Engineering networks, gas and oil transportation systems are a complex set of main, technological, utility, and energy pipelines that differ in length, nature and operating parameters of the transported medium. For high-quality construction and installation, efficient and long-term operation, the correct choice of pipes is necessary, taking into account a number of factors.
Main criteria:
- Diameter _ It is determined by the flow rate of the transported flow.
- Wall thickness . Determined according to the medium pressure.
- Steel grade . Depends on the corrosiveness of the steam/gas/liquid.
The materials used in the production of rolled pipes must ensure reliable operation throughout the entire service life under the specified operating conditions - at the design pressure, temperature, nature, composition of the environment and external influences.
Pipe application area
The profile pipe has many advantages compared to standard round pipes:
- low cost. A hollow square-section metal pipe is less expensive than analogues made of wood and can last longer;
- ease of installation. Thanks to its qualities, the pipe can be easily bent. The low weight of the products facilitates the process of transportation and self-installation;
- high resistance to damage. Profile pipes are not susceptible to mechanical stress. Pipes are protected from corrosion by a special coating;
- resistance to temperature changes. The pipe does not deform at both low and high air temperatures;
- reliability. Thanks to the stiffening ribs, the profile pipe can withstand quite heavy loads, and for a long period of time.
The main advantages of pipes determine the scope of their application. Pipes of various sections are used:
- for creating building frames, including as transverse beams, trusses, columns and vertical posts, as they are distinguished by their ability to withstand the load of the cladding and durability;
Frame of a residential building made of profile pipes
- for the construction of frames for gazebos, swings, benches and other small architectural forms;
- for the construction of fences, gates, wickets, both as main pillars and as transverse ribs;
Swing and fence frame made of square pipes
- to create pieces of furniture (tables, chairs, etc.).
Furniture items made from profile pipes
- as protective channels for various communications.
How to make a chair from pipes yourself, watch the video.
Source: vse-o-trubah.ru
Why choose metal for heating systems
For more than twenty years there was practically no alternative to pipes made of steel - carbon (in common parlance, ferrous metal), galvanized, stainless. The use of copper for heating was unheard of at that time; plastic pipes were not mentioned even in progressive scientific journals. Now the situation has changed radically: several types of inexpensive high-tech plastic have greatly displaced metal from heating systems.
However, metal pipes are still indispensable in many situations: when systems operate at very high operating pressures, in hot shops, when high strength is required from pipelines.
Steel grades of profile pipes
Carbon, alloy and high-alloy steels are used for the manufacture of profile pipes. They all have their own characteristics, which are given to them by the presence of one or another chemical element in their composition.
From this article you will learn what grades of steel are used in the production of profile pipes, and you will also be able to read more details about the popular materials used in the manufacture of such products.
Why is it so important what steel the profile pipe is made of?
This indicator affects the main characteristics of the product. Steel grades and pipe weight are inextricably linked. The brand also affects the durability of the product, its ability to withstand high and low temperatures, possible and maximum loads, its ability to withstand corrosion and atmospheric conditions, as well as its appearance.
Used grades of profile pipe steel: list and details
The choice of a specific material also depends on the method of manufacturing the product.
For example, pipes with a square cross-section and dimensions from 10 by 10 to 40 by 40 are made from cold-rolled steel, as well as with a rectangular cross-section, with dimensions from 12 by 10 to 60 by 40, with a wall thickness from 0.6 mm to 2 mm. The following steel grades are used: 08ps (details at https://atl-met.ru/stal-08ps), 1ps (more information here: https://atl-met.ru/stal-st1ps), 2ps.
From hot-rolled steel grades 3SP, 1ps, steel 2PS, square pipes with dimensions from 15 by 15 to 150 by 150 and rectangular pipes, with dimensions from 20 by 10 to 180 by 150, with wall thicknesses from 1.5 to 5 millimeters are made.
Closed profiles used for building structures make it possible to create square products with dimensions from 60 by 60 to 300 by 300 and rectangular ones, from 80 by 60 to 350 by 250. Steels 3sp/ps5 and 09G2S are used for them.
You can find out more information about profile pipes made of steel 20 at the link: https://atl-met.ru/stal-20. If you are interested in steel grade 10, which is also used in the manufacture of such products, then go to the appropriate page: https://atl-met.ru/stal-10
Profile pipe made of steel 09G2S: the most common option
These products are typically required for commercial and large-scale construction and industrial applications.
Low alloy steel grade 09G2S is very popular in the manufacture of such products.
The pipe obtained from such material has an attractive appearance, a minimum number of seams and high manufacturability.
Source: atl-met.ru
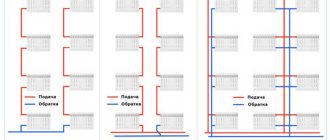
How to calculate the diameter of heating pipes
When replacing the heating system in an apartment, the internal diameter must coincide with the diameter of the incoming supply and return - you can neither reduce nor increase it, otherwise you may run into trouble with the heating network.
Calculator
The diameter of the heating system pipelines has to be calculated for a private house. There are two options here: simplified and more realistic, but complex.
Option one: simple. Most private houses have no more than two floors and 200-250 m2 of area. When building such houses, purchased designs are used, which indicate the required power of the heating device = the power of heat loss through walls, windows, doors, roofing, floors and ventilation. For certain heat losses, the optimal ratios of the internal diameter of the pipeline and the power consumed have already been calculated:
- with a boiler power of 3-5 kW – 15 mm;
- 6-9 kW – 25 mm;
- 10-15 kW – 32 mm;
- 16-21 kW – 40 mm;
- 22-32 kW – 50 mm.
If your house is larger, you cannot do without the work of designers.
Option two: creative.
It is necessary to calculate all heat losses through walls, doors, windows, roofing, floors and using a table to determine the diameter of the pipeline. The flow rate in the pipes is taken from the pump data sheet of the heating device; the difference in supply and return temperatures is taken to be 20°C. We round the diameter found from the table to the nearest larger standard size.
Approximately, you can assume a heat loss of 0.1 kW per 1 m² with a room height of 2.5 m.
Below is a table for selecting the pipe diameter for heating at ΔT=20° C:
.. | Types of profile pipe. Production and use of professional pipes. GOSTs and TU.
Types of profile pipe. Production and use of professional pipes. GOSTs and TU.
Profile steel pipe is a metal product of any cross-section except round: square, rectangular, oval or other.
Thus, depending on the cross-section, pipes are divided into:
square profile pipes,
rectangular profile pipes,
According to the production method and deformation method, profile pipes are distinguished:
a) hot- and cold-formed seamless;
b) electric-welded cold-deformed.
According to the types of steel from which the pipes are made, pipes are made:
carbon, low-alloy steels, stainless and aluminum.
According to the method of metal processing, a metal profile pipe is divided into:
Hot-rolled (hot-deformed) and cold-rolled (cold-deformed) seamless pipes,
electric welded pipe - using welding,
electric welded without heat treatment (cold-deformed).
Profile pipes have their own classification according to their purpose:
group A - produced with standardization of steel properties,
group B - produced with standardized mechanical properties and chemical composition of the metal.
Manufacturing of profile pipes
Profile pipes are produced according to two schemes: from round pipes and in a full cycle.
The production technology from round pipes involves passing a cold round pipe through special rollers in a mill, where it takes on a certain shape. Such mills usually produce profile pipes for non-critical elements, for furniture or decoration. Such a low-quality pipe is not used in structures with heavy loads.
The full cycle of production of corrugated pipes includes first the production of a round pipe from a strip (roll of sheet metal) using hot or cold deformation methods. The strip is cut into strips of 5 cm or more using longitudinal cutting, and the resulting strips are welded into one strip. The tape is then wound onto a drum for a continuous further process and passed through a forming mill, where the tape acquires a circular cross-section. At this stage, the round billet can be heated until the metal is completely plastic. Next, this workpiece is subjected to welding: inductor, gas-shielded, and others. In this case, the edges of the product are compressed by the rollers, and a melt is squeezed out - a burr, which is immediately removed using a cutter. The resulting product is cooled with the emulsion, passed through molding rollers to ensure a uniform cross-section along its entire length, and then crimped into a square or rectangular shape. Internal stresses in the pipe are removed by heat treatment, which improves the quality of the produced material. Finally, the pipe is checked for defects and cut into measured lengths.
Types and characteristics
Heating pipes are divided according to the material of manufacture. There are many standard sizes of any type, they are easily available in stores. Cast iron pipes are practically no longer found and are not used. According to the profile, only products with a round cross-section are used for heating. According to the manufacturing method, they can be welded or seamless. In terms of wall thickness - with a normal wall (for steel with running diameters 20-25 32 mm, the wall thickness is 3-3.5 mm).
Made of cast iron
The use of cast iron pipes for heating is very rare due to their low technology: difficulty or impossibility of welding, inability to cut threads in the right place, and high weight.
In practice, it is very rare to find finned tubes that are used as radiators. They are mounted using flanges. Such radiator pipes are not used in housing.
From copper
Copper pipes are a relatively new material for heating systems on our market. Copper is very durable, does not overgrow, has very thin walls - the system is light and compact. Installation has a certain complexity - using welding and brass fittings. The widespread use of copper heating systems is hampered by price and the need to hire a welder.
Copper products can be annealed or unannealed. There is no difference for heating systems, but unannealed products are more often used - they are harder and less deformed during operation.
Made of black steel
They are quite durable, they become overgrown with salts from the inside, which reduces the lumen of the pipes and the efficiency of the system.
The main installation method is by welding or on bends and threads. They are practically not used in houses and apartments - even partial repairs of the system are easier to perform with plastic.
Made from galvanized steel
Galvanized pipes do not become overgrown with salts from the inside for a long time (until the zinc layer is completely destroyed). The actual service life of old pipes for VGP is up to 50 years or more. Previously, they were used everywhere.
They have a rather complicated installation - the workpieces need to be threaded and then coated with zinc. Mounted on threaded fittings. The installation method is not suitable for use in private construction. You cannot use welding - the connection will begin to rust at the same rate as ferrous metal, and the effect of zinc coating will disappear.
Stainless steel
The material has been used for heating pipes for a very long time. Stainless steel does not overgrow and does not rust. Previously they were mounted by welding, now they use both welding and threaded fittings.
Distribution is limited by price and complex installation - both welding and thread cutting require certain skills from the master. The material is plastic and resistant to water hammer - therefore, for heating, GOST provides for pipes with a small wall thickness (for example, 2 mm). There are corrugated stainless steel products, but their strength is lower than ordinary smooth ones.
Which pipes are better for heating?
Pipes made of ordinary steel are practically no longer used in houses and apartments - the tendency to corrosion outweighs their other advantages. If homeowners want to install a heating system that does not require worries and hassle for many years, then they should choose pipes made of copper or stainless steel. Their service life is more than 50 years, theoretically it can reach 100 years. Installation is moderately complicated, but the costs are more than offset by durability.
Galvanized steel pipes can be very durable only under one condition: if all parts of the pipes are coated with zinc. In reality, all parts of the pipeline must be galvanized after threading and installed using galvanized threaded fittings. When installing home heating systems, it is impossible to organize galvanizing of all workpieces.
Conclusion: it is better to install pipes made of stainless steel and copper. In terms of quality, these materials are quite equivalent, and the choice is only a matter of personal preference. Copper pipelines are more compact.
What steel are square pipes made from?
Square pipes are a highly sought-after product of pipe factories. Unlike its round counterparts, this type will be of interest not to plumbers, but to installers who specialize in assembling metal structures. Today, the grades of steel used for the production of square pipes in Moscow can be different, which determines the scope of application of a particular product. Let's look at this issue in more detail.
What are square pipes made of?
The main material for the manufacture of square pipes is structural steel. If we talk about specific brands that are acceptable for use for certain products, then they are indicated in the corresponding GOST. The most commonly used steel grades are:
- An ordinary pipe, which, according to GOST, can be made of the following grades of steel: 10 and 10ps, 08kp, St4sp and St4ps, St2sp, 20, St4kp. Each brand must have a specific chemical composition.
- Some manufacturers also add stainless steel to the grades of structural steel. Stainless steel pipes are made from AISI 304 grade. A stainless steel pipe most often differs from a regular pipe not only in its cross-sectional shape, but also in its wall thickness. Therefore, in this case, the necessary choice may be complicated by such a discrepancy.
- Low-alloy steel, grade 09G2S, can also be used in production.
Features of square pipes
Regardless of the grade of steel used in the production of square pipes in Moscow, such products have the following advantages:
- High level of technology.
- Reliability and ease of connection.
- When using such pipes, the construction of various buildings is significantly accelerated. Welded wire is often used together with the profile pipe, which greatly facilitates installation.
- A minimum of welds, as well as the possibility of high-quality welding.
Abroad, most builders prefer square and rectangular pipes. New buildings made of concrete, metal and glass, including residential buildings, banks, offices, sports complexes, etc., are built using square pipes. This material is universal and allows you to easily create bent objects, for example, arched structures.
When purchasing a pipe, it is important that it corresponds to the design documentation; if there is none, it is better to turn to large metal rolling companies.
Source: www.oldor.ru
Rules for installing heating pipes with your own hands
Installing a copper heating system using special press fittings can be done with your own hands. Detachable connections are formed that can be disassembled and reassembled if necessary.
Required tools and materials
To wire the heating system you will need:
- a hacksaw for metal, or even better – a pipe cutter;
- file, sandpaper;
- calibrator;
- two wrenches;
- pipe bender
Drawings and diagrams
First of all, you need to draw a diagram or drawing. This will help you decide on the number of fittings and purchase the materials correctly.
Installation technology
Installation technology using compression fittings is simple. Fittings for copper pipelines are made of brass. They differ from fittings for plastic - the internal thrust ring is made without a cut (see photo). No special equipment required.
Work progress
First, it is cut off and cleared of burrs. Then the cut is calibrated with a calibrator so that it has a round shape (copper is soft and the workpiece crumples when cutting).
Then the crimp nut is twisted off the fitting, put on the workpiece, the pipe is inserted into the fitting, and the nut is tightened by hand with a little force.
Then grab the fitting with a wrench, and use a second wrench to tighten the nut 1-1.5 turns.
On the other hand, the work pieces are repeated. Then the entire workpiece is assembled into the system. Angle fittings are used for bends, but you can bend the pipe using a pipe bender.
After about 80 centimeters, brackets are installed.
After assembly, the system is filled with water and tested. If necessary, tighten the nuts using wrenches.
All the installation details can be seen in our video:
Installation features
Do not install piping on compression fittings for underfloor heating systems.
You should not increase or decrease the diameters of pipelines - this will not improve heating and will lead to imbalance of the system.
Electric welded pipes with straight seam
The range of steel pipes of this type is presented in GOST 10704-91. Unmeasured products are produced in lengths of 2...5 meters. Measuring pipes can have dimensions of 5...12 meters. Moreover, their diameter is 10-1420mm with a wall thickness of 1.0...32mm. Deviations and tolerances are discussed in the document separately and in sufficient detail.
Technical characteristics of longitudinally welded steel pipes are presented in two regulatory documents:
- GOST 10705-80;
- GOST 10706-76.
They define:
- mechanical properties of metal;
- the presence of seams and the correctness of their location;
- maximum deviations;
- presence of defects;
- process and types of tests;
- acceptance requirements.
Marking of steel pipes
Each steel pipe is marked taking into account the requirements of GOST 10692-80. It emphasizes that products with a diameter of more than 159 mm are subjected to this procedure. In this case, the wall thickness should not be less than 3.5 mm. Marking is done in several ways:
- rubber stamp;
- electric pencil;
- electrograph;
- branding;
- indelible paint by hand.
Smaller pipe diameters are marked with labels, especially if the products are supplied in bags.
The label must indicate:
- steel grade;
- Name of product;
- pipe size;
- manufacturer's trademark.
In addition, seamless pipes are marked with the wall thickness and batch number.
Differences and features of steel pipes
The main classification of round steel pipes is made according to the method of their manufacture:
- electric welded ones are available in two types - straight-seam and spiral-seam;
- seamless.
They also have differences in rolling methods:
- cold molding;
- hot molding.
An electric-welded round steel pipe is made from steel strips or rolled sheets using the molding method, followed by welding the seam along the axis or in a spiral. The process involves the use of special equipment. Spiral-seam pipes are much less common than straight-seam pipes, and they are obtained by molding the strip in a spiral. In this case, the joint is welded in a simultaneous continuous mode using a special seam. In the manufacture of products, two types of welding are used:
- contact high-frequency – for pipes from 10 to 530 mm;
- electric arc – from 428 to 1420 mm.
Visually, the seam during high-frequency welding is practically invisible. Electric arc welding technology involves the application of three seams, which increases the strength characteristics of the joint. First, the main central seam is laid, and then the connection is welded on the outside and inside of the product.
Electric-welded pipes, the diameter of which allows for internal work, are cleaned (polished) from the inside, removing irregularities and thickenings formed after welding. If it is impossible to carry out such work, the inner surface is left without treatment.
Seamless steel pipes are manufactured in several ways:
- pressing;
- drawing;
- forging;
- rolling;
- centrifugal casting.
Thermoforming is performed on special equipment. The workpiece is heated to the recrystallization temperature. This method allows us to obtain high-strength products that can withstand severe loads, including internal pressure. A cold-formed round metal tube is sized to its specifications by cold deformation using equipment designed for the process.
The difference between seamless and electric-welded pipes is the presence or absence of a weld. Their manufacturing methods have significant differences in technology, and, as a result, different technical characteristics.
Manufacturers produce several more types of steel pipes:
- soldering;
- with metal or non-metallic coating;
- with special processing - turned, ground, polished.
The most common today are water-gas pipes (WPG) and longitudinally welded electric welded (ESW) pipes. They are widely used in urban and suburban housing construction when performing utility networks. They are cheaper than seamless analogues, thanks to simpler production technology and the use of ordinary carbon steels, the most accessible in metallurgy.
Packaging and transportation
Products with a diameter of up to 159 mm are bundled into bags or tightly packed into wooden containers or boxes. The tying is done with wire in at least three places. Pipes over 159 mm are bundled exclusively in transport packages.
It should be noted that packing wire must not be used for lashing. For this purpose, special clamps must be provided.
It is allowed to move round steel pipes to the site by any type of long cargo transport. During storage, stacks are separated by spacers.