To begin with, I would like everyone to understand that a pipe inch is not a normal inch from the length notation system, and there are so many inches in the world that you can get confused with them, for example, if you convert inches to millimeters, it will look like this:
1/2 inch = 12.7 millimeters;
3/4 inch = 19.0 millimeters;
1 inch = 25.4 millimeters.
We looked - and now forget about these dimensions, since they do not correspond to real ones (this applies specifically to pipes) since they will be converted into other values, as read below.
It is worth noting that steel pipes for water and gas (water and gas) must comply with GOST 3262-75, but in this GOST you will not find a word about inches. I will return to the figures of this GOST later, but for now I would like to give an excerpt from the dictionary why such a discrepancy occurs:
The traditional designation of the diameters of water and gas pipes in inches does not directly express either the outer or inner diameters of the pipes. This designation is closer to the designation of the nominal diameter of pipeline elements, which can be expressed both in the Anglo-American inch and in the metric European system.
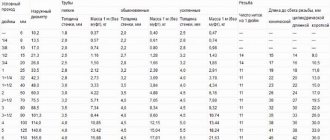
Also, there are no formulas for converting inch pipes to metric pipes, there is only a correspondence table, and data must be taken from it.
Here are the parameters these pipes contain:
Pressure classification
What is an inch?
what is 1 inch equal to? Since a certain pressure is created in the pipeline to transport the medium, polypropylene pipes have this classification. There are four categories:
- PN10. Working pressure 10 Bar (1 MPa), maximum temperature +45°C. For cold water and low pressure systems.
- PN16. Withstands pressure up to 15 Bar (1.5 MPa), temperature up to +60°C. Also for cold water, but can also be installed in high-rise buildings.
- PN20. Pressure 20 Bar (2 MPa) and heating up to +75°C. Usually these are reinforced pipes, but with a small wall thickness. Used for hot water supply.
- PN25. The most durable pipes. Working pressure 25 Bar or 2.5 MPa, long-term heating up to +95°C. These are exclusively reinforced, and with a thick wall. They are used for hot water supply with unstable pressure (in high-rise buildings) and for heating distribution.
The presence of reinforcement is visible on the cut. To make the fiberglass visible, it is tinted. Any colour
If we talk about which PPR pipes can withstand what pressure, then single-layer pipes (without reinforcement) can be used up to PN20. The difference is in the wall thickness and this can be seen in the table. The outer diameters of polypropylene pipes do not mean anything (first column). The same external dimension can be designed for different pressures. It depends on the wall thickness and the presence/absence of reinforcement. So pipe marking is mandatory. The pressure class is indicated there.
| Outer diameters of polypropylene pipes, mm | PN 10 | PN 20 | PN 25 | |||
| Inner diameter, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Inner diameter, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Inner diameter, mm | Wall thickness, mm | |
| 16 | — | — | 10,6 | 2,7 | — | — |
| 20 | 16,2 | 1,9 | 13,2 | 3,4 | 13,2 | 3,4 |
| 25 | 20,4 | 2,3 | 16,6 | 4,2 | 16,6 | 4,2 |
| 32 | 26,0 | 3,0 | 21,2 | 5,4 | 21,2 | 3,0 |
| 40 | 32,6 | 3,7 | 26,6 | 6,7 | 26,6 | 3,7 |
| 50 | 40,8 | 4,6 | 33,2 | 8,4 | 33,2 | 4,6 |
| 63 | 51,4 | 5,8 | 42,0 | 10,5 | 42,0 | 5,8 |
| 75 | 61,2 | 6,9 | 50,0 | 12,5 | 50,0 | 6,9 |
| 90 | 73,6 | 8,2 | 60,0 | 15,0 | — | — |
| 110 | 90,0 | 10,0 | 73,2 | 18,4 | — | — |
Please note that the wall thickness in the third column - PN25 - is less than in the previous ones, although the pipes are designed for higher pressure. It's not a mistake
It's just that the pipes here are only reinforced. And in the previous two categories the wall thickness and diameters of polypropylene pipes without a reinforcing layer are indicated.
Thread types
Thread characteristics
Inch
A thread as such is a sequence of helical grooves with a constant cross-section and pitch, which are applied to cylindrical or conical surfaces. Threads are used to make threaded connections for pipes for various purposes.
The thread is characterized by such indicators as:
- Diameter units
- Location
- Profile of thread-forming surface
- Direction
- Number of thread starts
Pipe thread is a fairly separate group of standards that regulate connection parameters using pipes made of various materials. Below we will look at several types of pipe threads.
Diameter of polypropylene pipes
Depending on the purpose of installing the system, the choice of brand, as well as the diameter of polypropylene pipes, directly depends.
The design of a heating pipeline is carried out based on the results of hydrodynamic calculations. Usually you need to choose the smallest possible diameter for successful operation.
Consider specific application examples of different sizes:
- From 200 mm. Scope of application – buildings designed for a large number of people (this could be a shopping center, store, hospital).
- 20-32 mm. Such a pipe is more often used in small construction work - private houses, etc. Good throughput and ease of shaping into any shape are the distinctive characteristics of this diameter range.
- The implementation of water supply is carried out using polypropylene with a diameter of 20 mm. The risers are mounted with pipes 25 mm in diameter.
- Heating systems use 25 mm PP pipe - the most common practice in centralized solutions. In stand-alone circuits, the size may vary.
To make it more convenient for you to familiarize yourself with the diameters of polypropylene pipes, read the following tables.
Pipes made of polypropylene base appeared on the market not so long ago. But they have already become quite common, both among owners of private buildings and among those involved in industrial facilities.
This is explained by the low price not only of the products themselves, but also of all their components. In addition, it is easy to select the desired diameter of polypropylene pipes for water supply.
Pipeline systems for water supply made of polypropylene are used not only in domestic buildings, but also in agriculture, industry, external pipelines for water supply, sewerage, and water supply.
There is the following classification for polypropylene pipes:
- PPs
. A special variety in which the internal environment moves while maintaining a temperature of 95 degrees - PPR
. The most common variety. The basis is a random copolymer. Conducts cold and hot water. Suitable for underfloor heating, conventional radiators. - PPB
. Block copolymer product. Relevant for systems that carry cold water, air, and heated floors. Polypropylene pipes have their own internal diameter. - PPH. The base is homopolypropylene. The strength characteristics have been improved; it is used in ventilation shafts, cold water supply, and in various industries.
Mixed sizes
Mixed is a complex size that consists of two simple, unequal sizes - bilobed and trilobed. The most common sizes you can find are 5/4; 7/4 and 5/8; 7/8.
In Rimsky-Korsakov's opera The Snow Maiden, the final chorus is in meter 11/4. The size is weird and rare. To make it easier for musicians to calculate and get used to it, they suggest first practicing the phrase “Rimsky-Korsakov has gone completely crazy.” This phrase consists of 11 syllables, which correspond to 11 beats. The phrase falls easily on the ear and after it the musical text is much easier to learn.
Sizes 5/4 and 5/8 are five-part. In essence, they are the same, but in the first case the pulse moves in quarters, in the second - in eighths. Since this is a complex size, it consists of several simple ones:
If a work is written in a mixed size, then in parentheses, as a rule, it is indicated which simple sizes it consists of. In the image below, the first measure is the sum of 2/4 + 3/4; the second is 3/4 + 2/4.
The location of the relatively strong beat depends on how the sequence of simple sizes changes within a complex one. In the first measure, the relatively strong beat will be the third, in the second - the fourth. The emphasis within the measure, and therefore its rhythmic organization, depends on the location of the relatively strong beat.
Sizes 7/4 and 7/8 are seven-lobed. They consist of three simple sizes, two of which are bilobed and one is trilobed.
A three-beat is usually used at the beginning or end of a measure, less often in the middle. Asymmetrical meters are most often found in the music of Russian composers, as well as in folk music. It is difficult for an unprepared listener to perceive such music, however, the Pink Floyd group composed the song “Money”, the motive of which is easy to hear and memorable.
https://earsfingers.ru/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/7-money.mp3 It’s clear - it’s simple205It’s really hard105
Converting inch to metric sections
The corresponding tables can be found in reference books. The same GOST, which defines the parameters of the VGP, contains indicators of conditional throughput in millimeters and inches. However, to create a functioning system, indicators of the actual internal cross-section are needed. In this case, as a rule, only external sections can be found in the tables.
Ideally, the table will include the nominal capacity values in inches, the external cross-section of the pipe and the corresponding cross-section in millimeters.
For example, a one-inch steel pipe can be connected to a plastic one, the nominal throughput of which is 25 mm.
Reliability
There is an opinion that ratchets with a large number of teeth are less reliable and break easily.
This is partly true, but it all depends on the manufacturer and the quality of the ratchets.
Tools with more teeth use slightly different locking mechanisms.
To see this, we disassemble models with 24 and 72 teeth.
This is quite easy to do, just unscrew the fixing bolts using a suitable star-shaped attachment.
The 24 tooth option is the one we considered second, it has a large pitch.
In the analysis, we see a locking mechanism in the form of two plates, supported by springs, which cling to 1 tooth of the gear, each on its own side.
When turning in one direction, one locking plate works, and when reverse is turned on, the rotation already goes in the other direction, and another locking plate works.
In a tool with 72 teeth, you can see that the teeth are noticeably smaller and of course there are more of them.
The locking plates here have a more complex shape, and they cling to 3-4 teeth.
In this example, it is clear that the locking mechanism differs in the number of hooks, and reliability in such cases depends not so much on the number of teeth, but on the quality of the materials.
In one case, for example: a ratchet with 72 teeth can withstand much more load than models with 24 or 15 teeth, and in another case, vice versa.
It depends on the material and how quickly the teeth wear off.
Now you know the differences between different ratchets, and you can choose the most suitable option for yourself.
Nuances of choice
The main parameters when choosing a liner are dimensions and service class. But there are a number of nuances that should not be overlooked.
- It is necessary to take into account not only the diameter, but also the type of thread (cylindrical, conical, metric). It can be found from documentation or measured.
- The total length of the threaded section of the fitting must be no less than the length of the threaded pipe of the connected device or the end of the pipe. At the same time, for a reliable connection there must be at least 5-7 turns of thread, and the optimal parameters are indicated in GOST standards for each standard size.
- For maximum compatibility, it is better to buy all pipes and fittings of the same brand and from the same manufacturer - such equipment is made to the same standards and is already adjusted.
- To switch to the desired size or standard of thread, sometimes you may need not one, but several futurki, connected to each other, like nesting dolls.
- Material compatibility must be taken into account. For cast iron pipes and batteries, only cast iron adapters are suitable, for copper pipes - made of brass or copper. For plastic ones, an adapter made of the same type of polymer as the pipe must be used.
- The fitting must have clearly visible markings containing information about the size and service class. “Unnamed” footwear causes distrust among many experts.
Ripple
In - inch. unit converter
The first concept that needs to be introduced is the pulse of a piece of music.
You've probably noticed that music is often described as something alive: cheerful, frivolous, thoughtful, determined. Indeed, music has a number of qualities characteristic of a living organism, such as character and mood. But the main thing is that in music, just like in a living organism, the pulse beats. You've probably been to concerts and clapped in time with the whole audience at the same time. This happens precisely because people feel the pulse of music.
Like the human heart, the pulse can slow down or speed up, but it beats evenly and continuously throughout the entire work.
Let us remember: pulsation is the uniformity that provides musical movement.
Calculation of diameter for autonomous heating
Questions about how to choose the diameter of polypropylene pipes for heating appear during installation
Calculation of the diameter of a polypropylene pipe for heating
contours in private homes. Let us note right away that the calculations are approximate, but this does not mean that they are incorrect. They can also be used for the circuits of apartments with central heating. Determining parameters of the diameter of a polypropylene pipe for heating a private house:
area of the heated room.
This determines how much heat is required to heat to the required level. In order not to delve into the jungle of formulas, you can follow the general example and take into account 0.1 kW of energy per square meter, with a standard ceiling height of 2.5 m. Of course, you need to take into account the degree of insulation of the room, based on which the heat loss coefficient is calculated. But in order not to get confused, we simply add 20% to the required number of kilowatts;
coolant speed.
This figure varies from 0.2 to 1.5 m/s. The higher the flow rate, the higher the pressure in the circuit. This often leads to noise in the system due to friction of the coolant against the walls. To calculate the diameter of pipes, it is customary to use a value of up to 0.6 m/s - optimal for autonomous circuits of private houses. The circulation speed also depends on the diameters of polypropylene heating pipes selected. The thicker the contour, the slower the water flows;
difference in supply and return temperatures.
The indicator is quite individual. It depends on the power and on the material of the pipes, their insulation, as well as on the speed of the coolant. The standards determine that the supply is carried out at a temperature of 80 degrees, while the return flow will be about 60 degrees. The coolant cools by 20 degrees, this value is usually taken into account.
What diameter of polypropylene pipes should be used for heating a one-story house with an area of 80 sq.m:
- the formula contains two constant values, multiplying which we get the value 304.44;
- then this number needs to be multiplied by 9.6 (80 sq.m x 0.1 kW of energy + 20% reserve), it comes out to 2100.636;
- divide the obtained result by 20 (temperature difference) and 0.6 (m/s, coolant flow rate);
- at the end we calculate the square root of the obtained value and get the value 13.23 mm.
Wall thickness of polypropylene pipes of different diameters
It turns out that the internal diameter of polypropylene pipes for heating a house with an area of 80 m2 is 13.23 mm
Please note once again that polypropylene pipes are marked according to their outer section. The marking also contains information about the wall thickness
You can calculate the conditional passage in one step, easier than a steamed turnip. You can also use the table of the ratio of pipe walls to their diameter.
Based on this, we can conclude that in this case a pipe with a diameter of 25 mm is suitable, since the twenty is a little short. For the calculation, we took a coolant flow rate of 0.6 m/s, although a value of 0.2 m/s is allowed. Accordingly, by choosing a pipe with a larger cross-section, we reduce the circulation rate, while it remains within the standard.
Existing thread cutting methods
Pipe threads are applied in the following ways:
- For cutting internal and external profiles, special metalworking tools - taps and dies - are used. This cutting method is often used by amateur plumbers in self-installation of household pipelines.
- Cutting using the knurling method is used for metal water and gas pipes with a diameter of 10 mm - 65 mm. The resulting profile is characterized by high accuracy.
- The workpiece is processed with special cutters on lathes. Using this method, pipe threads of any diameter are applied.
The first two methods are most often used in household utilities, the third is used in the construction of industrial pipelines.
Inch sizes - a little history
The following types of pipes are most often used for indoor water supply networks:
- metal - steel, copper or brass;
- plastic;
- metal-plastic (combined).
Water pipes made of various materials differ in the classification of measurement measures.
The dimensions of the water pipe are set by the following parameters (see Fig. 1):
- D n
- outer diameter; - D in
- internal; - h
is the wall thickness.
In the former USSR, in the apartments of unprivileged citizens there were only steel pipes, for which an original system for designating their sizes was invented. For example, a half-inch pipe has a half-inch (12.7 mm) internal diameter. Its outer diameter and thread diameter, respectively, are about 21 mm. Therefore, for carving, the word “pipe” is necessarily added. In our example: 1/2" pipes.
Popular manufacturers
In addition to the dimensions of the tool, the choice is difficult due to the many brands. Everyone knows that every manufacturer has both strengths and weaknesses.
Popular manufacturers include Valencia. This is a Melbourne brand specializing in the production of classical and electric-acoustic guitars. The biggest advantage of this company is maintaining quality at a relatively low price. Cheapness is achieved by assembling instruments in China and Indonesia. The most famous 3/4 guitars are the Valencia-104 and Valencia-204.
The instruments from this manufacturer are perfect for beginners, as they have a wide neck and nylon strings. This makes clamping the frets much easier. The Barcelona-CG11 series is most often found in stores.
Stagg specializes in the production of 3/4 size electric guitars. Guitars from this brand are easy to tune, the strings are located low to the neck, which does not require serious effort while playing. They are also easy to customize, and the design adds comfort to use. The Stagg S300 guitar is more popular among the others.