Classification of wood stoves
Wood-burning stoves differ from each other in such parameters as:
- material;
- operating principle;
- design features.
Wood burning stoves in terms of material
Most often, wood stoves are made of cast iron, steel or brick. The surface of these heating devices is smooth and quite attractive in appearance, thanks to which they fit well into the interior of any room.
The stove, made of metal, is equipped with a special door made of fireproof glass, which allows you to control the combustion process and add fuel in a timely manner.
Cast iron stoves are a kind of rarity; now they are very rare, mainly in villages. Such devices are beautiful, they smell of antiquity and some kind of rural romance.
Brick stoves are a “classic of the genre.” They are the ones that are most often built in our country in the form of high, almost to the ceiling, structures, lined with tiles. Such heating devices take a long time to heat up, but they also take a long time to cool down, keeping the room at a comfortable temperature for a long time. Therefore, it is worth finding out what types of bricks there are and their features.
Types of stoves according to operating principle
- traditional devices operating up to 5 hours;
- long-burning stoves, structurally more complex and capable of heating a room over a long period of time. This becomes possible by controlling the combustion intensity by adjusting the air supply.
Types of furnaces depending on design features
If you look at wood stoves from the point of view of their design, the classification will be as follows:
- heating;
- heating and cooking;
- fireplaces;
- ovens with a water circuit.
As the name suggests, wood-burning stoves are used exclusively to heat indoor air. The second type, that is, heating and cooking stoves, allows you to heat a room and cook food. Fireplaces are not just a heating device, they are a real decoration of the interior, a kind of “highlight”, the central element of the room, where it is so pleasant to gather with the whole family and share news.
Devices with a water circuit are used for heating the room and for heating water. Such devices are especially popular in places where there is no centralized hot water supply.
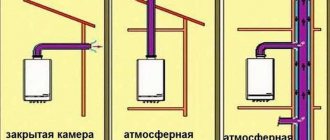
What is a chimney heat exchanger, why is it needed and how does it work?
A heat exchanger (or convector, or economizer, if water is heated) is a part that is installed on the chimney. Hot smoke passing through the chimney heats it. A heat exchanger can heat air or water with this heat.
Since the hottest section of the chimney is the first meter at the outlet of the stove, ideally the convector should be installed here. If the chimney is not very long and runs without bends, then heating is also possible further from the firebox. For example, in this way you can heat a room or attic on the 2nd floor above the room with the boiler.
This is what the stove firebox and the beginning of the chimney look like in a thermal imager
For full heating or instead of the “main” hot water boiler, a heat exchanger is not used - it will produce too little heat. But it is quite suitable for additional heating, since it is cheap and does not consume electricity. In fact, it does not allow you to simply lose the heat that a stove produces (solid fuel, or gas, or exhaust - any except an electric boiler).
For which chimneys can it be used?
For any solid fuel (wood, pellets) or gas boilers. This could be a sauna boiler, or a potbelly stove, or a fireplace in the room.
The main thing is that the chimney should be in the form of a metal pipe and not covered with anything. That is, if you have a brick fireplace with a brick rectangular chimney, you won’t be able to install such heat exchangers on it (you can use fireplace ventilation grilles instead).
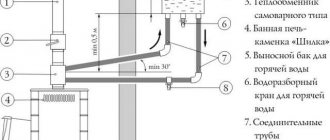
Rules for installing a chimney for a wood stove
It is better to place the chimney closer to the ridge. If this is not possible, you can mount it into an external wall, additionally protecting it with a layer of thermal insulation to prevent freezing during the cold season.
When choosing a material for making a pipe, you need to prioritize its properties such as fire resistance, resistance to corrosion and exposure to aggressive environments. It is also necessary to select the correct shape of the chimney, since the draft force depends on it. The optimal solution is a chimney with a round cross-section, because if the cross-section is square, the draft decreases, and soot will accumulate in the corners. Worry about methods and means for cleaning chimneys.
To ensure easy timely maintenance of the chimney, it is recommended to make its internal surface smooth. It accumulates less soot, which prevents combustion products from escaping and can even lead to a fire.
Those parts of the smoke exhaust duct that come into contact with the ceiling elements must be finished with metal plates to increase the level of fire safety. If there are wooden buildings located near the outer part of the chimney, you cannot do without a spark arrester.
Chimney diagram for a stove or fireplace
In our view, the chimney diagrams of a stove or fireplace are created only to discharge substances that are formed during the combustion process into the atmosphere.
The operation of any heating system, boiler, or fireplace is similar to the operation of an internal combustion engine. Changes in the amount of incoming air or fuel affect the heating power of the device and its unstable operation.
Examples of chimney location.
If we consider in general terms the operation of a fireplace or stove, then the chimney appears as part of a looped system in which combustion products are discharged into the air through it, creating a discharged zone in the receiving part of the fireplace or stove, into which, in turn, the next portion of air is sucked. Oxygen together with fuel, turning into combustion products, are removed from the installation due to the temperature difference, and the cycle repeats.
Today, according to the principle of construction, there are 3 main types of design of chimneys for stoves and fireplaces:
The rules for constructing these chimneys are similar, but there are certain features that need to be taken into account.
Chimney diagrams
With a similar external device, chimneys can differ greatly in the internal layout of the combustion product exhaust channels. In the explanatory drawings, blue arrows will show the movement of smoke, and red arrows will show the firebox itself and the walls of the chimney.
Direct smoke exhaust diagram
Rice. 1. Straight chimney.
Perhaps the first device for removing smoke from the combustion zone that people began to use was a straight chimney (Fig. 1).
The smoke began to be removed, but the heat also went away with it, which was a very serious drawback when trying to use such a system for heating rooms.
Taking into account the characteristics, such a chimney is installed mainly in stoves on which food is prepared, such as hobs, outdoor complexes, and can also be part of a fireplace that is not used for heating.
Horizontal chimneys
To obtain the maximum amount of heat from the exhaust smoke streams, the length of the chimney began to be increased. The advantage of such a system is undoubtedly: hot gases, passing through the horizontal sinuses of the chimney, give off their heat to them. However, along with the smoke, solid particles of combustion products fly - ash, soot, which settle in the chimney, primarily in horizontal sections, eventually clogging the outlet channel. This naturally increases the resistance to the smoke flow and reduces the draft of the channel. To clean this kind of deposits, during the construction of the chimney it is necessary to provide cleaning hatches or knockout bricks in it, which can be mounted on any side. The need for such cleaning is a major operational disadvantage of this smoke exhaust system.
Vertical chimneys
- single-turn, in which the smoke goes down 1 time;
- multi-rotation, when the smoke repeats the movement from top to bottom several times.
Multi-turn chimney: a - vertical; b - horizontal.
The disadvantages of this scheme are:
- high resistance of the channel to exhaust combustion products;
- uneven heating of the pipe (the first channel from the firebox warms up more than the last one).
Uneven heating causes damage to the integrity of the chimney walls. With high resistance of the smoke exhaust channel to combustion products, the draft weakens, which causes smoke in the room from the stove during lighting. In order to avoid smoke, arrange a direct channel into the pipe and install a damper on it. The specified valve is opened when the furnace is lit, as a result of which the smoke is discharged into the open nearby channel. After the stove has warmed up and draft appears (after 5-10 minutes), the damper is closed, as a result of which the main smoke exhaust circuit begins to work.
To eliminate or minimize the disadvantages of such a scheme, they began to use a single-turn multi-channel chimney scheme. In rooms with such stoves, there is a pronounced difference in the temperature of the floor and ceiling surfaces, as a result of which it is unpleasant to be in such buildings. To avoid such discomfort, stoves with bottom heating are used.
Vertical chimneys with bottom heating
In a device with such an exhaust design, hot gases from the furnace are initially directed to the lower part of the furnace. As a result, it heats up, and the gases then enter the chimney. The temperature difference between the floor and ceiling in buildings with heating according to the above diagram does not exceed a few degrees - this is normal.
Direct-flow chimneys with splits
Fire safety requirements for furnaces.
A direct-flow smoke flow exhaust system with cuts is also used. It is used in gas-fired ovens.
The exhaust system used ensures that in the event of an accidental leak, the gas will not explode. It will simply exit into the chimney, where there are no stagnant zones allowing gas to accumulate.
In a chimney arranged according to this scheme, the smoke flow, after exiting the combustion zone, initially flows through a horizontal channel, after which, passing between the cuts, it heats the walls of the furnace. In the upper part, the gases, already cooled, pass into the chimney channel.
Counterflow chimneys
The design of such chimneys is similar to a multi-turn one, but differs in that the channel through which the exhaust smoke flows descend is wider and, accordingly, the speed of movement of gases in it is lower. These circuit features provide more uniform heating.
Smoke exhaust hoods
For the first time such a scheme was used in a Russian stove. In it, the hottest combustion products rise to the roof of the furnace and heat it. The cooling gases descend, pass through the threshold and go into the chimney channel. In this model, free movement of combustion products occurs, and the draft of the chimney does not affect this process. The main disadvantage of smoke removal in a classic Russian stove is the non-use of bottom heating.
Double-bell schemes
To eliminate overheating of the horizontal ceiling, the stove chimney is made into 2 tiers (Fig. 12). The overlap of the lower hood heats up the most in it.
The advantages of a two-bell chimney exhaust: low resistance to exhaust combustion products, the presence of lower heating, uniform heating and a gas view.
The two-bell chimney scheme is considered the most optimal.
The above diagrams of chimneys can be used depending on the stoves, fireplaces or boilers installed.
Types of heat exchangers for chimneys
The main difference between such devices is what they heat. There are 2 options:
- Air. It only heats up in the room where the heat exchanger is located.
- Water. In this case, the economizer is located on the chimney pipe, and 2 pipes are connected to it. One at a time, cold water comes in. According to the second, the heated one is removed.
Below we will consider the types of such products in more detail.
Coil (for heating water) (+ video with a corrugated coil)
The simplest water economizer has the form of a coil (a pipe “wound” many times around the chimney). Water is supplied from one end of the pipe, passes through a coil, and exits from the other end. Heating occurs due to the large contact area of the coil with the hot chimney. The more turns, the larger the contact area, and the better the heating.
It is this type of heat exchanger that is easiest to make with your own hands. For work it is better to use a copper tube.
Disadvantages of this option:
- It will not be possible to regulate the water temperature.
- It is difficult to calculate how long the coil should be - because the temperature of the chimney is not constant. A coil that is too short can break (the water will just boil). Too long and will not heat the water properly.
Registered (for heating water) (+video)
Factory product. In fact, it is the same copper coil, but enclosed in an outer casing and manufactured according to calculations. That is, the length is not chosen at random, unlike a homemade coil.
Also, with register heat exchangers, the copper tube does not come into contact with the chimney, but passes at a short distance of a few millimeters. This reduces the likelihood of water boiling. And the outer casing looks more beautiful indoors and improves the heating of water in the coil.
Air heat exchanger
The simplest option is to weld steel pipes 0.5-1 m high around the chimney.
Cold air is “heavier” than warm air and sinks. In contact with a hot pipe, it heats up and rises, “giving way” to cold air from below.
In principle, the air in the room is heated in the same way by the chimney itself. The purpose of a convector (welded around pipes) is to increase the heating area. The larger the area, the more heat it will give off to the air.
Theoretically, it is possible to create an air heat exchanger by running empty pipes directly through the firebox, or through the chimney inside. But in practice this is harmful because:
- you can worsen cravings if you do it without calculations, with your own hands;
- The contamination of the chimney will accelerate, and it will be difficult to clean the soot around the chimney.
There is also a more successful design that allows you to heat not only the room with the boiler, but also adjacent rooms located nearby, through the wall. To do this, a closed housing is “put on” over the tubes. From below - it is open (not blind, that is, air can get from below to the tubes). Another option is that there is an outlet at the bottom through which air will enter the body for heating.
At the top of the body, a pipe is diverted to the side (1 or 2, depending on how many rooms you want to heat from the chimney). It goes through the wall and goes into the next room.
The principle of operation is this: cold air enters from below to the heated pipes from the chimney. It takes heat from them, and through a side pipe it enters the room through the wall.
Types of chimneys
Exhaust shafts through which harmful gases saturated with combustion products are removed are required not only for standard stoves, but also for fireplaces and gas boilers. Today, several types of chimneys are known. These include:
Straight streaming. This variety is considered a popular structure, which is most often used for arranging living space. The only drawback of such a chimney is rapid heat loss. In addition to toxic substances, most of the thermal energy evaporates here.
Straight flow pipes with jumpers. They retain most of the heat during the combustion process of materials. This design is quite often used in baths. Such a long-burning chimney for a stove requires constant cleaning. Ash quickly settles on the surface of the lintels, thereby preventing the rapid removal of toxic substances.
Straight flow chimney with a labyrinth. This variety is characterized by high heat transfer. Carbon monoxide passes through numerous jumpers. They quickly heat the walls of the chimney, thereby contributing to maximum heating of the room.
Kolpakovy. It is used for Russian stoves. The hot smoke quickly rises, where it gradually begins to cool. After this, it descends along the arch of the chimney masonry. The only drawback of such a structure is its uneven heating.
Modular. They are made from a metal alloy. They are intended for heating systems running on gas. Metal chimneys for stoves are able to cope with acidic compounds of methane combustion products. In this case, the brickwork will quickly collapse.
Which device option should I choose?
- If you need to equip a chimney for a stove in an apartment on the 2-3rd floor, a clear solution to this problem is to lay pipes outside and lead them through the wall. In this option, we will not have to make possible horizontal sections, which make it difficult to clear soot from pipelines and reduce draft.
- For stoves or boilers running on gas, we reduce the cross-section of the internal plane. For solid fuel equipment this size should be significantly larger.
Basic Rules:
- The minimum chimney diameter for wood-burning stoves is 115 mm. Coaxial pipelines installed outside cope with their task. External pipelines, like internal ones, should be covered under a layer of thermal insulation. But the best option for external installation of chimneys is to use sandwich pipes.
- The internal gasket is used when installing a brick chimney or when equipping a private household. In this option, the installation is carried out through the floor slabs and the roof structure. To thermally insulate a brick pipe in these places, they are covered with sheets of thermal insulation or special boxes are made, making an internal cavity for the passage of the pipe slightly larger than its dimensions.
- Installation of steel sandwich pipes is carried out using mounting couplings and fittings. All rules and recommendations for installing chimneys are collected in SNiP 2.04.05 dated 1991. This document indicates methods for laying the chimney of a bathhouse, country house or apartment building. All necessary clearances, recommendations for the length and cross-section of pipes are given here.
Chimney device
The effective operation of a chimney shaft directly depends on several criteria. For example, the section, height and material from which it is made.
What needs to be taken into account when constructing such a structure:
Experienced experts recommend choosing a cylindrical chimney shape. A minimum of soot collects on its surface. This form retains the generated heat indoors as much as possible.
The size of the outlet of the heating device should be slightly smaller than the cross-section of the chimney duct. If the diameter is slightly larger, you will need an additional adapter that will regulate the smoke removal process.
Particular attention must be paid to the horizontal part of the structure. Warm air moves upward quickly. Soot and combustion products quickly begin to settle here.
Regulation of traction by reducing the length of these segments will help shorten this process. They must be less than one meter. In addition, it is necessary to provide a condensate trap and doors for cleaning the chimney.
For a sauna stove, it is best to use a vertical chimney. In some cases, a metal pipe can be laid. During the fixation process, it is recommended to maintain the correct angle of inclination. It should be no more than 2 meters.