The volume of water or coolant in various pipelines, such as low-pressure polyethylene (HDPE pipe), polypropylene pipes, fiberglass-reinforced pipes, metal-plastic pipes, steel pipes, must be known when selecting any equipment, in particular an expansion tank.
For example, in a metal-plastic pipe with a diameter of 16, a meter of pipe is 0.115 g. coolant.
Did you know? Most likely no. And why do you actually need to know this until you are faced with the selection of, for example, an expansion tank. Knowing the volume of coolant in the heating system is necessary not only for selecting an expansion tank, but also for purchasing antifreeze. Antifreeze is sold undiluted to -65 degrees and diluted to -30 degrees. Once you know the volume of coolant in the heating system, you can buy an even amount of antifreeze. For example, undiluted antifreeze must be diluted 50*50 (water*antifreeze), which means that with a coolant volume of 50 liters, you will need to buy only 25 liters of antifreeze.
We present to your attention a form for calculating the volume of water (coolant) in the pipeline and heating radiators. Enter the length of a pipe of a certain diameter and instantly find out how much coolant is in this section.
If you are setting up a house or apartment
When creating a project for a standard private house or apartment, there is no need to carry out precise calculations. The number of plumbing fixtures will be minimal, and the difference in price for pipes of different diameters will differ minimally, which will have virtually no effect on the budget.
If you look at the faucet hose, you can see what a small diameter they have, that is, through what minimal holes water flows into the sink. Taking into account the fact that the cross-section of the polypropylene pipe will be much larger, it will always be sufficient, since the bottleneck in this case will be precisely this hose. That is, the patency of the entire system will rest on its narrowest point.
conclusions
We hope everyone understands what diameter polypropylene pipes are measured by. Selecting them will not be difficult. As practice shows, you can often simply purchase the simplest and cheapest pipe - the result will be a high-quality and properly functioning water supply system.
Two-pipe circuit in a private house
How to correctly calculate the volume of water in a pipe
First, let's generalize a little. Let’s take, for example, calculating the diameter of polypropylene pipes for heating in a private house. Basically, products with a cross section of 25 mm are used for the circuit, and bends to radiators are set to 20 mm.
Due to the fact that the size of the heating pipes in a private house, used as pipes to the batteries, is smaller, the following processes occur:
the coolant speed increases; circulation in the radiator improves; The battery warms up evenly, which is important when connected at the bottom.
Combinations of a main circuit diameter of 20 mm and branches of 16 mm are also possible.
To verify the above data, you can calculate the diameter of pipes for heating a private house yourself. This will require the following values:
square footage of the room.
Knowing the number of heated square meters, we can calculate the boiler power and what pipe diameter to choose for heating. The more powerful the heater, the larger the cross-section of the product that can be used in tandem with it.
To heat one square meter of space, 0.1 kW of boiler power is required. The data is valid if the ceilings are standard 2.5 m;
heat loss
The indicator depends on the region and wall insulation. The bottom line is that the greater the heat loss, the more powerful the heater should be. To get around the complex calculations that are not appropriate in the approximate calculation, simply add 20% to the boiler power calculated above;
water speed in the circuit.
Allowed coolant speed is in the range from 0.2 to 1.5 m/s. Moreover, in most calculations of the diameter of pipes for heating with forced circulation, it is customary to take an average value of 0.6 m/s.
At this speed, noise from friction of the coolant against the walls is eliminated;
how much the coolant cools down.
To do this, subtract the return temperature from the supply temperature. Naturally, you cannot know the exact data, especially since you are at the design stage.
Now the calculation itself is how to choose the diameter of the pipe for heating. To do this, let's take a formula that initially contains two constant values, the sum of which is 304.44.
Conditional flow of the circuit, squared = 304.44 x (area of the room x 0.1 kW + 20%) / heat loss of the coolant / flow rate.
The last step is to extract the square root of the result. For clarity, let’s calculate what pipe diameter to use for heating a private house with one floor with an area of 120 m2:
304.44 x (120 x 0.1 + 20%) / 20 / 0.6 = 368.328
Now let's calculate the square root of 368.328, which is equal to 19.11 mm. Before choosing the diameter of the heating pipe, we once again emphasize that this is the so-called conditional diameter.
Products made from different materials have different wall thicknesses. For example, polypropylene has thicker walls than metal-plastic. Since we have knitted a polypropylene circuit as a sample, we will continue to consider this material.
The marking of these products indicates the outer cross-section and wall thickness. Using the subtraction method, we find out the size we need and select it in the store.
For convenience, we will use the table.
Based on the results of the table, we can conclude:
- if a nominal pressure of 10 atmospheres is sufficient, then an outer section of the heating pipe of 25 mm is suitable;
- if a nominal pressure of 20 or 25 atmospheres is required, then 32 mm.
VOLUME OF WATER IN THE PIPES
VOLUME OF WATER IN THE PIPES
| Pipe internal diameter, mm | Internal volume of 1 m running pipe, liters | Internal volume of 10 m linear pipes, liters |
| 4 | 0,0126 | 0,1257 |
| 5 | 0,0196 | 0,1963 |
| 6 | 0,0283 | 0,2827 |
| 7 | 0,0385 | 0,3848 |
| 8 | 0,0503 | 0,5027 |
| 9 | 0,0636 | 0,6362 |
| 10 | 0,0785 | 0,7854 |
| 11 | 0,0950 | 0,9503 |
| 12 | 0,1131 | 1,1310 |
| 13 | 0,1327 | 1,3273 |
| 14 | 0,1539 | 1,5394 |
| 15 | 0,1767 | 1,7671 |
| 16 | 0,2011 | 2,0106 |
| 17 | 0,2270 | 2,2698 |
| 18 | 0,2545 | 2,5447 |
| 19 | 0,2835 | 2,8353 |
| 20 | 0,3142 | 3,1416 |
| 21 | 0,3464 | 3,4636 |
| 22 | 0,3801 | 3,8013 |
| 23 | 0,4155 | 4,1548 |
| 24 | 0,4524 | 4,5239 |
| 26 | 0,5309 | 5,3093 |
| 28 | 0,6158 | 6,1575 |
| 30 | 0,7069 | 7,0686 |
| 32 | 0,8042 | 8,0425 |
| 34 | 0,9079 | 9,0792 |
| 36 | 1,0179 | 10,1788 |
| 38 | 1,1341 | 11,3411 |
| 40 | 1,2566 | 12,5664 |
| 42 | 1,3854 | 13,8544 |
| 44 | 1,5205 | 15,2053 |
| 46 | 1,6619 | 16,6190 |
| 48 | 1,8096 | 18,0956 |
| 50 | 1,9635 | 19,6350 |
| 52 | 2,1237 | 21,2372 |
| 54 | 2,2902 | 22,9022 |
| 56 | 2,4630 | 24,6301 |
| 58 | 2,6421 | 26,4208 |
| 60 | 2,8274 | 28,2743 |
| 62 | 3,0191 | 30,1907 |
| 64 | 3,2170 | 32,1699 |
| 66 | 3,4212 | 34,2119 |
| 68 | 3,6317 | 36,3168 |
| 70 | 3,8485 | 38,4845 |
| 72 | 4,0715 | 40,7150 |
| 74 | 4,3008 | 43,0084 |
| 76 | 4,5365 | 45,3646 |
| 78 | 4,7784 | 47,7836 |
| 82 | 5,2810 | 52,8102 |
| 84 | 5,5418 | 55,4177 |
| 86 | 5,8088 | 58,0880 |
| 88 | 6,0821 | 60,8212 |
| 90 | 6,3617 | 63,6173 |
| 92 | 6,6476 | 66,4761 |
| 94 | 6,9398 | 69,3978 |
| 96 | 7,2382 | 72,3823 |
| 98 | 7,5430 | 75,4296 |
| 100 | 7,8540 | 78,5398 |
| 105 | 8,6590 | 86,5901 |
| 110 | 9,5033 | 95,0332 |
| 115 | 10,3869 | 103,8689 |
| 120 | 11,3097 | 113,0973 |
| 125 | 12,2718 | 122,7185 |
| 130 | 13,2732 | 132,7323 |
| 135 | 14,3139 | 143,1388 |
| 140 | 15,3938 | 153,9380 |
| 145 | 16,5130 | 165,1300 |
| 150 | 17,6715 | 176,7146 |
| 160 | 20,1062 | 201,0619 |
| 170 | 22,6980 | 226,9801 |
| 180 | 25,4469 | 254,4690 |
| 190 | 28,3529 | 283,5287 |
| 200 | 31,4159 | 314,1593 |
| 210 | 34,6361 | 346,3606 |
| 220 | 38,0133 | 380,1327 |
| 230 | 41,5476 | 415,4756 |
| 240 | 45,2389 | 452,3893 |
| 250 | 49,0874 | 490,8739 |
| 260 | 53,0929 | 530,9292 |
| 270 | 57,2555 | 572,5553 |
| 280 | 61,5752 | 615,7522 |
| 290 | 66,0520 | 660,5199 |
| 300 | 70,6858 | 706,8583 |
| 320 | 80,4248 | 804,2477 |
| 340 | 90,7920 | 907,9203 |
| 360 | 101,7876 | 1017,8760 |
| 380 | 113,4115 | 1134,1149 |
| 400 | 125,6637 | 1256,6371 |
| 420 | 138,5442 | 1385,4424 |
| 440 | 152,0531 | 1520,5308 |
| 460 | 166,1903 | 1661,9025 |
| 480 | 180,9557 | 1809,5574 |
| 500 | 196,3495 | 1963,4954 |
| 520 | 212,3717 | 2123,7166 |
| 540 | 229,0221 | 2290,2210 |
| 560 | 246,3009 | 2463,0086 |
| 580 | 264,2079 | 2642,0794 |
| 600 | 282,7433 | 2827,4334 |
| 620 | 301,9071 | 3019,0705 |
| 640 | 321,6991 | 3216,9909 |
| 660 | 342,1194 | 3421,1944 |
| 680 | 363,1681 | 3631,6811 |
| 700 | 384,8451 | 3848,4510 |
| 720 | 407,1504 | 4071,5041 |
| 740 | 430,0840 | 4300,8403 |
| 760 | 453,6460 | 4536,4598 |
| 780 | 477,8362 | 4778,3624 |
| 800 | 502,6548 | 5026,5482 |
| 820 | 528,1017 | 5281,0173 |
| 840 | 554,1769 | 5541,7694 |
| 860 | 580,8805 | 5808,8048 |
| 880 | 608,2123 | 6082,1234 |
| 900 | 636,1725 | 6361,7251 |
| 920 | 664,7610 | 6647,6101 |
| 940 | 693,9778 | 6939,7782 |
| 960 | 723,8229 | 7238,2295 |
| 980 | 754,2994 | 7542,9640 |
| 1000 | 785,3982 | 7853,9816 |
Feedback
Feedback
The influence of pipe diameter on efficiency for a heating system in a private house
How to choose pipes for heated floors?
It is a mistake to rely on the “bigger is better” principle when choosing a pipeline cross-section. Too large a pipe cross-section leads to a decrease in pressure in it, and hence the speed of the coolant and heat flow.
Moreover, if the diameter is too large, the pump simply may not have enough performance to move such a large volume of coolant.
Important! A larger volume of coolant in the system implies a high total heat capacity, which means more time and energy will be spent on heating it, which also affects the efficiency in a negative way
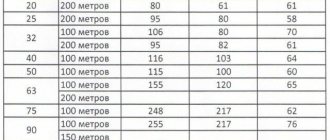
Selection of pipe section: table
The optimal pipe cross-section should be the smallest possible for a given configuration (see table) for the following reasons:
However, you should not overdo it: in addition to the fact that the small diameter creates an increased load on the connecting and shut-off valves, it is also not able to transfer enough thermal energy.
To determine the optimal pipe cross-section, use the following table.
Photo 1. Table showing the values for a standard two-pipe heating system.
Advantages and disadvantages
None of the materials is ideal and has its drawbacks. However, there are also materials on the list whose properties force them to leave the market. PVC is practically not used for heating due to the low operating temperature limit.
Not far behind it, for the same reason, is polypropylene. The actual candidates for which pipes to choose for heating are:
Metal-plastic
Press fitting for metal-plastic
This is a material with very high performance characteristics (if it is of proper quality). It has almost the lowest resistance to water flow. It is easy to install and can withstand temperatures of 90-100, and in short-term surges – 110-130 °C, which are practically unrealistic in individual heating systems.
An additional benefit is its flexibility. In addition to the fact that it can be hidden in walls or behind furniture, it allows you to lay long, seamless sections of arbitrary shape, with any turns. None of the other materials can boast of this.
Private house or apartment
Calculation of pipes for heated floors. method and online calculator
In a situation where you are drawing up a project for a water supply system for a small private house or apartment, you can easily do without carrying out complex calculations. There is a minimum number of water collection points here, and therefore differences in cost between pipes of different diameters, taking into account the small volume of purchases, will not greatly affect the modest budget.
It would be a good idea to look into the mixer body. There you will find thin holes through which water flows into the sink. For polypropylene pipes, the internal diameter should be such that these mixer holes are the bottleneck in the water supply system.
For this reason, many owners do not carry out complex calculations, but immediately decide to install polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 20 mm. This choice seems to be the most optimal solution, taking into account the reasonable number of consumption points used in the house in the form of sinks, washbasins, bathtubs and bidets.
Types and purpose
Polypropylene pipes can be single-layer or three-layer. Single-layer ones are used for water supply, sewerage, ventilation and other pipelines with a temperature of the transported medium not exceeding +45 °C.
Three-layer PPR pipes are reinforced. Reinforcement is designed to reduce the amount of thermal expansion and nothing more. PPR pipes are reinforced with fiberglass and foil. Those with glass fiber are suitable for hot water supply, provided that the water temperature is not higher than 80 °C. For heating and systems where water can heat above 80 °C, foil-reinforced polypropylene is used. The foiling may not be continuous. For such pipes, the permissible temperature of the transported medium is +95 °C.
Color is just a dye. It does not affect the properties in any way.
Can polypropylene pipes be used in underfloor heating systems? I guess, yes. The coolant temperature does not rise above +45 °C, which is quite acceptable even for single-layer ones. But due to high thermal expansion, PPR pipes for heated floors are not the best option, even those reinforced with foil. There are more stable options and not more expensive.
Key selection criteria
To choose the right size of polypropylene pipes, it is important to consider:
- Purpose of the pipeline line.
- Operating conditions of the highway.
- Maximum water temperature in the system.
- Working fluid pressure on the walls.
The efficiency and service life of utilities depends on the correct size chosen.
Home piping
Installation of a home cold water supply line with a working pressure of 1 MPa is carried out with thin-walled polypropylene pipes marked PN10 or PN16. The diameter of the water supply in city apartments is usually 20 mm. The risers are mounted from pipes of larger diameter.
The home hot water supply pipeline is installed from PN20 pipes, designed to move coolant heated to a temperature of +85 degrees. The design operating pressure in such a network is 2 MPa.
Formula for a single pipe
From a geometry standpoint, the pipe is a straight circular cylinder.
The volume of such an object is equal to the cross-sectional area multiplied by the length:
V = l * S
In it:
- V – volume (m3);
- l – length (m);
- S – cross-sectional area (m2).
The cross-sectional area of a pipe shaped like a circle with a known diameter is calculated using the formula:
S = π * d2 / 4
Here:
- π = 3.1415926;
- d – circle diameter (m).
The final formula for the volume of a pipe with a known internal diameter and length will be as follows:
V = π * l * d2 / 4
If the unit of measurement for the length and diameter of the pipe is another value (dm, cm or mm), then the volume will be expressed in dm3, cm3 or mm3, respectively.
Also, I wanted to show you a simple way to measure the outer diameter of a pipe (D) without a caliper. D = L / π, where L is the circumference:
To correctly calculate the volume of pipes, you need to substitute two parameters into a simple formula: length and internal diameter. The more accurately they are measured or calculated, the more accurate the result will be.
To calculate the internal volume of a pipe, you will need simple geometric formulas, which are used at school in physics, algebra, chemistry, geometry and other subjects.
Installation features
All fittings for polypropylene are made in diameter larger than that of the pipe, and have a hole with an internal diameter slightly smaller than the external diameter of the pipe. When cold, the fitting should not be pushed onto the pipe. Only with the help of special equipment, a soldering iron with several types of nozzles, can a layer of polypropylene on the surface of the pipe and inside the fitting be evenly heated to a state of melting. After this, the parts are connected with force, without twisting, and the relationship between the axes of the pipe and the fitting is checked. After cooling, the connection is considered ready, but requires additional testing before starting the system.
It should be remembered that when using polypropylene pipes for heating, their characteristics only allow them to withstand temperatures above 95°C for a short time, and at the boundary temperature the permissible pressure decreases. Therefore, when installing autonomous heating systems, you should first remove the pipe at least half a meter from the boiler with metal, and then switch to plastic. This is especially true for boilers running on solid fuel and gas, as well as without automatic control. They may experience overheating of the coolant or excessive heating directly at the outlet.
It is good that hardness salts, places of tension, and deformations are not formed at the joint, as when welding metal structures. However, the strength of the joint directly depends on the cleanliness of the surfaces being connected. Therefore, before welding, the joints must be cleaned of dirt and degreased.
All fittings intended for connecting polypropylene products are designed to create a uniform internal surface. However, for this you must adhere to strict installation rules. Inside the fitting, for example a coupling, there is a stop stop, up to which the edge of the pipe must be inserted. This limiter, together with the walls of the pipes and the seam layer, forms the most even surface possible. In case of incorrect installation, for example, when the fitting is not fully inserted, a depression is formed, creating additional resistance to fluid flow.
Having received generalized information about polypropylene pipes and their technical characteristics, you can safely analyze your own heating system. As mentioned earlier, it is not necessary to strive for the most expensive reinforced pipes if the PN10-PN20 pipe format is sufficient. For each case, it is better to choose the most practical option. Which option for heating systems did you choose? Please share your criteria. What influenced the choice of certain pipes as the basis for your own heating system?
How to choose the diameter of a heating pipe
It will not be possible to calculate exactly what cross-section of pipes you need. You will have to choose from several options. And all because the same effect can be achieved in different ways.
Let's explain
It is important for us to deliver the right amount of heat to the radiators and at the same time achieve uniform heating of the radiators. In systems with forced circulation we do this using pipes, coolant and a pump
In principle, all we need is to “drive” a certain amount of coolant over a certain period of time. There are two options: install pipes of a smaller diameter and supply coolant at a higher speed, or make a system of a larger cross-section, but with less traffic. Usually the first option is chosen. And that's why:
- the cost of products with a smaller diameter is lower;
- they are easier to work with;
- when laid open, they do not attract so much attention, and when laid in the floor or walls, smaller grooves are required;
- with a small diameter, there is less coolant in the system, which reduces its inertia and leads to fuel savings.
Since there is a certain set of diameters and a certain amount of heat that needs to be delivered through them, it is unreasonable to calculate the same thing every time. Therefore, special tables have been developed, according to which, depending on the required amount of heat, the speed of movement of the coolant and the temperature indicators of the system, the possible size is determined. That is, to determine the cross-section of pipes in the heating system, find the required table and select the appropriate cross-section from it.
The diameter of the heating pipes was calculated using the following formula (you can calculate it if you wish). Then the calculated values were recorded in a table.
Formula for calculating the diameter of a heating pipe
Where:
D - required pipeline diameter, mm ∆t° - temperature delta (difference between supply and return), °C Q - load on a given section of the system, kW - determined amount of heat required to heat the room V - coolant velocity, m/s - selected from a certain range.
In individual heating systems, the coolant movement speed can be from 0.2 m/s to 1.5 m/s. Based on operating experience, it is known that the optimal speed is in the range of 0.3 m/s - 0.7 m/s. If the coolant moves more slowly, air jams occur; if it moves faster, the noise level increases significantly. The optimal speed range is selected in the table. The tables are designed for different types of pipes: metal, polypropylene, metal-plastic, copper. The values are calculated for standard operating modes: high and medium temperatures. To make the selection process more clear, let’s look at specific examples.
The procedure for calculating the volume of the heating system
If your heating system consists of pipes with a diameter of 80-100 mm, as is often the case in an open-type heating system, then you should move on to the next point - pipe calculations. If your heating system uses standard radiators, then it makes more sense to start with them.
Calculation of coolant volume in heating radiators
In addition to the fact that heating radiators come in different types, they also have different heights. To determine the volume of coolant in heating radiators, it is convenient to first calculate the number of sections of the same size and type and multiply them by the internal volume of one section.
Table 1. Internal volume of 1 section of the heating radiator in liters, depending on the size and material of the radiator.
Apparently there is no more significant discovery in the production and use of pipes than the invention of polypropylene. This material made it possible to create polypropylene pipes for heating. The technical characteristics of polypropylene heating pipes exceed their metal counterparts, notable for their high strength and unprecedented durability.
Initially, several modifications of polypropylene were presented, of which three became widespread:
- propylene homopolymer, code PPH, is called "Type 1";
- polypropylene copolymers, code PPB, called "Type 2" or block copolymer;
- static polypropylene copolymer with ethylene inclusion, code PPRC, is called "Type 3" or random copolymer.
The importance and distribution of polypropylene shows the volume of its use in the world. Among all plastics, it ranks second, immediately following polyethylene. Makes up a quarter of the plastics market. It is used in virtually all areas where polyethylene is already used, and has also received its own niche.
Particular attention is paid to the use of the third type of PPR polypropylene for pipes. Their scope of application includes:
- formation of a water pipeline for the delivery of cold and hot water;
- pipelines for various chemical compounds, including aggressive ones;
- gas pipelines;
- irrigation and drainage systems in agriculture.
Polypropylene is resistant to corrosion better than its metal counterparts or even ceramic ones. The inner surface of products made from PPR polypropylene has less roughness, which creates less resistance to fluid flow. The material weighs significantly less than steel or ceramics. PPR polypropylene pipes for heating are many times lighter than their analogues, which simplifies transportation and installation. It is not necessary to involve a large number of workers to lay a water pipeline. Often two craftsmen are enough to complete work of any complexity.
How to choose the diameter of heating pipes
In the article we will consider systems with forced circulation. In them, the movement of the coolant is ensured by a constantly running circulation pump.
When choosing the diameter of heating pipes, it is assumed that their main task is to ensure the delivery of the required amount of heat to heating devices - radiators or registers. For the calculation you will need the following data:
- General heat loss of a house or apartment.
- The power of heating devices (radiators) in each room.
- Pipeline length.
Method of wiring the system (one-pipe, two-pipe, with forced or natural circulation).
That is, before you start calculating the diameters of the pipes, you first calculate the total heat loss, determine the power of the boiler and calculate the power of the radiators for each room.
You will also need to decide on the wiring method. Using these data, you draw up a diagram and then just start calculating.
What else do you need to pay attention to? The fact that the outer diameter of polypropylene and copper pipes is marked, and the inner diameter is calculated (subtract the wall thickness)
For steel and metal-plastic ones, the internal size is indicated when marking. So don't forget this little thing.
Calculator for calculating the total volume of the heating system - with a detailed description
Sometimes owners of houses or apartments in which autonomous water heating is installed have a need to accurately determine the total volume of the system. Most often this is due to the need to carry out certain preventive and routine maintenance, during which the system will have to be completely emptied and then filled with new coolant. When using ordinary water, this may not be so relevant (although it is advisable to properly prepare it for such a “mission”), but when you purchase a special coolant, which can be expensive, you cannot do without knowing the volume to plan the purchase.
Calculator for calculating the total volume of the heating system
Information about the volume of the heating system is also necessary for other needs. For example, this value is required for the correct selection of an expansion tank. Some calculations carried out when upgrading the system and replacing certain equipment may also require this value to be substituted into thermal formulas.
In a word, knowing this parameter will never be superfluous. And the calculator below for calculating the total volume of the heating system will help you decide.
During the calculation, ambiguities may arise; in this case, the necessary explanations are located below the calculator.
Calculator for calculating the total volume of the heating system
Explanations for calculations
So, if there is no way to measure the volume of the heating system experimentally (for example, by carefully filling it from the water supply, noting the readings of the water flow meter), then you will have to carry out mathematical calculations. They boil down to summing up the volumes of all devices and pipe circuits installed in the system. Some of the values should already be known, the rest can be calculated using geometric volume formulas.
- Boiler heat exchanger volume - this value is always included in the technical documentation of any model.
- Expansion tank volume. It should also be known to the owners. The fact that any tank should never be filled to the top is taken into account in the calculator program.
By the way, sometimes it is necessary to solve a slightly different problem - to find out the volume of the system without an expansion tank, precisely for its correct selection. In this case, the “expansion tank volume” slider must be set to “0”, and the resulting final value will become the starting point for choosing the optimal model.
How is an expansion tank calculated?
This is a mandatory element of the heating system, which must fully comply with its parameters. How to calculate the required volume of a membrane expansion tank - read in the publication devoted to the creation of a closed-type heating system.
- The next position is the volume of installed heat exchange devices. For collapsible batteries, you can specify the number of sections and their type - the volume of the most common radiators is already included in the calculation program. If radiators or convectors are non-separable, then their capacity is indicated according to the passport and, accordingly, the number of devices.
If heated floors are installed in the house, then the calculation will be made based on the total length of the circuits and the type of pipes used for this. The program database contains the necessary parameters for contours made of metal-plastic pipes and for unreinforced PEX - made of cross-linked polyethylene.
- A significant part of the total volume of the heating system always falls on circuits - supply and return pipes. It is characteristic that during installation, various types are often used, not only in terms of outer diameter, but also in terms of material of manufacture. And since different types may have significantly different internal diameters (due to different wall thicknesses with equal external diameters), this also affects the volumes.
The calculation algorithm takes this into account. You just need to measure the length of sections of each type of pipe in advance, and then indicate them in the corresponding data entry fields of the calculator. For example, the system uses VGP steel pipes. We note in the calculator that yes, they are available - and a group of sliders appears in which you only need to enter the length of the sections for each of their existing standard diameters.
How to calculate cross-sectional area
If the pipe is round, the cross-sectional area should be calculated using the formula for the area of a circle: S = π*R2. Where R is the radius (internal), π is 3.14. In total, you need to square the radius and multiply it by 3.14. For example, the cross-sectional area of a pipe with a diameter of 90 mm. We find the radius - 90 mm / 2 = 45 mm. In centimeters this is 4.5 cm. We square it: 4.5 * 4.5 = 2.025 cm2, substitute it into the formula S = 2 * 20.25 cm2 = 40.5 cm2.
The cross-sectional area of a profiled product is calculated using the formula for the area of a rectangle: S = a * b, where a and b are the lengths of the sides of the rectangle. If we consider the cross-section of the profile to be 40 x 50 mm, we get S = 40 mm * 50 mm = 2000 mm2 or 20 cm2 or 0.002 m2.
What else to look for when choosing polypropylene pipes for heating
Above we looked at different types of polypropylene pipes that can be used for heating installation, their advantages and disadvantages. Based on this information, we can conclude that if price is not a decisive factor for you, then it is better to choose reinforced varieties. Moreover, it is better to choose products reinforced with foil if they are made by a well-known, trusted manufacturer. Otherwise, it is better to opt for polypropylene pipes reinforced with a layer of fiberglass. Moreover, there are fewer problems with them when soldering.
In addition to choosing a type, there are also criteria such as:
- operating pressure;
- maximum operating temperature;
- diameter;
- manufacturer.
Pressure
The operating pressure must be indicated on the label. As a rule, this is the number after the letters PN (PN20, PN25) and it indicates what maximum long-term operating pressure (in atmospheres or bar) the pipe can withstand at a coolant temperature of 20˚C. It must be remembered that as the temperature of the coolant increases, this indicator decreases. So, for example, for a pipe with the designation PN20 at a temperature of 90˚C it is no more than 6.5 atm (bar, kgf/cm2). Although for most heating systems this is quite enough. For example, in autonomous systems, it rarely exceeds 1.5 atm.
Temperature
The maximum operating temperature must also be indicated on the pipe markings. Since they will be used for heating, its value should be at least 90˚C. Most manufacturers usually indicate the maximum temperature value in numbers. But the designation “hot&cold” may also occur, which means that the pipes can be used for hot water.
Diameter
The minimum diameter of polypropylene pipes for heating is 20-26 mm, and the maximum is 32-40 mm and depends on the type of boiler, type of circulation, length of lines and other factors. In order to know what diameter and how many pipes to buy, you must first calculate the heating system. For different systems, the diameters of the pipes and their number will be different. It is best if such a calculation is made by an experienced specialist. It should be remembered that when calculating, we obtain the minimum internal diameter, and on the marking of polypropylene pipes, as a rule, the outer diameter is indicated.
Manufacturer
Currently, quite a few manufacturers, both domestic and foreign, are engaged in the production of polypropylene pipes. The more reliable the manufacturer, the higher the price of its products. Although you can find decent options among inexpensive products.
Let us give an example of manufacturers whose product quality has been tested by time.
Among the European brands one can name German Rehau, Banninger, Akwatherm, Wefatherm and Czech FV-Plast, Ekoplastik. Their products are high quality, but they are also the most expensive on the market.
If the prices of these manufacturers are not suitable for you, you can pay attention to the products of Turkish manufacturers such as Vesbo, Firat, TEBO, Pilsa, Kalde and Jakko. Their products are cheaper and the quality is decent.
Pipes from Chinese manufacturers Blue Ocean and Dizayn have proven themselves to be of good quality at a low price.
Domestic ones include Polytek, RVK, PRO AQUA, Heisskraft or Santrade.
Selection of metal-plastic products
To make the right choice when purchasing metal-plastic pipes, you need to understand the purposes for which they are needed. Then, based on the purpose, product parameters are selected. These include:
- wall thickness;
- internal permeability and external radius;
- the weight of the pipe in accordance with the weight of the entire water supply system;
- minimum and maximum heating rates;
- maximum bending radius;
- life time.
All parameters are standardized; if there are deviations from the norm, they are small. Wall thickness is important. The installation of the pipeline depends on it. The fitting and shut-off valves are selected taking into account the thickness, especially when replacing old metal pipes with new, metal-plastic ones.
When choosing, it is worth considering the method of connecting the foil layer in the structure. It is indicated on the product labeling. More durable and resistant pipes are made using seamless butt welding. The thickness of the layer should not exceed the standard of 0.3-0.6 mm. The outer and inner shell material is cross-linked or heat-resistant polyethylene such as PERT or PEX. If the product is made from other raw materials, this will affect the further operation of the system. Upon visual inspection, the pipes should be intact. Cracks and delaminations are not acceptable.
High-quality products are certified and comply with international and domestic standards, so when purchasing, you need to find out whether the product has a certificate from the Scientific Research Institute of Plumbing.
It is better to purchase metal-plastic pipes from a reputable manufacturer. Different countries are engaged in the production of polyethylene products, among them Russia, Italy and Germany stand out. You can pay attention to pipes of the domestic brand “Nanoplast”, the Italian company Valtec or the German company Oventrop. The products are made of the highest quality material, the foil is made of pure aluminum.
To make the right choice, the buyer needs to familiarize himself with the markings that are applied with indelible paint to the pipe in accordance with accepted international rules. It may differ from one manufacturer to another, but most often it has a general appearance. The markings indicate:
- Manufacturer.
- Pipe name or certificate of conformity.
- Material type.
- Stitching method.
- Standard size ratio.
- Nominal sizes.
- Nominal pressure.
- Production standards (date of manufacture, batch number).
If questions arise when choosing pipes, you can contact a consultant for help in specialized stores.
Pressure classification
Markings used for polypropylene structures often contain the designation N25, N10, etc. Based on this indicator, it is possible to determine the ability of the material to withstand the pressure of the liquid that circulates along the line.
All polypropylene pipe products offered on the market can be classified into the following types:
РN10
The main performance characteristics of these products are a pressure on the wall of 1 MPa, as well as a thickness of the order of 1.9–10 mm. On their basis, heated floors are often installed, as well as cold water supply systems at an operating temperature not exceeding 45 degrees. The following can be said about the geometry of these structures: the outer diameter is 20–110 mm, the inner diameter is 16–90 mm.
PN16
Products of this type often find application in major areas. The working pressure for it is 1.6 MPa. These products can be used in the installation of cold and hot water supply systems, for which the heating limit of the coolant is not 60 degrees.
PN20
During operation, polypropylene structures of this category can withstand a pressure on the wall of 2 MPa, the wall thickness is 16–18.4 mm. Most often, hot and cold water supply systems are created based on this material, in which the temperature of the transported liquid does not exceed 80 degrees. Products are manufactured with an outer diameter of 16–110 mm and an inner diameter of 10.6–73.2 mm.
РN25
These polypropylene products are designed for a pressure of 2.5 MPa and are distinguished by the presence of a reinforcing layer based on aluminum foil. Most often they are used in the construction of heating systems, as well as the installation of hot water supply systems, which are used to deliver liquids with temperatures up to + 95 degrees. A special feature of these structures is their multilayer structure, which allows them to withstand thermal and impact loads well. Finished products have a diameter of 13.2–50 mm, the outer diameter is 21.2–77.9 mm.
Materials market
All existing pipeline systems can be divided into two large groups:
Metal
- "Black metal
- Stainless steel
- Copper, brass, bronze
Galvanized steel is used much less frequently; in isolated cases, titanium, aluminum, and other non-ferrous metals and alloys are used.
Polymer
- Polypropylene
- Polyethylene
- Metal-plastic
- PVC
Moreover, in the group of polymers, the structure is actually much more complex than this simple classification. Indeed, in addition to the fact that each material itself has several modifications, it can also have several layers.
For metal-plastic pipes for heating, this is clear from its name, but here everything is not so simple. This is a three-layer material made of aluminum foil located between two layers of polymer.
The material itself is either cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) or polypropylene (PP), but in each of these cases there are still several varieties, depending on the method of manufacturing the plastic and its class.
Metal-plastic pipes based on polyethylene
The procedure for calculating the cross-section of heat supply lines
Before calculating the diameter of the heating pipe, it is necessary to determine their basic geometric parameters. To do this, you need to know the main characteristics of highways. These include not only performance qualities, but also dimensions.
Each manufacturer indicates the value of the pipe cross-section - diameter. But in fact it depends on the wall thickness and material of manufacture. Before purchasing a specific model of pipelines, you need to know the following features of the designation of geometric dimensions:
- Calculation of the diameter of polypropylene pipes for heating is done taking into account the fact that manufacturers indicate external overall dimensions. To calculate the useful cross-section, it is necessary to subtract two wall thicknesses;
- Internal dimensions are given for steel and copper pipelines.
Knowing these features, you can calculate the diameter of the heating collector, pipes and other components for installation.
When choosing polymer heating pipes, it is necessary to clarify the presence of a reinforcing layer in the structure. Without it, when exposed to hot water, the line will not have the proper rigidity.
Determination of system thermal power
How to choose the correct diameter of heating pipes and should this be done without calculated data? For a small heating system you can do without complex calculations
It is only important to know the following rules:
- The optimal diameter of pipes with natural heating circulation should be from 30 to 40 mm;
- For a closed system with forced movement of coolant, pipes of a smaller cross-section should be used to create optimal pressure and water flow rate.
For accurate calculations, it is recommended to use a program for calculating the diameter of heating pipes. If they are not there, you can use approximate calculations. First you need to find the thermal power of the system. To do this you need to use the following formula:
Where Q is the calculated thermal heating power, kW/h, V is the volume of the room (house), m³, Δt is the difference between the temperatures outside and indoors, °C, K is the calculated heat loss coefficient of the house, 860 is the value for converting the obtained values into an acceptable kW/h format.
The greatest difficulty in preliminary calculation of the diameter of plastic pipes for heating is caused by the correction factor K. It depends on the thermal insulation of the house. It is best taken from the table data.
The degree of thermal insulation of the building
High-quality insulation of the house, modern windows and doors installed
As an example of calculating the diameters of polypropylene pipes for heating, you can calculate the required thermal power of a room with a total volume of 47 m³. In this case, the temperature outside will be -23°C, and indoors - +20°C. Accordingly, the difference Δt will be 43°C. Let's take the correction factor equal to 1.1. Then the required thermal power will be.
The next stage in choosing the diameter of the heating pipe is determining the optimal speed of movement of the coolant.
The presented calculations do not take into account the correction for the roughness of the internal surface of the highways.
Water speed in pipes
Table for calculating the diameter of the heating pipe
Optimal coolant pressure in the lines is necessary for uniform distribution of thermal energy across radiators and radiators. To correctly select the diameters of heating pipes, you should take the optimal values for the speed of water movement in the pipelines.
It is worth remembering that if the intensity of coolant movement in the system is exceeded, extraneous noise may occur. Therefore, this value should be between 0.36 and 0.7 m/s. If the parameter is smaller, additional heat losses will inevitably occur. If it is exceeded, noise will appear in pipelines and radiators.
To final calculate the diameter of the heating pipe, you should use the data from the table below.
By substituting the previously obtained values into the formula for calculating the diameter of the heating pipe, you can determine that the optimal pipe diameter for a particular room will be 12 mm. This is just an approximate calculation. In practice, experts recommend adding 10-15% to the obtained values. This is because the formula for calculating the diameter of the heating pipe may change due to the addition of new components to the system. For an accurate calculation, you will need a special program for calculating the diameter of heating pipes. Such software packages can be downloaded in demo versions with limited calculation capabilities.
How many liters of water are in 1 meter of 125 pipe?
Internal volume of a linear meter of pipe in liters - table. Weight of water in the pipeline.
| Inner diameter, mm | Internal volume 1 m of pipe, liters = mass of water in 1 m, kg | Internal volume 10 m of pipe, liters = mass of water in 10 m, kg |
| 115 | 10,3869 | 103,8689 |
| 120 | 11,3097 | 113,0973 |
| 125 | 12,2718 | 122,7185 |
| 130 | 13,2732 | 132,7323 |
Water flow through the pipe at the required pressure
The main task of calculating the volume of water consumption in a pipe according to its cross-section (diameter) is to select pipes so that the water consumption is not too high and the pressure remains good. In this case, it is necessary to take into account:
- diameters (DN internal section),
- pressure loss in the calculated area,
- speed of hydraulic flow,
- maximum pressure,
- the influence of turns and shutters in the system,
- material (characteristics of pipeline walls) and length, etc.
Selecting the pipe diameter based on water flow using a table is considered a simpler, but less accurate method than measuring and calculating pressure, water speed and other parameters in the pipeline, made locally.
Tabular standard data and average indicators for main parameters
To determine the estimated maximum water flow through a pipe, a table is provided for the 9 most common diameters at various pressures.
The average pressure value in most risers is in the range of 1.5-2.5 atmospheres. The existing dependence on the number of floors (especially noticeable in high-rise buildings) is regulated by dividing the water supply system into several segments. Water injection using pumps also affects the change in the speed of hydraulic flow. In addition, when referring to the tables, when calculating water consumption, not only the number of taps is taken into account, but also the number of water heaters, bathtubs and other sources.
Changes in the characteristics of the faucet's permeability with the help of water flow regulators, savers similar to WaterSave (https://water-save.com/), are not recorded in the tables and, as a rule, are not taken into account when calculating the water flow on (through) the pipe.
Methods for calculating dependencies between water flow and pipeline diameter
Using the formulas below, you can both calculate the water flow in the pipe and determine the dependence of the pipe diameter on the water flow.
In this water consumption formula:
- under q the flow rate in l/s is taken,
- V – determines the speed of hydraulic flow in m/s,
- d – internal section (diameter in cm).
Knowing the water flow and d cross-section, you can use reverse calculations to set the speed, or, knowing the flow and speed, determine the diameter. If there is an additional supercharger (for example, in high-rise buildings), the pressure it creates and the speed of the hydraulic flow are indicated in the device passport. Without additional injection, the flow speed most often varies in the range of 0.8-1.5 m/sec.
For more accurate calculations, head losses are taken into account using the Darcy formula:
To calculate, you must additionally install:
- pipeline length (L),
- loss coefficient, which depends on the roughness of the pipeline walls, turbulence, curvature and sections with shut-off valves (λ),
- fluid viscosity (ρ).
The relationship between the value D of the pipeline, the speed of the hydraulic flow (V) and the water consumption (q) taking into account the slope angle (i) can be expressed in a table where two known quantities are connected by a straight line, and the value of the desired quantity will be visible at the intersection of the scale and the straight line.
For technical justification, graphs of the dependence of operating and capital costs are also drawn to determine the optimal value of D, which is set at the intersection point of the operating and capital cost curves.
Calculation of water flow through a pipe taking into account the pressure drop can be carried out using online calculators (for example: https://allcalc.ru/node/498; https://www.calc.ru/gidravlicheskiy-raschet-truboprovoda.html). For hydraulic calculation, as in the formula, you need to take into account the loss coefficient, which involves choosing:
method for calculating the resistance, material and type of pipeline systems (steel, cast iron, asbestos cement, reinforced concrete, plastic), where it is taken into account that, for example, plastic surfaces are less rough than steel and are not subject to corrosion, internal diameters, section lengths, drops pressure per meter of pipeline.
Some calculators take into account additional characteristics of piping systems, for example:
- new or not new with or without bitumen coating,
- with an external plastic or polymer-cement coating,
- with an external cement-sand coating applied using different methods, etc.
Selection of metal-plastic products
When choosing, you should consider the following parameters of metal-plastic pipes:
- Wall thickness;
- Internal patency and external section;
- Weight, since in some cases it is important to know the weight of the heating system, etc.;
- Thermal conductivity indicators;
- Maximum and minimum temperature indicators;
- Allowable bending radius;
- Life time.
As a rule, all parameters given in the table are standard, slight deviations are possible. It depends on the manufacturer.
Obtaining the result using the experimental method
In practice, problematic situations arise when the hydraulic system has a complex structure or some of its fragments are laid in a secret way. In this case, it becomes impossible to determine the geometry of its parts and calculate the total volume. Then the only way out is to conduct an experiment.
Using a collector and laying pipes under a screed is an advanced method of secretly supplying hot water to heating radiators. It is impossible to accurately calculate the length of communications in the absence of a plan.
It is necessary to drain all the liquid, take some kind of measuring container (for example, a bucket) and fill the system to the desired level. Filling occurs through the highest point: an open-type expansion tank or an upper drain valve. At the same time, all other valves must be open to avoid the formation of air locks.
If the water movement along the circuit is carried out by a pump, then you need to let it run for an hour or two without heating the coolant. This will help expel any remaining air pockets. After this, you need to add liquid to the circuit again.
This method can also be used for individual parts of the heating circuit, for example, a heated floor. To do this, you need to disconnect it from the system and “spill” it in the same way.
Instrumental question
If you install the system yourself, the necessary tool can play an important role in the question of which heating pipe to choose. After all, almost every type of pipe requires specific equipment for installation, which is quite expensive.
Moreover, even if there are press fittings from any manufacturer, it is not a fact that a crimping machine from another company will allow them to be pressed properly. The same applies to soldering machines for polyethylene. This means that it may not be possible to rent equipment.
Soldering the same copper pipes requires very specific skills and a clear knowledge of the technology of work, so experts do not recommend undertaking this operation without the appropriate qualifications.
Soldering iron for polyethylene pipes
There are also some nuances in welding polyethylene. All these points should also be considered and taken into account before finally choosing heating pipes. In this sense, the most democratic system is the connection on split rings, also called “O-ring”.