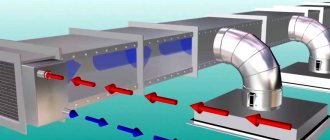
Not only the joints of structural elements of a building need to be sealed, but also some utility lines. In particular, the ventilation system functions effectively only if the airtightness of the air ducts is ensured. If they are not airtight enough, the flow of fresh air into the room is reduced due to leaks. To compensate, the load on ventilation equipment has to be increased, and energy consumption increases. This can be avoided by taking care to seal the air ducts.
Numerous air duct joints require sealing
Sealing process
The tightness of the ventilation system must be taken care of even during its installation; after completion of the installation work, tests are carried out. But airtightness, which initially complied with regulatory requirements, may decrease during system operation. In this case, secondary sealing is required. Sealing techniques depend on the method of connecting the air ducts and their cross-section; the characteristics of the working environment are also important - temperature, the presence of vapors of aggressive substances in the air.
- The sealing of the flange connections of the air ducts is carried out during the installation process; a sealant in the form of a cord, bundle, tape or a gasket of the required shape and size is placed between the flanges. The connection bolts pass through the seal, holes are pre-made in the rigid seals and gaskets, and the threads are pulled apart in the asbestos cord. During the sealing process, you need to ensure that the lumen of the air duct is not blocked by the seal protruding inward;
- It is recommended not only to seal conventional flange connections during installation, but also to post-installation coat the joint with sealant. If so-called Euro flanges are used (a flange made of corners and tire rails), coating sealing is not required, a gasket gasket is sufficient;
- To seal wafer joints of air ducts through which air moves at temperatures up to 40 ° C, self-adhesive sealing non-hardening tape made of butyl rubber, backed with non-woven material, is used. The tape is glued over the joint onto a thoroughly cleaned, dry surface and carefully rolled by hand or with a roller to prevent wrinkles and bubbles from forming. To avoid vulcanization of the tape, the surface should not be very hot;
- Round air ducts with a working environment temperature of up to 60 °C are sealed with aluminum tape, which closes the seam from the outside. Heat-shrinkable cuffs can also be used;
- In bandage type connections, a non-drying sealing mastic is used. The internal cavity of the connection is filled with a preheated composition;
- Wafer-type glass-to-glass connections can be sealed with sealant or mastic. They must be applied to the outer surface of a narrower pipe, then after connecting the pipes, the excess will be squeezed out. If you apply a sealing compound to the inner surface of a larger diameter pipe, it will get inside the air duct and block its lumen. The sealed joint can be further sealed by gluing the top with butyl rubber tape, or cover the seam with sealant (strip width up to 1.5 cm) and wrap it with aluminum tape;
- in difficult areas (connections of pipes of different diameters, joints with a protruding weld), heat-shrinkable polymer couplings and cuffs are used. They are put on one of the pipes, and after connecting them, they close the joint. The heated cuff tightly compresses the uneven surface, and the melted adhesive composition fills microcracks and crevices.
if the temperature of the working medium in the air duct exceeds 70 °C, heat-resistant seals are used, and the air ducts can also be welded to the flange;
Fighting condensation using an example
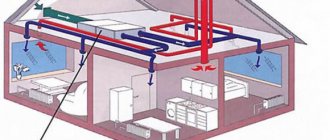
Let's consider a specific situation. A one-story private house has a ventilation system that provides air exchange in the bathroom and kitchen. Metal ventilation pipes are connected to these rooms.
They are laid through the attic with subsequent access to the roof. With daily temperature fluctuations, condensation forms in the pipes. But a particularly large amount of it is observed in winter, when water drips from the hood, collecting in a puddle.
Attics are usually not heated, so ventilation pipes laid in this room need to be insulated along their entire length
The problem is solved comprehensively. The exhaust and supply pipes are insulated. The pipes are insulated from the entrance to the ceiling to the exit to the outside. In areas passing through an unheated attic, pipes are insulated with rolled mineral wool 70-100 mm thick.
A shell is used in places where it passes through the ceiling and ceiling. A tee with a condenser collector is installed at the lowest point.
If the ventilation ducts do not pass through the roof, but through the wall, the section in the wall is insulated using the shell. Outside the house, a 90-degree tee is installed on the ventilation pipe, a condensate collector and an umbrella (deflector) are mounted.
Materials for sealing air ducts
To seal air ducts, seals, gaskets made of sheet materials, tapes with an adhesive layer, which can be used both as an inter-seam seal and for sealing over the joint, adhesive tape, heat-shrinkable cuffs and couplings (STUM, TsRT), coating materials (mastics, sealants) are used. .
Coating sealants and mastics:
- sealant based on polyacrylic dispersion without silicone after hardening provides sealing in the temperature range from -20 ° C to +80 ° C ;
- acrylic sealant “Accent-128” with high adhesion to metal, non-shrinking, vapor-tight, vulcanizes after application;
- sealant-mastic for ventilation ducts;
- non-drying mastic based on butyl rubber and ethylene rubber with added plasticizers. Retains elasticity after application and can be used for sealing air ducts with a working environment temperature of up to 70 °C;
- non-hardening and non-drying synthetic mastic.
Tape seals for flange connections:
- asbestos cord is heat-resistant and vibration-resistant, used for smoke exhaust ducts;
- chrysolite strand – withstands operating temperatures above 70 °C;
- polymer mastic rope with a diameter of 8-10 mm PMZH-1 and flat tape 20x2 mm PMZH-2 are highly elastic and fit tightly to the rebate mirror;
- Thermal sealing tape made of graphite is fire resistant, swells in the event of a fire and does not allow smoke to leak through, can withstand up to 4 hours;
- Due to its high rigidity, PRK polymer tape is less popular than permanent residence.
Sheet materials for making gaskets:
- porous rubber made from hard rubbers (there are acid-resistant, heat-resistant and frost-resistant varieties);
- asbestos cardboard has the same advantages as asbestos cord;
- PVC-based cushioning plastic can withstand temperatures up to 70 °C.
- butyl rubber tapes for sealing flanged and wafer joints (mostly tape with a duplicating non-woven layer is used);
- wafer sealing tape based on foamed polyethylene with an adhesive layer for flange connections of square air ducts;
- heat-resistant asbestos-free fiberglass foam tape with contact adhesive based on acrylic dispersion;
- self-adhesive foam tape - tire seal (Euro flange);
- aluminum tape, including reinforced and high-temperature. Made from aluminum foil and acrylic, polyacrylic glue. Used for additional or secondary sealing of air duct joints over the seam.
To ensure airtightness of the ventilation, air conditioning, and smoke removal system, it is necessary to use high-quality connecting elements and sealing materials. It is equally important to carry out the work correctly - connecting air ducts, installing seals, preparing the surface for applying mastic, sealant or winding self-adhesive tape.
Tytan Professional sealant for ventilation ducts
- Product description
- Advantages
- Application area
- Specifications
- Mode of application
- Technical documentation
- Reviews
Tytan Professional ventilation duct sealant is a one-component acrylic plastoelastic sealant designed for sealing ventilation ducts made of galvanized metal sheets and other zinc elements in various fields: plastic production, metal structures, window and automotive industries, households, can be used for filling cracks and seams subject to slight deformation. Acrylic sealant for ventilation ducts TITAN has excellent adhesion to most building materials such as galvanized sheets, concrete, plaster, brick, asbestos cement, cement.
- Without smell.
- Water based, environmentally friendly.
- Easy to clean with water.
- Can be painted.
- Excellent adhesion to galvanized metal sheets, PVC and most porous materials.
- Does not cause corrosion.
- Can be used on damp porous surfaces.
- Can be used indoors and outdoors.
- Short film formation time.
- Waterproof after curing.
- Glossy finish.
- Wide range of construction works.
- Resistant to aging, weather and ultraviolet radiation.
- Sealing of ventilation ducts made of galvanized metal sheets.
- Sealing of various elements made of concrete, metal, brick, PVC.
- Sealing of ventilation ducts in sanitary areas, laundries, drying chambers, and large kitchens.
- Filling cracks in porous building materials.
- Sealing of joints in plasterboard technology.
- Minor repairs to plaster before painting.
- Sealing of low expansion structural joints between brick, concrete, wood, etc.
| Consistency | paste |
| Color | silver gray |
| Curing system | evaporation of water |
| Density | 1.53 ± 0.05 g/cm³ |
| Curing time | OK. 1 mm/day, depending on the thickness of the seam, air humidity and environment |
| Film Formation | from 10 to 25 min. |
| Application temperature | +5°C ÷ +50 °C (hardening speed is slower at negative temperatures) |
| Heat resistance after curing | -30°C ÷ +80°C |
| Curing time | 1 - 4 weeks, depends on layer thickness, ambient temperature and humidity |
Surface preparation: The surface must be clean from dust, grease, dirt, bitumen and ice. Metal surfaces must be degreased. Remove any remaining old sealant or other material. Clean and degrease the surface with acetone, isopropanol, ethanol (metal, glass) or detergent (plastics). Dry the surface. Protect the surface from contamination with TYTAN masking tape. If the sealant is applied to an unknown surface, it is necessary to conduct preliminary testing.
Primer: TYTAN Professional Ventilation Duct Sealant does not require the use of a primer on most surfaces, however, on a few specific surfaces, the use of a liner is required to improve adhesion. In case of any questions or doubts, please contact our Technical Department.
Joint Design: The joint width should be calculated from approximately twelve times the expected joint movement and fall within a range of 6 to 24 mm. The joint depth should be a minimum of 6 mm and a maximum of 9 mm. The seam size should not exceed 12 mm x 12 mm. If the seam depth exceeds 12 mm, it is necessary to use the TYTAN Sealing Cord.
Sealing the air duct network of ventilation systems
Recently, with increasing quality standards for ventilation systems and their maintenance
, more and more attention is paid to such a criterion as
the tightness or airtightness of air ducts
.
Why is this parameter so important? There are several reasons for this. Firstly, loss of air duct tightness negatively affects the efficiency and complexity of servicing the ventilation system. Modern sanitary standards, which set out the requirements for various types of premises, are becoming more and more strict regarding the volume of fresh air inflow. To increase this volume, duct leakage must be minimized
. Secondly, if air losses are not compensated by the performance of the system, which usually happens, then the microclimate of the room deteriorates significantly, and this, in turn, adversely affects the well-being of the people in it. Thirdly, reducing the loss of air flow passing through the ventilation system allows you to reduce the cost of electricity, which ensures the operation of key units of the system. Finally, depressurization of the air duct can lead to immediate negative consequences for the ventilated room itself. If sections of the air duct without thermal insulation pass through unheated or cold rooms (basement, attic, warehouse, etc.), then condensation will form in them, as a result of which water coming from the cracks of the air duct can flood the building.
Duct tightness
measured using the leakage coefficient, which reflects the relative loss of airflow in the ventilation system. Leakage standards are established by both Russian and European standards. Russian SNiP define two classes of air duct leakage: normal (with a coefficient of 1.61 l/sec/m at 400 Pa) and dense (with a coefficient of 0.53 l/sec/m at 400 Pa). The European standard Eurovent 2.2 distinguishes three classes of tightness: A, B and C. The highest class C characterizes air ducts with the lowest leakage coefficient (0.15 l/sec/m at 400 Pa), the air tightness of class B equipment is three times lower, and class A - at nine. Thus, the Russian class P (dense) is located between the middle and lowest European classes, and normal class leaks have shown to be worse than those of the European class A. Today, many Russian manufacturers are also switching to producing equipment that meets European quality standards, which are guarantee of its airtightness.
In general, the issue of air duct tightness should be resolved at the equipment installation stage. High airtightness is achieved through high-quality installation and correct choice of air duct
.
Back in Soviet times, the Instruction for sealing ventilation and sanitary systems VSN 279-85 was developed, which describes in detail the requirements for various work on sealing air ducts. This instruction lists the main factors that must be taken into account to ensure the airtightness of ventilation equipment
, these include:
- quality control of manufacturing of connecting parts (flanges, bandages, slats, etc.)
- maintaining alignment and parallelism of the ends of the connected parts
- correct installation of sealing materials
- uniform tightening of bolts
- quality of air duct surface cleaning before sealing
- quality of the sealing composition and its application to the surface
- tightness of sealing compounds to the surface of the air duct.
Experts note that at the stage of design and installation of the ventilation system
To ensure the tightness of the air ducts, it is necessary to make design reserves, which must be included in the cross-section of the initial and long sections of the air duct network. As for the choice of equipment, it is usually noted that it is advisable to use air ducts with a round cross-section, since their air tightness is higher than that of equipment with a rectangular cross-section. This is because connecting two round ducts is simpler and requires the use of only one fitting. Also, their installation is more economical compared to the installation of air ducts with a rectangular cross-section, since the perimeter to be sealed for sealing purposes is smaller for round air ducts. To connect air ducts, it is recommended to use fittings with a rubber seal, specially designed and made from durable and wear-resistant rubber, which make it possible to dispense with the installation without treating the seams with sealants, which tend to lose their performance characteristics over time.
Air duct tightness standards
The criterion for the tightness of air ducts is the air leakage coefficient. It shows how many liters per second are lost per linear meter at a system pressure of 400 Pa. In Russia and Europe, the airtightness of ventilation systems is regulated by various regulatory documents:
- SNiP 3.05.01-85;
- Eurovent 2.2.
In accordance with Russian standards, two classes of air ducts are distinguished:
- normal – leakage coefficient 1.61 l/sec/m;
- dense – 0.53 l/sec/m.
- A – 1.35 l/sec/m;
- B – 0.45 l/sec/m;
- C – 0.15 l/sec/m.
Normal air ducts are used in general supply and exhaust ventilation, dense air ducts are used in transit sections of ventilation systems, in smoke removal and aspiration systems (air purification in hazardous industries), and in pneumatic grain conveyors.
In Europe, the requirements are more stringent; air ducts are divided into three classes:
Types of sealants
Asbestos cord
Often, sealant is used to seal joints of smoke exhaust ducts. It is used for sealing if the surface temperature is up to 400 °C. Use cords with thicknesses from 0.7 mm to 32 mm. To seal, cut a piece of the cord and lay it on the flange. Then the bolts are passed through the seal so that the threads go around them on both sides. This type of sealant promotes increased vibration resistance and temperature performance. To extend the shelf life, it is recommended to store the asbestos cord in a dry place.
Foam rubber
This sealant is used for air ducts, inside which dust and waste move at a temperature of 42-70 ° C. Made from hard rubbers, it has high shock-absorbing and sealing properties. The porous rubber gasket is made at the installation site. A ring or frame of the required size is cut out of it. After that, holes are punched in it for the bolts and placed between the flanges. In this case, the flange plane must be free of rust. Acid-resistant, frost-resistant and heat-resistant rubber is used in ventilation work. Acid-resistant rubber perfectly resists the effects of acids and alkalis. Heat-resistant rubber, which contains asbestos, retains its properties in an air environment at temperatures up to 90°C.
Polymer mastic tourniquet (PMZh-1)
Made from polyisobutylene, petroleum bitumen, paraffin, asbestos and neutral oil; with a diameter of 8 to 10 mm. This seal is very elastic, which allows it to fit very tightly to the flange surface. It is stored wound in spools and sprinkled with talc. PMZH-2 is used more often than PMZH-1. It looks like a flat tape 20mm wide and 2mm thick. The tape creates a very reliable hermetic connection.
Thermal sealing tape
Refers to fire-resistant sealants. It is used for sealing flange connections of air ducts and is one of the best sealants. The tape is made of graphite. When a fire occurs, the sealant swells, thereby demonstrating its fire-resistant properties. It prevents smoke from entering adjacent rooms for 4 hours. This is a very good indicator.
PKR - Polymer type material is produced in the form of a tape, up to 6 mm thick and up to 50 mm wide. The tape is placed on the flange mirror, the holes for the connecting bolts are pierced and tightened. The disadvantage of this sealant is its high rigidity, which is why the holes for the bolts have to be pierced using a beard.
Heat-shrinkable cuffs. Made from polymers. Products with a diameter of 130-355 mm are produced. They are used in the temperature range – 40°С – + 60°С.
A non-drying compound used for bandage-type connections in round air ducts through which an air flow heated to +70°C passes. To ensure the tightness of the bandage joint, the inside of the bandage is filled with Buteprol sealing mastic. This sealant is a homogeneous mass of butyl rubber, ethylene rubber, fillers and plasticizers. When applying sealant, it must be heated. The mastic retains its properties at temperatures from -50 to +70°C.
Non-hardening flat tape. Made from non-woven material. The sealant is used for flange connections at temperatures not exceeding +40°C. Available in the form of a tape 12 m long and 80-200 mm wide.
Speaking about “Guerlain” type tapes, one cannot help but add that aluminum mounting tape is often used for mounting seals or as a seal directly.
Synthetic mastic that does not dry out or harden. Well suited for sealing ventilation system equipment.
Spacer plastic
Gasket plastic is made from polyvinyl chloride and is used as a sealing material. The plastic compound can withstand temperatures from -30 to 70° C.
Asbestos cardboard
Asbestos cardboard is produced in the form of sheets with dimensions from 900 X 900 to 1000 X 1000 mm, thickness from 2 to 6 mm. Sheets of cardboard must be smooth, free from cracks, dented areas and foreign mechanical inclusions. Gaskets from this sealant for flange joints are made in the same way as gaskets are made from sheet rubber.
Acrylic sealant for ventilation ducts TYTAN PROFESSIONAL 310ml 20348
There are 6 pieces in a package. Price per package: RUB 2,016. Price per one. product: 336 rub.
Write off up to 152 rubles. bonuses We will award 3 bonuses
- In your city: 23 pcs. In stock: 48 pcs.
- Pickup: tomorrow, after 09:00, from 1 store
- By courier: August 1, from 190 rub.
Acrylic sealant for ventilation ducts TYTAN PROFESSIONAL 310ml 20348 can be painted after complete drying.
The product is intended for sealing ventilation ducts made of galvanized metal sheets and other zinc elements in various fields of construction and industry.
Technical characteristics of sealant Tytan 310ml
Advantages of Tytan 310ml sealant
- Acrylic sealant TYTAN PROFESSIONAL 20348 for sealing ventilation ducts made of galvanized metal sheets and other zinc elements in various fields of construction and industry;
- Density 1.53 ± 0.05 g?/?cm3;
- Film formation from 10 to 25 minutes;
- Curing time is about 1 mm?/? day, depends on the thickness of the layer, ambient temperature and humidity;
- Application temperature 5 °C ÷ 50 °C (hardening speed is slower at negative temperatures);
- Temperature resistance -30 °C ÷ 80 °C;
- Shelf life: 24 months;
- Can be painted;
- Without smell.
- *The manufacturer reserves the right to change the characteristics, appearance, configuration of the product and the place of its production without notifying the dealer. The information provided is not a public offer
Quality control of air duct sealing work
To ensure the required quality of sealing gaps in joints and other places in air ducts by surface application of sealants, it is necessary to control:
- the quality of cleaning the surface of the air duct before sealing;
- quality of the sealing composition and its application to the surface;
- tightness of sealing compounds to the surface of the air duct.
Gaskets between flanges must not protrude into the air ducts.
Effective operation of the air duct implies high-quality sealing. Reliable sealing of air ducts is ensured by: high-quality cleaning of the air duct (see the article Cleaning ventilation) before sealing, high adhesion of the sealing compound and the tightness of its adherence to the surface of the air duct.
INSTALLATION OF FLEXIBLE HEAT-INSULATED SOUND-MAKING AIR DUCTS
- The air duct must be inserted onto the pipe to a length of at least 50 mm. For optimal sound absorption, put the air duct over the entire length of the pipe;
- After sealing with tape, securely fasten the air duct with a clamp.
Leaky ducts are installed in the same way as insulated ducts. However, it is necessary to additionally tape the polyester separator to the micro-perforated internal duct. After this, perform the operations described above. For sound-attenuating ducts, airtightness is more important. Due to microperforation, the outer shell experiences significant pressure. Pressure losses increase, and the noise attenuation coefficient decreases due to incomplete sealing of the air duct. Poor sealing causes additional noise, as well as additional air loss (Fig. 11).
rice. eleven
How to properly insulate air ducts?
Theoretically, the thermal insulation of air ducts can be both internal and external. However, in practice, only external insulation is used due to the complexity of working with the internal type of insulation.
The quality of the insulating layer depends on its thickness, which correlates with temperature conditions, environmental aggressiveness, humidity and other factors. Calculations must be made by specialists, and the formula for these measurements is given in SNIP 2.04.14-88. It is not recommended to carry out calculations on your own, since the final result will depend on many important factors.
Insulation of ventilation ducts is carried out in accordance with SNiP rules, which require preliminary calculations
The requirements presented in SNIP are regulated for systems used in industrial premises and in private or civil construction projects. The temperature of transported media in the described structures ranges from -180 degrees to +600 degrees.
When using roll insulation, the working diagram will look like this:
- the air channel is wrapped with insulation of the required thickness;
- the insulation layer is attached using flexible wire applied at equal intervals. The self-adhesive insulation layer does not require additional reinforcement.
When insulating large diameter air ducts using mineral wool, additional fastening with pins is required. Metal pins are welded to the air duct, after which it is wrapped with mineral wool. In this case, the mineral wool should be pinned onto the pins. The wound layer of insulation is additionally strengthened by pressure washers, which are placed on each pin. The last step in fixing is to use wire as in the previous step.
If ready-made polystyrene foam shells are used, special attention should be paid to sealing the joints between the two halves of the product. Waterproof glue is applied to the grooves of the shells; it is also recommended to secure the insulation with tape.
Insulating air ducts with mineral wool requires compliance with safety precautions, as this material can be harmful to humans