Nominal pressure
- The letters PN indicate the nominal pressure. It is expressed in bars (kg/cm2). PN is the constant nominal internal pressure of water at a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius, which the pipes can withstand without failure for 50 years.
- The most common polypropylene pipes are PN 25, PN 20, PN 16 and PN 10. Here you need to take into account that the thicker the pipe wall, the higher the PN designation. The markings of polypropylene pipes for heating are PN 20 and PN 25. They are also suitable for installing hot water supply.
- Some manufacturers produce pipes with a blue longitudinal stripe for cold water (PN 10). The red stripe on the pipes indicates that they are intended for hot water (PN 20). There are tables that calculate the service life of a pipe, based on data on water temperature and pressure. The higher the pressure and if the water temperature is higher than 20 degrees, the less the pipe will last.
Installation of polypropylene pipelines
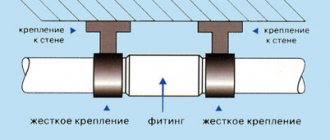
Welding of polypropylene pipes
The most common method of joining polypropylene pipes is diffusion welding. During the joining process by diffusion welding, the materials of the molten edges of the products interpenetrate.
Welding machine
During the welding process, it is necessary to use products made from the same material. The durability of the structure is ensured by the special physical properties of the seam formed as a result of welding.
- Before work, the product is cut to the required size strictly at right angles.
- The welding machine must be set to soldering mode at a temperature of 260°C.
- Before starting the welding process, you need to clean the surface of the pipe and then degrease it with a solvent.
- If the material is reinforced with aluminum, before welding the end of the pipe is cleaned of this metal using a special device.
- After completing the welding, both connected ends need to be fixed. The pipe should remain in this position for 4 to 8 minutes.
During the welding process, the duration of heating of the material depends not only on the diameter of the pipe, but also on the thickness. The welding time, the width of the weld seam formed, as well as other parameters depend on the characteristics of the pipe (its diameters, composition). Therefore, before you begin, you need a table of polypropylene pipes.
Pipe welding table
Installation work
Pipeline installation consists of the following steps:
- To begin with, a detailed diagram is drawn up, on which taps, filters, as well as corners and tees are marked. When planning, you need to take into account what temperature polypropylene pipes can withstand.
- Then you should assemble the individual elements of the water or heat pipeline into a complete system.
- It is advisable to carry out welding while holding the elements that need to be connected in a horizontal position. If the sections of the system are not particularly large, welding can be carried out by one person. In case of more complex installation, vertical soldering should be performed. The coefficient of linear expansion of polypropylene pipes will depend on the result.
Installation recommendations:
- After welding or soldering PP pipes, it is necessary to check whether “seals” have formed, causing a decrease in clearance. If they are detected, they must be eliminated immediately. This phenomenon most often occurs in small-diameter heating pipes.
- If polypropylene pipes are not placed in the wall, then the fasteners that will hold them are recommended to be placed every 40-50 cm.
- Pipes with rubber seals at the ends must be manually inserted into one another.
Material designation
- Different pipe manufacturers use different designations. But the letters PP always indicate that the pipes are made of polypropylene. If you see the designations PRN, PP-type 1 or PP-1, then this product is made from the first type of polypropylene - homopolymer. Designations PP-type 2, PP-2, or PPV - pipes are made of block copolymer. However, the random copolymer is recognized as the best: PP-3, PPR, PP-random, PPRC.
- The marking of polypropylene pipes for cold water supply will be marked PRN . Such pipes are also used when laying ventilation. Pipes marked RRV find their application in central and autonomous heating and cold water supply.
- Pipe products labeled PPR are most common due to their increased heat resistance. Therefore, they are suitable for both hot and cold water, as well as for heating systems of various types.
Related publications:
- Characteristics of metal-plastic pipes
- Pressure in polypropylene pipes
- HDPE pipes: marking, application, manufacturers
- How to choose polypropylene pipes for heating
- What you need to know about plastic pipes
- All about laying polypropylene pipes
THANK YOU SO MUCH BUT I WOULD LIKE TO DECODE THE ABBREVIATION ON THE PIPES
Tell me, what does the letter STD mean on German pipes? Thanks in advance for your answer.
The random copolymer, as I understand it, will be polypropylene of the third type and, accordingly, PP-3, and not PP-2, as indicated. In general, the error crept into the text.
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic high temperature polymer. It is produced by polymerization from a mixture of propylene with the addition of metal-complex catalysts and stabilizers. PP pipes belong to the group of plastic pipes, which also includes products made from metal-plastic, PVC, HDPE and PEX.
What else is indicated in the labeling
- The diameter of the pipe and the minimum size of its walls. The specially adopted scheme for this designation is similar to our metric system of measures. Pipe diameters are indicated in millimeters with numbers - from 10 to 1200 mm.
- Release date, batch number and more. Information in 15 digits is indicated by the last two digits of the year when the pipes were manufactured, the month and decade number of the year, shift number, batch number, machine and production line.
- Trademark of the product manufacturer, information about the certificate. There is also information about the assignment of a quality mark to a pipe manufacturer, which confirms the ability to produce products according to the national standard, designating the material used in production.
truba-info.ru
Polymer piping systems for cold, hot water and heating —
classification “S” “SDR” “PN”
The outer diameter and wall thickness of polymer pipes are determined by the relevant standards. Pipes made from the same material, but with different wall thicknesses, differ in different operational parameters (working pressure/working temperature/service life). Initially, pipes were divided according to wall thickness into categories of pressure values (pressure series) designated “PN”. Gradually, as the properties of polymer materials improved, the “PN” classification ceased to correspond to the values that determine the properties of products, especially hot water distribution systems, and the “S” and “SDR” classifications were introduced.
- · PN – maximum permissible operating pressure with which the system can be operated at a temperature of 20°C over a service life of 50 years.
- · S =(SDR-1)/2, SDR approximately corresponds to D/t, where D... is the outer diameter of the pipe, and t... is the thickness of the pipe walls
For example, polyethylene pipes for water distribution systems, pressure sewer connections and sewerage systems are standard (ČSN EN 12201-2) and now there are S, SDR and PN designations:
The EN 12201 standard gives a clear definition of PN: the numerical value corresponds to the permissible working pressure (PFA) of water at a temperature of 20°C, expressed in bar and the minimum design factor. As can be seen from the table, PN values differ for different types of polyethylene (PE) pipes of the same S series (i.e. pipes with the same wall thickness). When using polyethylene pipes for cold water distribution systems, the PN value quite reliably expresses the hydrostatic strength of the pipes at an operating temperature of 20°C. This does not apply to pipes for hot and cold water distribution systems . In such cases, separate standards are used for different materials:
- · ČSN EN ISO 15874 Plastic piping systems for hot and cold water supply. Polypropylene (PP)
- · ČSN EN ISO 15875 Plastic piping systems for hot and cold water supply. Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX)
- · ČSN EN ISO 15876 Plastic piping systems for hot and cold water supply. Polybutylene (PB)
- · ČSN EN ISO 15877 Plastic piping systems for hot and cold water supply. Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (PVC-C)
- · ČSN EN ISO 22391 Plastic piping systems for hot and cold water supply. Polyethylene with increased temperature resistance (PE-RT)
These standards no longer provide for PN marking. For pipes, the S series marking is used. For example, polypropylene pipes, previously marked PN 10, are currently designated as S5 according to standards (manufacturers usually use both classifications, since customers are accustomed to the classic PN designations). For the transition period, the German standard DIN 8077/1997 provided a table of correspondences of PN, S and SDR values for three types of polypropylene: PP-H, PP-B, PP-R:
Not long ago, a new type of polypropylene appeared on the market - type 4, PP-RCT, which has higher pressure resistance at high temperatures. This material has already been approved by the standards ČSN EN ISO 15874 and DIN 8077, which have also been supplemented with new series of pipes S (S8, S6,3, S4) specifically and exclusively for PP-RCT. Pipes made of this material cannot be marked with the PN marking, since the new standards no longer contain these designations, thus, the pipes of the new S series do not even have the corresponding PN values. Below is part of the table ČSN EN ISO 15874-2. As the wall thickness increases, the “S” value decreases (see definition of S):
The new type of polypropylene has higher pressure resistance at high temperatures (60°C and above), which is an important factor for hot water distribution and heating systems. Pipes made from this material can be used at higher temperatures and pressures, and pipes with thinner walls can be used compared to pipes made from polypropylene type 3 (PP-R)
Comparative table of pressure resistance of pipes made of polypropylene PP-R and PP-RCT with the same “S” value - the same wall thickness:
Comparative table of pressure resistance of pipes made of polypropylene PP-R and PP-RCT at different values of “S” - even with smaller wall thickness, PP-RCT pipes have higher pressure resistance:
How, in this case, will the user figure out what a certain pipe is intended for?
The manufacturer must indicate information on the use of a specific type of pipe on each pipe according to the formula: service class/working pressure.
According to the ISO 10508 standard, the areas of use of pipes of various classes are defined as follows:
- Class 1 (hot water distribution systems 60°C, service life 50 years)
- Class 2 (hot water distribution systems 70°C, service life 50 years)
- · Class 4 (underfloor heating, low temperature radiators, service life 50 years, with the system expected to operate (within 50 years) 2.5 years at 20°C, 20 years at 40°C, 25 years at 60°C and 2.5 years at 70°C)
- · Class 5 (high temperature radiators, 50 year service life, with (over 50 years) the system expected to operate for 14 years at 20°C, 25 years at 60°C, 10 years at 80°C and 1 year at 90°C)
For each material and each S series, the maximum operating pressure (4, 6, 8, 10 bar) is calculated for a specific service class.
For example, for a PP-RCT-S3.2 pipe, the information on the pipe will be presented in the following form:
Class 1/10bar, 2/10bar, 4/10bar, 5/8bar - this means that the pipe can be used:
for hot water distribution systems at a temperature of 60°C, an operating pressure of 10 bar and a service life of 50 years (class 1/10); for hot water distribution systems at a temperature of 70°C, an operating pressure of 10 bar and a service life of 50 years (class 2/10); for underfloor heating and low-temperature radiators with an operating pressure of 10 bar and a service life of 50 years (class 4/10); for high-temperature radiators with an operating pressure of 8 bar and a service life of 50 years (class 5/8)
Pipes made of other materials are also marked in the same way (see the list of standards at the beginning of the article).
www.wavinekoplastik.ru
Features of using products in heating systems
Polypropylene pipes for hot water
Considering that ordinary polypropylene pipes have a fairly large expansion coefficient when heated, special PN25 reinforced PP pipes are used for heating systems . Due to the reinforcing layer made of perforated aluminum sheet or fiberglass, the expansion coefficient is reduced by 5-6 times.
They can also be used in hot and cold water plumbing systems.
The technology of pipe reinforcement with glass fiber (fiber), which manufacturers have begun to use very actively in recent years, has a number of advantages compared to the traditional technology of reinforcement with aluminum foil.
Pipes with fiberglass have the same technical parameters as pipes with a reinforcing aluminum layer.
Moreover, the former have additional advantages:
- light weight;
- low cost;
- quick installation process, since pipes with fiber do not require preliminary trimming.
In some situations, for the installation of low-temperature heating systems with a maximum heating of the coolant up to 65-70°C, it is possible to use unreinforced PN20 pipes . However, this should only be done in extreme circumstances, only if it is not possible to purchase special PN25 products.
In this case, it is necessary to install the system with special care, taking into account the large linear expansion of unreinforced PN20 pipes.
Description of a heating system with natural circulation of coolant, recommendations for design and installation.
We use the Excel program to hydraulically calculate the heating system. You can also see ready-made hydraulic calculation options here.
Which batteries have better heat dissipation? Copper ones, but they are very expensive, so we recommend using cast iron ones. Compare the characteristics of radiators made of different materials https://teplius.ru/radiatory/vybor/samye-luchshie.html
2 comments
Polypropylene pipes fail after 4 - 5 years when used in hot water at 60 - 70 C. Destruction and cracking of the inner layer when interacting with oxygen dissolved in water
Czech polypropylene ecoplastic has been operating the heating system for 20 years. It’s just that the installation should be done by specialists, and not by all sorts of cheap monkeys. Which do not follow the installation rules. Then accidents happen.
Polypropylene pipes: technical characteristics, application
What are polypropylene pipes? What is their scope of application, technical characteristics, what does their marking mean? In this article we will try to understand all these issues. And understand why this type of pipe structures is truly considered a unique material, without which today it is impossible to imagine the installation or repair of water supply, heating or sewer lines.
Polypropylene pipe - what is it?
Polypropylene is a type of thermoplastic polymer. It is produced by combining (polymerizing) molecules of a derivative of ethylene gas. The international designation of polypropylene is “PP”. Next, we will take a closer look at polypropylene pipes: technical characteristics, properties and manufacturing technology of this new generation material.
Having unique resistance to the effects of alkaline solvents and aggressive substances, the material is widely used in the installation of heating systems, water supply systems and sanitary facilities. Can withstand low temperatures (up to -10 degrees) or high temperatures (up to +110 degrees).
Basic properties of polypropylene pipes and their GOST
Modern polypropylene pipes, the technical characteristics and properties of which can be seen in the table, are reliable, durable and quite affordable. The main and indisputable advantage is the fact that they are not subject to corrosive processes, are resistant to temperature conditions, are easy to install, and are made of environmentally friendly materials. The main properties according to GOST are presented below.
| GOST | Parameter | Index |
| DIN52612 | Thermal conductivity, at +200С | 0.24 W/cm |
| 15139 | Density | 0.9 g/cm3 |
| 23630 | Heat capacity at +200С (specific) | 2 kJ/kgf |
| 21553 | Melting | +1490С |
| 11262 | Tensile strength (at break) | 34 ÷ 35 N/mm2 |
| 18599 | Yield Strength Elongation | 50% |
| 11262 | Yield strength (tensile) | 24 ÷ 25 N/mm2 |
| 15173 | Expansion coefficient | 0.15 mm |
A type of polypropylene pipe. Scope of application
The latest technologies for the production of plastic products are polypropylene pipes. Specifications are presented below.
- PN10 – thin pipe. Service life is approximately 50 years. It is used when installing cold water supply and heated floors (the coolant temperature should not exceed + 450C). Standard dimensions: Ø outside 20÷110 mm, Ø inside 16.2÷90 mm, pipe wall thickness 1.9÷10 mm. Nominal pressure – 1 MPa.
- PN20 - this type of pipe is used in cold water supply systems in residential or industrial buildings or hot water supply systems (up to +800C). The service life is 25 years. Nominal pressure – 2 MPa. Dimensions: outer Ø 16÷110 mm, inner Ø 10.6÷73.2 mm, pipe wall thickness 16÷18.4 mm.
- PN25 – polypropylene pipe reinforced with aluminum film or glass fiber. Its properties are identical to metal-plastic. The service life depends on the pressure inside it and temperature media. Used for installation of heating and hot water supply systems. Nominal pressure – 2.5 MPa. Dimensions: Ø outside 21.2÷77.9 mm, Ø inside 13.2÷50 mm, pipe wall thickness 4÷13.4 mm
The main advantages of polypropylene pipes
What undeniable advantages do polypropylene pipes have? The technical characteristics of polypropylene, according to manufacturers, are truly amazing. It is considered a universal building material for the installation and reconstruction of utility lines in residential and industrial complexes. They have successfully passed tests in independent European and world laboratories and have confirming quality certificates. Let's consider the advantages.
- Their main advantage is their long service life - about 50 years, and when used in a cold water supply system they can last up to 100 years.
- Thanks to the specially designed inner surface of the pipe, which is constantly in contact with water, no deposits form on their surfaces.
- Noise insulation. When transporting hot water from the heating medium or during a simple flow of water, noise may occur. Polypropylene is able to absorb them.
- No condensation. PPR polypropylene pipe is resistant to temperature changes due to low thermal conductivity.
- Light weight. Compared to their metal counterpart, they are 9 times lighter.
- Easy to install.
- No additional maintenance is required.
- Resistance to acid-base substances.
- The elasticity of polypropylene pipe is very high.
- Affordable price.
Product technical data sheet pn25
Not long ago, manufacturers developed and put into mass production a polypropylene pipe pn25. Its technical characteristics are described in detail in the product passport.
| № | Characteristic name | Values for polypropylene pipes: dimensions | |||||
| 20÷3,4 | 25÷4,2 | 32÷5,4 | 40÷6,7 | 50÷8,3 | 63÷10,5 | ||
| 1 | Inner Ø | 13.2 mm | 16.6 mm | 21.2 mm | 26.6 mm | 33.4 mm | 42.0 mm |
| 2 | Specific heat capacity | 1.75 kJ/kg0С | |||||
| 3 | Ø tolerance | +0.3mm | +0.3mm | +0.3mm | +0.4mm | +0.5mm | +0.6mm |
| 4 | Linear expansion, (1/0С) | 3,5÷10-5 | |||||
| 5 | Heating time during welding | 5 sec | 7 sec | 8 sec | 12 sec | 18 sec | 24 sec |
| 6 | Roughness coefficient(equivalent) | 0.015 mm | |||||
| 7 | Cooling time, (seconds) | 120 sec | 120 sec | 120 sec | 240 sec | 250 sec | 360 sec |
| 8 | Tensile strength | 35 MPa | |||||
| 9 | Normative series | S2.5 | |||||
| 10 | Elongation at break (relative) | 350% | |||||
| 11 | Weight (kg/linear meter) | 0,175 | 0,272 | 0,446 | 0,693 | 1,075 | 1,712 |
| 12 | Tensile yield strength | 30 MPa | |||||
| 13 | Melt flow index PPR | 0.25 g/10 min | |||||
| 14 | Thermal conductivity | 0.15 W m/0С | |||||
| 15 | Heating time during welding | 5 sec | 7 sec | 8 sec | 12 sec | 18 sec | 24 sec |
| 16 | Modulus of elastic layer PPR | 900 MPa | |||||
| 17 | Depth of the pipe socket (minimum) when welding | 14 mm | 15 mm | 17 mm | 1 8 mm | 20 mm | 24 mm |
| 18 | Pipe density (equivalent) | 0.989 g/m3 | |||||
| 19 | Volume (internal) linear meter/l | 0,137 | 0,217 | 0,353 | 0,556 | 0,876 | 1,385 |
| 20 | Modulus of elastic layer PPR + fiber | 1200MPa | |||||
| 21 | Dimensional ratio(standard) | 6SDR | |||||
| 22 | PPR Density | 0.91 g/m3 | |||||
| 23 | Pressure (nominal), PN | 25 bar | 25 bar | 25 bar | 25 bar | 25 bar | 25 bar |
| 24 | Welding time | 4 sec | 4 sec | 6 sec | 6 sec | 6 sec | 8 sec |
A new product in the metal-plastic industry with high quality and properties is a polypropylene pipe pn25. The technical characteristics are presented in detail in the table above. It was she who was able to solve the problem with the high coefficient of thermal expansion of plastic pipe products. This makes it possible to use it in drinking water supply systems, hot water supply, installation of heating and other utilities. And also for transporting other liquids or gases that are not aggressive to the materials from which they are made.
Design Features
The layers on the inside and outside are made of special polypropylene grade PPR100. The percentage of fiberglass fiber in it is at least 12%. The inner layer is made of the same material, but the fiber content is increased to 70%, and also contains red dye. The presence of fiberglass fiber in the pipe reduces the level of deformation due to temperature influences, but, unfortunately, cannot cope with oxygen diffusion.
What is reinforcement of polypropylene pipes? Types of reinforcement
Let's consider universal reinforced polypropylene pipes, their technical characteristics, types of reinforcement, where they are used. Special reinforcement makes it possible to use it in a heating or hot water supply system. In addition, they are not only famous for their long service life, but also for their high quality and efficiency indicators. Today, there are two methods of reinforcing this type of product: fiberglass and aluminum. Let's consider each of them separately.
Glass fiber reinforcement
Fiberglass reinforcement is a three-layer pipe structure: two layers of polypropylene (internal and external) and a layer of fiberglass. Marked as PPR-FB-PPR. This abbreviation in the marking confirms the monolithic structure and fiberglass reinforcement. During installation, these products do not require calibration or cleaning; experts recommend installing more additional fasteners during installation.
Aluminum reinforcement
Pipe products with such reinforcement are a material for the installation of heating or hot water supply systems with a high level of structural rigidity. They are identical in strength to metal analogues with thin walls. Their surface must be marked PPR-AL-PPR. They are reinforced with two layers of aluminum: the first is perforated with small holes, and the second is continuous and integral over the entire surface of the pipe structure. When installing heating, the pipe needs to be stripped of the aluminum layer; only the polypropylene layer is soldered. If the technology is implemented correctly, the installed system will work for many years without problems.
Polypropylene and its use in the sewer system
So, we have found that polypropylene as a pipe material is highly resistant to the effects of aggressive alkaline and chemical substances. Therefore, to the question “which is better to choose pipes for utilities?” The answer is clear - modern polypropylene sewer pipes. Technical characteristics: stability, strength and durability. In addition to their resistance to the effects of aggressive substances, and there are a lot of such in gutters, they will also last for quite a long period. They are not susceptible to corrosion processes in comparison with metal pipes. The length of the pipe for the sewer system is about 4 meters, the diameter of polypropylene pipes (technical specifications contain such information) ranges from 16 mm to 125 mm. That is, their scope of application in the sewerage system is quite wide. They are connected to each other by diffuse welding or using special fittings.
Valtec polypropylene pipes
Today there are a lot of offers from manufacturing companies of these products for buyers in our country. And when choosing a material for laying engineering systems, it is sometimes quite difficult to make a choice in favor of one of them. In appearance they are absolutely identical, and differ only in manufacturing technology. And even then, if a person is incompetent in the matter of pipe products, then he is unlikely to understand the characteristics. This is especially true for new companies that have recently appeared on the sales market.
The Italians present their new Valtec polypropylene pipes to the buyer. Technical characteristics: excellent quality, new manufacturing techniques, durability and reliability. Moreover, this company has been a leader in the sales market for several years. Its products have always been and are in demand. The quality is high due to the fact that the company keeps pace with the development of new technologies and introduces them into its production. Manufacturers provide a 7-year warranty on the product.
The price for the entire range of products is quite affordable. We always have in stock solid and composite fiberglass- or aluminum-reinforced polypropylene pipes for cold water supply systems with a cross-sectional diameter of 20÷90 mm. The company's employees very carefully monitor the quality of their products, so errors or deviations from standards are completely excluded. Available in special tubes up to 4 meters with markings, with accompanying documentation and certificates.
PPRC pipes
These are pipes made of high-temperature polypropylene. Available with a cross-sectional diameter of 20÷160 mm. Reinforced with fiberglass or aluminum. Their main difference is their low temperature expansion and low pressure loss. The production technology fully complies with GOST and the requirements of foreign standards. What are polypropylene pprc pipes? Technical characteristics, properties and advantages of a plastic product:
- low thermal conductivity;
- high level of sound insulation;
- resistance to corrosion processes;
- resistance to the effects of aggressive substances;
- high strength;
- resistance to bending more than once;
- environmentally friendly material;
- ease of installation;
- affordable price;
- long service life.
The use of polypropylene in the water supply system
Plastic pipe products are rapidly entering the list of popular building materials, and polypropylene water pipes are no exception. Technical characteristics, advantages and disadvantages are presented below.
Advantages:
- resistant to corrosion;
- service life - from 50 years;
- zero conductivity, hygiene;
- ease of installation;
- do not require additional care;
- affordable price;
- ability to withstand pressure of about 20 bar;
- excellent thermal insulation.
Flaws:
- cannot withstand temperatures exceeding 1000C;
- inability to repair or repair;
- welding work is required.
Available in different colors: gray, green, black and white. The color of the pipe does not depend on the properties and quality, except black. It has the ability to protect it from ultraviolet radiation. To install the water supply system, pipes with a diameter of 16÷110 mm are used. For cold water supply, pipes marked PPH homopolymer or PPB block copolymer are suitable. To supply hot water or heating, pipes marked PEX-AL-PEX are used. They are reinforced with either fiberglass or aluminum.
Classification of polypropylene pipes
All polypropylene pipe products are classified in a certain way.
- PPB - marking means that these are pipes with a high level of mechanical strength; polypropylene pipes are used for heating. Characteristics: reinforced (fiberglass or aluminum foil), strong, durable, affordable.
- PPH – marking of products with large diameters. Used in ventilation systems or cold water supply systems.
- PPR is the most popular and versatile brand. Its versatility lies in the fact that it is able to withstand high temperatures of water flow. Used in hot water supply and heating systems.
All these three brands differ from each other only in the type of plastic used in production. They contain special additives that make them more elastic and durable.
fb.ru>
Main purpose
Due to the special properties of polypropylene, the scope of application of pipes made from this material is quite wide.
In this case, the laying of pipes can be carried out in an open or closed way: inside walls under various finishing materials, in channels and shafts; pipes can be laid directly underground - in general, there are a lot of installation options.
Advantages
Thermoplastic polymer products for pipelines have an impressive list of advantages.
These include:
PP pipe design
- sufficient mechanical strength and resistance to sudden changes in pressure or temperature;
- high environmental friendliness of materials and aesthetic design;
- chemical resistance to aggressive environments and toxic substances;
- high dielectric properties that prevent electrical conductivity of the material;
- good noise absorption (polypropylene muffles the vibrating and rumbling sounds that the coolant makes as it flows through the pipeline);
- high anti-corrosion properties and absence of deposits inside the pipes;
- the elastic properties of the material prevent water from freezing, which ensures reliable operation and long service life of the heating system; the highest reliability of connections among other types of plastic pipes;
- a wide range of different types of connecting and shut-off valves, allowing the installation of pipeline systems of any configuration and complexity;
- convenience, simplicity and speed of installation;
- light weight, low cost of materials and connecting elements;
- low maintenance and long service life.
Flaws
Disadvantages relate to the operating features of the product:
Bending a pipe using a gas torch
- The low heat resistance of the material requires you to approach the choice of PP pipes very carefully (you need to take into account the heat resistance indicator or immediately look for insulation for heating pipes).
- Polypropylene is difficult to deform, making it impossible to change the direction of the pipe. It is necessary to resort to the help of additional fittings (angles, tees, contours).
- Quite high linear expansion when heated (especially for unreinforced pipes) requires the use of special installation rules and special compensators.
- To lay pipes, you need a special welding machine, which, due to its design, cannot always be used in limited space or in hard-to-reach places.
- Polypropylene is exposed to direct sunlight - this causes premature aging of the material.
How are modern water and gas taps marked? for example DN 15, PN 40? what does 1-1/4, 1-1/2 mean?
Ambulance
1-1/4 is called an inch and a quarter, i.e. 32mm. i.e. DN-32; 1-1/2 one and a half inches, i.e. 40mm. or DN-40. What DN what Du is nominal (conditional) INTERNAL! diameter of the pipe opening, since the outer diameter of the pipe varies depending on the wall thickness. The wall thickness is determined by the area of application of the pipes. (reinforced, normal, lightweight)
Guy from the future...
You have already been absolutely correctly answered to this question DN - nominal diameter in mm (here 15) PN - nominal pressure (here 4 MPa or 40 atmospheres) fractions - thread size in inches (1 inch = 2.54 cm) And there are also markings , indicating the type of material. Type in a search engine - there is a lot of information there
zna4enie.ru
What parameters need to be considered when purchasing
Let us consider in more detail the individual technical characteristics of polypropylene pipes that influence their choice when used in water supply and heating systems.
Pipes are most often produced in the form of straight sections (2, 4 or 5 meters in length), which ensures their ease of transportation and storage. If you need a custom product length, this parameter can be agreed upon during ordering.
Dimensions of polypropylene pipes
All pipes have standardized dimensions of outer and inner diameters, which are measured in millimeters.
The outer diameter can vary within the following limits: from 16 mm to 500 mm or more.
The inner diameter can be measured in inches. Based on this indicator, the required pipe is selected based on the calculation of the required water flow, operating temperature and permissible pressure. It is also used to select connecting elements and other fittings for pipeline installation.
Depending on the size of the outer diameter, products can be divided into three main categories.
1. Small pipes (16-63 mm) are used in water supply and heating systems of private and apartment buildings, for premises for various purposes, as well as for connecting pipelines to central heating networks.
2. The middle category (75-135 mm) is used in sewer and ventilation systems of residential buildings and other buildings, as well as for transporting compressed air and various chemicals. The most popular size in this group is the diameter of 110 mm - for installation of internal sewerage systems of various buildings.
Marking on polypropylene pipes.
Everyone who bought polypropylene pipes saw that they had some strange inscriptions on them. Let's figure out what is written there in order:
- PPR pipe is a designation of the material from which the pipe is made. In this case, PPR is polypropylene with rand copolymer (the most common type of polypropylene pipes on the market, suitable for both heating and hot water supply). In addition, there are other types: PPH - polypropylene homopolymer, suitable for laying cables or ventilation; PPB is a polypropylene block copolymer, suitable for cold water supply, but is rarely found in our stores.
- SDR - standard dimension ratio. It is calculated as the ratio of the outer diameter of the pipe to the thickness of the pipe wall. That is, the lower this coefficient is, the thicker the walls of the pipe will be. This means that it will be designed for higher pressure (or operating temperature). There is a standard range of values for this coefficient from 6 to 41.
- 40 * 6.7 - outer diameter of the pipe * wall thickness. People often confuse the diameter designations for steel and plastic pipes - for plastic pipes the outer diameter is always indicated, and for steel pipes the nominal diameter (inner diameter) is always indicated.
- PN 20 - nominal pressure. If the water temperature is 20 degrees Celsius, then the pipe must withstand the nominal pressure for 50 years. As temperature or pressure increases, the service life of the pipe will be reduced. In particularly unfavorable pipe conditions (at temperatures above 90° Celsius), polypropylene will fail within several heating seasons.
- EN ISO... - standards by which the pipe is manufactured. In Russia, GOST 32415-2013 applies to polypropylene pipes.
Regulations
In addition to GOST standards, the pipe may contain various DIN and ISO standards - standards of other countries, in particular those where the brand comes from. This does not mean at all that a pipe with European standards was produced in Europe - many products are made in China, under European brands. In general, if a pipe is supplied to Russia, then it must comply with a number of GOST standards (links at the end).
Often, pipes are sold on store shelves that do not comply with GOST standards at all - here we can only advise you to pay attention to these points and not trust the quality of such a product. Sometimes on the pipes there are inscriptions in English “for heating only, not for drinking water” - apparently the plastic releases harmful substances that are contraindicated for drinking water. Therefore, it is recommended to translate unclear inscriptions.
And finally, let’s decipher the inscription on the pipe from the first photo: PP-ALUX PP-R100/AL/PP-R100 32×5.4 PN25 SDR6/S2.5 CLASS5/9 BAR GOST R 53630-2015
. This is a pipe reinforced with aluminum foil, three layers: polypropylene random copolymer on the outside and inside, foil in the middle. The outer diameter of the pipe is 32 mm. with a wall thickness of 5.4 mm. The pipe can be used for 50 years in cold water with a pressure of 25 bar. The ratio of diameter to wall thickness is 6, size series is 2.5. The pipe can be used for a long time at all 5 classes with a pressure of up to 9 bar (classes 1,2,3 and 4 have higher pressure, you need to look at the documentation). The product meets all parameters from GOST R 53630-2015.
GOST 32415-2013 Pressure pipes made of thermoplastics and connecting parts for them for water supply and heating systems. General technical conditions
GOST R 53630-2015 Multilayer pressure pipes for water supply and heating systems. General technical conditions
GOST ISO 4065-2005 Thermoplastic pipes. Table of universal wall thicknesses (with amendment)
Marking of metal-plastic pipes.
The marking of metal-plastic pipes in accordance with GOST 53630-2009 reads as follows:
- PE-Xb/Al/PE-Xb - this inscription indicates that the pipe has 3 main layers (not counting two layers of glue): PE-Xb - outer layer of cross-linked polyethylene with crosslink type b, Al - layer of aluminum, which can be butt welded or overlap welded (a barrier layer that prevents the diffusion of oxygen through the walls), PE-Xb is the inner layer of cross-linked polyethylene. For clarity, look at the following picture:
- 16×2 - from this inscription you can find out that this pipe has an outer diameter of 16 mm and a wall thickness of 2 mm.
- Class 5 – operating class (operating conditions). These conditions are standardized by GOST 52134-2003 and look like this:
- Tmax—maximum operating temperature. In this example it is 90° Celsius.
- PN - nominal pressure expressed in MPa.
Cross-linked polyethylene is marked in the same way. Therefore, I did not write a separate subparagraph.
Marking of copper pipes.
With the marking of copper pipes the situation is somewhat more complicated. The fact is that Russian and imported pipes are labeled differently. To begin with, I will give a breakdown of the markings in accordance with Russian GOST 52318-2005.
Russian marking of copper pipes.
For copper pipe in sections, the markings will look like this:
European marking of copper pipes.
Below is an example of marking copper pipes according to the European standard EN-1057-2006. Look at the picture below:
This is exactly what the marking of a copper pipe should look like according to the European standard. For completeness, I will add one more table from this standard. Perhaps it will be useful to you
In addition to what is described above, the marking may contain other designations. For example:
- DVGW Cu - this designation is given by German manufacturers, it means that this pipe has been tested by the organization “German Water and Gas Association”. After this designation, as a rule, there is a registration number of the manufacturer in this association.
- DIN 1786 is the European standard for solid drawn copper pipes.
And so on. I see no point in listing all possible marking parameters, since the main ones are given in the EN-1057-2006 standard.
Marking of plastic sewerage.
Now let's look at what is written on sewer pipes made of PVC or polypropylene. Let's take, for example, the symbols on the external sewerage system in accordance with GOST 32413-2013
The figure shows that the marking is very similar to the marking of polypropylene pipes for heating or water supply. But one important element is added - the SN coefficient. This coefficient is called the nominal ring stiffness coefficient and is measured in kN/m2. The higher this coefficient, the greater the load the pipe can withstand under the soil layer. In everyday life, the concept is used that SN determines the depth in meters to which an external sewer can be buried.
For internal sewerage, marking is regulated by GOST 32414-2013. See the picture below for an example of markings:
As can be seen from the figure, there is no indication of ring stiffness for internal sewerage.
Summary.
From all of the above it is clear that the main characteristics of pipes can be determined by markings. This means that when choosing a pipe in a store, you will not make a mistake and will not use the wrong material. For example, there are cases when people use pipes for heating, which are designed for laying water-heated floors. Such pipes are not designed for high temperatures and quickly become completely unusable. As a result, the heating system will need to be completely redone, which will result in large expenses and discomfort. Therefore, read the markings carefully and understand them before installing anything. Returning a product purchased by mistake to a store is always easier than opening up floors or walls in order to correct such serious mistakes. That's all, write your questions in the comments!
znayteplo.ru
Additional data
In addition to the basic characteristics indicated, the marking of plastic pipes for hot water contains the following information:
- data on compliance with the requirements of international and domestic technical regulations;
- manufacturer – brand or trademark;
- name and number of the quality mark - this data confirms the product’s compliance with international standards;
- the type of production technology used and the minimum long-term strength (MRS) characteristic;
- production date, batch number and other information contained in the 15-digit code.