This technology is mainly found in installations in country houses, where there are more possibilities. In rare cases, such a system is used in commercial real estate and almost never in ordinary apartment buildings.
Often this system is the main source of heating in a house where the climate is not too harsh. In severe frosts, it is necessary to install auxiliary heating systems.
Features of the material
Pipelines for heated floors are made from various raw materials: copper, metal-plastic, but the most modern type is considered to be a cross-linked polyethylene pipe.
Cross-linked polyethylene is a type of ethylene obtained by chemical and physical exposure to it. During production, a three-dimensional cellular network is formed from ethylene molecules. This model is called PEX.
Strength
The strength of this product is given by the transverse connections formed during the production process, in addition to the longitudinal ones. The expansion rate of PEX tubing ranges from 250 to 800%.
In addition, unlike polypropylene, the material has increased durability and does not collapse even with significant temperature changes.
Temperature resistance
When using cross-linked polyethylene hoses, a maximum temperature of 140 degrees is recommended. But melting processes begin when heated from +190 degrees.
The subzero temperatures that this pipeline can withstand, and at which the strength and elasticity of the product are maintained, are -50 degrees Celsius.
For your information! Cross-linked polyethylene has increased resistance to short-term temperature extremes.
Therefore, it is recommended to use it in a low-temperature heating system, where heating is not significant and frequent temperature changes occur. But polyethylene should be used where the pipeline is constantly hot.
Physical properties
Despite the high density of PEX tubes, the material is soft and elastic, and has the following properties:
- liquid and gases do not pass through it;
- It bends easily, allowing you to make the tightest turns.
Chemical properties
An improved production process - cross-linking - has made polyethylene more resistant to organic and inorganic influences, and it is also not subject to the destructive effects of solvents.
In addition, the material is resistant to the negative effects of the environment: sunlight and oxygen. This quality is due to the presence of a protective anti-diffusion coating on most models.
Other characteristics
Polyethylene contours have a diameter from 10 to 200 mm. For water heated floors, the recommended size is 16 mm.
Main technical characteristics:
- wall thickness - 2 mm;
- meter weight - 110 g;
- meter volume - 0.113 l;
- density - 940 sq. m3;
- degree of thermal conductivity - 0.39 W/mK.
Types of mats
A total of four types of mats are produced for installation under water-heated floors. All of them have individual characteristics and are designed for installation in specific conditions. Expanded polystyrene mats include:
- Roll backing;
- Expanded polystyrene boards;
- Polystyrene with foil;
- Expanded polystyrene mats with bosses.
The choice of insulating mat depends on the characteristics of the room and the load that will need to be withstood. Please note that the slabs have different thicknesses.
Rolled backing
All experts agree that roll backing can be called an insulating material at a stretch. The reason for this is its small thickness from 2 to 10 mm. Therefore, the scope of use of this material is quite limited.
This type of insulation is used only in cases where it is installed as an auxiliary material or if the heated floor is used extremely rarely.
It is strictly not recommended to install roll insulation over basements or other unheated areas. Their effectiveness in this case will be zero.
The roll backing is not very convenient during installation. To install it, you will need special tape, and when installing underfloor heating pipes, they must be additionally secured to the floor.
In the only justified case, it is worth using a rolled underlay for a heated floor - this is when the architectural features of the room do not allow raising the floor level.
In general, this type of insulation is used extremely rarely under heated floors and is not recommended by most experts due to its low efficiency.
Expanded polystyrene boards
Expanded polystyrene boards, which can be divided into two types, are well suited for insulating heated floors. A cheaper option is regular foam. If you choose this option, you should remember that the density of the insulation should not be less than 35 kg/m3. Such requirements must be met to ensure that the substrate will not bend or burst under the weight of the structure.
More durable, but also more expensive insulation is extruded polystyrene boards. This material has a cellular structure, can withstand loads well, and has good strength.
To obtain an even greater thermal insulation effect, a roll backing can be mounted on top of the slabs.
Each plate has special locks that facilitate the installation of insulation. If you buy insulation with markings already made, it will make it easier to lay pipes on the insulation.
Expanded polystyrene with foil
These insulating mats for heated floors are also made from polystyrene foam. They come in two types:
- Panels connected to each other by continuous foil film. During installation, such insulation is laid out over the surface;
- separate mats with special locks on the sides. When laying the slabs, they are connected to each other using grooves on the locks.
A coordinate grid is applied to such panels, allowing you to quickly navigate when laying a pipe or heating cable.
To attach the heated floor, staples or reinforcement mesh are used.
Expanded polystyrene mats with bosses
This type of insulation was specially invented for installation under heated floors. The texture is the same as polystyrene foam in slabs that have special convexities on one side, called “bobs.”
The protrusions, depending on the manufacturer, can vary greatly in shape and are located one from the other at a certain distance. This design is intended to fix the water pipe on the surface of the insulation and does not require additional fastening.
The height of the boss is 20-25 mm, which allows you to easily attach a 20 mm pipe, which is typical when laying a water-heated floor. The height of the entire slab can be 40 - 50 mm.
The slabs have connections with locks that ensure good tightness of the insulation, so any type of screed can be laid on it. Another advantage of this type of mat for heated floors is sound insulation. They allow you to reduce noise levels by up to 25 dB.
Advantages and disadvantages of cross-linked polyethylene
Pipeline made of cross-linked polyethylene, like any other type, has its pros and cons.
Advantages:
- Elasticity - this allows it to be used when laying circuits with a large bend, without fear of the product creasing.
- Environmentally friendly - it does not contain harmful components, so when heated, substances hazardous to human health are not released.
- The combustion temperature is high - the complete melting process begins at +400 degrees. But even when decomposed, all components are non-toxic.
- Performance indicators - the device does not rot, is not susceptible to corrosion and is not exposed to chemicals. All this guarantees a long service life of water heated floors made from this material.
- Frost resistance - no deformation occurs at high sub-zero temperatures.
- It has sound-absorbing properties - the floor with a heating element made of cross-linked polyethylene operates silently.
- It has the property of “shape memory” - it is able to restore its original appearance.
- Has a reasonable price.
One cannot help but mention the minor disadvantages that cross-linked polyethylene pipes have. First of all, this concerns some difficulties during installation.
Pipe bends require reliable fixation. In addition, when laying them in a heated floor structure, you need to be extremely careful so as not to damage the protective coating.
Another disadvantage is the negative impact of direct ultraviolet rays, under which the material becomes fragile.
Methods for obtaining PEx
Polyethylene for pipes intended for liquid underfloor heating lines is produced using the peroxide method. The raw materials are heated to 200 0C, hydrogen peroxide is added to the mixture. The reaction results in uniform cross-linking; more than 85% of the polymer molecules bind. The production process takes a long time. The products are expensive, but have good characteristics. Designates the material PEX-a.
The silane method of producing PEX reduces the cost of products. Instead of hydrogen peroxide, silane, water and a catalyst are added to the mixture. Cross-linking of molecules up to 65%. Designated polyethylene PEX-v. It is harder, less elastic, and releases silane when heated strongly. It is not used for the heating system.
Cross-linking is carried out using the radiation method. The raw materials are driven through an electron accelerator. As a result of the reaction, homogeneous atoms form new bonds. Crosslinking is 60%. The material is designated PEX-s. The products are used for cold water pipes.
Construction of polyethylene pipe
Polyethylene contour is a structure of several layers with a reinforcing layer. Reinforcement increases the strength of the product, reduces the degree of expansion and softens pressure surges inside.
The reinforcing gasket can be polypropylene, fiberglass, aluminum foil or sheets. When connecting several pipes, it is necessary to strip this layer by 1 cm.
It is important to know! It is worth noting that for underfloor heating structures, a contour without reinforcement is more often used.
In addition, cross-linked polyethylene has an “oxygen barrier” - anti-diffusion protection. This layer is present in all PEX products. If it is not there, then oxygen penetrates deeper, which leads, albeit slowly, to destruction of the product.
There are several types of cross-linked polyethylene that are used in the manufacture of pipes for heated floors:
- PEX - hydrogen peroxide is used in its production. Peroxide cross-linking adds strength and elasticity. Such pipes have the best molecular memory.
- PEX-b - silane is used to stitch polyethylene, it holds up to 80% of the molecules together. Contours are equal in strength to the PEX type, but are less elastic and hold their shape less well.
- PEX-c - cross-linking is carried out under the influence of radioactive radiation. Pipes are less flexible, as a result of which kinks may form during installation. Eliminated using a coupling.
- PEX-d - nitrogen is used for cross-linking, but the technology is complex and rarely used.
How to understand the marking of polypropylene pipes?
To avoid errors during installation, the assembler of heated floors must be guided by the existing markings of polypropylene pipes
This is especially important for the owner who assembles the circuit with his own hands
Typical marking of polypropylene pipe:
- PN10 – index of polymers with a homogeneous structure. Consumables are used in water supply systems up to 20 degrees Celsius at 10 atmospheres. PN10 pipes have a diameter from 20 to 110 mm;
- PN16 is an index of homogeneous polymers suitable for installation of water floor heating. The coolant should not warm up above 80 degrees Celsius at 10 atmospheres of operating pressure. The diameters of PN16 are similar to PN10, but have thicker walls;
- PN20 - homogeneous pipes for coolant with operating modes at 95 degrees Celsius and 6 atmospheres of pressure. Pipe diameters PN20 from 20 to 110 mm;
- PN20 GF or PN20 AL – polypropylene pipes with fiberglass or aluminum reinforcement. All other characteristics are similar to PN20, but have lower thermal expansion parameters.
Types of fittings for joining cross-linked polyethylene
Today, to sew polyethylene pipes together, the following types of fittings are used.
Pipes and fittings for heating and water supply systems // FORUMHOUSE
Compression
Compression, also called crimp, is a detachable connection method. Fitting - a nut, a split ring and a fitting, most often the elements are made of brass.
Press fittings
With this type of fitting, a non-detachable connection is formed; it is strong and durable. Recommended for use in a structure with a screed, in a system with a high level of pressure and high temperature.
The press fitting includes a body, a ferrule and a sleeve.
Axial
An axial fitting is a device that has a fitting and a sleeve. It is installed using expansion and tension tools.
Causes of malfunction and repair of water heated floors
Correct installation of a water floor guarantees its service for a very long time (up to 50 years) provided that high-quality solid pipes are used.
Methods for laying underfloor heating pipes
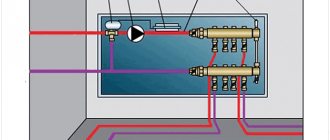
In terms of configuration and principle of operation, a water heated floor is quite complex and its performance depends on the high-quality functioning of several important components. The water floor consists of the following elements:
- Pipes with water circulating through them, which is the coolant.
- Bypass.
- Circulation pump.
- Collector and electric drive, with the help of which the water flow is regulated.
- A balancing valve that mixes heated and cooled water.
- Thermostat and thermostat responsible for maintaining the required temperature. If they break down, not only cooling, but also overheating of the coolant is possible.
Basic elements of a warm water floor
As in the case of an electric floor, when identifying the causes of insufficient heating, poor-quality thermal insulation work is allowed, as a result of which significant heat loss is observed. The situation can be corrected only by completely reworking the system from scratch. The reason for poor heat transfer is also incorrect calculation and selection of the characteristics of the main components of the system. A weak boiler can cause a lack of energy to heat the coolant.
Pipeline damage
The cause of a breakthrough and leakage of a water floor is often a sharp drop in pressure inside the pipe. The amount of water in the pipes decreases, and the water that flows out begins to destroy the screed and leak to the lower floor.
To identify a possible leak, first carry out a visual inspection of the floor covering, where wet spots can be found at the joints of the lamellas or directly on the surface. If the presence of moisture cannot be determined by the naked eye or by touch, then use a thermal imager.
If the location of a damaged pipe fragment is discovered, local repairs are carried out by partially dismantling the floor covering and dismantling the screed. Before replacing the pipe, the water from the circuit is drained, and after restarting, the system must be deaerated.
Table 2. Repair for damaged pipes
| Illustration | Description |
| To remove tiles if damage to the pipeline occurred in the bathroom, the first step is to free the grout from the seams. | |
| The tiles are being dismantled. | |
| To remove the screed, use a hammer drill. | |
| To repair such damage to pipes, a press coupling is used. | |
| At the site of pipe damage, a cut is made using a hacksaw. | |
| The pipe is cleaned of contaminants. | |
| Using a reamer, align the holes on both sides. | |
| A coupling is put on both pipe fragments. | |
| The coupling is crimped with pliers. |
Before pouring cement, the repaired area is checked for leaks. To protect the coupling from the acidic environment of the solution, it is wrapped with a piece of foamed polyethylene.
Uneven heating
If the heated floor heats up poorly, the cause may be uneven distribution of water in the pipes. This is due to the different lengths of the circuits - in longer ones, at the same water supply rate, the coolant cools faster. In this case, it will be necessary to adjust the water supply to each circuit on the manifold, and adjust the levels of electric drives on the supply valves.
Warm water floor collector
To understand the results of the changes made to the system, you will need to wait some time. The heating time of a heated floor depends on many nuances: the number and type of layers of the floor structure, the temperature of the coolant and its flow rate, the power of the heater, the type of finishing coating, and weather conditions.
Electrical faults
If there is no leakage, the cause should be sought in the malfunction of system elements operating from the electrical network.
The circulation pump or thermostat, located in the manifold mixing unit, may fail. The presence of voltage in them is checked using a multimeter or an indicator screwdriver. The fact that the pump is not working will be indicated by any difference in sounds when it is turned on.
Heated floor collector elements
Each thermostat terminal will need to be checked for voltage. It is also worth checking the temperature sensor.
Prices for heated floors Caleo
warm floor caleo
If the cause of the breakdown of the heated floor could not be discovered on your own, then it is better to contact specialists who have the necessary tools, skills and experience in eliminating such problems.
Installation of heated floors with cross-linked polyethylene pipelines
Technologically, the installation process for the construction of heated floors from cross-linked polyethylene contours is a step-by-step work of laying layers of the structure. The total thickness of the structure is about 15 cm.
Warm floor made of cross-linked polyethylene
Preparatory work
Before you begin installing the system, you should carry out preparatory steps. First you need to decide on the model of pipes and components.
To install a heated structure you will need:
- polyethylene pipeline;
- expansion tank;
- boiler for heating water;
- circulation pump;
- sanitary fittings;
- fastening elements;
- manifold, ideally with a hydraulic arrow;
- damper tape;
- insulation material and fittings;
- screed solution.
When choosing a collector unit, it is recommended to give preference to a device with balancing valves and flow meters, this will simplify the process of adjusting the system.
All necessary components should be prepared before installation, so as not to be distracted during the work.
Layout diagram of the heating element
There are several basic schemes that are used when laying underfloor heating pipelines: “snake”, “snail” and “double helix”:
- “Snail” is the most common design; it is easy to install and ensures uniform heating of the entire room, since all angles are 90 degrees.
- “Snake” - the installation process is more complicated, since the turns reach 180 degrees. According to this scheme, it is good to lay pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene, because they bend easily.
The choice of installation scheme for water floor heating should take into account the characteristics of the room. If the area is large, then a “double snail” or “spiral” is recommended. Also, this model should be used if you want to project the zoning of areas according to the degree of heating.
With a standard “snake” or “snail”, the maximum length of the highway is 60 - 80 meters. In rooms with a significant excess of length over the width of the room, it is allowed to increase the size of the circuit to 120 meters, but the diameter of the pipes must be larger.
An important point when laying pipes is the step of their placement. Usually it is 10 - 35 cm, the smaller it is, the more heat the floor will give off. In some areas where the degree of heat loss is high (near the door and window), the step should be minimized, but in the center of the room it can be increased. Installation of pipes from the walls is carried out at a distance of at least 30 cm.
For your information! It is also recommended to place the collector in the center of the apartment or house, this will allow all rooms to be heated evenly.
Calculation of the number of pipes
Before purchasing cross-linked polyethylene pipes for heated floors, you need to calculate the required size and diameter of the product. According to current practice, contours with a diameter of 16 mm and a wall thickness of 2 mm are considered a suitable option. For a large area, a size of 20 - 25 mm is recommended.
To calculate the amount of product for heating a room, you can use the formula:
D=S / M x k, where:
- D—design pipe size;
- S is the size of the room area;
- M - laying step;
- k is the safety factor, if the area is 30 m2 - 1.1, larger - 1.4.
The maximum length of the pipeline is affected by the diameter of the circuit. With a diameter of 16 mm - 90 m, 20 - 120, 25 - 150 meters.
Preparing the base for pipes
The actual work on installing the heated floor “pie” should begin with the preparation of the rough base. The process consists of:
- dismantling the old finishing coating and screed, cleaning and leveling the base;
- laying waterproofing material - polyethylene film;
For your information! If you have the means, it is better to use a polymer membrane; it will allow the floor to “breathe”.
- thermal insulation of the base - extruded polystyrene foam tiles or cork are used;
- placing a reinforcing grid - there is no need for it if polystyrene foam is used as thermal insulation;
- installation of a damper tape - it is necessary to compensate for the thermal expansion of the screed.
Then, the boiler and manifold are installed at the planned location. The device must be connected to water supply and power supply.
Installation of polyethylene pipes
Polyethylene pipes are laid according to the diagram on polystyrene foam sheets or a reinforcing grid. If the room is large, then the area is divided into several circuits.
To simplify the installation process, it is recommended to make markings on the slabs. You should start from the collector, the second end should also return to it.
Important! Before starting installation, you should consider the method of connecting and fixing the pipes.
It is recommended that the contour be solid (seamless). But if necessary, the tubes are connected to each other, or to the manifold, by welding, or by crimping and pressing fittings.
Sewing the outline using press fittings is a reliable and uncomplicated method. A coupling is put on the hose, then the diameter of the pipe inside is increased to the desired size using an expander. The fitting is screwed in well and the sleeve is put on it.
Fixing pipes to fittings or polystyrene foam boards is done in several ways:
- polyethylene clamps;
- steel wire;
- fixing tracks.
Using clamps is the simplest and most cost-effective option. Only 2 pieces per 1 meter are required. In a straight line, they are mounted every 50 cm, at a turn - 20 cm.
Basic rules for installing a cross-linked polyethylene pipeline:
- when turning, do not make sharp bends;
- installation work should be carried out at a temperature of at least +18;
- if the pipes were in the cold, they should lie in a warm room before laying;
- the turning radius of a pipeline with a diameter of 16 mm should not exceed 12 cm;
- cut off the excess length of the circuit only before connecting;
- It is prohibited to place heavy objects or step on pipes during installation;
- The contour should be positioned evenly, without twisting.
Water connection and pressure testing
Before pouring the screed, you should check the system for operation and for defects in the line.
Connecting the floor consists of connecting the supply and return hoses to the manifold. After which, it is necessary to open the control and air valves. Then turn on the circulation pump and compressor with a pressure of 5 - 6 bar.
With their help, water is supplied to the main line for 12 hours. In this case, the pressure should exceed the working pressure by 1.5 times. If the clamps were shot off during the process, they are placed again, but 5 cm lower.
After this time, all valves are closed except one, the pressure is set to the operating level, and each branch is adjusted in turn.
Preparatory work for laying pipes
It’s worth figuring out how to lay pipes for a warm water floor. At the initial stage, you will need to perform the operations described below.
First of all, you need to get rid of the existing concrete screed. If there are any differences within 7-10 mm, you will need to level the surface.
Next, waterproofing material is laid on the prepared base. This is necessary to prevent moisture from seeping into the system, which often causes pipes to rust or bacteria to begin to multiply in them.
Moisture-repellent material can serve as:
- Polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride film with a heat-repellent layer. The joining of the panels is carried out by soldering or using a special adhesive tape. The finished coating should have a uniform shape.
- Cement-polymer screed.
- Cast screed.
It is better if the moisture-repellent layer when laying heated floor pipes with your own hands is in the form of a screed. The finished coating will be as durable as possible compared to a simple film. Heating pipes laid in the floor under the screed will last for many years.
Now you need to lay a damper tape around the perimeter of the room, which will serve as a compensator for expansion due to heating. If you plan to install several circuits in a room, then the tape will need to be laid between all circuits.
Filling the screed
Only after checking the device can you proceed to laying the next layer of the structure. There are two options - concrete screed and dry floor.
Concrete screed
For screeding, a mortar, either purchased or made independently from M300 cement, is suitable. The minimum layer of concrete that can protect polyethylene pipes is 3 cm, and the maximum is 7 cm.
Most often, the screed is installed without thermal joints; they are necessary:
- if the room area is more than 33 m2;
- if the length of the room exceeds 10 m;
- with a complex layout.
It is possible to pour reinforcing screed, that is, using reinforcing mesh, this gives strength to the structure.
The screed is poured at a time, the process should begin from the front corner of the room and end at the door. After leveling the concrete surface, the floor is left for 4 weeks to dry completely.
Dry floors
Installing a dry floor over pipes is an easier and faster method, since there are no wet processes, which are labor-intensive and require hardening.
An inexpensive type of dry flooring is expanded clay sand. In addition, if there is a leak, the sand is simply removed and, after the damage is repaired, it is filled up again.
Construction of a base for a heated floor.
Warm floors must be installed on a solid foundation. For example, on a concrete slab. Then the thickness of the “general” floor layer will not exceed 8 cm. When laying the floor directly on the ground, it is necessary to level it as much as possible and insulate it as best as possible. The thickness of the insulation will depend on the weather conditions of the area and the specific location. In the event that the warm floor is laid above the basement, or on floors above the first, the thickness of the insulation will be minimal. About 3 cm.
Insulation and waterproofing.
Instead of thick plastic film, you can use roofing felt. Pieces are cut from a roll of film or roofing felt along the length of the room and laid overlapping each other (overlapping about 20 cm). Also, the waterproofing must be wrapped on the walls.
Insulation is placed on top of the laid waterproofing, which serves to retain heat in the room. Of the many options that modern manufacturers can offer, professionals advise choosing from two options:
- Extruded polystyrene foam. It has all the necessary advantages. It has reduced thermal conductivity and increased moisture resistance. It is also very wear-resistant.
- Expanded polystyrene in the form of profile mats. The main feature of this type of insulation is the surface with protrusions. This makes it easier to lay pipes. The pitch of the protrusions in this insulation is 5 cm. The main disadvantage is the increased cost compared to EPS.
When choosing the thickness of the insulation layer, several important conditions should be taken into account.
- When laying insulation directly on the ground, its thickness must be at least 10 cm. You can also consider the option of two-level installation. Two layers of insulation 5 cm thick.
- When laying insulation in the room under which the basement is located, a layer of 5 cm.
- When laying on all subsequent floors, its thickness can be up to 3 cm.
To attach the insulation you will need umbrella dowels or disc dowels. Harpoon clamps are required to secure the pipes.
Procedure for laying out insulation:
- Level the surface where the thermal insulation will lie. This is best done with sand or rough screed.
- Laying pieces of waterproofing. The seams must be taped.
- Direct laying of insulation boards joint to joint. (marked side should be up)
- The seams between the plates must also be taped.
- Secure the insulation with dowels.
If you lay insulation in two layers, you should follow the principle of brickwork. The seams of the top and bottom layers should not match.
Operating rules
The service life of heated floors made of polyethylene pipes is affected by operating conditions - temperature level of the coolant and pressure. PEX pipes withstand temperature changes well, but over time, this leads to their aging.
Basic operating rules that will extend the life of the floor:
- after installation, it is forbidden to turn on the device to maximum;
- the water heating level entering the circuit should not exceed +45;
- When commissioning the system, especially in winter, switching on should be gradual, starting from 2 hours, with a subsequent increase in operating time every day.
Comparison of polyethylene pipes with other materials
A comparison of the polyethylene circuit with pipes made of other materials is shown in the table:
| Pipes from | pros | Minuses |
| Cross-linked polyethylene | Products made from this material can restore their shape. They are heat-resistant, durable, do not corrode, are lightweight, provide noise protection, are environmentally friendly and inexpensive. | Cross-linked polyethylene reacts negatively to ultraviolet radiation, so it can only be installed in closed communications. |
| Copper | Copper pipes are durable, they will not melt or crack, they do not allow bacteria to grow and corrosion to develop. Copper products tolerate high and sub-zero temperatures well and are not subject to mechanical stress. | Pipes made from this material are expensive and heavy, and do not tolerate hard water saturated with acidity. You cannot combine copper and steel products in one system. |
| Polypropylene | This material is non-toxic, resistant to chemicals, pressure and temperature changes. Pipes made from it are lightweight, which simplifies installation. | Polypropylene pipes have low flexibility and a high expansion coefficient, which leads to an increase in their dimensions. |
| Metal-plastic | Despite the reasonable cost of metal-plastic pipes, they are durable, not subject to corrosion and are equipped with anti-acid protection. They are light in weight, keep their shape and are environmentally friendly. They bend easily, making installation easier. | The two layers that make up the pipes - polyethylene and aluminum - have different amounts of linear expansion, which can cause delamination of the product. There is a risk of pipe rupture when the fitting is pinched, and if threaded fittings are used, then there is a possibility of scale forming inside. |
To summarize, we can say that copper pipes for heated floors are an excellent option, but not everyone can afford it. Polypropylene products are cheaper, but not flexible enough, and metal-plastic does not tolerate temperature changes well.
Therefore, the use of cross-linked polyethylene pipelines in heating floors is practical and convenient, and is gaining great popularity every year. In addition, it can withstand freezing, and minor deformations disappear at a comfortable temperature.
However, when choosing pipes for underfloor heating, experts advise taking into account the characteristics of the room and operating conditions; the comfort in the home and the service life of the device depend on this.
Uponor pipe applications
Uponor PE-Xa pipes can restore their original shape, as they have a “thermal memory” effect. In addition, the pipes are coated with an anti-diffusion coating, which prevents the risk of corrosion. Pipes have the following advantages:
- heat resistance;
- excellent elasticity;
- durable service life of at least 50 years;
- resistance to ultraviolet radiation;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- resistance to mechanical deformation.
Thanks to the advantages of PE-Xa pipe, Uponor storm drains will last a very long time.