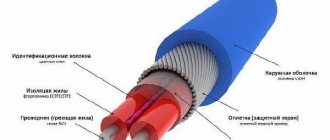
To transfer electrical energy from supplier to consumer, it must pass through a special line via cable.
To protect the cable, preserve it from external influences and vandalism, it is laid in trenches.
Previously, the method of laying above ground was widely used, but today this method has become outdated and has been replaced by laying communication networks underground. Digging technology and cable laying features will tell you how to avoid mistakes while performing the work.
Regulatory acts of process and technology
To correctly lay the wire in the trench, SNiP 3.05.06-85 “Electrical Devices” is used, as well as SNiP 12-03-99. These collections indicate the regulations governing electrical work, how to dig a trench, and the standards that must be followed when performing the procedure.
Additionally, the Construction Rules for Electrical Installations (PUE) are used in construction. The 7th edition of the PUE is studying this issue. The conditions for laying power cables underground are described in detail here.
For example, paragraph 2.3.17 of PUE-7 describes how to calculate the mass of wire, soil and road surface, and based on this, design an underground structure. In paragraph 2.3.83 of PUE-7, it is allowed not to additionally protect the cable with bricks or other structures if its voltage does not exceed 1 kV.
Norms and requirements
There are several requirements for laying wires in a rut:
- The depth should be such that it is impossible to dig a trench with a shovel. The degree of occurrence is regulated by the type of soil, the degree of its freezing and the groundwater level.
- The wire must be protected from mechanical damage.
- It is necessary to add sand to the trench: the sand cushion will not allow the wire to come into contact with solid soil.
- When laid under the road, a thick-walled metal pipe is used. This reduces the risk of damage due to excessive load on the coating.
According to the requirements of the PUE, it is not recommended to lay 2 cables in parallel in one pipe. If one wire is damaged, there is a risk of damage to the second. It is prohibited to lay cables with different voltages in the same trench. The distance between them when laying simultaneously should be at least 15 cm.
Why is the cable placed in a metal pipe?
During operation, electrical wiring is subject to various influences. From the inside, these are voltage surges that can lead to destruction of the wire and braid. From the outside, the strength of the electrical cable can be threatened by humidity, ultraviolet radiation, and chemically aggressive substances. But the most common cause of cable damage is physical impact: impact, compression, stretching. Even wiring hidden in a wall, floor, ceiling or underground can be damaged by a drill or chisel during repairs, elements of supporting structures during shrinkage, or soil compression when moving equipment over buried communication lines.
In most cases, a polymer box or corrugated steel casing will provide sufficient protection for power cables.
But there are situations when you have to resort to a more expensive and technically complex solution - laying electrical cables in a metal pipeline:
- If the room in which the electrical network section is located is built from flammable materials, or such materials are used in decoration and furnishings. In a wooden house, in a bathhouse or on a terrace, wooden walls or cladding can easily catch fire even from a small spark if the cable’s braid is damaged.
Note! Building codes do not provide for laying electrical wiring in metal pipes in such premises, but only this method of protecting electrical cables can ensure fire safety.
- If the room itself is a fire hazard due to its functional purpose. For example, in a workshop where they work with metal, a spark from a welding machine or grinder can burn through the braid of an electrical wire and cause a short circuit. In the kitchen or boiler room, the wiring of an oven, stove, or heating boiler is dangerous. In such rooms, not all electrical wiring can be hidden in metal pipes, but only areas located in fire hazardous areas.
- The use of pipes when laying electrical cables underground is necessary, especially in rocky soil, under roads and footpaths. In such areas, the wire is threatened by the movement of stones during soil shrinkage, soil pressure and rodents living underground.
- If the electrical wiring is laid openly, where there is a high risk of mechanical damage. For example, in a gym where they work with exercise equipment, it is easy to pinch or break the cable; in a workshop where glass, wood or stone is processed, a splinter of the material being processed can damage the braid.
- If metal pipes are a decorative element. The loft style, in which they try to give the room a resemblance to an industrial facility, involves laying communications in an open way. Vintage or retro style also involves laying wiring along the walls and ceiling - metal for insulation in this case is more suitable than other materials both in style and in safety.
Mechanisms and tools
Digging a trench for laying wires is done manually or using mechanized equipment.
When digging by hand, a bayonet shovel is used to collect soil and a shovel is used to bring the developed soil to the surface.
If the volume of work is large, they use equipment: bucket and chain excavators.
If the soil has a high degree of freezing or the work is carried out in winter, a greater trench depth is needed - it is more advisable to use a chain excavator.
A regular bucket unit is suitable if you need to do a lot of work in a short period of time.
Manual labor will be relevant if communications have already been laid on the site and you need to dig carefully. This method is also useful if it is impossible to ensure comfortable transport access to the site.
Track depth
The depth for laying the power cable is selected in accordance with the power of the wire.
A few examples:
- electrical wire with a power of up to 20,000 W - at least 70 cm;
- cable up to 35000 W – 100 cm;
- busy areas and road intersections - at least 100 cm.
The greater the power, the greater the depth of the dug trench should be. If the line is laid in arable areas, as well as in the case of cable power over 110 kV, the trench depth must be at least 1.5 meters. At building entrances, a cable trench can be dug to a depth of 50 cm.
Scheme for laying cables in a trench:
The minimum distance between cables laid in one trench is 100 mm. Based on this indicator, it is necessary to dig a trench of a certain width.
Digging process
Before starting to dig a trench, it is necessary to draw up or obtain a diagram of the site with the laying of all communication networks underground.
After this, you can use the step-by-step instructions:
- Determine the type of trench - with slopes, with vertical walls or mixed.
- Prepare the surface. Clear the area of debris, remove stones and branches, and uproot stumps.
- Make markings. Place pegs or posts at the beginning and end of the trench, and stretch the cord between them.
- Do some digging. Mechanized or manual. It is better to put the earth from the trench on one side of the trench. Recommended distance is 50 cm.
Subsequently, it will be more convenient and easier to fill the trench if the soil is located nearby. After digging, the walls need to be strengthened if a trench with steep walls is used.
At the final stage, you can build walking bridges if the trench is wide. It is also recommended to install lighting and fencing if digging is carried out on the roadway.
Technology and process of making a bed at the bottom of the track for wires
When the trench for the cable is dug, they begin to organize the bed. This is a kind of “cushion” for the power cable. This is a sandy layer of a certain height, which is located at the bottom of the trench. A bed or pillow is laid around the entire perimeter of the excavated trench. The layer should be uniform and the sand should be well compacted.
Why and when is this needed?
A sand bed is necessary when you need to protect the cable from external damage.
Due to the layer of sand, the power wire will not be able to contact solid soil particles. Another purpose is to preserve the cable from breaking. Since the soil is hard, the wire in it can break and bend.
Sand provides softness. The soil may move or be pressed under the weight of the wire, and sand will protect against the consequences of repairs. If water seeps into the ground, the sand will absorb it, which will not violate safety regulations .
When located in a cushion, the cable is very easy to dig out, but if it was simply lying in the ground, the work would be more complicated: the wire could be easily damaged during repair and dismantling.
Materials and technology
A sand bed is used when the ground is too hard. If the soil in the trench is soft and loose, it is permissible not to place sand at the bottom. Then the wire must be enclosed in a protective casing that will protect it from damage.
The process of laying a sand bed requires the use of ordinary river sand , since neither SNiP nor PUE says otherwise. Sand is delivered to the construction site in advance.
A sand bed is made throughout the entire trench and cable laying route. Sand is poured to a depth of at least 10 cm with a shovel and leveled. At the end, be sure to compact the pillow. To do this, use a hand-held vibrator.
If it is difficult to get a tool, you can create a homemade tamper: take a beam the width of the trench and attach handles to it. After filling the sand, walk the surface with a beam.
Pillow device process
The underlying layer is able to protect the cable from damage and contact with groundwater. This helps create many years of trouble-free operation of the power cable. For this purpose, sifted sand without foreign particles and debris is used.
Technology:
- After digging a trench and strengthening the walls where necessary, they begin to organize a sand bed.
- Using shovels, sand is evenly scattered along the entire length of the route.
- The sand is leveled to achieve a layer of 10-11 cm.
- The sand is compacted using a hand vibrator or other tools.
You can use any sand, the main caveat is that it should not contain construction waste or stones. River sand or sand from a quarry works well.
Installation features
During installation, it is important to follow the installation rules:
- It is advisable to minimize the number of pipe turns, since each angle complicates cable pulling.
- At network nodes - turns, branches and places where electrical appliances are connected - distribution and wiring boxes are installed. This will simplify cable pulling after pipeline assembly and maintenance of the electrical network during operation.
- To pull electrical cables, a steel string is used: first, it is pulled through the resulting cable channel, the string is connected to the cable and pulled out from the opposite side. Thus, cables are gradually laid throughout the pipeline and the sections of wires in boxes are connected, forming a single electrical network.
- Plastic bushings are fixed at the ends of the pipes, the purpose of which is to prevent chafing of the cable braid.
- It is better to connect pipes using threaded fittings - special connecting elements, and not by welding. This will simplify installation and further repairs.
- The pipeline is secured using clamps and brackets, the distance between which depends on the internal diameter of the pipes.
Wire laying
To ensure that the wire is not damaged and lasts a long time, the following rules are followed during its installation:
in one trench it is allowed to place no more than 6 wires with a voltage of 6 to 10 kV;- it is allowed to lay two cables with a voltage of 35 kV in one trench;
- no more than 1 bundle of control wires can be laid next to these cables;
- trench width for one wire at voltages up to 10 kV - 20 cm, at voltages up to 35 kV - 30 cm;
- in the presence of harmful soil conditions, the wire is laid on overpasses;
- laying is carried out with a small margin of distance;
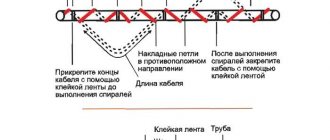
- A wavy or “snake” gasket is allowed.
The distance between wires of different power loads is:
- 100 mm for wires up to 10 kV;
- 250 mm for wires from 20 to 35 kV;
- 500 mm for cables from 110 to 220 kV.
Laying takes place in certain weather conditions. The norm is to carry out work in dry, clear weather with no precipitation. In winter, the cable is preheated. At temperatures from -20, work outside is carried out for no more than 1 hour.
The process of laying one cable with a power of up to 35 kW
To lay an electrical wire with a power of up to 35 kV, follow the step-by-step steps:
- Acceptance of the route. The cable line route must be accepted according to the act from the builders.
- Preparatory work. When the trench is dug and the sand bed is arranged, it is necessary to check the installation of support posts for the end couplings, the absence of water in the trench, and the passability of block pipes if the wire is placed in a casing.
- Drum installation. The drum is removed no earlier than 1 day before the start of work. Its external inspection is carried out, installation is carried out, smooth running is ensured, and linear rollers are placed.
- Laying. Straight sections do not require a large number of people. If the cable is laid at an angle, a worker must be there. One worker monitors the unrolling and feeding of the cable, several workers accompany the end and beginning of the wire. The laying speed does not exceed 30 meters per minute.
At the end, the cable is sprinkled with a layer of sand or soft soil. In case of risk of damage, the cable is additionally protected with bricks. A warning tape is also laid at a distance of 25 cm from the surface of the wire. At the final stage, the trench is backfilled and compactions are made every 200 mm.
Laying mutually redundant wires
According to clause 2.1.16 of the PUE, it is prohibited to lay mutually redundant cables with a power of up to 42 V with wires with a power of over 42 V
. They can be laid in the same trench only in different compartments with solid longitudinal partitions. Such boxes must be fireproof.
According to regulatory documents, laying mutually redundant cables is permitted in one trench only if there are different boxes with a distance of at least 1 meter between them.
If it is not possible to lay the cables separately, joint laying is allowed, provided that the wire is protected in the event of a short circuit.
Laying two wires
Two cables can be laid in a trench if they are of equal strength. In this case, the width between them will vary. For wires with a power of up to 10 kV it will be 11 cm, and for cables with a power of 20-35 kV - 26 cm.
In this case, it is important to observe the intersection with other utility networks. The distance between them must be at least 60 cm. The cable must be at the same distance from the foundation.
Laying a line over 35 kV
High-voltage cables with voltage from 35 kV are laid in accordance with the safety requirements of the PUE. The laying depth of such a cable is at least 1 meter. Oil-filled cable lines are laid to a depth of 1.5 meters.
It is allowed to lay only 1 layer of high-voltage cable from 35 kV, and no more than two layers in pipes. It is forbidden to lay high voltage wires under the roadway . Such a cable must be protected by concrete slabs with a thickness of at least 50 cm.
Do you need protection and why?
The most common problem when laying cables using the trench method is their damage. They occur when excavating soil at the site of backfilling a trench: the cable is damaged by shovels or mechanized equipment due to unsuccessful digging with a bucket. To avoid this, use wire protection.
If you do not protect the cable from mechanical damage, this will lead to a long-term disruption of the power supply. As a result, there will be a long and expensive, and also labor-intensive, repair. The consequences include accidents, electric shock, and equipment failure.
Methods of protection
There are several methods of protection:
- reinforced concrete slabs;
- ceramic bricks;
- boxes and pipes;
- protective signal tapes.
Reinforced concrete slabs are laid on top of the cable line backfill. The bricks used are special, made of ceramic and solid inside.
Boxes can be made of durable plastic, and pipes are made of metal.
There are two types of protective signal tapes:
- made of high-strength polyethylene;
- made of polymer material, they are produced in large layers.
The tapes themselves have a thickness of 3.5-5 mm. They can be reinforced with fiberglass tape. A bright and noticeable inscription runs across their surface. Concrete slabs are used for cables from 35 kV, and bricks and signal tapes are used for cables of lower power.
Using brick, concrete
Reinforced concrete slabs must have a thickness of at least 50 mm. They are laid on high-voltage cables after constructing a trench and adding a sand cushion. Brick protection is used on wires with lower voltage.
A layer of brick is placed above the trench in the longitudinal and transverse directions. The laying method depends on the width of the trench. Hollow bricks cannot be used. The clay material has a characteristic red color, which will be an excellent signal when excavating a trench.
Using warning tape
Safety signal tape is used when laying 2 lines in one trench. Their power should not exceed 20 kV. This is a flexible polymer material that is laid at a height of 25 cm from the top sheath of the wire.
The tape should protrude 50 mm from the sides. This method of protection cannot be used if the cable line has a voltage above 1 kV and provides consumers of category 1. Also, the tape is not laid when the route intersects with other communications.
Selection of metal pipes for cable laying
The electric cable can be laid in almost any pipes.
The minimum requirement for the casing is the absence of rust, burrs and internal irregularities.
Metal pipes are selected according to various parameters: price, decorativeness. Pay attention to the resistance of the pipes against corrosion, as well as how easy it is to install the system.
- The most decorative are copper and brass pipes; they cope better than others with the task of decorating electrical wiring laid in an open way and do not require painting. At the same time, thin-walled pipes allow the casing to be given any necessary shape without the use of shaped elements, while thick-walled pipes can further emphasize the deliberate roughness of the communication by assembling the pipeline using fittings.
- Stainless steel pipes are the most expensive, but reliable and easy to install: they do not need to be painted, they are smooth inside and out, do not corrode and are suitable for laying cables in any way.
- Galvanized ones have the same advantages as stainless steel ones, but their price is lower, so galvanizing is often preferred. However, the service life of galvanized pipes is half as long.
- Steel pipes that do not have a protective coating and aluminum pipes will need to be painted inside and out before installation to prevent oxidation. If an electrical cable in a steel casing is laid in a cement screed, the outer surface of the pipe does not need to be painted.
- Corrugated pipes are easy to install as they easily take on the required shape. Their disadvantage is a weak level of cable protection from compression and impact, so corrugation should not be used for underground communications and in rooms where the risk of strong physical impact is high.
In construction stores you can choose consumables for laying electrical cables to suit every taste. But pipes remaining after the dismantling of a gas or water supply system are also suitable.
It is important to first inspect the future casing and assess its condition: if the pipes do not have cracks, internal seams or other irregularities, they can be used.
It is important! Before installation, it is necessary to clean the internal surface of any deposits that have formed by pulling the steel brush through with a cable.
If the pipe does not have a protective coating, it must be painted. Painting from the inside is done by pulling a sponge with paint or pouring paint into a vertically located pipe.
Filling the rut with earth
At the final stage, the trench is covered with earth:
- soil excavated from the trench is used;
- the earth must be clean, without large stones and impurities;
- in urban environments, sand is used;
- backfilling occurs in stages;
- each layer is 20 cm thick, it is moistened and compacted.
Before backfilling, all spacers and auxiliary elements are removed. It is better to use a bulldozer for backfilling - this will save time and allow you to level the site.
Problems and errors
The most common mistakes and what not to do:
- Bury a cable in a trench that is not intended for outdoor installation.
- Dig a trench close to the foundation.
- Make the trench depth less than 900 mm.
- Do not create a sand bed.
- Do not compact sand when laying the wire on loose soil.
- Lay the cable in rings.
- Use sand-lime or hollow bricks for protection.
All of these errors can be corrected if you adhere to the correct cable laying technology in advance.
How to check current leakage
After laying the power cable, the soil is examined at different sections of the route. If leaks are detected, they strengthen the protection or change the wires to more resistant ones. On highways with aggressive soils, a vapor barrier is additionally used.
The integrity of the sheath of the laid cable is checked with a megometer. If it is absent, check the cable for breakage with a multimeter or tester.
A certificate of completion of hidden work is drawn up by the electrical installation organization and the customer. The document is the basis for future repair work.