Residents of apartment buildings often complain about the cold indoors. One of the main reasons for this may be the low temperature of the water in the heating radiators. We have already written about the reasons why batteries are cold. What should be the temperature of the radiators in the apartment so as not to freeze? It also depends on the ambient temperature. But it is worth considering not only the temperature of the water, but also the material from which the radiator is made. If the temperature in the heating radiators in the apartment does not satisfy the residents, then they can call a commission to take measurements. Measurements are carried out using tested devices. This is how the temperature of the battery in the apartment is determined, the norm of which fluctuates depending on changes in weather conditions.
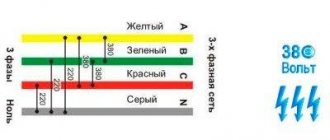
Types of electric boilers
Depending on the method of transferring thermal energy to the coolant, electric boilers are divided into three types:
- Tenovye.
- Induction.
- Electrode.
All these heating units are produced in two versions: 220 and 380 volts.
Heating boilers
These electric boilers for home heating are the most popular. The principle of their operation is as follows:
- The tubular element heats the water circulating in the closed system.
- Circulation ensures fast and uniform heating of the entire system.
- The number of heating elements required depends on the power of the device and can vary from 1 to 6 heating elements.
Such boilers are equipped with a reliable automation system that allows you to monitor and regulate the temperature of the coolant. The advantages of heating elements heating units are:
- Simplicity and reliability of design.
- Easy to install.
- Cheap design.
- The ability to use almost any liquid as a coolant.
- These 380 volt boilers have a modern design and fit well into any interior.
Induction boilers
The principle of electromagnetic induction has long been successfully used for heating residential premises. This boiler has the following device:
- A metal core is inserted into a cylindrical body (usually a piece of pipe), on which a coil is wound.
- When voltage is applied to the coil and winding, vortex flows arise, as a result of which the pipe through which the coolant circulates heats up and transfers heat to the water.
- The water circulation must be constant so that the coil and core do not overheat.
This electric heating system has the following advantages:
- High efficiency, reaching 98%.
- This 380 volt boiler is not susceptible to scale formation.
- Increased safety - no heating elements.
- Small dimensions and low weight ensure easy and quick installation of induction boilers.
Electrode systems
In its operation, the 380 volt electrode boiler uses specially prepared water. Preparing the coolant involves dissolving a certain amount of salts in it to give the required density. The general operating principle of electrode heating devices is as follows:
- Two electrodes are inserted into a pipe of suitable diameter.
- Due to the potential difference and frequent polarity changes, the ions begin to move chaotically. This way the coolant heats up quickly.
- Due to the rapid heating of the coolant, powerful convection currents are created, allowing you to quickly warm up a large volume without the use of a circulation pump.
The electrode boiler has obvious advantages, including:
- Small sizes.
- Fast ramp up to rated power.
- Compact and simple design.
- No emergency situation, even if water leaks from the heating system.
The impact of temperature on the characteristics of the coolant
In addition to the factors listed above, the temperature of the water in the heating pipes affects its characteristics. The method of functioning of gravity heating systems is based on this. As the water heating value increases, it expands and circulation appears.
Coolants for heating systems
But when using antifreeze, exceeding normal temperatures in radiators can lead to different results. Therefore, for heating with a coolant other than water, it is necessary to first determine the permissible heating values. This does not apply to the temperature of the central heating radiators in the apartment, since such devices do not use antifreeze-based liquids.
Antifreeze is used if there is a risk of exposure to low temperatures on radiators. Unlike water, it does not change from liquid to crystalline at 0 degrees. But if the heat supply operation exceeds the norms of the temperature table for heating to a greater extent, the following phenomena may be observed:
- foaming This contributes to an increase in coolant volume and pressure level. There will be no reverse process when the antifreeze cools;
- the appearance of limescale. Antifreeze contains mineral components. If the heating temperature in the apartment is violated, they precipitate. Over time, this leads to clogged pipes and radiators;
- increase in density. Malfunctions of the circulation pump may occur if its rated power was not designed to handle such situations.
We recommend: Which radiators are best suited for autonomous heating?
Therefore, it is much easier to monitor the water temperature in the heating system of a private home than to control the heating level of antifreeze. Moreover, substances based on ethylene glycol emit gases that are harmful to humans when evaporated.
Today they are almost never used as a coolant in autonomous heating systems. Before using antifreeze in heating, it is necessary to replace all rubber seals with paranitic ones. This is due to the high level of permeability of this type of coolant.
Options for normalizing heating temperature
Minimum water temperatures in the heating system are not considered the main threat to its operation. This affects the microclimate in living rooms, but does not affect the operation of the heating supply. If the water heating norm is exceeded, emergency situations may occur.
Safety group for autonomous heating
When creating a heating scheme, you need to provide a list of measures aimed at preventing a critical increase in water temperature. First of all, this will lead to increased pressure and stress on the inside of pipes and radiators. If this happened once and lasted a short time, then the heating parts will not be damaged.
But such cases appear under the constant influence of specific factors. Most often this is the incorrect operation of a solid fuel boiler. To avoid breakdowns, it is necessary to upgrade the heating in the following way:
- installation of a security group. It consists of an air vent, a bleed valve and a pressure gauge. If the water temperature reaches a critical level, these parts will eliminate excess coolant, thereby ensuring normal circulation of the liquid for its natural cooling;
- mixing unit. It connects the return and supply pipes. Additionally, a two-way valve with a servo drive is mounted. The latter is connected to the temperature sensor. If the heating level exceeds the norm, the valve will open and a mixing of hot and cooled water flows will occur;
- electronic heating control unit. It distributes the water temperature in different parts of the system. If the thermal regime is violated, it sends a corresponding signal to the boiler processor to reduce power.
These measures will prevent improper heating operation at the initial stage of the problem. It is most difficult to control the water temperature in systems with a solid fuel boiler
Therefore, for them, special attention must be paid to the selection of indicators of the safety group and mixing unit
YouTube responded with an error: Access Not Configured. YouTube Data API has not been used in project 268921522881 before or it is disabled. Enable it by visiting https://console.developers.google.com/apis/api/youtube.googleapis.com/overview?project=268921522881 then retry. If you enabled this API recently, wait a few minutes for the action to propagate to our systems and retry.
Battery temperature
There are minimum and maximum standards. Sometimes, even when heating is started, there is not enough heat in the room due to the fact that the temperature of the radiators is far from the standards. The reason for this is the banal airiness of the system. You can fix the problems with the help of a specialist or yourself using a Mayevsky crane.
If the problem arises due to worn-out riser pipes or batteries, then you simply cannot do without the help of specialists. If the heating system did not work and the air in the apartment was colder than specified in GOST standards, then this entire period is not subject to payment.
There are no minimum temperature standards for heating radiators, so it is customary to rely on the air parameters in the apartment. Normal air parameters during the heating period are +16…+25°C.
To document that the temperature of the heating system does not meet the norm, it is necessary to invite an authorized representative of the heating service provider. What the water temperature in the batteries should be is described in SNiP 41−01 of 2003:
- If a two-pipe design is used in the room, then 95°C is the maximum.
- The norm for a single-pipe design is +115°C.
- The winter temperature norm for heating radiators in an apartment is +80…+90°C. If it approaches +100°C, then urgent measures must be taken to prevent water from boiling in the system.
To ensure that the heating complies with GOST standards, you need to take your own measurements and understand what the temperature of the water in the heating radiators is:
- An ordinary mercury thermometer can be used, but then 2°C will need to be added to the result obtained.
- An infrared thermometer will also work.
- The alcohol thermometer must be tightly tied to the battery, wrapped in thermal insulation.
If the results obtained are far from normal, then you need to submit an application to the heating network office with a request to carry out control measurements. A commission will visit the apartment and make all the necessary calculations.
Why are there cold radiators in the apartment?
Very often situations arise when it becomes very cold outside, and the temperature of the water in the heating pipes does not increase. Moreover, often the coolant is not poured into the pipes at all. The reason for this lies, most likely, in the service organization’s dishonest attitude towards its responsibilities.
Among the probable reasons for the lack of heat in the house are:
- failures and breakdowns of heating system elements;
- system repair work not completed;
- presence of air pockets in the heating circuit.
In cases where the temperature of the water in the batteries does not rise due to preventive or repair work in the general heating system of the house, you will only have to wait until they are completed. But if the reason lies in air plugs in the circuit, you need to either open the Mayevsky valves on the radiators and drain it, or contact a service organization. Within 24 hours, they must send a specialist to blow out the pipes and restore coolant circulation.
Procedure in case of no heating
Residents of apartment buildings are sometimes faced with a situation where the apartment is already very cold, and the temperature of the radiator in the apartment is not only below normal - the heating is completely turned off. If the reason for this is a breakdown of the heating system in the house, they must be eliminated
But if the culprit of the delay is the service company, it is important to provide evidence that the apartment is very cold
A representative is invited from the service company and together with him they measure the temperatures in each room, recording the results in writing. After receiving the results, the heat supplier must urgently take measures to turn on the heating and recalculate the charge for the period of interruption. In the absence of any response from the service organization, compensation can be obtained through the court for violation of the rules for servicing the population by utility companies.
In winter, the minimum air temperature in the apartment is 18 ℃. Provided that the temperature falls below this level, the heat supplier must reduce the payment by 0.15% for each hour of the violation period.
The water temperature standards in house heating radiators must comply with SNiP and be strictly observed throughout the heating season.
To protect themselves from violations by heat suppliers, consumers should familiarize themselves with the standards, deadlines and temperature limits of water in radiators and indoor air during the heating season. Then, if necessary, they can check all values with simple measurements.
If there is any discrepancy between the heating system and GOST, you need to find the cause of the cold radiators. The best person to deal with this will be the specialists of the supplier company, who will be able to officially record the temperature in the living room.
If the problem is caused by poor quality maintenance of the systems of an apartment building, then the solution to the problem lies entirely with the organization supplying the heat. At the same time, all residents should be recalculated for heat or they should be completely exempt from paying if the radiators did not heat at all.
Knowing what the temperature of the radiators in the apartment should be and at what period the heating starts, each resident of an apartment building can determine for himself whether the temperature indicators comply with the established standards. This will help you take action in time and solve the heat problem.
When does the heating season start?
According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation, heating in apartment buildings is turned on as soon as the average daily air temperature drops below 8 ℃ and does not rise above this mark for more than 5 days. If the weather is warm in the fall, then the supply of heat to apartments may be delayed for some time - utility services have the right to do this, since a comfortable temperature in the apartment is maintained even without heating.
It is noteworthy that central heating systems are turned on only on the 6th day after the air reaches the specified temperature values. As a rule, the official start of the heating season in most regions of the country falls in mid-October, and its end in April.
How to correctly measure and find the average standard
The heating is turned on in your house and you want to measure the air temperature in the apartment, but you don’t know how to do it correctly? Now let's clarify this issue.
To do this you need to use a certain method:
In each room, a thermometer is placed on the inside of the wall.
It should be located at a distance of one meter from the outer wall and one and a half meters from the floor surface. Measurements are taken for at least ten minutes.
Users of residential premises in apartment buildings must receive heating services continuously and around the clock throughout the entire established period.
The permissible rate of heating failure is no more than one day within thirty days (24 hours in total).
At a time, no more than 14 - 16 hours (the air temperature in the rooms should remain at least twelve degrees).
If the air temperature in the living room is ten to twelve degrees, no more than eight hours.
And no more than four hours if the temperature is eight to ten degrees.
If the standards are not met, the heating fee for each hour must be revised and reduced by 0.15%.
Now take a calculator and do some simple calculations and find out how much you should pay for batteries that are barely warm.
Perhaps some individuals do not agree with the established norms and requirements of legal acts.
If the temperature in your apartment corresponds to the requirements, but you do not agree with it (this is not enough for you), then in this case there is only one way out - buy a heater.
For many, this is a way out of the situation so as not to freeze.
And if, on the contrary, you feel hot, you can adjust the temperature using a thermal head installed on the radiator.
But keep in mind that in this case you will have to pay for the services provided in full. There will be no concessions to you from the service organization.
Of course, you can only pay for the heat you used; for this you will have to install heating heat meters.
The standard temperature in a living space in winter, according to SanPiN, is predetermined in conjunction with such indicators as air humidity and air flow speed.
This applies only to rooms in which the optimal humidity value is between 30 and 45%.
For other premises, these parameters are not standardized. In this case, air flows should move at a speed of 2 m/s.
So, we have figured out the air temperature in the apartment during the heating season and found out the permissible errors in one direction or another.
Temperature standards for heating radiators
Since the heating of an apartment building is a complex and extensive system, we have developed a special standard for the temperature of water in the radiators, compliance with which allows us to judge the efficiency of the operation of all equipment.
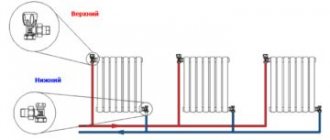
In this regard, it is very important when installing or replacing radiators to comply with all rules and technical requirements for this type of work. If there are errors and violations of the radiator installation technology, the heat will not be evenly distributed throughout the entire circuit. This means that in neighboring rooms or even apartments the temperature of the water in the central heating radiators will be different - it’s hot in one and cold in the other.
In addition, when installing batteries, it is important to correctly calculate the sections, which will allow you to maintain the normal temperature of the heating battery in the apartment.
How everything works
There are two different types of charts:
- For heating networks.
- For indoor heating system.
The relationship between supply temperatures in the route and in the house.
To explain the difference between these concepts, it is probably worth starting with a brief excursion into how central heating works.
CHP - heating networks
The function of this bundle is to heat the coolant and deliver it to the end user. The length of heating mains is usually measured in kilometers, the total surface area is measured in thousands and thousands of square meters. Despite measures to insulate pipes, heat loss is inevitable: after traveling from the thermal power plant or boiler room to the border of the house, process water will have time to partially cool.
Hence the conclusion: in order for it to reach the consumer while maintaining an acceptable temperature, the supply of the heating main at the exit from the thermal power plant must be as hot as possible. The limiting factor is the boiling point; however, as the pressure increases, it shifts towards increasing temperature:
| Pressure, atmosphere | Boiling point, degrees Celsius |
| 1 | 100 |
| 1,5 | 110 |
| 2 | 119 |
| 2,5 | 127 |
| 3 | 132 |
| 4 | 142 |
| 5 | 151 |
| 6 | 158 |
| 7 | 164 |
| 8 | 169 |
Typical pressure in the supply pipeline of a heating main is 7-8 atmospheres. This value, even taking into account pressure losses during transportation, allows you to start a heating system in buildings up to 16 floors high without additional pumps. At the same time, it is safe for routes, risers and connections, mixer hoses and other elements of heating and hot water systems.
Inside the flexible hoses of the mixer the pressure is the same as in the heating main.
With some margin, the upper limit of the supply temperature is taken to be 150 degrees. The most typical heating temperature curves for heating mains are in the range of 150/70 – 105/70 (supply and return temperatures).
House
There are a number of additional limiting factors in a home heating system.
The maximum coolant temperature in it cannot exceed 95 C for a two-pipe and 105 C for a single-pipe building heating system.
A row of heating radiators stretches along the walls.
For obvious reasons, the temperature delta between the supply and return pipelines should be as small as possible - otherwise the temperature of the batteries in the building will vary greatly. This implies rapid circulation of the coolant. However, too fast circulation through the house heating system will lead to the return water returning to the route at an excessively high temperature, which is unacceptable due to a number of technical limitations in the operation of thermal power plants.
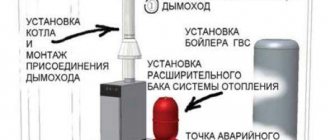
The problem is solved by installing one or more elevator units in each house, in which return water is mixed with the flow of water from the supply pipeline. The resulting mixture, in fact, ensures rapid circulation of a large volume of coolant without overheating the return pipeline of the route.
Elevator operation diagram.
For intra-house networks, a separate temperature schedule is set taking into account the elevator operation scheme. For two-pipe circuits, the typical heating temperature curve is 95-70, for single-pipe circuits (which, however, is rare in apartment buildings) - 105-70.
Requirements for heating networks
With centralized heat supply, the heat source is a boiler house or a thermal power plant, where high-temperature water-heating boilers are installed (in thermal power plants - steam boilers). The fuel is usually natural gas, with other energy sources being used to a lesser extent. The temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the hot water boiler is 115 °C, but the water does not boil when it is under pressure. The need to heat up to 115 °C is explained by the fact that boiler plants operate at maximum efficiency in this mode.
The transition from 115 °C to the required temperature value is provided by plate or shell-and-tube heat exchangers. At a thermal power plant, waste steam from turbines enters heat exchangers to produce electricity. According to regulatory requirements, the water temperature in heating pipes should not exceed 105 ° C, the lower limit depends on street conditions. In this range, the heating of water in the heating network is regulated depending on the weather, for which each boiler room has a temperature graph of the heating system. For home networks, 2 calculation schedules are used:
- 105/70 °C;
- 95/70 °C.
These figures show the maximum temperature of the supply and return water during the most severe frosts in a particular area. But at the beginning and end of the heating season, when the weather is not yet too cold, there is no point in heating the coolant to 105 °C, so a real temperature heating schedule is drawn up, which describes to what extent the water should be heated at different outside temperatures. The dependence of heating on weather conditions is shown in the table, which presents excerpts from the graph for the city of Ufa:
| Temperature, °C | |||
| street air average daily | on feed with design schedule 105/70 | on supply with a design schedule of 95/70 | in the return |
| +8 | 43 | 41 | 36 |
| 56 | 52 | 43 | |
| -5 | 64 | 59 | 48 |
| -10 | 71 | 65 | 52 |
| -15 | 78 | 72 | 56 |
| -20 | 85 | 78 | 59 |
| -25 | 92 | 84 | 63 |
| -30 | 99 | 89 | 67 |
| -35 | 105 | 95 | 70 |
It is quite difficult to find out exactly what the coolant temperature is in a centralized heating network. To do this, you need to have a remote thermometer that determines the degree of surface heating. So, it is possible to determine to what extent the heating standards in the apartment are met only by the air temperature in the rooms.
Reasons for interruption of heat transfer
It is worth noting that at the very beginning of the heating season, the temperature standards in the heating radiators are constantly observed and the heating works all the time. There is a heating system temperature schedule that is usually followed. In some cases, boiler houses may interrupt the heat supply to apartments.
By law, interruptions in the operation of the heating system cannot exceed the following values:
- 24 hours – if the minimum temperature in the apartment is 12 ℃;
- 8 hours – provided that the temperature in the apartment fluctuates between 10 ℃ and 12 ℃;
- 4 hours – if the room temperature drops to 8 ℃ or even lower.
All intervals given are based on a monthly basis. If these numbers are exceeded, residents have the right to file a complaint with the appropriate authorities.