheme with a conventional boiler and a three-way thermal mixer
Why is there no hot water?
Sometimes, especially in summer, turning off hot water is due to scheduled work. You can find out about planned hot water outages in news feeds. RSOs are required to publish this information in the media.
Management companies and homeowners associations are required to inform residents in advance about the timing of repair work. Let us remind you that the maximum period for turning off hot water is 14 days.
For questions about turning off hot water supply, residents can contact the Central Dispatch Service of Housing and Communal Services of Perm (057)
Summer shutdown of hot water is a planned shutdown organized by the heat supply organization.
The water is turned off to diagnose heating systems. Heat supply network pipes are checked under high pressure and pressure tested in preparation for the heating season.
We also repair hot water pipelines or replace pipes with new ones. It is advisable to use plastic pipes for hot water to avoid rusty water from the tap. Polypropylene pipes significantly improve the quality of hot water.
Tired of waiting for the water to heat up? Then this article is for you
Whoever gets up first... has to drain the hot water for a long time to wash himself. We learned this simple truth thanks to houses built in the mid-20th century.
Heated towel rails cooling down in the absence of water supply and, as a result, a damp and cool bathroom complete the dull picture. Not everyone knows that both problems have long been solved by engineers. Meet: hot water supply with recirculation!
Calculation
How to calculate hot water supply with circulation?
Let us all turn to the same SP 30.13330.2016. According to Appendix “B” to the set of rules, the circulation flow rate of hot water supply is calculated using the formula Qc=Qht/(p*c*Dt).
In this formula:
- Qc - flow rate through the circulation pipeline in liters per second;
- Qht is the heat loss of the circuit in watts;
Specific heat transfer of a smooth steel pipe depending on the diameter and temperature difference with air
- p is the density of water in kg/m3;
Hint: with a simplified calculation, you can take it to be equal to its density at 0°C - 1000 kg/m3.
- c is the specific heat capacity of water in kJ/(kg*C);
Reference: the heat capacity of water changes as its temperature changes, however, if high accuracy of calculations is not required, it can be taken equal to 4.2 kJ/(kg*C).
- Dt is the target temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the circulation circuit.
Let's perform the calculation for the following simplified conditions as an example:
- The circulation circuit is a smooth pipe 3/4 inch in size and 50 meters long;
- It is heated to 75 degrees Celsius at an ambient temperature of +20°C;
- When passing through the circuit, hot water can cool by no more than 15 degrees.
A nuance: such a range of water temperatures in the hot water system (60-75 degrees) was allowed by SP 30.13330.2012. In the latest edition of the document, published in 2021, the requirements have become more stringent: now hot water cannot be heated above 65 ° C at the same minimum permissible temperature.
The previous version of the document had slightly larger tolerances for DHW temperature
So:
- At a water temperature of 65°C and air temperature of 20°C, the difference on the surface of the pipe will be 55 degrees;
- According to the table above, the heat loss of a meter of pipe under these conditions is 60 W/m, which, with a circuit length of 50 meters and the absence of thermal insulation, will give a total heat loss of 3 kW (3000 W);
- We substitute the data into the formula: Qc=3000/(1000*4.2*15)=0.047 l/s (0.17 m3/hour).
Traditional DHW wiring
The installation of a hot water supply system in Stalinist and early Khrushchev buildings is no different from the distribution of cold water. The only bottling ends with dead-end risers, from which the apartment wiring departs. In the elevator unit, the bottling branch branches into two connections - into the supply and return threads.
Schematic diagram of an elevator unit and a hot water supply system without recirculation
Switching DHW from supply to return is done manually in accordance with the heating temperature schedule:
- When the temperature of process water at the outlet of the thermal power plant is up to 80-90 degrees, hot water is supplied from the supply;
- If 90°C is exceeded, the water supply switches to return water supply.
Hot water enters the house from the supply line. The return valve is closed
Why is this bad?
The advantages of this scheme are low cost of implementation and extremely simple maintenance. There are downsides too.
We have already mentioned two of them:
- Without water tapping, the water in the risers and connections cools down. To wash or take a shower, you have to pour it down the drain for a long time (up to several minutes). For apartment residents, this means not only a loss of time, but also significant costs: in fact, you drain cold water, but if you have a water meter, you pay for it as for hot water;
Advantages of a hot water supply system with circulation and its scope
The practical advantages are obvious:
- the stream is at least well warm immediately after opening the tap;
- It’s easy to adjust the temperature by turning the valve and adding a little cold water;
- there is no overspending - precious liters of liquid do not pour into the drain, because you do not wait for it to heat up;
- with constant use there are no traffic jams or clogging of pipes, and if they appear, they are immediately noticeable;
- a large number of end consumers are seamlessly integrated within one solution;
- it can be implemented on the basis of any heater - storage, indirect heating boiler or double-circuit boiler.
Hence the scope of application is clear. Such systems are relevant for one- and multi-story buildings, in which water treatment equipment is installed in a technical room, away from the inhabited rooms, and/or there are several bathrooms and many intake points. They are in demand at facilities with long communication lines and help reduce fluid losses and increase the efficiency of its heating and use.
Attention, this is a global solution, and therefore its implementation (regardless of the topology) is possible at the construction stage or at least a major renovation. It is futile to modernize an existing and standard plumbing complex - too much money will be required, it is cheaper and easier to implement everything from scratch.
MBFT-75 Membrane for 75GPD
SF-mix Clack up to 0.8 m3/h
SF-mix Runxin up to 0.8 m3/h
Implementation
What hot water supply schemes with recirculation are possible in apartment buildings and private buildings?
Apartment buildings
To create continuous circulation of water, the DHW system needs to be looped.
In apartment buildings this is achieved as follows:
| Image | Description |
The basement is filled with cold water, hot water and heated towel rails.
The riser of heated towel rails serves as a return for hot water supply
It’s interesting: in some houses built in the late 80s, the author observed jumpers between the hot water supply risers, placed in a cold attic. The solution raises doubts about the adequacy of the authors: at street temperatures of -30°C and below, they freeze within an hour after stopping circulation in the hot water system (for example, for emergency repair of a valve in an elevator unit).
It is clear that the described water supply scheme with recirculation will not work without a pressure difference.
How it is provided:
- Outside the heating season, the DHW is switched on between the supply and return lines;
Summer mode: DHW circulation between the supply and return lines
- During heating operation with such a connection, the hot water supply system will represent a bypass for the heating system, catastrophically reducing the drop in the water jet elevator. Therefore, the DHW is connected depending on the temperature of the water from supply to supply or from return to return, and the difference is ensured by retaining washers installed on the flanges between the taps.
Modern elevator unit with circulation connections
Reference: a retaining washer is a steel plate with a hole in the middle. The hole diameter is usually 1 mm larger than the elevator nozzle diameter. When water moves through the washer, a difference of 0.1 - 0.3 kgf/cm is created on it, which is quite sufficient for circulation in the hot water system.
If the risers are airy
What should I do if, after resetting the hot water supply system, the air pocket remaining in the risers prevents circulation and the heated towel rails remain cold?
To bleed air, use the Mayevsky valve at the top point of the jumper. However, to access it you need to get into the upper apartment via the riser, which is not always possible.
Here are simple step-by-step instructions that will help you fix the problem yourself:
- We block any of the hot water supply risers connected by a jumper;
- We open one, or better yet, two hot water taps in any apartment along this riser all the way. The air plug flies out through the mixer at the front of the water flow;
Open the faucet completely and the air will fly out of the riser at the front of the water flow
- We start the risers in normal mode.
Private houses
What hot water recycling schemes can be implemented in a private house with autonomous hot water preparation? Quite predictably, a minimum power circulation pump (from 25 watts) will be responsible for creating circulation pressure in such a system.
Circulation in the DHW circuit can be ensured by a minimum power pump
The DHW circuit must be looped along its entire length: after the plumbing fixture farthest from the water heater, the filling returns to the starting point. But the connection diagram for the water heater depends on whether it has an additional outlet for recirculation.
Diagram for a boiler with a pipe for connecting a recirculation circuit
The presence of three pipes for connecting DHW and cold water is typical for most indirect heating boilers and some storage electric water heaters.
Boiler with additional outlet for recirculation
The closed circuit is supplied only with a circulation pump: since the temperature of the water in the circuit is constant after its start, the problem of thermal expansion of water does not have to be solved, and if so, a safety valve and an expansion tank are not required.
Is it possible to use a regular boiler with two outlets (for DHW and cold water) in such a scheme? Yes, but in this case the wiring will be noticeably more complicated.
Water supply with recirculation: diagram for a boiler with two pipes
- A three-way thermostatic mixer is responsible for maintaining a constant water temperature in the recirculation circuit. As it cools, he mixes in hot water from the boiler;
The three-way thermostat mixer is capable of providing a constant outlet water temperature at any inlet temperature
- To compensate for the flow of hot water, cold water is supplied to the three-way mixer;
- Check valves limit the movement of water in the circuit in one direction, regardless of its flow.
Useful: it makes sense to install an automatic air vent at the top point of the DHW circuit. Air pockets in the presence of a pump will not interfere with circulation, but they can become a source of annoying hydraulic noise.
Problems
Circulation in a water supply system is a process that is quite easy to disrupt. In the next section of the article, we will analyze typical problems that can lead to a stop in circulation and the associated cooling of hot water risers and heated towel rails in an apartment building.
Airlock
- Symptoms: after turning off the hot water, one riser or a group of risers has cooled down. The neighbors' pipes are still heated.
- Reason: air lock in the ring jumper. A pressure drop of 0.2 atmospheres is not enough to force it into bottling.
- Solution: expel air through the vent at the top of the jumper. If this is not possible (for example, due to the absence of residents on the upper floor), you can pass the riser through the basement or water fittings in the apartments.
To do this you need:
- Shut off one of the problematic hot water risers with a tap or valve in the basement;
- If there is a vent on this riser, open it and wait for the air to escape;
The hot water riser is equipped with a vent that allows it to be bypassed from the basement
- If there is not a waste pipe on the riser, but a plug, you can open hot water to capacity on one or two mixers in any apartment located along the same riser;
Air can be expelled from the riser through any mixer connected to it
- After bleeding the air, open the valve or tap at the base of the riser.
Closed valve
- Symptoms: when drawing water, the riser heats up from above due to the hot water supply being inserted into it. It is obvious that water flows to the liner through the ring jumper.
- Reasons: after turning off the riser, the faucet or valve remained completely or partially closed.
- Solution: go down to the basement and open the shut-off valves on yours and the adjacent DHW risers all the way to failure.
With an open ball valve, the handle is always directed parallel to the axis of the body
Valve valve separation
Symptoms: water enters the line through the ring jumper from above. A screw valve is installed at the base of the DHW supply riser in the basement. The arrow on the valve body is directed towards the hot water supply.
The arrow on the screw valve body indicates the only possible direction of water flow
- Causes: valve valve separation from the stem. This happens if you try to open an incorrectly installed shut-off valve of this type, overcoming the water pressure on the valve.
- Solution: replacing the valve with a ball valve (on a steel riser, in this case, you have to change the flow to a longer one), installing a new screw valve in the correct position (with an arrow in the direction of flow).
The riser valve in the photo has been replaced by an assembly with a ball valve
No difference in the heating main
In houses with open heating, the hot water circulation system often stops immediately after the end of the heating season. Symptoms: Cold heated towel rails throughout the house. The reason is that local Heating Networks completely eliminate the difference between the threads of the heating main.
Why is this being done?
The fact is that the heating season begins when the temperature outside is +8 °C or higher for at least five days in a row. Even if after stopping the heating there is a new frost, the heating will not be turned on, since on a city scale, restarting it is associated with colossal costs.
However, residents of a separate house may well, having access to a heating point, turn the heating back on. To do this, you just need to open a couple of so-called house valves (after the water jet elevator) or taps. But in the absence of a difference, this will not lead to the resumption of circulation in the heating system, and, therefore, to unpaid heat consumption.
At the end of the heating season, the DHW circulation may stop for some time.
Unfortunately, there is no reasonable solution for this scenario. All you can do is wait a couple of weeks. As soon as truly spring weather sets in, the circulation-providing difference will return.