Compensation for linear expansion is solved constructively; for this, angles of rotation (angular expansion) or U-shaped (loop-shaped) methods, sliding and fixed supports, as well as ready-made compensators are used.
The angular expansion method is based on changing the straight direction of laying the pipeline with an angular connection. In cases where compensation by changing the direction of laying is impossible, that is, the direction of laying the pipeline must be straight, the U-shaped method is used. Compensation for linear expansion. In this case, some of the fasteners are made stationary, or fixing: they direct the extension through movable (sliding) fasteners towards the compensating elements.
The design of the sliding support must ensure movement of the pipe in the axial direction.
Linear Expansion Compensation - Fixed Support Design
Linear Expansion Compensation - Sliding Bearing Design
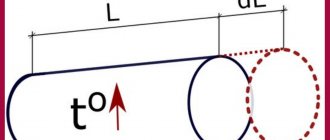
Linear expansion compensation angular method:
The compensation area is calculated using the following formula:
- Ls = K√(dx ΔL)
Angular compensation method for a linear section
ZhO - rigid support, SO - sliding support
Ls - length of the compensation section: K - material constant (for polypropylene) = 15; ΔL - linear expansion, (ΔL = α x L x ΔT)α = pipe diameter
What is thermal expansion compensation?
To compensate for thermal elongations of heating network pipelines, compensating devices are used. They serve to absorb the deformations of steel pipelines when the temperature of the coolant changes and to unload them from the resulting temperature stresses, as well as to protect the fittings installed on the heat pipelines from destruction.
Thermal expansion of pipelines at a coolant temperature of 50 °C and above must be accommodated by special compensating devices that protect the pipeline from the occurrence of unacceptable deformations and stresses. The reliability and trouble-free operation of heating networks largely depend on the correct solution to the issues of compensating for thermal expansion of heat pipelines, the choice of the method of laying heating networks and other local conditions. Methods for compensating for temperature expansions used in heating networks are very diverse.
According to the principle of operation, compensators are divided into two groups:
- radial or flexible devices that accommodate the elongation of pipelines by bending;
- axial devices of sliding and elastic types, in which elongations are perceived by telescopic movement of pipes or compression of spring inserts.
Radial compensation is performed using U-shaped compensators, pipeline rotation angles, Z -shaped sections, etc., axial compensation is performed using axial (stuffing box, lens, wavy) compensators.
Flexible expansion joints made of steel pipes (U-shaped, etc.), as well as pipeline rotation angles from 90 to 130° (self-compensation), are used to compensate for thermal elongation of pipelines, regardless of the coolant parameters, installation method and pipe diameter. All parts of bent expansion joints are connected by welding. The diameter, wall thickness and steel grade of pipes for bent expansion joints must be the same as for pipelines of the main sections.
The most reliable in operation is the so-called natural compensation, or self-compensation, which is allowed for all methods of laying heating networks and is widely used in practice. Natural compensation for thermal expansion is achieved at turns and bends of the route due to the flexibility of the pipes themselves. The advantages of this type of compensation are the simplicity of the device, reliability, lack of need for supervision and maintenance, and the unloading of fixed supports from internal pressure forces. The installation of natural compensation does not require additional consumption of pipes and special building structures.
To calculate compensation for thermal elongations, compensators and calculate the strength of heating networks, use the START-PROF program.
Let's look at an example:
Initial data: the diameter of the straight section of the pipeline is 219 mm. It is made of black carbon steel, its length is 100m. tmin = -20°C and tmax = 140°C.
The calculation is as follows: ∆t = 140 - (-20) = 160°C. Next, we calculate the change in the length of the pipeline, the calculation is as follows: ∆L = 0.0115 x 160 x 100 = 184 mm.
The result shows that the length of the pipeline can vary by 184mm at these values. To ensure uninterrupted operation of the pipeline, an axial bellows compensator is required, the nominal diameter of which is 200 mm, and the compensating capacity is 200 mm (KSO 200-16-200).
If the value of thermal expansion of the pipeline (∆L) is greater than the available compensating capabilities of the expansion joints, then the length of the pipeline is reduced in proportion to the compensating capacity and the appropriate bellows compensator is selected.
Compensator 50 PP
| № | Name of works | Price |
| 01 | Call a specialist for inspection | 300 |
| Shower cabins, corners, fences (the price is indicated without dismantling) | ||
| 02 | Shower cabin 80*80; 90*90 | 2450 |
| 03 | Shower cabin 100*100; 110*110; 120*85; 130*85; | 2450 |
| 04 | Shower cabin 140*85; 150*85; 160*85; 170*85 | 3450 |
| 05 | Shower cabin 120*120; 130*130; 135*135 | 10% of the price |
| 06 | Shower cabin 140*140; 150*150; 155*155, exclusive models and models costing over 30,000 rubles, as well as shower cabins with a steam generator | |
| 07 | Shower corner (tray + curtain) 80*80; 90*90 | 1950 |
| 08 | Shower corner (tray + curtain) 120*80 | 1950 |
| 09 | Inconveniences when installing a shower stall (podium, hatch, cramped conditions), dismantling plumbing fixtures | from 500 to 1500 |
| Bathtubs (the price is indicated without dismantling) | ||
| 10 | Cast iron bathtub | 1450 |
| 11 | Steel bath | 1000 |
| 12 | Acrylic straight-sided bathtub | 1450 |
| 13 | Acrylic corner bathtub | 2000 |
| 14 | Hydro-air massage baths costing up to 50,000 rubles. | 10% of the price |
| 15 | Hydro-air massage baths cost from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles. | 8% of the cost |
| 16 | Bath screen | from 500 |
| Toilets, bidets (the price is indicated without dismantling) | ||
| 17 | Compact toilet; monoblock PROMOTION: installation + dismantling! | 850* |
| 18 | Compact toilet, monoblock costing over 12,000 rubles. | 6% of the cost |
| 19 | Wall-hung toilet | 1000 |
| 20 | Toilet with installation | 2500 |
| 21 | Installation of a bidet (with connection to water supply and sewerage) | 1450 |
| 22 | Pouring the floor | 300** |
| Sinks, sinks (the price is indicated without dismantling) | ||
| 23 | Cabinet with sink PROMOTION: installation+dismantling+installation of faucet | 850 |
| 24 | Pedestal washbasin (without faucet installation) | 450 |
| 25 | Wall-hung sink (without faucet installation) | from 400 |
| 26 | Overhead sink, mortise (with installation of a mixer) | 700 |
| 27 | I drank out the walls and shelves of the cabinet for water supply/sewage | from 100 to 500 |
| 28 | Drank the countertops under the sink | 500 |
| 29 | Hole for faucet on sinks | 500 |
| Faucets | ||
| 30 | Mixer with shower; faucets for sinks and sinks PROMOTION: installation + dismantling! | 490 |
| 31 | Installation of a mixer on the side of an acrylic bathtub (with connection) | 1500 |
| Accessories and other plumbing fixtures | ||
| 32 | Water purifier installation | 500 |
| 33 | Replacing the meter (removing the old one and installing a new one in the same place) | 400 |
| 34 | Simple mirrors | 550 |
| 35 | Wall-mounted, mirrored, kitchen cabinets | 550 |
| 36 | Replacing a bath siphon (plastic sewer) | 450 |
| 37 | Replacing a siphon for a sink, sink | 350 |
| 38 | Replacing fittings in the flush cistern | 500 |
| 39 | Installation of a shower stand with punching 2 holes | 500 |
| 40 | Bathroom furniture (glass, acrylic) | 10% of the price |
| 41 | Installing accessories per hole | from 100 |
| 42 | Cast iron, steel, acrylic pallets | from 1000 |
| Dismantling | ||
| 43 | Shower cabin | 50% of installation |
| 44 | Toilet, sink, faucet | 300 |
| 45 | Bath | 500-800 |
* When dismantling the toilet, it may be necessary to level the floor by filling it with a cement-sand mixture. This service is not included in the indicated price; payment is made in accordance with clause 22 of this price list. ** The price is indicated taking into account the required material
Features of plastic pipelines
Polypropylene is a polymer whose advantages have led to its widespread use in internal communications networks.
Among which:
- the operating pressure for pipes made of this material is up to 10 atmospheres (it may be necessary to test the pipelines for strength and tightness);
- The upper limit of the operating temperature range exceeds 90 degrees. This is enough for wiring hot water supply and heating systems;
- the material is absolutely not subject to corrosion , inert to most chemicals used in everyday life, and is not biodegradable;
- the surface quality of polypropylene pipes and the properties of the material prevent the deposition of plaque, including limescale, on the walls;
- the service life of polyethylene pipelines is at least 30-50 years;
- polypropylene is absolutely safe for human health and does not release toxic compounds into water or air;
- this polymer is fireproof.
The installation technology involves the use of welding (iron for soldering polypropylene pipes) to obtain reliable connections.
If you have the appropriate equipment, anyone can master the skills of installing systems made of polypropylene pipes.
What do you know about the indications and contraindications of pearl baths, reviews of which were published in a useful article? Follow the link and read about the advisability of installing equipment at home.
Read reviews on which bathtub is better, acrylic or cast iron, on this page.
Among the disadvantages of polypropylene pipes, experts note the inability to give them the required shape.
Due to this, turns of highways are performed exclusively using fittings.
Another serious disadvantage of this polymer is its high coefficient of thermal expansion.
Thanks to it, polypropylene pipes are characterized by significant elongation and/or sagging when transporting hot media (hot water or coolant of heating systems), and at high outside temperatures.
Polymer pipelines for modern open plumbing and heating installations
Modern metal-polymer pipelines are a cross-linked polyethylene pipe in which a layer of aluminum is firmly glued to an internal self-supporting layer of PE-Xa. Such pipelines have the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion, because the aluminum layer compensates for thermal expansion and keeps the inner polymer layer from thermal deformation.
The coefficient of thermal expansion of metal-polymer pipelines is only 0.026 mm/m K, which is 5.76 times less than that of conventional pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene.
The thermal elongation of a section of a metal-polymer pipeline 10 m long at ambient temperature (i.e. installation temperature 20 °C and maximum operating temperature 70 °C) will be only:
ΔL = L • α • (t max. work. – t installation) = 10 • 0.026 • (70 – 20) = 13 mm.
For comparison: we previously calculated the thermal elongation of a conventional PE-Xa pipeline 10 m long, which amounted to 75 mm.
Therefore, metal-polymer pipelines are positioned as pipelines for open installation. But the option with metal-polymer pipes will be more expensive, because... these pipes cost more than conventional PE-Xa cross-linked polyethylene pipes.
Dependence of the structure of the material on the influence of temperature
It is necessary to distinguish the maximum temperature that PP pipes can withstand from their actual physical properties. Despite the fact that the manufacturer indicates the melting point of polypropylene at 170 °C, in fact, polypropylene products begin to soften already at 135-140 °C.
We recommend that you read: How to properly solder polypropylene pipes to create strong connections
Installing such pipes without taking into account thermal expansion is not just a risk of deformation. The consequences of errors in the design of engineering systems can be significant:
- fastening elements break down;
- air accumulates in the deformed area, reducing the throughput of the system (so-called airing);
- the temperature of radiators and risers decreases, the system operates less efficiently;
- pipes burst and coolant leaks occur.
Important! For installation of engineering systems, unreinforced and reinforced PP pipes are used. The latter have an additional layer that protects the outer layer of the polymer from overheating. Due to this, the coefficient of thermal expansion of the pipe is reduced, but it is not completely leveled.
Reinforced polypropylene pipes have a lower CTE, but it still needs to be taken into account.
Average coefficient of thermal expansion:
- unreinforced – 0.15 mm/mK;
- metal reinforced – 0.03 mm/mK;
- glass fiber reinforced - 0.035 mm/mK.
In fact, the coefficient of thermal expansion for unreinforced PP pipes of 0.15 mm looks like an extension of the section by 1 cm for each meter of pipeline if the temperature of the working medium reaches 70°C.
Attention! This does not mean that a 5 m long pipe will lengthen by 5 cm when hot water is turned on. In hot water supply systems, the water temperature is a maximum of 65°C, therefore the expansion coefficient will also be lower.
But, ultimately, when calculating the length of the engineering system, real temperature indicators must be taken into account. For a heating system, the length of the pipe can increase by 5 cm or more.
How to choose the right compensator?
| Model | Thread | DN, mm | PN, Bar | D,mm | axial movement, mm | length, L mm | Weight, kg | Axial stiffness, kg/mm | Eff. Area (cm2) |
| KSO Plast 15-16-50 | 1/2″ | 15 | 16 | 32,0 | 50 (-45;+5) | 285 | 1,50 | 148,75 | 6,40 |
| KSO Plast 20-16-50 | 3/4″ | 20 | 16 | 38,0 | 50 (-45;+5) | 285 | 1,70 | 88,56 | 7,21 |
| KSO Plast 25-16-50 | 1″ | 25 | 16 | 48,0 | 50 (-45;+5) | 285 | 2,30 | 106,45 | 12,10 |
| KSO Plast 32-16-50 | 1 1/4″ | 32 | 16 | 57,0 | 50 (-45;+5) | 285 | 2,80 | 68,72 | 16,11 |
| KSO Plast 40-16-50 | 1 1/2″ | 40 | 16 | 57,0 | 50 (-45;+5) | 285 | 3,00 | 72,51 | 16,80 |
| KSO Plast 50-16-50 | 2″ | 50 | 16 | 70,0 | 50 (-45;+5) | 285 | 3,90 | 63,12 | 24,30 |
Table of models and technical characteristics of pipe expansion joints
When choosing a compensator for polypropylene pipes, as already noted, you need to take into account the diameter - the elements must match. In most cases, the diameter of such products ranges from 2-4 centimeters. But if we are talking about a house/apartment, then expansion joints with a diameter of 2 centimeters are most suitable.
Average prices
Table: Technical characteristics Polypropylene compensator FV Plast Ф 32 mm
| Manufacturer | FV Plast |
| Name | bypass elbow and compensator |
| Diameter | 32 mm |
| Thread | — |
| Wall thickness | — |
| Operating pressure | 20 atm |
| Reinforcement | — |
| Operating water temperature, °C | up to 80°C |
| Short-term increase, °C | 90°C |
| Permissible pressure at T=10°C | 36 bar |
| Permissible pressure at T=max°C | 8 bar |
| Connection type | welding |
| Estimated service life | 25-50 years |
| Section length | — |
| Color | grey |
| Manufacturer country | Czech |
As for specific manufacturing companies, there are many of them on the domestic market, including world-famous companies. Such a large number is explained by the fact that polypropylene pipelines, like any others, require high-quality equipment.
One of the most famous manufacturers is Kayse from Turkey. And it is popular primarily because of the huge range of its products. All models from this range are present on the domestic market today. An equally significant manufacturer is Kompencator PPHV, which has been known in many countries for many years for the high quality of its products, which are used in many industrial areas.
Important additional information
Thermal insulation
PVC pipes
Some thermal insulation products can be destructive to thermoplastic pipes. It is recommended to insulate using the following materials (only some options are shown in the list):
- Mineral felt
- Armaflex class 1 NT
- Penofenoplast
- Polystyrene.
Some types of foam rubber and adhesives can be toxic when used together with foam rubber. Therefore, it is not recommended to use them as a means of fastening thermal insulation of a pipeline. Adhesives should only be used for bonding purposes.
Pipeline heating
Thermoplastic piping can be damaged by the plasticizers used in the outer coating of some electric heating tapes. Tapes with a plasticized PVC sheath should not be used. (This comment also applies to any tapes, adhesives, or other substances used to attach electric heating tape elements to the pipeline.) Recommended electric heating elements—Tape heaters with a silicone rubber, woven wire mesh, or woven polyester sheath will minimize the risk of plasticizer interaction with pipeline material. Therefore, it is preferable to use these tapes on thermoplastic systems.
PVC-U pipeline marking
Do not place adhesive labels directly on the surface of the pipe as the adhesive may damage the outer surface of the pipe. It is recommended to use a spacer material such as aluminum foil between the pipe and the identification tag.
Foaming mastics and sealants
Certain sealants contain phthalates. Phthalates are extremely aggressive to PVC-based materials, therefore, before using any sealants and mastics for PVC pipes, it is necessary to obtain confirmation that the selected sealant matches the chemical composition of the unplasticized PVC pipeline.
Clamps for fastening PVC pipes
It is important that the staples and their coating do not contain substances that could have a destructive effect on the unplasticized PVC pipe. Check the selected products for compatibility with the pipeline material. We recommend using Cobra clamps for pipes up to and including 160mm OD/6" nominal ID
We recommend using Cobra clamps for pipes up to and including 160 mm outside diameter/6 inch nominal inside diameter.
Freezing conditions
Care must be taken to prevent the contents of the pipeline from freezing, as this may cause the pipe to burst.
Contact of uPVC with various fluxes
Some fluxes can be destructive to unplasticized PVC piping
Special precautions should be taken when soldering copper piping directly above or near unplasticized PVC piping
Thread sealants
Some thread sealants may damage unplasticized PVC piping. It is recommended to use Teflon tape for threaded connections.
Resistance of unplasticized PVC to ultraviolet rays
Protection from ultraviolet rays such as sunlight should be provided, especially during storage. Exposure to them may cause discoloration and deterioration of the material. And, although these are only superficial changes, it is nevertheless recommended to avoid exposure to ultraviolet radiation. When storing outdoors, pipes should be covered with opaque material. When installed outdoors, PVC pipes are recommended to be protected from ultraviolet rays by insulation or painting.
Underground pipeline
It is prohibited to lay the pipeline in contaminated soil. It is prohibited to lay the pipeline in soil where liquid chemicals are released.
UPVC pipes and pressure surges
A pipeline made of unplasticized PVC is able to withstand pressure surges within the designated limits. Under no circumstances should pressure surges exceed the continuous operating pressure shown in the chart.
Compensators for polypropylene pipes: bellows, U-shaped, Kozlov compensator
Today, almost any engineering communication is easy to build with your own hands. All the necessary components are assembled very easily (based on the principle of a designer). Such components are compensators for polypropylene pipes. Compensators for polypropylene pipes are an integral part of any modern engineering communication system. It is not difficult to buy them in a specialized store and install them on the pipeline yourself. Compensators are an ordinary design with a flexible shape. Externally, they resemble a wrapped loop. These seemingly simple details have a very important function. This will be discussed further.
And if expansion joints for polypropylene pipes are installed using a combined method (with a metal water supply), then the connection should be made slightly differently - using not only welding, but also threads. This happens as follows. First, the risers are turned off and the water is drained from the system. Then the valves are removed and the pipes are cleaned using a cable. Only after this is a combined option installed. The plastic component is welded to the pipeline, and the metal component is connected to the mixer using a thread. The installation technology itself depends on what type of compensator was chosen. Typically, the threaded method of installing the device in a polypropylene pipeline does not provide high strength to the system as a whole. And this is its main drawback. To ensure that the strength is at the required level, it is recommended to resort to welding.
Layout of the entire highway.
Today, most of the engineering communications can be built by yourself, on your own. All the components required for this are freely available, and their installation is in many ways similar to the assembly of a construction set. And if you have an idea of their technical purpose, then you can easily complete all the work, taking into account all the technological stages. Today we will talk about expansion joints for polypropylene pipes; we will find out what they are for, what they are, how much they cost, how to attach them and what their function is in the water supply system. Compensators for polypropylene pipes
- 1 Classification of compensators
- 2 Installation of expansion joints for PP pipes
- 3 Features of fastening compensators
- 4 Compensators are installed – what next?
- 5 How to choose the right compensator?
- 6 Areas of use
- 7 Distinctive features of installing polypropylene pipes 7.1 Video - How to install polypropylene pipes
- 7.2 Video - Compensators for polypropylene pipes
- 8.1 Video - Axial expansion joints for PP pipelines