When planning heating systems, various wiring methods are used, one of the elements of which is bypass. Every specialist in the development and installation of household heating systems knows what a bypass is in a heating system; the information can also be useful to the owner of a cottage or summer house if he is engaged in arranging the heating of his home with his own hands.
Although the bypass is the simplest part, it cannot be avoided in multi-apartment high-rise buildings with economical single-pipe wiring; the use of the element is also widely practiced in domestic heating networks. When arranging heating, correct placement of the bypass in the right places allows you to achieve high efficiency in heating the room, save money, and avoid the negative consequences of emergency situations that arise during the operation of the equipment.
Rice. 1 One-pipe and two-pipe connection
What is a bypass in a heating system
Bypass is the Russian pronunciation of the English word “bypass”, which means to go around, bypass, a detour, a detour. The device plays a similar role in the pipeline system - it creates a bypass path for the working fluid, becoming a kind of bypass jumper between the entry and exit points of the switched on heat exchange devices.
Structurally, the part is a short section of pipe, made of a material similar to pipes, installed at a short distance from the inlet and outlet fittings of the connected heat exchanger. The pipe section can be welded when using metal pipes, secured to threaded fittings when using metal plastic, or soldered into a polypropylene line.
Rice. 2 Radiator connection diagrams
Shut-off and control valves for radiators
A heating system cannot operate as efficiently as possible if it does not provide for the installation of various valves, faucets, faucets, sensors, etc. With the help of shut-off and control valves in the heating network, the movement of the coolant is controlled, as well as its correct distribution. For example, when the temperature of the external air (outside) decreases, the supply of coolant to the heating devices is reduced and vice versa.
There are two types of coolant adjustment:
- high quality. It is designed to change the temperature of the coolant in pipelines and heating devices. Can operate on the basis of an automatic control system.
- quantitative. With its help, you can change (increase or decrease) the flow of coolant in the heating system if necessary.
Shut-off and control valves for radiators refer to local control of a certain section of the heating line. This means that residents of apartments, country houses, and dachas can independently change the supply and temperature of the coolant in heating devices. To do this, automatic or manual valves, air vents, taps, etc. are installed in front of the radiators. Each device has its own purpose.
Most often, three-way valves or double adjustment valves are installed to locally regulate water flow. The fittings are mounted on every heating device in an apartment or house. Specialists are constantly working on the production of walk-through valves. They make changes to the valve design to make it work more efficiently. The straight-through valves are equipped with a throttling element. This allows you to regulate the coolant supply more accurately.
Thermostatic fittings facilitate the operation of the heating system. Valves with sensors are also installed directly in front of heating devices. They have a temperature scale. With its help, the user sets the operating mode of the heating network.
Thermostatic head is sensitive to changes in the microclimate in the room. With the help of its work, the desired temperature regime is set in the apartment, depending on the weather conditions outside.
Why do you need a bypass in a heating system?
To understand why a bypass is needed and to appreciate the importance of installing this element, you should consider the main types of wiring of household heating systems.
When installing household heating networks, a distinction is made between sequential (single-pipe) and parallel (two-pipe, collector) supply of the working fluid to heat exchange units; in the first case, the coolant passes sequentially through all devices, gradually cooling at the end. In a sequential scheme, the coolant is supplied to the heat exchangers from the highest point or from the bottom, while it circulates through a closed ring, returning to the boiler through the return pipes.
A single-pipe system requires less materials when placing it and is widely used in multi-apartment housing; during installation, the installation of a bypass jumper helps to avoid the main drawback - weak heating of the most distant radiator in the network. The purpose of the bypass is to create an additional path bypassing all radiators, ensuring the supply of coolant of the same temperature to each of them, this contributes to more uniform heating.
Rice. 3 Metal bypass design and its connection
The second important function of the installed bypass pipe is to ensure uninterrupted delivery of coolant to all radiators in the event of a breakdown or disconnection of one of them in a series circuit. From the diagram in Fig. 1 it is clear that in the absence of a bypass between the pipes, if one of the radiators fails (leakage, blockage), the delivery of coolant to subsequent circuits stops, as a result of which residents are left without heat, and the entire system is in danger of freezing.
The third purpose of the bypass is to maintain constant coolant circulation in the event of a breakdown of the heating system’s compression pump. If a bypass is used, the system works naturally, providing circulation bypassing the pumping branch - this guarantees uninterrupted heating of the premises in the home. It should be noted that to ensure a natural circulation mode when the pump is turned off, an appropriate design is required (large diameter pipes, slopes); if these conditions are not met, the circular movement of the liquid due to thermal expansion should not work.
An important advantage of the bypass is the ability to turn off any radiator for repair, preventative maintenance or replacement. This is achieved by placing two ball valves on the radiator inlet and outlet fittings; after they are locked, the radiator can be easily removed for repair, maintenance, and extension of additional sections. The bypass performs similar functions when installed in parallel in the circuit of a compression electric pump - with the help of two ball valves, the electric pump is easily disconnected from the heat-conducting network for repair, maintenance, replacement of equipment without draining the water and stopping the heating of the premises.
Fig.4 Bypass in the heating system and the principle of operation in the radiator circuit
Blitz tips
- Installing a bypass is desirable in conditions of insufficient natural circulation of fluid in the heating circuit.
- When constructing a bypass yourself , it is not necessary to select each of its elements separately; it is better to purchase a ready-made assembly from a specialized store, which will save time and guarantee against inconsistencies between elements during the assembly process.
- To automatically regulate the temperature in your home, you can use a thermostat with a built-in ball valve.
- Horizontal installation of the device is preferable due to the lower likelihood of air accumulation in it.
- When installing the device, additional support points and clamps should be provided in advance to prevent it from moving under the influence of gravity or other factors.
- In case of poor water quality with a large number of impurities and suspended matter, to increase service life, you should choose special pumps with filters, which are recommended to be periodically removed and cleaned.
What types of bypasses are there?
Although the bypass is a fairly simple element, the range of its functions can be significantly expanded through the use of various types of plumbing fixtures built into it. The design of the bypass depends on the line in which it is used, the type of residential or industrial buildings with single-pipe heating installed.
Fixed bypass
The simplest bypass design is a bypass unregulated pipe connecting the pipelines between the inlet and outlet lines. Such an element is usually installed in apartment buildings, where the absence of a shut-off device prevents accidental blocking or partial blocking of the bypass and, accordingly, disruption of the operation of the entire system and its imbalance.
The unregulated unit is widely used in the common “Leningradka” - a single-pipe line with a large-diameter straight bypass pipe and a chain of heating batteries connected to it in parallel.
Rice. 5 “Leningradka” - a popular piping scheme for a single-pipe structure
Manually controlled bypass
Since part of the coolant passes through the bypass, installed parallel to the connected heat exchange devices, bypassing the heating devices, to increase the supply of coolant to the radiator, its cross-section is made smaller than other pipes, increasing the hydraulic resistance. Typically, the diameter of the bypass in a one-pipe heating system is smaller than the pipes coming from the central riser to the radiator by a quarter of an inch, which in turn have an external size smaller than the riser pipes by the same amount.
It is clear that this system is unregulated and does not allow efficient use of the system - the radiator with a large number of sections does not always warm up completely due to the coolant escaping through the bypass pipe.
Installation instructions
In order to avoid making mistakes during installation and carry out the correct calculation, you need to take into account the nuances of connecting the bypass. You can install the tube when creating a new system or repairing an installed structure. In the second case, you will need to install shut-off valves, pipes and tees made of polypropylene or other materials. When it comes to connecting a radiator, you need to remember:
Compliance with standard rules for installing and operating a bypass will help ensure full operation of the system and avoid possible emergency situations.
Bypass in the heating radiator piping
When installing a jumper assembly, observe the following basic rules:
- The jumper is placed as close as possible to the inlet radiator fittings - this contributes to more efficient heating of the heat exchangers as a result of the passage of large volumes of coolant through them.
- Shut-off ball valves must be placed at the inlet and outlet of the batteries, allowing them to be disconnected from the network for maintenance and repair work without draining the coolant and stopping heating.
- When using pipelines made of modern materials - metal-plastic or polypropylene - for heating individual residential buildings, it is better to install a control valve in the bypass bypass. With its help, you can reduce the flow passing through the jumper, as well as adjust the heating temperature of all radiators in the line by changing the cross-section of its passage channel.
Rice. 8 Examples of installation of a control valve between the bypass
Why is a bypass on the radiator required?
As noted earlier, the use of a bypass with heating radiators is effective only in single-pipe circuits; the part allows for more uniform heating of all heat exchange units. Also, the presence of a bypass allows water to be supplied to subsequent heat exchange devices in the event of failure or shutdown of one of them.
Using a tap installed in the jumper, you can manually adjust the system so that all radiators heat up evenly. To do this, the cross-section of the bypass bypass to the heat exchangers closest to the boiler is increased, and at the most distant radiators it is reduced, thus controlling the flow passing through the batteries.
Rice. 9 Radiator piping with polypropylene and metal-plastic pipes
Self-installation of a bypass in the radiator piping
Before installing a bypass, you can consider factory samples - the industry produces finished products for radiator heat exchangers, in which the distance between the connecting inlet fittings corresponds to the standard axial size from the upper and lower connection points of the radiators.
The problem of how to make a bypass for a heating system has different solutions depending on the material of the pipes used. Typically, self-installation of this element does not cause any particular difficulties for any owner (with the exception of polypropylene pipes) who has minimal plumbing skills and the necessary tools (you need one or two adjustable wrenches).
Figure 8 shows the installation of a bypass in a polypropylene water line, which is connected to the riser 1 through adapter couplings 2. Bypass 6 is connected through a tee 4, connected to the main by pipe sections 3 and 5. To the thermostat 10, connected to the radiator 8 via an American connection 9 , a pipe section made of polypropylene is connected using a fitting adapter from metal to polypropylene 7, and the line is connected to shut-off valve 11 in the same way.
In this scheme, all pipes have the same outer size, so the operation of this design is ineffective (the internal channel cross-section of the bypass pipe in a single-pipe connection should be smaller); for its normal operation, it is necessary to insert a control valve into section 6, which reduces the passage channel opening.
The bypass jumper is mounted on the battery in a similar way when using metal-plastic; the structure can be assembled most quickly using compression fittings (Fig. 8).
It should be noted that in the diagram in Fig. 8 pipe sections 5 are not required; the tee can be connected directly to the ball valve and thermostat by extending section 3.
If metal pipes are used for heating for water supply, a bypass jumper can be placed directly near the taps on the inlet and outlet battery fittings by connecting two tees to them. It is easy to make the diameter of the bypass jumper smaller than the main line using a small-section jumper pipe; in this case, it is not necessary to install a shut-off valve in the jumper.
Rice. 10 Parallel bypass branch in the circulation pump circuit
Laws of physics
Let's look at the laws of physics first!
Water always follows the path of least resistance. There is less resistance where the pipe diameter is larger. When water comes to your apartment, it is divided into 2 streams: through the jumper and through the battery. According to the rules, the diameter of the jumper should be one caliber less than the diameter of the forward and return pipes. For example, if the diameter of the pipe from the wall is 1 inch, then the diameter of the header should be 3/4 inch.
Why is this being done? So that the main flow of water still passes through the battery, and not through the jumper. If the diameter of all pipes is the same, then it will be much easier for water to pass only through the jumper. Now imagine that the water pressure is weak or insufficient. In this case, if you have many bends in the battery, then only the first ones will be hot, and the last ones will be barely warm, haven’t you noticed?
So, by reducing the diameter of the jumper (increasing the resistance to water flow in it), a greater flow through the battery is achieved. Now look at my second picture where there is no tap on the lintel. You see, all the pipes are the same, which means that the master did not do his job well here too.
Why is this happening? Probably the masters are lazy, and there’s more fuss. It is necessary to purchase pipes of different diameters and install them.
Where else is bypass used in heating?
The answer to the question of what a bypass is for in a heating system cannot be complete without considering other options for its placement. Many people encounter a similar device every day, using a heated towel rail connected parallel to the central riser. We will consider other areas of use of the bypass pipe below.
Rice. 11 Heated towel rail - connection options
Bypass in the water heated floor circuit
If there are a large number of warm water floors in a private house, they are connected using a manifold circuit - this ensures the same pressure and temperature of water in each circuit.
Unlike an in-house heating system, the heating of the underfloor heating fluid should not exceed 45 degrees - this is due to the ease of use of the floors (a too hot surface of the floor covering is impractical and harmful to health) and the maximum temperature characteristics of the heat-carrying pipes.
The fact is that polyethylene with increased heat resistance PE-RT, which is an excellent option when used as a pipeline for heated floors, has a maximum temperature threshold of +70 C, so liquid with higher temperature values should not be supplied to it.
Rice. 12 Multi-circuit collector circuit for heating a cottage
Related article:
Connecting a heated floor to a heating system - options, diagrams, system components . While reading what a bypass is in a heating system, you may want to learn more about the options for connecting underfloor heating pipes to the heating system, you can read about this in a separate article on our website.
A bypass connecting the supply line located at the bottom of the manifold group (determined by the presence of flow meters) and the upper return line (control valves with removable caps for screwing on servos are located on its manifold) supplies cooled water from the return line to the direct collector inlet. Thus, through a mixing unit in the form of a tee, a decrease in the overall temperature of the incoming liquid is achieved by mixing a cold water flow into it.
There are ready-made manifold mixing units on sale, in which a circulation electric pump, balancing valves for each branch, water meters, a thermostat, air vents are installed, some models are equipped with pressure control devices. Many modifications do not have a built-in bypass, which is usually not installed in two-pipe systems and is considered an unnecessary part in them. But some models have this element, another role of which is to compensate for excess pressure in the underfloor heating pipeline, when it increases, part of the flow enters the return line if its collector is located below the direct one. At the same time, the element reduces the consequences of hydraulic shocks that occur when turning on and off a circular electric pump in a heated floor line.
Rice. 13 Manifold assembly with jumper tube
Hydraulic calculation of a single-pipe system
Hydraulic calculations are carried out to determine the diameter of the connecting pipes in each section of the circuit and the performance of the circulation pump.
Sequence of calculations:
- Determination of heat loss through building structures.
- Calculation of the required heat transfer from radiators for each room.
- Selecting a boiler of the required power.
- Calculation of the diameter of the supply pipes, taking into account the circulation rate of the coolant in the coldest time of the year.
- Selecting a circulation pump if you need a remote option.
Determination of heat loss and calculation of radiators
The heat generated by the boiler is dissipated through the floor, walls and ceiling of the building. They take into account the material of the walls, the number and area of windows and doors, and the quality of insulation.
You can use the calculator on our website:
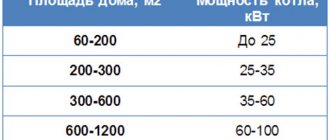
For small houses, an approximate option is used. It is believed that in the northern regions, to heat 10 m2 of area, 1.5-2 kW of boiler power and radiator heat transfer performance are required. In the middle zone the figure is 1-1.5 kW, in the southern regions - 0.6-1 kW. The data is correct for houses with solid walls and medium or high-quality thermal insulation.
Knowing the dimensions of the house, they obtain the necessary data for subsequent calculations. It is important to determine the required number of radiators for each room. Aluminum and bimetallic radiators in most cases emit from 120 to 210 W per section. By dividing the power required for the room by the performance of the section, the battery dimensions are obtained.
Boiler selection
The heating boiler will work much longer if it does not heat the coolant at maximum mode. In this regard, equipment is chosen that is 10-20% more powerful than the heat loss obtained in the calculations. For example, with a loss of 10 kW, a boiler designed for 12-14 kW is purchased.
Determination of pipe cross-section
The optimal speed of coolant movement through the pipes is from 0.3 to 0.7 m/s. If the parameter is lower, then at low temperatures the radiators may not warm up sufficiently. At higher speeds, the radiators often become airy and noise is heard. Based on the flow rate, pipes with the required internal cross-section are selected.
The required coolant flow is determined by the formula: G=860* q/ΔT , in which:
- G—flow rate kg/h;
- q is the thermal power in the circuit section (kW);
- ΔT is the difference in temperature of the coolant at the inlet and outlet of the radiator, usually taken to be 20 °C.
For example, to ensure heat transfer from a circuit of 2 kW, we obtain the coolant flow rate: 860*2/20=85 kg/h.
Next, special tables compare the flow rate and the generated thermal performance. In our example, for 2 kW radiators, a pipe with an internal cross-section of 8 to 12 mm is sufficient. Highlighted in the table with a red frame.
Table for determining the diameter of pipes of a gravity heating system
Data for each circuit is plotted on a general diagram. By summing up the data obtained, they determine which pipe diameter to choose for connecting to a group of circuits or for each riser.
Pump selection
Modern gas and electric boilers are equipped with a built-in pump. Its performance is selected by the manufacturer based on the boiler power.
The required performance of the remote pump is determined by summing the coolant flows in each circuit. They provide a reserve of 15-20% in performance so that the pump operates in a gentle mode.
Bypass in the piping system of a solid fuel heating boiler
The main difference between a solid fuel boiler and a gas boiler is the high combustion temperature of heating materials (charcoal and coal, firewood, peat briquettes, pellets) and the impossibility of adjusting it.
If you heat up solid fuel heating boilers, they reach very high temperatures within a short time, and the interaction of hot air with cold coolant leads to too large a temperature difference. This factor negatively affects the strength characteristics of the materials separating the sources, leading to their accelerated wear - cast iron does not like such temperature changes and can crack, and steel is subject to increased corrosion. In addition, rapid high-temperature heating promotes the formation of condensation on the surface of the chimney, on which soot arriving with the smoke settles.
The only technically acceptable and competent way out of the situation is to reduce the period of time the hot air in the boiler interacts with the cold coolant. To solve this problem, a small heating circuit of a solid fuel boiler is created, in which a small amount of liquid circulates. Moving in a closed circle through the bypass jumper, the water quickly warms up, after which it gradually enters the main system through a slightly opening thermostatic valve set to a certain temperature. Hot water is mixed with the main coolant and gradually heats it, ensuring a smooth start of the entire system without sudden temperature changes. This technique significantly extends the service life of all equipment, reduces the frequency of preventive maintenance work on cleaning chimney channels, and increases the efficiency of the system.
Rice. 14 Bypass in the piping system of a solid fuel boiler
Bypass for circulation pump
Bypass for a circulation pump
It is best to connect a pump using a bypass in gravity-flow systems. Also here it is necessary to install an accelerating manifold and it is necessary to comply with slopes and certain pipe diameters. A circulation pump, in this case, is necessary to increase its productivity.
Bypass for circulation pump
When installing a bypass in a system with a circulation pump, it must have a ball valve (possibly a valve). During operation of the circulation pump, the tap (valve) completely closes the bypass lumen. If the pump stops, the bypass opens and the coolant moves through it.
Expert answers to questions
Most often, people who are not well versed in individual heating ask the question: is a bypass needed in a two-pipe heating system near the radiators? If we consider a single-pipe heating system, a jumper is usually installed in it to ensure the operability of the entire line in the event of a shutdown or malfunction of one of the heat exchange elements in the circuit, their uniform heating, and the need for a bypass is beyond doubt. In a two-pipe distribution, such problems do not arise by definition; each circuit is connected independently of the others, and all receive coolant at the same temperature.
The simplest jumper from a piece of pipe in a heating line performs many functions in a single-pipe wiring diagram - it maintains constant temperatures on all heat exchangers and uninterrupted functioning of the entire system, and ensures high maintainability of heating elements. The bypass pipe can also be found in underfloor heating systems and piping solid fuel heating boilers, where it increases the efficiency and reliability of the equipment.
Application
If there is a pump in the heating circuit, it is installed directly on the bypass part. This is a common practice when an electric pump is installed in a gravity circuit - a single pipeline in which the coolant circulates by gravity.
It accelerates the speed of water flow through the pipes and thereby increases the efficiency of the entire heating system. This is due to the fact that due to the high flow rate of the coolant, it manages to pass through the entire circuit without losing most of the thermal energy.
In practice, this is expressed in the fact that the last radiator of the circuit receives not cold or barely warm water, but rather hot water, which still has a sufficient amount of thermal energy to ensure heating of the room in which it is installed.
Radiator connection options
In modern construction, several schemes for connecting heating devices are practiced. Radiator connection options: diagonal, bottom, side. The installation of each heating device circuit has its own characteristics.
Diagonal connection
Radiators in operation are the most efficient. The coolant supply pipeline is connected to the heating device from above. The return line is connected to the radiator from below, on the opposite side. The diagonal connection allows you to warm up the heating device, which has a large thermal output (many sections). Typically, this scheme is used in large rooms. Installing radiators in a diagonal manner is complex and time-consuming. It requires the involvement of experienced, qualified craftsmen.
The main advantages of this scheme:
- quick and easy installation;
- saving on expensive materials and energy resources;
- It is possible to install a bypass.
Lateral connection of radiators is used not only in apartments of multi-storey buildings, but also in cottages, townhouses, dachas, office and industrial premises.
What functions does it perform?
The purpose of a bypass valve (what is it) in a heating system is to intercept part or all of the coolant flow passing through heating devices or sections of pipeline.
Do you know how to make a bailer with your own hands?
This useful article describes how to provide a country house with uninterrupted water supply in autonomous mode. How to make a bailer with your own hands is written on this page.
Its main functions:
- Regulating the flow of liquid (about filling the heating system with antifreeze is written here) through heating radiators, and, consequently, the efficiency of heat transfer and room temperature;
- Ensuring that batteries are disconnected and dismantled for repair work in a full system;
- Accelerating the filling of pipelines after a long period of inactivity and draining the coolant after the end of the heating season.
In addition, the bypass must be installed together with the circulation pump, which ensures operation in the event of a power failure to the pump and saves energy consumption.
Choosing a location for installing heating devices
Radiators are installed under windows. This is a long established rule. The largest heat losses occur from windows in a room. The length of the radiator should be 0.7-0.9 times the length of the window sill. If it is necessary to install several heating devices in a room, but there is only one window, it is advisable to mount them on load-bearing walls.
The distance between the floor and the radiator must be no less than 100 mm. Ignoring this rule leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the heating device. It will also be difficult to clean, repair, or replace individual parts of the radiator. The distance between the heating device and the wall must be at least 50 mm. So the radiators will not heat the wall, but will give off their heat to increase the temperature of the internal air. It is prohibited to change the connection diagram of heating devices on your own in apartments and country houses. Repair of heating systems must be carried out in advance with the locality management services.
Bypasses with manual adjustment
Bypasses that are adjusted manually (manual bypasses) are equipped with ball valves. The use of ball valves is determined by the fact that they do not change the pipeline capacity at all when switching, since the hydraulic resistance in the system does not change. This quality makes the ball valve an optimal option for bypass.
Shut-off valves of this type allow you to regulate the volume of liquid that passes through the bypass section. When the tap is closed, the coolant moves in full along the main line. The operation of ball valves has one important nuance - they need to be turned regularly, even if there is no need to adjust the system. This is due to the fact that if left stagnant for a long time, the taps may become tightly stuck and will have to be replaced. Sometimes a heating system feed valve is also installed, which plays a significant role.
Manual bypasses in heating systems can be used in several ways. Most often they are used to connect batteries to a single-pipe main, as well as for piping circulation pumps.
Installation steps for a bypass valve (for radiators and with a circulation pump)
Installing a bypass valve with your own hands
Installing a bypass in a heating system equipped with a circular pump is done as follows:
- excess liquid is drained from the common pipe;
- a section of pipe measuring 40 cm is removed from the coolant;
- holes of the required diameter are cut at the ends of the pipe to connect the bypass;
- a filter is installed on the cut areas;
- then the bypass valve is installed;
- the hydraulic pump crashes.
Important! Installation of incoming water distribution screws is carried out in the direction of the general flow of the pipeline.
Installation of a bypass in a heating system
The following installation diagram applies to heating radiators:
- the diameters of the bypass and main pipes are checked;
- the following are mounted at the connecting ends: single-pipe jumpers and an adjustment valve;
- Next, the valve is installed at the closest possible distance from the heating radiator.
Important! Before inserting the bypass, the pipe must be checked for the presence of an air lock.
Necessary tool
You can install the bypass line yourself using installation tools, the list of which consists of the following items:
- tape measures for measuring the length and volume of a pipe;
- level for adjusting heating devices and water supply slope;
- pliers for removing and maintaining individual parts of the heating system;
- adjustable wrenches for joining the structure;
- a set of keys for installation (regular);
- metal cutter;
- screwdrivers: Phillips and flathead;
- pipe cutter (for large diameter pipes);
- welding machine;
- a grinding machine for leveling the corners of pipes and pipes;
- hammer drill;
- gas burner.
For a one-time job, it is not necessary to purchase all the tools, but you can rent them.
Recommendations and common mistakes
The insertion of the bypass valve should be done according to the rules of SNIP and the recommendations below:
- Before installation, it is advisable to install filters (mesh type).
- Installing monomers will help control water pressure.
- Do not twist, compress or stretch the pipes during installation.
- The average size of pipe joints should not exceed 5 DN before and 10 DN after the bypass.
The bypass valve can be mounted on horizontally and vertically directed sections of pipes, in accordance with the installation instructions.
Battery tying
If the installation of the system is carried out independently, then you need to know all the requirements that apply to this or that element. This also applies to the bypass. It is often installed in places where radiators are mounted. But why do you need a bypass in a heating system? This issue needs to be looked at more carefully.
Radiators are tied according to a simple pattern
Why is it needed?
Previously, single-pipe heating was used in the construction and improvement of houses. This greatly simplified the work and also reduced costs. In this case, two collectors were installed in the elevator unit, which were responsible for supplying and processing the coolant. Further heating was developed according to different schemes:
- Top feed. There was a pipe running from the collector to the top floor. The coolant was supplied upward through this riser. After that, it went down, passing through all the radiators.
- Bottom feed. In this case, the coolant begins to flow into the radiator when it is raised up. This series connection of devices has some disadvantages.
In both the first and second cases, the connection is made in series. This means that if a problem occurs on some equipment, you will have to turn off the entire system. To circumvent this problem, special jumper pipes were included in the system. So, if necessary, the radiator is disconnected from the system using taps without disturbing its operation. This makes it possible to easily repair the battery.
The jumper is installed closer to the battery
This is not the only reason for using a jumper in heating. The room is heated using radiators. If there is a bypass with valves, apartment owners have the opportunity to independently adjust the coolant supply. Thus, controlling the temperature in the house is not difficult.
Important! Taps and valves are installed closer to the radiators. This will allow them to be turned off without affecting the coolant flow.
The dressing tube has different shapes
Bypass installation
To carry out heating installation, you must have certain knowledge and skills. This takes into account the method of pipeline assembly. For this purpose, threaded and fitting connections are used, as well as pipe soldering. Having these skills will make the job easier. It is worth considering some rules and recommendations from experts:
- There should be no valves between the rack and the bypass. Otherwise, the coolant circulation may be disrupted.
- On the vertical riser pipe, the jumper is mounted in close proximity to the battery. In this case, space must be provided for installing shut-off valves. It is mounted on both sides of the radiator.
- Do not install valves on the bypass unless necessary. If you install taps on the jumper, the circuit will become unbalanced. In an autonomous system of a private house, this in turn allows you to redirect the flow. In a multi-story building, this option is ineffective and is a violation of standards.
- The size of the pipes is important. The diameter of the insert is two sizes smaller than the section of the stand. The pipes that go to the radiators are made one size smaller. In the horizontal scheme, the size ratio is somewhat different.
Compliance with the dimensions of pipes and pipes will ensure normal operation of the system, in accordance with all the laws of hydraulics. As for installation, its features directly depend on the type of material used. If we are talking about a metal pipeline, then it is enough to simply weld the jumper and install the taps.
Installation is carried out in different ways
The use of polypropylene, as well as metal-plastic, requires the use of special fittings. You can build a bypass yourself from a pipe of the required size or purchase a ready-made part.
Important! In a system with two risers, a jumper is not needed. The radiator is disconnected from the system using taps, which are installed in the section between the riser. But is a bypass needed in a one-pipe system? The purpose of this element is definite.
The pump is often installed on a jumper