Central heating systems of multi-storey communal buildings and individual residential buildings have not only significant design differences, but also different physical characteristics of the coolant used. When designing intra-house heating networks, the main design criterion is the pressure in the heating system, the parameters of which have a significant impact on the correct functioning of the entire heating system.
In individual residential buildings, autonomous systems are used for heating, which include various equipment; when independently filling the circuit with a coolant, it is important to maintain the correct pressure parameters. Monitoring and adjusting pressure within specified limits during operation of the heating system will ensure the longevity of its operation, optimize the consumption of thermal resources, and increase the efficiency of heat exchange devices.
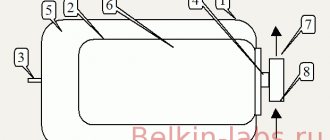
Rice. 1 Heating equipment in the house - appearance
Types of coolant pressure
Pressure in a heating system is a complex concept; it is divided into several types:
- Working - constantly present in the system throughout the entire heating period.
- Maximum (limit) operating – manufacturers indicate in the passports of radiators and boilers.
- Static - measured with the boiler turned off, the circulation pump not working, coolant at room temperature and the system completely filled, i.e. This is the pressure of the liquid column in pipes and radiators.
- Dynamic - created by a circulation pump and serves to move the coolant along the circuits.
- Pressure testing (test) – increases briefly during hydraulic tests for the strength of structural elements and density (detection of leaks in connections).
The parameters vary greatly in apartment buildings of different heights and in individual buildings.
How to actually choose the cheapest heating radiators on the market
What should normal blood pressure be?
The term “normal” means an indicator at which optimal coolant circulation is formed and there is no threat of an emergency. Each element of the heating system has a design strength and resistance to a certain temperature.
There are the following criteria for normal pressure (in atmospheres):
- seamless steel pipes - 20;
- steel pipes with seam -16;
- polypropylene reinforced products - 5;
- aluminum radiators - 6;
- panel batteries - 9;
- cast iron sections - 15.
In all cases, before making a decision to replace radiators, piping and risers in an apartment, you must consult with specialists.
It is advisable to purchase products designed for double dynamic pressure. This is necessary because hydrodynamic shocks in the system are not uncommon when pumping equipment malfunctions.
Pressure standards in multi-apartment building systems
The operating and test pressure indicators in the heating system of apartment buildings are specified in SP 60.13330.2020 (SNiP 41-01-2003) “Heating, ventilation, air conditioning”, which came into force on July 1, 2021, as well as in the Decree of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated September 27 2003 N 170 “On approval of the Rules and Standards for the technical operation of the housing stock.”
The maximum operating pressure standards are as follows:
- in systems with cast iron and stamped steel radiators – 0.6 MPa (6 kgf/cm2);
- with steel and combined 1.0 MPa (10 kgf/cm2).
For your information! A pressure of 1 MPa corresponds to 9.68 atm or 10.1 kgf/cm2.
The pressure in apartment buildings must be sufficient to ensure the delivery of coolant to the upper floors.
In buildings up to 5 floors inclusive, the parameter is 3-6 atm, in buildings from 5 to 9 floors - 5-7 atm, for high-rise buildings - from 7 to 10 atm.
Important! According to the documents, during hydraulic tests the pressure must exceed the maximum operating pressure by at least 1.5 times, i.e. in high-rise buildings it can rise to 16 atm.
Taking into account annual hydraulic tests, radiators and supply pipes that are resistant to such pressure drops are selected to replace these elements during repairs.
Some features of heating multi-storey buildings
The vast majority of apartment buildings are equipped with a heating system, where the apartment radiators are connected to a common access riser. The pressure in it is stable and varies slightly only between floors due to the influence of the water column (according to standards, no more than 0.3 atm for every 10 m of height).
Modern development often involves individual pipe distribution to each apartment from the floor collector, and pressure gauges are also installed here.
The owner should find out the intended operating pressure and if it changes, contact the management company. A decrease in the indicator leads to a decrease in temperature, an increase indicates a malfunction.
Norms and requirements of GOST and SNIP
The requirements for heating systems are set out in SNiP 2.04.05-91 as amended on January 21, 1994 N 18-3, May 15, 1997 N 18-11 and October 22, 2002 N 137.
GOST and SNiP regulate the following provisions regarding the heating system:
- climatic and meteorological conditions;
- noise and vibration levels of equipment;
- maintainability of the highway;
- design safety;
- area and volume of premises;
- economic justification;
- material resistance to corrosion;
- use of products permitted for construction;
- amount of heat per unit area.
SNiP recommends using water with or without additives as a coolant. The use of other materials is permitted if economic feasibility calculations are available.
Filling the line with toxic liquids is prohibited.
Pressure standards in heating systems of private houses
Water heating of a private house, as a rule, consists of a boiler, distribution pipes, radiators (warm floor pipes) and auxiliary elements (expansion tank, safety group).
In open (gravity) systems with natural circulation, the static pressure does not exceed 1-2 atm.
To move liquid in closed types of heating, a circulation pump creates a dynamic pressure that is 0.5 atm higher than the static pressure, i.e. for a private house with a height of up to 10 m, 1.5-3 atm is considered normal.
All modern boilers and radiators can withstand this parameter with a margin. If the pressure increases for any reason, the emergency valve is activated, releasing a certain amount of coolant or steam formed in the system.
Modern boilers have a built-in emergency valve; when purchasing, it is important to find out the maximum pressure (indicated on the cap) for which it is designed, and when debugging the system, carry out adjustments (if necessary). By turning the adjustment knob, you change the characteristic at which the trigger will occur.
Adjustable spring safety valve. Most often used in individual heating systems.
Pressure testing of heating in private houses is carried out by increasing the pressure to 0.2-0.4 MPa (2-4 atm), which is 1.5 times more than normal working pressure. Boilers and expansion tanks are turned off for the test period, as they are the most susceptible to destruction.
An increase and deviation of the indicator by 15-20% from the norm indicates the appearance of a malfunction. The cause must be identified and eliminated as soon as possible.
Leak test
To ensure that the heating is reliable, after installation it is checked for leaks (pressure tested).
This can be done immediately on the entire structure or its individual elements. If a partial pressure test is carried out, then after its completion the entire system must be checked for leaks. Regardless of which heating system is installed (open or closed), the sequence of work will be almost the same.
Preparation
A test pressure is considered to be 1.5 times the working pressure. But this is not enough to completely detect a coolant leak. Pipes and couplings can withstand up to 25 atmospheres, so it is better to check the heating system under this pressure.
The corresponding indicators are created using a hand pump. There should be no air in the pipes: even a small amount of it will distort the tightness of the pipeline.
The highest pressure will be in the lowest place of the system; a monometer is installed there (reading accuracy 0.01 MPa).
Stage 1 - cold test
Over the course of half an hour, the pressure in the water-filled system is increased to the initial values. Do this twice, every 10-15 minutes. The fall will continue for another half hour, but without exceeding 0.06 MPa, and after two hours - 0.02 MPa.
At the end of the inspection, the pipeline is inspected for leaks.
Stage 2 - hot check
The first stage has been successfully completed, you can begin hot leak testing. To do this, connect a heating device, most often a boiler. Maximum performance indicators are established; they should not be greater than the calculated values.
Houses are preheated for at least 72 hours. The test is passed if no water leakage is detected.
Plastic pipeline
The plastic heating system is checked at the same temperature of the coolant in the pipeline and the environment. Changing these values will increase the pressure, but in fact there is a water leak in the system. For half an hour the pressure is maintained at a value one and a half times higher than the standard value. If necessary, pump it up slightly.
After 30 minutes, the pressure is sharply reduced to a reading equal to half the working one, and held for an hour and a half. If the indicators begin to increase, it means that the pipes are expanding and the structure is sealed.
Often, when checking a system, technicians perform a pressure drop several times, either increasing or decreasing it, so that it resembles normal, everyday working conditions. This method will help identify leaky connections.
Air test
Multi-storey buildings undergo airtightness testing in the fall. Instead of liquid in such cases, air can be used. The test results are slightly inaccurate due to the fact that the air is first heated during compression, then cooled, which contributes to a drop in pressure. Compressors will help increase this parameter.
The sequence for checking the heating system is as follows:
- The structure is filled with air (test values - 1.5 atmospheres).
- If a hiss is heard, it means there are defects, the pressure is reduced to atmospheric pressure and the defects are eliminated (for this, a foaming substance is used, it is applied to the joints).
- The pipeline is again filled with air (pressure - 1 atmosphere), held for 5 minutes.
What to do if the indicator rises above normal
Liquid, unlike gas (including air), is practically not compressible. When heated, the volume of the coolant increases. This must be taken into account when filling a refrigerated system.
There should be a free volume left in the communication, which will be filled with expanded liquid. If this is not done, after starting the heating, the pressure may increase above the safe level - the excess will pour out of the expansion tank of the gravity system or the emergency valve will operate in closed types of communication.
In the event of a malfunction, for example, jamming or oxidation of the emergency valve in the boiler or safety group, the pressure may increase to critical values that can destroy the radiators or boiler.
How to choose a room thermostat and save up to 30% per month on heating
Table. Causes of increased pressure and methods of elimination.
| Possible reason | Manifestation | Remedy |
| Faulty make-up tap connected to the water supply - “excess” liquid enters the system | When the system is turned off, the noise of water flowing through a closed tap can be heard; reset must be done at regular intervals | Drain water, replace or repair faucet |
| Insufficient volume of the expansion tank - the liquid does not fit into the device and increased pressure is created | Detected upon first start. The volume of the expansion tank should be at least 10% of the volume of the entire system | Replace with a tank of sufficient volume |
| Damaged expansion tank membrane | When tapping the case, the sound is the same everywhere, i.e. no air cavity. When you press on the nipple, the coolant flows out of the tank, but the air is not released | Replace the membrane or tank assembly |
| Air locks in a closed heating system | When you open the drain valves on radiators or risers, you hear the sound of air escaping |
|
| Installing an expansion tank directly behind the circulation pump | Sudden pressure surges, audible sound of water hammer | Install a hydraulic accumulator before the pump |
| Overlapping of shut-off valves (accidentally, due to forgetfulness, by children) | Perceived difference in temperature of different radiators, cooling of disconnected devices | Check the positions of the shut-off valve handles and thermostats |
| Malfunctions in the boiler automation | Continued heating after the coolant reaches the set temperature | Call a service technician |
Advice! We advise inexperienced users to limit themselves to checking the position of shut-off valves and radiator thermostats, as well as attempting to drain the coolant through the Mayevsky taps. In other cases, it is advisable to call a technician and remember what he did so that next time you can fix the simplest faults yourself.
Interfering with the operation of the boiler is strictly prohibited.
Elimination of differences
Adjustment and adjustment of the pressure and temperature of the coolant is carried out through the elevator heating unit. The elevator is located in the basement of a residential building. It is responsible for mixing the supply and return flows. In its mixing chamber there is a nozzle, the size of which regulates the amount of incoming hot water (its temperature upon arrival is too high to be sent to the radiators).
In emergency cases, when there is a threat of defrosting the entire house, the control unit can be completely removed and the coolant will go directly to the apartments. Or a nozzle hole is drilled in it. Residents, of course, cannot do this.
Elevator unit maintenance
Specialists must also ensure that equipment and pumps are in good working order. In case of malfunction and breakdown, the pumps are replaced. They check for leaks, find them and fix them.
So many problems with pressure are solved from the basement, by the hands of specialists. But something also depends on the residents:
- For risers, pipes with a diameter of 25–33 mm are used. The same diameter should be on the outlet to the radiator. When replacing any section, be sure to install exactly the same pipe as it was, without narrowing or widening the passage!
- You need to monitor the condition of radiators and pipes in your apartment. It may be necessary to bleed air periodically. This is not at all difficult to do on new batteries, because special air taps and valves are provided for them from the factory.
The heating system of a private house is another matter. Here, all the “control levers” are in the hands of the owner, and he can and must monitor the pressure himself.
The most common reasons why the pressure in the heating system drops
Low pressure is not dangerous for structural elements, but almost always leads to heating stopping:
- gas boilers turn off when the pressure drops to 1-1.2 atm;
- in gravity systems, the coolant cannot rise to the upper distribution pipe, and water circulation stops.
The pressure in the heating system drops for several reasons, most of which can be eliminated independently.
Malfunction of the boiler feed tap
Location of the feed tap in wall-mounted gas boilers.
Check the operating instructions for the exact location of the tap in your model. The problem is detected during an external examination. There are visible drips on the faucet, and traces of coolant drainage on the floor. It is important to understand that the heated liquid can evaporate immediately, so you need to monitor the condition of the tap for several minutes.
If the make-up valve is embedded in the water supply, then the pressure in the system drops when the water supply to the mains is turned off. Sometimes you can hear the noise of flowing liquid.
Important! Cases of faucet malfunction due to loose closure of the supply channel are rare, since if a malfunction occurs, the pressure in the system will regularly rise in normal water supply mode, which cannot be ignored for a long time.
Eliminate the malfunction by replacing the ball valve or repairing (replacing the gasket, cleaning the seat) the screw valve.
Coolant leak
Leaks should be looked for in threaded and welded connections between radiator sections. Pure coolant leaves almost no traces after evaporation; antifreeze is tinted to make the leak easier to find.
This is what a typical antifreeze for a heating system looks like.
When identified, try to eliminate the leak by tightening the threaded connection. In welding areas, you will have to resort to the help of a gas welder (electric devices are not used).
Advice! Sectional radiators can be repaired by replacing a section, but if the batteries are in a low or medium price category, it is more profitable to replace the entire radiator - the price is comparable to calling a technician and buying spare parts.
Air jams
The mechanism for reducing pressure in the system due to air locks is based on the fact that some of the radiators become blocked for coolant flow, the water cools, and the pressure decreases.
The phenomenon is dangerous for all components of communication: at high temperatures and air access, oxidative processes are accelerated (especially in aluminum radiators). Insoluble chemical compounds are deposited on the walls of pipes and batteries, the circulation rate of the coolant slows down, heat transfer decreases, and energy consumption increases.
Air can be sucked into the system through leaky connections, a circulation pump, or formed as a result of chemical reactions.
Eliminate the malfunction by bleeding through manual or automatic Mayevsky taps or other used air vents.
This is what Mayevsky's crane looks like.
Expansion tank malfunction
In a closed heating system, excess pressure is created in the air chamber of the tank, which keeps the membrane from expanding.
Cracks in the hydraulic accumulator housing or a malfunction of the nipple can lead to the pressure in the air chamber of the tank being compared to atmospheric pressure. The coolant flows into the storage tank without resistance, and the pressure in the system drops.
If leaks through cracks are visible on the body, then the tank cannot be restored and should be replaced. Bleeding air through the nipple is eliminated by replacing the part with a new one, the price of which does not exceed 10-20 rubles.
Depressurization of the boiler heat exchanger
The coolant can leave the heating system through cracks in the boiler heat exchanger.
When the boiler is turned on, the fault cannot be seen, since the coolant instantly evaporates, heating up from the flame of the burners. If you turn off the boiler and let it cool, you may notice streaks on the walls of the part.
The heat exchangers of modern boilers cannot be repaired and must be replaced.
Automatic air vent malfunction
Failure manifests itself in the form of a coolant leak.
The device of a modern automatic air vent.
The locking is controlled by a float connected to a needle valve or spool. When there is air in the system, the float drops, the valve opens, and the air comes out under coolant pressure. After this, the liquid level rises, the float floats up, and the needle closes the hole communicating with the indoor air.
When the float is destroyed and deposits appear on the locking needle, the coolant flows out of the system and the pressure drops.
To correct the operation, try to clean the needle and seat with a rag, and if necessary, change the entire relief valve.
Relief valve failure
The relief valve is installed in the boiler or as part of the safety group.
The operating principle of a spring safety valve designed for an individual heating system. When the pressure in the system exceeds the clamping force of the spring, the spool rod rises, causing the coolant or steam to escape through the outlet pipe.
Under normal control conditions, the valve is closed. When the pressure exceeds the coolant compresses the spring, the bypass hole opens. Steam or liquid is released through it, and the pressure returns to normal.
Breakage of the spring or its weakening leads to the release of water at low pressure.
The cost of the valve is 180-300 rubles and it must be replaced.
How to choose a water softener for a gas boiler and extend the life of the heat exchanger
Incorrect operation of instrumentation
In cases where the system is functioning properly, and the pressure gauge of the boiler or safety group shows low or high pressure, it can be assumed that the instruments are giving incorrect readings. You can check them by installing a known-good pressure gauge. A faulty device must be replaced.
Pressure deviations in the heating system can cause malfunctions or lead to destruction of individual elements. It is important to identify and fix the problem yourself based on the initial signs or seek help from specialists. Delays in repairs lead to high costs for repairs or replacement of expensive equipment.
Reasons for increasing power
An uncontrolled increase in pressure is an emergency.
May occur due to:
- the automatic control of the fuel supply process is faulty;
- the boiler operates in manual high-burning mode and is not switched to medium or low-burning;
- malfunction of the storage tank;
- malfunction of the fill valve.
The main reason is overheating of the coolant. What can be done?
- The operation of the boiler and automation should be checked. In manual mode, reduce the fuel supply.
- If the pressure gauge readings are critically high, drain some of the water until the readings drop into the work area. Next, check the readings.
- If no boiler malfunctions are identified, check the condition of the storage tank. It accepts a volume of water that increases when heated. If the damping rubber cuff of the tank is damaged, or there is no air in the air chamber, it will fill completely with water. When heated, the coolant will have nowhere to be displaced, and the increase in water pressure will be significant.
Checking the tank is easy. You need to press the nipple in the valve to fill the tank with air. If there is no air hissing, then the reason is a loss of air pressure. If water appears, the membrane is damaged.
A dangerous increase in power can lead to the following consequences:
- damage to heating elements, up to rupture;
- overheating of water, when a crack appears in the boiler structure, instantaneous vaporization will occur, releasing energy equal in power to an explosion;
- irreversible deformation of boiler and heating elements and rendering them unusable.
The most dangerous thing is a boiler explosion. At high pressure, water can heat up to a temperature of 140 C without boiling. When the slightest crack appears in the jacket of the boiler heat exchanger or even in the heating system next to the boiler, the pressure drops sharply.
Superheated water, with a sharp decrease in pressure, instantly boils with the formation of steam throughout the entire volume. The pressure instantly increases from steam formation, and this can lead to an explosion.
At high pressure and water temperature above 100 C, you cannot suddenly reduce power near the boiler. Do not fill the firebox with water: strong temperature changes may cause cracks.
It is necessary to take measures to lower the temperature and smoothly lower the pressure by draining the coolant in small portions at a point far from the boiler.
If the water temperature is below 95 C, adjusted for the thermometer error, then the pressure is reduced by releasing part of the water from the system. In this case, steam formation will not occur.
How to deal with pressure changes?
Possible solutions to problems when reducing the load inside communications:
- When a leak is detected, the system is repaired. If necessary, the sealing gasket and section of the pipeline are replaced, and couplings are installed.
- The equipment is being adjusted, which is necessary in cases where the coolant parameters were initially set that do not correspond to environmental conditions.
- If the clearance of communications has decreased, the system is flushed from scale. In this case, the boiler is first dismantled.
- When the heating system circuit has been changed, the area of the facility has increased, a more suitable pipe diameter is determined, and then the communications are replaced.
If the question of why differences occur and how to deal with them is being resolved, it is necessary to inspect the entire circuit for leaks and check the operation of the equipment.