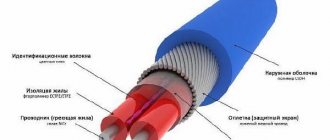
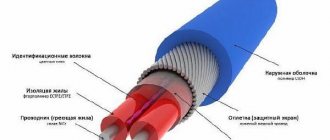
What is an air duct and why is it needed?
An air duct is a pipeline network of a ventilation circuit designed to collect and supply a flow of air masses into a room or discharge them outside.
The numerous functions of air ducts are as follows:
- Balancing air parameters (humidity, temperature, etc.) in one or more rooms.
- Providing an influx of fresh or heated air from outside (recovery).
- Removal of polluted air masses from the premises.
- Organization of a smoke removal system or supply of a special gas mixture that prevents the spread of fire.
Galvanized ventilation ducts
Operating temperature range of galvanized air ducts
is between -40 and +80 degrees. The range expands with increasing mass fraction of zinc in the protective layer. The zinc layer acts as a barrier to accelerate the oxidation of iron as ambient temperatures rise. Therefore, galvanized air ducts have different corrosion resistance depending on the quality of the galvanized layer of metal from which they are made.
In construction, metal rectangular, square and round air ducts made of galvanized steel are most often used for ventilation systems. Plastic, aluminum corrugated, and fabric air ducts are less in demand. For special smoke removal systems, air ducts are made of black steel. Galvanized air ducts
are produced in our production of different shapes of sections. Advice. When choosing the shape of air ducts, do not lose sight of all the pros and cons and design features of the products. For example, round galvanized air ducts, having a simpler and more economical design, favorable aerodynamics, convenience and low installation cost, are limited in application due to the height of the premises. If you have doubts about the choice of air ducts, call our specialists.
Application area
Air ducts are used everywhere:
- Not a single shopping, entertainment or office complex, clinic or kindergarten can do without ventilation and smoke removal systems.
- In industry, scientific and research centers, countless air ducts for various purposes are used.
- The familiar exhaust circuit above the stove is present in every house and apartment. Bathrooms and toilets are equipped with ventilation systems.
Steel thickness of air ducts according to SNiP
Central Research and Design Experimental Institute of Engineering Equipment for Cities, Residential and Public Buildings (TSNIIEP Engineering Equipment) of the State Committee for Architecture
Reference manual for SNiP
HEATING AND VENTILATION OF RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS
unofficial edition
Recommended for publication by the section of heating, ventilation and air conditioning of the Scientific and Technical Council of the TsNIIEP engineering equipment of the State Committee for Architecture
PREFACE
The manual was developed in accordance with SNiP 2.08.01-89 Residential buildings.
The microclimate parameters in the premises of residential buildings and the air-thermal regime established by SNiP are determined not only by the operation of heating and ventilation systems, but also by the architectural, planning and design solutions of these buildings, as well as by the thermophysical characteristics of enclosing structures.
In addition to the above, in residential buildings the microclimate is greatly influenced by the characteristics of the use of apartments by residents.
The combination of these factors determines the operating costs of heat and the level of air-thermal comfort.
Taking this into account, organizing and rationally maintaining air-thermal conditions in residential buildings is a complex task.
However, the current system of regulatory documents, specialized in individual sections of design, does not take this complexity into account.
The design of heating and ventilation systems is carried out in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.04.05-86.
In this case, reference manuals for SNiP, reference books, advisory and other literature are used, containing methods for thermal and hydraulic calculations of systems, instructions for their design, and equipment characteristics.
The listed documents, aimed at specialists in the field of designing heating and ventilation systems, do not address the entire range of issues of ensuring standardized air-thermal conditions in the premises of residential buildings with minimal thermal energy consumption.
Therefore, in compiling this Manual, the main attention is paid to the questions that most often arise among designers and indicate not only the lack of clarity of certain provisions of the standardization, but also the lack in some cases of understanding of the significance of various elements of residential buildings in their air-thermal conditions.
The manual was developed by the TsNIIEP of engineering equipment of the State Committee for Architecture (candidates of technical sciences A. Z. Ivyansky and I. B. Pavlinova).
CONSTRUCTION AND PLANNING SOLUTIONS FOR RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS
1.1.
The air-thermal regime in premises is one of the main factors determining the level of comfort of residential buildings. An unsatisfactory microclimate makes them unsuitable for living.
1.2.
Optimizing the air-thermal conditions of apartments requires their isolation from adjacent rooms in order to minimize the amount of flowing air.
The flow of air into apartments from adjacent apartments and (or) stairwells is one of the main reasons that reduces the efficiency of the ventilation system and leads to an unsatisfactory state of the air environment in apartments.
Taking this into account, the construction part of the residential building project must include planning, design and technological solutions that minimize the possibility of air flowing through the entrance doors to apartments, junction points of enclosing structures, passage of utility lines through them, etc.
1.3.
As experience in the operation of modern mass residential buildings shows, one of the most common reasons for underheating of premises at the calculated heat transfer of the heating system is the actual underestimation of the air permeability resistance of the window filling compared to the regulated SNiP II-3-79** for the window design provided for by the project. This underestimation occurs due to the low quality of manufacturing of window blocks; poor-quality sealing of window blocks into the wall panel; absence of gaskets sealing the rebates or their non-compliance with the design, etc.
To avoid underheating of the premises of residential buildings at low outside temperatures as a result of the above-mentioned factor, it is recommended to conduct random full-scale tests of windows in order to determine their actual resistance to air permeation, characteristic of a specific building area, for example, according to the method of full-scale air exchange tests of residential buildings TsNIIEP engineering equipment.
What materials are air ducts made of?
Ventilation pipes are available in plastic and metal. The latter are presented in models made of aluminum, stainless, galvanized or black steel. Some are additionally equipped with noise-absorbing and heat-insulating materials.
- Steel ducts are fireproof, strong and durable.
One of the disadvantages is the instability of black rolled steel to corrosion processes. However, galvanized products are practically free of this drawback, and stainless steel air ducts, although more expensive, are not at all susceptible to corrosion.
- The main advantage of aluminum models is ductility, which is why they are made flexible.
The low strength of aluminum foil is compensated for during production, due to which the service life of flexible (semi-rigid) air ducts is 10 years. Additional bonuses include anti-corrosion and non-flammability.
- Air ducts made of plastic are an order of magnitude cheaper, but due to instability to mechanical and shock loads, their service life is not so long.
In addition, not all models cope well with transporting hot air, and the flammability of products limits their scope of application. The chemical inertness of plastic to alkalis and acids is a definite plus. This allows the use of plastic pipes in chemical and pharmaceutical plants, and also facilitates the task of sealing the line. Unlike metal, plastic is not susceptible to corrosion and is lightweight, which simplifies its installation. The smooth surface improves aerodynamic performance.
Class H air ducts (normal)
- Leakage coefficient : 1.61 l/sec/m at a pressure of 400 Pa.
- Manufacturing materials : black, stainless, galvanized steel.
- The use of sealant and sealant is mandatory in most cases.
- Scope of application : domestic ventilation, air exchange systems in rooms with a low level of fire hazard.
- Installation : fairly simple installation, it is possible to use flange or nipple connections for air ducts.
Production technology
Steel air ducts of circular cross-section are manufactured in accordance with the standards of SNIP 41-01-2003 and TU 4863-001-75263987-2006. The required configuration is given to the metal sheets using special steel rolling equipment, and welding or the seam lock method is used to connect the workpieces.
Flexible air ducts are produced using a spiral-wound method from aluminum foil folded into 5 or more layers, reinforced with metallized tape or wire. The winding technology and flexibility of products does not limit the length of the latter.
Rigid ventilation ducts are also manufactured using the spiral-wound method. For their production, metal tape (strip) up to 1 mm thick and no more than 13 cm wide is used.
Polymer air ducts are first cut from a sheet blank, then the sheet is rolled up, and its edges are welded under the action of a heating element.
The concept of ventilation ducts
Air ducts are a structural system of pipes of different diameters and cross-sections, which are connected using shaped components. During production, the weight of galvanized steel in the duct is taken into account. The calculator for calculating the circular cross-sectional area takes into account the diameter of the pipe, and in a rectangular product, the important criteria are length and width. The value is multiplied by the length and the volume of air passed through is calculated.
Diversion channels are selected taking into account design features, design requirements, sanitary and construction standards. Small air ducts are made of galvanized steel 0.5-0.6 mm, and large-section bends are made of sheets 0.7-1.0 mm thick. The following types of ventilation are distinguished depending on the internal pressure indicator:
- Class H - normal pressure. Used in ventilation and smoke removal systems. The requirements for tightness are minimal; a certain percentage of losses during transportation of air masses is provided.
- Class P - dense type. It is installed at atmospheric pressure in the channels above 0.6 kPa. The connecting seams are sealed and a locking connection is made.
The weight of a linear meter of a 0.5 mm galvanized round pipe with a diameter of 100 mm is 1.4 kg. Diameters over 400 mm are made from 0.7 mm sheet, a linear meter weighs 7 kg. A powerful flow requires a pipe size of 110 or 120 mm, a meter of pipe weighs 28 or 31.5 kg.
Purpose of products
Industrial production requires the movement of gas, aerosol mixtures or air flows. For these purposes, ventilation ducts are manufactured in accordance with building codes and meet the required standards. Unified connecting inserts, turns and branches are used, manufactured in the factory with an existing quality certificate. Ventilation ducts are used:
- when installing ventilation;
- to remove smoke at the appropriate temperature;
- in case of movement of gas flows to the production site.
Advantages of galvanizing
Connecting elements are made of galvanized steel. In this case, the use of black steel with a thickness of 0.4-1.2 mm is allowed. The production of galvanized steel air ducts provides a large number of standard sizes. The air duct network is constructed from standardized components and branch units. Galvanized steel is used because it has many advantages:
- Attachments can be used for up to 20 years while maintaining quality and without changing their appearance. Pipelines resist corrosion.
- During installation, painting costs are saved; products are installed without the use of a protective primer layer. External air ducts withstand exposure to the sun and precipitation. The products do not require painting due to the attractiveness of the metal.
- During production, the sheets are bent and stamped without damaging the external galvanized coating. The layer remains inseparable, chips and cracks are not observed.
- The material is considered environmentally friendly and has no harmful effects on health.
- The cost of galvanized air collectors is lower than the same products made of stainless steel and other materials.
- Air ducts are durable and have low aerodynamic drag.
- Installation is simple. After installation and during operation, the pipeline does not require complex maintenance. The internal smooth surface does not contribute to contamination of the walls.
- In case of fire, the material does not burn and has a high fire resistance. Channels are installed in buildings of varying degrees of fire hazard.
- The lightness of the material facilitates transportation and reduces transportation costs.
- Air pipelines are made of rectangular and circular cross-section. Each of these types has advantages and disadvantages. During installation, various connections of pipe sections to each other are provided.
Pros and cons of round ducts
Compared to rectangular ones, round ones have a number of advantages:
- More uniform airflow distribution and low aerodynamic drag.
- Lower noise figure.
- Better sealing of the circuit, because the use of long straight sections minimizes the number of connecting elements.
- Lower cost of both the products themselves and installation work, which is facilitated by lower material consumption during production and reduced costs for fittings and fastening elements that prevent the line from sagging.
There is only one drawback - bulkiness. Because of this, the use of round ventilation ducts in small rooms, suspended ceilings and decorative plasterboard boxes is limited.
Checking the tightness of air ducts
It is carried out when a new system is launched or the efficiency of an existing one sharply decreases. The most common cause of air leaks is a violation of the tightness of the joints. Eliminated by repeated application of sealant.
The easiest way to check is visual. However, if there is a branched system with hidden sections, when constructing systems in unique buildings or with increased requirements for tightness, it is not suitable and an instrumental check of air flow and static pressure with smoke in the forced air and the use of portable fans is necessary.
Types and sizes
The manufacturing method predetermines the division of round ventilation ducts into:
- Straight-seam.
- Spiral welded.
- Spiral wound.
Based on their rigidity, products are divided into rigid, semi-rigid and flexible (corrugated hoses). Flexible ones, in turn, are divided into frame and frameless.
On a note! A special advantage of corrugated hoses is the possibility of using them as a fitting connection that changes the direction of the contour.
According to the density coefficient, air ducts are classified as dense (marked “P”) and normal (“N”). This classification predetermines the possibility of using the ventilation duct in a ventilation system with forced circulation.
According to the connection method, flanged and wafer models are distinguished:
- The flange method involves joining individual pipeline elements using bolts and sealing gaskets.
- Wafer-free air ducts are connected like a bandage.
Long-seam (industrial)
A special feature of straight-seam air ducts is the additional structural rigidity imparted by a welded or interlocking seam. Welding provides the ventilation line with the greatest strength and tightness.
The length of straight-seam ventilation ducts is standardized and, as a rule, does not exceed 1.25 m. This complicates the design of the ventilation circuit and requires the installation of fasteners on each connecting block.
The range of diameters of straight-seam circular air ducts is quite wide: from 10 centimeters to 2 meters.
Spiral welded and spiral wound (lock)
Spiral type ducts are only round. They are considered the most effective because... Spiral seams provide strength to the ventilation ducts and increase the aerodynamic characteristics of the air flow.
The diameters of spiral ventilation ducts start from 10 cm and do not exceed 2 m, and standard lengths vary from 3 to 12 meters. Correct selection of the straight contour length will help save on the number of components.
Standard distances
Air ducts are attached to different surfaces:
- ceiling slab
- ceiling trusses or load-bearing elements attached to them
- walls
- floor
When installing the system, the following standards must be observed:
- the distance from round air ducts to the ceiling must be at least 0.1 m, and to walls or other elements - at least 0.05 m
- the distance between round air ducts and communications (water supply, ventilation, gas lines), as well as between two round air ducts should not be less than 0.25 m
- from the surface of the air duct (round or rectangular) to the electrical wires there must be at least 0.3 m
- the distance from the surface of rectangular air ducts to the ceiling must be at least 0.1 m (for air ducts with a width of up to 0.4 m), at least 0.2 m (for ducts with a width of 0.4-0.8 m) and at least 0 .4 m (for air ducts 0.8-1.5 m wide)
- all channel connections are made no closer than 1 m from the point of passage through the walls, ceiling or other structural elements of the building
The axes of the air channels must be positioned parallel to the planes of the ceiling slabs or walls. Exceptions occur when ducts transition from one level to another or in the presence of equipment, protruding elements of the building structure, which do not allow the installation of air ducts parallel to the plane of the building structure.
In addition, it is allowed to install pipelines at a slope of 0.01-0.015 towards drainage devices if the transported medium is prone to condensation.
Tips for choosing
When choosing a suitable duct model, you need to be guided by the compliance of its technical characteristics with the operating conditions of the facility and the design calculation data:
- The area of the room.
- Temperature conditions.
- The chemical composition and humidity level of the transported medium.
- Type of ventilation (natural or forced).
- The power of ventilation equipment and the pressure it creates in the circuit.
- Target airflow speed.
The indicated features determine the material of the ventilation duct, its length, tortuosity, wall thickness and diameter:
- To equip ventilation lines with the function of supplying (removing) cooled or hot air, heat-resistant materials are selected - steel, PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or PVDF (fluoroplastic).
- Polypropylene pipes are resistant to alkalis, acids and organics. They will also withstand heat from a kitchen stove. This allows them to be used when installing a kitchen hood.
- When installing air ducts in rooms with high humidity (baths, saunas, swimming pools, etc.), priority should be given to plastic or stainless steel.
- For laying vertical contours, only rigid structures are used.
- When purchasing flexible or semi-rigid corrugated hoses, their stretched length is taken into account.
- In semi-basements and basements, only rigid pipes are used.
To determine the diameter of the ventilation pipeline, various formulas and tables are used.
Mandatory requirements
When installing air ducts of different types, the following requirements must be strictly observed:
- Flexible channels are fully stretchable
- sagging of channels due to possible loss of pressure is not allowed
- it is necessary to ensure that the channels are grounded to remove static charge
- flexible and semi-rigid ducts can only be used up to a height of 2 floors
- in the basement areas of buildings, basements, crawl spaces and other places of possible contact with the ground, only rigid channels can be installed
- the air path inside the channel has a spiral configuration, which should be taken into account when designing the system
- the turning radius of the channels must be at least twice the diameter of the pipe
- passage through walls is carried out only with the help of special devices
- the use of an air duct damaged during installation is not permitted
Installation is carried out according to one of two options:
- each room has its own air duct
- a single air duct with branches for all rooms is installed
The choice of the most convenient option is determined by the configuration of the premises, the location of the rooms and the features of the placement of equipment, structural elements, the position of communications, etc.
approximate price
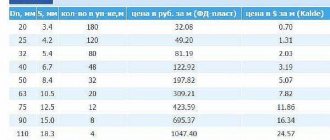
The cost of air ducts depends on a number of factors: the structure of the material from which it is made, the production method, dimensions and manufacturer.
| Brand | Manufacturer country | Type | Material | Diameter, mm | Length, m | Price, rub |
| Diaflex | Russia | Flexible, insulated | Aluminum foil and glass wool | 315 | 10 | 5550 |
| DEC | Netherlands | Flexible, semi-rigid, spiral wound | Aluminum and polyester | 100 | 3 | 500 |
| Era | Russia | Hard | PVC | 125 | 1 | 160 |
| — | Russia | Rigid, straight-seam | Galvanization | 150 | 1 | 320 |
Why is thin steel used and why shouldn’t it be done?
For air ducts of various sizes, some unscrupulous manufacturers use steel thinner than necessary. As a result, the walls are “underestimated” in their thickness by up to 1-2 mm. This is done for a banal reason – dumping. So if the cost of the air duct is unreasonably low, then there is a possibility that thinner steel was used than required by SNiPs.
Installing air ducts made of thin metal is already considered a violation. This is a threat to the lives of people inside the building. “Thin” ventilation will either quickly fail or simply work extremely ineffectively. The reason is simple - air flows moving inside the box place a high load on the thin walls, as a result of which the latter fail.
Consequences of using thin steel for air duct:
- Air loss – inefficient operation of the entire system + constant noise and high vibration
- Rapid appearance of corrosion on the surface of the pipeline itself
In a word, repairing air ducts is not only a considerable expense for the repair itself, but also for the downtime of the entire ventilation network. Therefore, you need to carefully select air ducts and shaped elements, not make questionable savings, and check the compliance of the supplied products with the standards.
Which is better for ventilation: round or rectangular duct
If the question posed is answered from the point of view of efficiency, then round ones are certainly better. Comparing the throughput with the same cross-sectional area, the round ones win. Due to minimal resistance, the speed of movement of air masses in them is higher. In rectangular ones, unnecessary vortex flows are created at the corners, reducing speed indicators.
If you prioritize aesthetics, then rectangular air ducts are beyond competition. They are compact and not conspicuous, and if necessary, they can be hidden, easily hidden under a suspended (suspended) ceiling. However, to compensate for the lack of speed, you should choose models with a diameter slightly larger than the calculated one, or you will have to force ventilation.
Shaped elements
Standard unified connectors are used to install an air duct of the required configuration. Sometimes circular sections are connected to rectangular ones, which requires branching into two or more routes.
Increased demands are placed on the docking sections, since they are located in areas of increased turbulence (at turns or diametrical transitions) and carry an increased load. Any change in the geometry of the air duct is carried out using shaped elements. Standard types used:
We recommend that you read: Bathroom hood
- round and rectangular bends for turning the direction of the route, available at 15, 30, 45, 60 and 90°;
- transitions from one pipe diameter to another;
- tees provide branching of lines and connection of two air ducts into one line;
- a round nipple is used to connect pipeline sections (inserted inside);
- the coupling connects sections of a round pipe and is placed over the joint;
- a rectangular insert is used to join two lines at an angle;
- the cross connects rectangular and round air ducts at an angle of 90°;
- a duck (S-shaped element) is used to connect lines that do not coincide in plane or axis; there are options for combining pipes of different diameters;
- The plug is placed at the end of the channel and closes it hermetically.
Installation Tips
Construction requirements for the installation of air ducts are set out in SP 60.13330.2016. and SP 73.13330.2016.
Let's consider the main aspects:
- The assembly begins with large straight sections, which are then joined together using shaped elements (adapters, corners, tees, etc.).
- Flexible and semi-rigid corrugated hoses are installed while fully stretched.
- To avoid sagging, every 1-1.5 m the hose is fixed to the support using traverses, hangers and clamps. The fastening system is selected depending on the load (see photo).
- The number of turns and bends should be kept to a minimum, and the angle of rotation itself should be 2 times the diameter of the ventilation pipe used.
- The holes in the walls and ceilings through which the main line is laid are pre-lined.
- The seams are treated with sealant.
Important! Aluminum structures tend to accumulate static electricity and therefore require grounding.
Rules for installing galvanized ventilation
The laying of ventilation ducts from thin-sheet galvanized steel takes place in stages.
- The links are assembled into blocks. Sealed.
- Fasteners are installed on the mounting plane.
- The prepared blocks are lifted and fixed in a given position using galvanized punched tape.
- The blocks are connected into a single network.
- If necessary, work is carried out on thermal insulation and decoration of the highway.
The thickness of the punched paper tape is selected depending on the weight of the elements (from 0.55 to 0.7 mm).