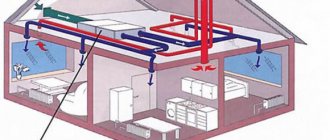
Why is ventilation needed? Let's give some illustrative examples.
Lack of ventilation in the under-roof space will lead to increased humidity. The wooden substructure and thermal insulation will become damp. Wet insulation will no longer retain heat and will begin to deteriorate. The sheathing and rafter system will mold and rot.
If we mean a living space, due to insufficient ventilation the air will stagnate. The house will be too humid. Because of this, the wallpaper will begin to peel off and mold will appear in the corners. The fungus can trigger allergies or asthma in the residents of the house.
If the pressure in the sewer system is not balanced, unpleasant odors will not be removed. There will be a specific “aroma” in the house. To avoid this, natural ventilation must be provided.
High-quality ventilation is the key to a comfortable microclimate in the house. The air must actively circulate and be renewed. In this case, excess moisture and unpleasant odors will be eliminated in time.
We will tell you how to ensure ventilation in the living room and under-roof space. We recommend using the following items from the range:
- Ridge ventilation tape.
- Ridge valve (deflector).
- Ventilation outlet.
- Roof valves KTV and P-KTV.
- MP MAXI hood output.
- The output is universal.
- Hood outlet.
- Sewer outlet.
Let's consider their functions and features. We will also learn how to attach ventilation elements to corrugated sheets and metal tiles.
Specifications
The main requirement for ventilation ducts is that they are made of galvanized steel sheet. Such elements have stood the test of time and have shown that there are no cheaper or better analogues today. And other characteristics that you need to pay attention to.
- The section can be in the form of a circle or a rectangle.
- The ends of the sheets are connected in the form of a welded or folded seam.
- The direction of connection of galvanized sheets is straight or spiral.
- The tightness class of either “N” or “P” can be used.
- Galvanized air ducts are used up to +80C.
- The thickness of the galvanized sheet used is from 0.5 to 1.25 mm.
- Diameter 100-1250 mm.
- Length 3-25 m.
GOST
As mentioned above, all ventilation ducts are manufactured according to a certain state standard. In this case, galvanized sheets are used for production, which are produced under different GOST standards. The classification is based on the operating conditions of the ventilation pipes themselves. Eg:
- If air with a humidity of no more than 60% and a temperature of no more than +80C is passed through the ventilation, then a galvanized sheet made in accordance with GOST 14918-80 is used for the air ducts. In this case, material with a thickness of 0.5-1 mm is used.
- If the parameters of the transported air or gases are up to +500C, and they contain active chemical components, then the ventilation is assembled from pipes made of heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant steel, which is produced in accordance with GOST 5632-72.
The GOST designation is made in the quality certificate, which is issued for each batch of galvanized sheet.
Bottom line
We learned how to ventilate a roof made of corrugated sheets or metal tiles, what elements are required and how to install them.
Ventilation elements “Metal Profile” are equipped with everything except self-tapping screws. You do not need to choose caps, passage elements, or insulated pipes. Vilpe products will have to be “assembled” like a construction set: you will have to order passage elements and caps separately. But self-tapping screws and other necessary accessories (sealant, template, water seal ring) will be included in the kit.
Choose ventilation elements from the Metal Profile catalog. You will purchase high-quality products that will delight you with a long service life. You only need to select the required product and color.
Now you know how to ensure high-quality ventilation of a roof made of corrugated sheets or steel tiles!
Steel thickness for air ducts according to SNiP
This is a fairly serious indicator that determines the rigidity of the air ducts. And it depends on the diameter of the pipes being manufactured.
- diameter 80-315 mm – thickness of galvanized sheet used – 0.5 mm:
- diameter 355-800 mm – thickness 0.7 mm;
- diameter 900-1250 mm – thickness 0.9 mm;
- 1400-1600 mm – wall thickness 1.2 mm.
The thickness of steel for air ducts is one of the important parameters; it is not for nothing that it is precisely designated in SNiP. Therefore, when making ventilation pipes, you must strictly adhere to the above-mentioned ratios. At the same time, it should be noted that there is no difference what kind of pipes will be manufactured - class P or N air ducts. More on them below.
Average cost and where to buy
The cost of air ducts made of galvanized steel depends on the size of its cross-section and the thickness of the metal. The price is calculated per 1 m². On average, the market cost of 1 m² of product is about 320 rubles. Installation work will cost an average of 700 rubles. for the same square meter.
Despite the wide presence of air ducts in online stores, it is still worth buying them directly from the manufacturer, who can provide each product with a quality certificate.
Duct weight
| Diameter, mm | Weight of one meter, kg |
| 100 | 1,4 |
| 125 | 1,8 |
| 140 | 2 |
| 160 | 2,3 |
| 180 | 2,5 |
| 200 | 2,8 |
| 225 | 3,2 |
| 250 | 3,6 |
| 280 | 4 |
| 315 | 4,5 |
| 355 | 5,1 |
| 400 | 5,7 |
| 450 | 9 |
| 500 | 10 |
| 560 | 11,3 |
| 630 | 12,7 |
| 710 | 14,3 |
| 800 | 16,15 |
| 900 | 26 |
| 1400 | 48,4 |
| 1600 | 55,3 |
Fire resistance limit
Galvanized air ducts must provide certain conditions for maintaining their parameters during fires and non-propagation of fire. For this purpose, there are fire resistance standards that divide all building materials into five classes. So, galvanized air ducts belong to class zero. Therefore, pipes laid under the ceiling must withstand the fire temperature for 90 minutes, and pipes laid along the walls - 30 minutes.
Fire resistance testing of air ducts is carried out at the facilities themselves where the ventilation and air conditioning system is being constructed. In this case, SNiP 2.04.05-91 is used. Methods of protection:
- traditional using foil material;
- applying protective fire-resistant compounds using equipment;
- combined method.
Marking
In SNiPs, on the basis of which ventilation and air conditioning systems are built, there are no strict requirements for the marking of air ducts. That is why builders do not carry it out. But many contracting organizations are silent or do not know that GOST 14202 clearly states that air ducts must be marked. If air is transported through them, then they should be painted blue on the outside. The appendix of this GOST indicates exactly what shade the blue paint should be.
In Europe and America, marking is mandatory. In Russia, at some facilities, installation organizations also carry out painting of air ducts if these facilities are constructed according to international standards.
Ventilation ridge tape
The ventilation tape protects the under-roof space from dust, debris, snow, rain, insects, birds and does not interfere with air circulation. With its help you will ensure ventilation of the roof made of corrugated sheets or metal tiles.
The central part of the tape consists of polypropylene fibers and geotextiles. Polypropylene has water-repellent properties and does not allow moisture to penetrate into the under-roof space. At the same time, the tape breathes.
The tape has corrugated edges. They are made of profiled aluminum. During installation, the edges are straightened and the tape takes the shape of any roofing material.
On the reverse side of the tape there are strips of butyl adhesive-sealant. They ensure reliable fixation of the tape on the roof.
Length - 5000 mm. Width - 250 or 300 mm.
For which profiles it is suitable : for all profiles of metal tiles and corrugated sheets.
How to install : the ridge tape is laid before installing the ridge strip. Roll the tape along the ridge, pressing it tightly against the roofing. The corrugated edges will straighten out, the tape will adapt to the relief of the metal tile or corrugated sheet. The tape has an adhesive layer, so it will stick straight into place.
Density classes
When understanding the density classes of air ducts, you need to understand that these transporting elements can be used in different systems: ventilation and air conditioning, air heating and smoke removal. That is, in some of these categories, increased density of elements and 100% tightness of connecting joints are required, therefore galvanized air ducts are divided into two classes.
Air ducts class "P"
A system of galvanized air ducts, marked with the letter “P”, that is, dense, is installed in ventilation, where powerful pumping equipment is used, creating a maximum air pressure of up to 1.4 kPa. Air ducts of class “P” have certain characteristics:
- connection density is high, for which sealants or other sealing materials are used;
- the presence of a sealed lock at the junction of two air ducts.
Such air ducts are used in almost all systems related to the removal of air and smoke, as well as when transporting gases. In addition, SNiPs recommend installation of this type in buildings that are classified as explosion and fire hazardous.
Class "N"
The letter “H” in the marking of galvanized air ducts indicates the word normal. That is, the most stringent requirements are not imposed on their connection. A certain amount of leakage is allowed. Therefore, air ducts of class “H” can be used in rooms of fire hazard category “B” or “G”, that is, with minimal indicators.
This does not mean that the joints between the air ducts are not sealed. Small leaks, cracks and other defects are simply allowed. Rubber is most often used for sealing.
Tightness classes
The modern approach to properly organized ventilation is to ensure complete tightness of the air ducts. The density of this system was mentioned above. And these two classes can also be included in the tightness category. It is they who determine the work carried out in Russian construction organizations, because all this is indicated by SNiP 3.05.01-85.
It clearly states that there are several very important reasons why the tightness of galvanized air ducts is monitored.
- The effectiveness of a ventilation system decreases sharply when the airtightness of ventilation sections and pipes decreases. At the same time, repair and maintenance processes become more complicated. And since sanitary standards clearly stipulate what the air exchange should be in certain rooms, accordingly it is necessary to strictly adhere to the established requirements. This means that leaks have to be minimized.
- The insufficient supply of fresh air and the outflow of used air from the premises creates conditions in which a person is uncomfortable to be. In addition, it is harmful to health. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the power of application equipment. Which entails an increase in energy costs.
- If the tightness of galvanized air ducts is broken, and if the ventilation area is located in an unheated room, then there is a high probability of condensation forming inside the pipes.
In Europe they use their own document regulating the sealing of air ducts. It is designated as Eurovent 2.2. It has three classes of ventilation air duct tightness.
Class "A"
This is the lowest class of air duct tightness, which is determined by such an indicator as air tightness. So it should not be less than 1.35 l/sec/m, provided that the air pressure passing through the galvanized air ducts is 400 Pa.
Class "B"
This class includes air ducts with an air tightness of 0.45 l/sec/m at the same pressure of 400 Pa.
Class "C"
And the last class with an air tightness of 0.15 l/sec/m. As in previous classes, the air pressure in the system is 400 Pa.
Leak test
Regardless of whether a new ventilation system is being built or an existing one is being checked, it must be clearly understood that tests must be carried out. This is especially true for a working ventilation system that has become ineffective. For this purpose, aerodynamic testing technology is used. Not the easiest process, but you can’t do without it.
If deficiencies are identified, measures must be taken to eliminate them. Usually this is depressurization of joints. Therefore, it is necessary to re-seal by applying sealant, mastic or self-adhesive tapes.
How to choose?
The operation of the air exhaust system (AWS) depends on how correctly its cross-sectional area is calculated.
S=P/v, where
S - Sectional area.
P — SVO performance.
v - The speed of movement of the air mass (for residential premises an indicator of 3-4 m/s is used).
Determining ventilation performance involves determining the amount of air required for a comfortable stay in the room. It is calculated in 2 ways:
- By volume of air required:
P=A × n, where
P — SVO performance.
A - Number of people in the room during an hour.
n — Air consumption rate according to SNIP 41-01-2003 and MGSCh 3.01.01.
- By frequency of ventilation (ventilation):
P=V × k, where
P — SVO performance.
V - Volume of the room (with equal data, the entire room)
k - ventilation rate established by SNIP standards 41-01-2003.
Shape and diameter
The quality of air exchange, energy efficiency and room design depend on the selected configuration and size of the air duct cross-section. Therefore, the choice of air channels should be approached carefully:
- The smaller the diameter of the air duct, the higher the speed of movement of the air mass. It is important to be guided by the principle of the “golden mean”, because the higher the speed, the higher the noise level.
- Round ducts provide faster air movement, are easier to install and are cheaper.
- Rectangular ones are stronger and fit harmoniously into the design of any room.
Construction and rigidity
Depending on the specific application of the design, there are:
- rigid, semi-rigid or flexible;
- standard or thermally insulated;
- fire retardant.
The tighter the seams, the stronger the connection and the longer the service life.
Material
Galvanized ventilation ducts are manufactured in a standard type and insulated.
- The design of insulated models includes a special insulating layer made of mineral fiber, polyurethane, foam elastomer, felt or other materials. They maintain the optimal air temperature inside the circuit, preventing the formation and freezing of condensation on the walls. In addition, the noise level is reduced.
- The zinc coating can be single-sided or double-sided. Due to the formation of condensation inside the circuit, double-sided galvanizing is more practical, because protects the circuit from internal corrosion process.
Not long ago, aluminum-zinc-coated air ducts appeared on the market, the coating of which is 95% zinc and 5% aluminum. They are characterized by greater ductility and improved anti-corrosion properties.
Fastening
Methods for fixing air ducts depend on the configuration:
- with a round cross-section, coupling, bandage and nipple connections of elements are used;
- rectangular air ducts are fastened using latches and mounting angles.
Sometimes welding is used.
Kinds
The broad classification of galvanized air ducts is due to their widespread use in various ventilation systems. Therefore, in order to make it convenient to somehow distinguish and classify them, the division was carried out according to the following parameters.
- The cross-sectional shape can be round, elliptical or rectangular.
- Diameter.
- Execution in a purely structural form: with a straight seam or a spiral one.
- Depending on the materials from which they are made: metal (galvanized or stainless steel), plastic, metal-plastic.
- Connection option: with or without flanges.
- Type of connection: couplings, tees, diffusers and other types of shaped parts of air ducts.
- Element stiffness.
Rectangular
Most often, rectangular or round shapes of air ducts are used in the design of ventilation systems. The former have one very important advantage - they can be adjusted to the necessary conditions of the structure. That is, taking into account the architectural delights of the room, you can reduce the height of the air duct, but increase the width, thereby leaving the cross-sectional area unchanged. The latter plays the most important role in design and calculations. It is the cross-sectional area that ensures the unhindered movement of the required amount of air through the ventilation system.
For example, if there is a need to lay ventilation ducts under a suspended ceiling, then you just need to change the dimensions of the rectangular section. That is, increase the width and decrease the height as required so that the cross-sectional area does not change. For example, we can give this ratio - 20x20 cm, and a modified one - 10x40 cm.
Most often, rectangular air ducts are installed in residential and office buildings. They try to use them in systems with low air speed, because turbulence occurs in the inner corners of the air duct, which leads to a drop in speed, and therefore to a decrease in the efficiency of ventilation as a whole.
Round
Round air ducts made of galvanized steel, firstly, are easier to manufacture. At the same time, they require 20-30% less metal. Secondly, such pipes can be as long as possible. Let us add that turbulence does not appear inside round pipes, hence the efficiency of ventilation, optimal air speed, low noise level and ease of installation work. By the way, the last criterion ensures low weight of the elements due to the use of less metal.
Such air ducts are most often used in industry, when there is a need to assemble an extensive ventilation network with minimal material costs. Although no one prohibits using them in residential construction.
Straight-seam
Straight-seam air ducts are used mainly in industrial facilities. Their main difference from other varieties is a straight seam along the entire length of the pipe. They are made from galvanized iron with a thickness of 0.5-1.2 mm and an average length of 1.25 m.
For rectangular air ducts, the seam is placed on a bend, which gives the structure additional rigidity.
Spiral wound
Essentially, this is a metal strip that is curled into a pipe in a spiral, and its edges are connected to each other. Today, manufacturers of galvanized air ducts offer two types of such structures.
- Spiral welded. From the name it becomes clear that the edges of the tape are connected to each other by welding, which makes the seam strong and airtight. For this, a tape with a thickness of 0.8-2.2 mm and a width of 400-750 mm is used. It is possible to make pipes from it, the length of which is limited only by the consumer’s order. It should be noted that for the production of such air ducts, a tape coated with an anti-corrosion layer is used.
- Spiral-lock. For them, the same tape is used only with a thickness of 0.5 to 1 mm and a width of 130 mm with slight deviations. As in the first case, the length is not limited.
The production technology of spiral-type air ducts itself is divided into two categories: in a tape or in a ring. It should be noted that the second technology is considered more expensive, but the quality of such pipes is much higher.
Corrugated
This type of air duct came into use relatively recently. These are mainly pipes coated with aluminum alloy or polymer. In this case, corrugations are divided into flexible and semi-flexible.
The former are distinguished by such a property as stretching the air duct and returning it to its previous state without loss of technical qualities. Essentially, it is a spiral of wire on which an aluminum or polymer layer is stretched. Or a combination of both. Foil, films made of polyvinyl chloride, polyester or polyurethane are used as shells.
The second are air ducts assembled using spiral laying technology. The material used is galvanized steel, stainless or aluminum tape. They come to the market in compressed form, the length of which can reach up to 3 m. And they usually stretch three times longer. These air ducts themselves are very flexible, but what distinguishes them from the first model is the fact that after stretching, it is impossible to put them back together.
Insulated
It is imperative to insulate air ducts located in unheated rooms and outdoors. What are various thermal insulation materials used for? The insulation process itself involves a large amount of work, which takes time. Today, manufacturers offer corrugated air ducts, which are insulated at the factory during their manufacturing process. For this, aluminum foil and polymer compounds are most often used.
Elements of the ventilation system
A ventilation duct is always a complex structure, consisting of numerous elements that allow:
- change the direction of the contour depending on the configuration of the premises;
- go around ledges;
- connect several circuits into a single network.
Bends and boxes
The main elements of the air duct that determine its direction are ducts and bends. The former pave the path in a straight line, the latter change the contour geometry at an angle of 15⁰, 30⁰, 45⁰, 60⁰ or 90⁰.
Other shaped elements
Ventilation is a complex and extensive network of channels, which is problematic to install without the appropriate elements. Such components are usually called shaped products.
These include:
- Adapters connecting circuits of different diameters to each other - confusers and diffusers. The former narrow the highway, the latter widen it.
- Tees and collar inserts that ensure the adjacency of two highways to each other.
- Crosses used to intersect two perpendicular air flows.
- S-shaped adapters (canards) connecting two contours that do not coincide in axis and/or cross-section.
- Round nipples and couplings connecting two round boxes. The first ones are inserted inside, the second ones are put on top of the pipes.
- Plugs installed at the ends of the circuit.
- A roof umbrella that prevents precipitation from entering the ventilation shaft.
- Supply and exhaust grilles and other fittings.
Materials
Galvanized air ducts are most often used. They are installed in a ventilation system that pumps air up to a temperature of +80C without aggressive components.
Stainless steel air ducts are the most expensive material, so they are used very rarely. This requires special operating conditions for the ventilation system: temperature +500C, aggressive gas or air composition.
Metal-plastic pipes are a layered structure of the product, where a plastic component is laid between two layers of aluminum. Positive factors include low specific gravity and attractive appearance. In addition, these air ducts belong to the insulated category. The only drawback is the high price. Metal-plastic air ducts are mainly used in ventilation systems installed in the chemical, pharmaceutical and food industries.
Today, manufacturers offer air ducts from other materials. For example, their polyethylene, fiberglass. The latter often appear in the form of a shaped product, with the help of which the fan and distribution chamber can be connected to each other. Ventilation pipes made of vinyl plastic are installed in chemical industries when acidic vapors are present in the atmosphere. Note that this type is a very flexible material that does not corrode.
Advantages and disadvantages of galvanizing
Galvanized air ducts are the most common type of ventilation pipes. This is easily explained by the characteristics of the metal.
Advantages of galvanizing:
- Light weight, due to which the installed structures create insignificant loads on buildings. In addition, the lightness of the material facilitates the process of delivery to the installation site and engineering work.
- The flexibility of the material makes it possible to give the air duct elements any shape, which not only expands their model range, but also improves the aerodynamic characteristics of the line.
- Durability and resistance to open fire and aggressive environments. This significantly expands the scope of use and increases the service life of ventilation pipes made of thin-sheet galvanized steel from 10 years or more.
- Low cost compared to other metal analogues.
Galvanized ventilation ducts are easy to maintain. They do not require preliminary priming, since the metal is not subject to active corrosion. The aesthetic appeal allows them not to be painted.
The disadvantages of galvanized steel include:
- Increased noise level, typical of any metal structure. However, this problem can be solved either by a well-thought-out wiring diagram that minimizes the number of bends and transitions, or by sound insulation.
- Tendency to form and accumulate condensation. The solution is to insulate the pipeline.
- Susceptibility to deformation as a result of powerful mechanical stress caused by a strong impact, displacement or fall of the structure. Under normal operating conditions, such difficulties do not arise.
The combination of quality, cost of material and a variety of technologies to minimize disadvantages makes galvanized pipelines the most popular types of air ducts used in the construction of ventilation mains.