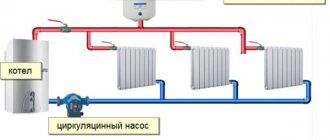
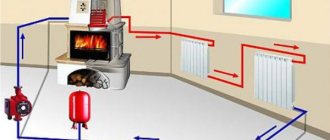
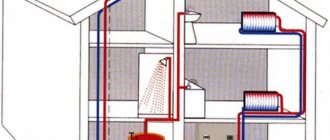
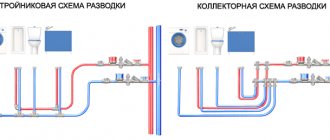
Water heating in a modern home is a complex system that must work reliably and uninterruptedly. However, there are a number of reasons why a failure occurs, such as installation errors, equipment wear and tear over time, etc. All these factors can affect the tightness of the circuits and cause malfunctions. To find the damaged area, a pressure test of the entire water heating system is required. How is this manipulation performed in a private (country) house and is it possible to do it with your own strength and hands? What level of pressure should it be? You can read about all this and watch the video.
Why hydrotest?
As you know, the heating system is a closed circuit operating under excess pressure. Any leaks in the threaded connections of the fittings or at the connection points of radiators will lead to water leakage, flooding of premises, damage to building structures, finishing, etc. And since the system operates in winter under pressure and high temperatures of the coolant, accidents may also occur situations that threaten the life and health of people. The consequences of leaking heating systems can be very expensive and problematic in terms of eliminating them, especially in winter.
Therefore, hydraulic tests of heating and heat supply systems are mandatory measures both at the time of commissioning of the facility and at the stage of preparatory work before the heating season.
In some cases, the absence of an act on testing the building’s heat supply systems is a guaranteed refusal of the heat supply organization to release heat into the building before the start of the heating period. Therefore, the organization operating the building must be aware of the procedure for preparing networks and must have the appropriate qualifications to test heating systems. In addition, pressure testing of heating systems connected to the heating networks of a city or town is part of the heat supply contract.
The main preparatory work and testing of heating systems include the following activities:
- system pressure testing,
- flushing of pipelines.
Conditions for performing crimping work
Pressure testing of the heating was carried out correctly and in full if all conditions were met during its implementation:
- During testing, no other work is allowed at the site.
- If pressure testing of the heating system and radiators is carried out by a specialist company, it must proceed in accordance with the plan agreed by the lead engineer. The instructions must contain information about the work to be done, their sequence and the equipment used.
- The presence of persons other than specialists conducting tests at the facility, turning it on and off is not allowed.
- If any work is being carried out at adjacent facilities simultaneously with testing, it is important to ensure the safety of its implementation.
A visual assessment of the operation of heating devices during their inspection should be carried out only under operating pressure conditions. Upon completion of the work, a report is drawn up confirming the tightness of the heating system.
Types of tests and timing
Pressure testing of the heated floor is carried out before pouring the concrete.
Leak testing of the heating unit is carried out in the following situations:
- In a private house, an initial check of the system is carried out at the stage of preparing the house for commissioning. Diagnostics of the pipeline in the grooves and the contours of the heated floor is carried out before sealing and pouring the screed. When the mortar has completely dried, it is recommended to conduct additional hydraulic tests to identify and eliminate possible leaks before laying expensive finishing material.
- To prepare the heating supply network for unplanned switching on, a periodic hydraulic test is carried out once a year after the end of the heating season. The check is also carried out immediately before the start of the heating season at positive ambient temperatures.
- One-time extraordinary checks of the strength and tightness of the system follow immediately after the completion of scheduled and unscheduled repair activities.
All of the above measures are diagnostic in nature and allow timely identification of problems with the heating system, leading to its shutdown and repair.
What is system testing?
Pressure testing of heating systems means a hydrodynamic test of the pipeline network, that is, the system is maintained under a certain excess pressure for a certain period of time.
All heating system equipment is also subject to strength testing: heat exchangers, radiators, shut-off and control valves, pumping stations and other network elements.
In addition to hydraulic tests of heating systems, all other heat supply systems are subject to annual inspection: heat input units into the building, individual heating points, heating units, heat supply systems for supply ventilation and air-thermal curtains, heating systems and underfloor heating, boiler rooms, etc.
Where can leaks occur?
Pipes, plumbing fittings and appliances (boilers, radiators, expansion tanks) leak as a result of corrosion, aging gaskets or mechanical damage.
When using steel heating pipes, depressurized joints lead to leaks in couplings, drains (battery connection areas), bends, connection points for shut-off valves, heating and measuring instruments, pumping and water heating equipment. Similar problems arise when using a metal-plastic pipeline; in addition to the above, water can flow out after some time through the threaded connections of compression couplings as a result of their self-unscrewing.
Rice. 3 Search devices for detecting leaks in hidden pipelines
Standards governing testing procedures
Both in design, installation, and testing work, without knowledge of the regulatory framework, it will be impossible to competently perform pressure testing of heating systems.
For example, SNiP 41-01-2003 provides basic recommendations for testing heating systems:
- the air temperature in the building must be above zero degrees;
- pressure testing should not be greater than the maximum maximum pressure of equipment and materials in the heating system;
- the pressure test pressure must be 50% greater than the operating pressure of the heating system and equipment, but the indicator should not be lower than 0.6 MPa.
SNiP 3.05.01-85 regulates:
- carry out hydraulic tests of large-scale components at the assembly site;
- if the pressure in the system drops during hydraulic tests, it is necessary to visually detect the location of the leak, eliminate the leak, and then continue testing for leaks;
- Pressure testing of pipelines with installed valves or wedge valves should be performed by turning the control knob twice;
- sectional heating devices that are not factory assembled must also be pressed on site;
- hidden wiring pipelines must be tested under high pressure before finishing work;
- insulated pipes are subject to pressure testing before applying thermal insulation;
- During testing of heat supply systems, hot water boilers and membrane tanks must be turned off;
- the system is considered operational and has passed the testing measures if the pressure test has not decreased within 30 minutes and no water leaks have been detected by the visual method;
- Testing a heating system for correct and uniform heating is called a thermal test. Such activities must be carried out for seven hours with water at a temperature of at least 60 degrees. If in the summer the heat source does not produce the pressure test temperature, then the tests are postponed until the temporary heat supply is resumed, or until it is connected to the heat source.
All hydraulic tests are recorded in the pressure test report, and tests of hidden pipelines are accompanied by a sheet for hidden work.
Necessary tool
To create the required conditions during pressure testing, you need equipment that allows you to achieve the required pressure level. A pump is most often used. It, together with the check valve, is connected using a high-pressure hose to the system through a pipe. The main characteristics when choosing a device are the level of performance and the pressure it can create. If the device is powered by electricity, then pay attention to the operating voltage (220 V or 380 V).
Required Tools
When carrying out work with a small volume of the circuit, it is advisable to use a manual crimping machine equipped with a hydraulic cylinder. Greater efficiency and ease of use can be achieved by using an electrically driven piston device. The electric type of crimping machine will create the required pressure in a short time without applying any muscular effort. These devices, in addition to the pressure gauge, have monitoring and control equipment.
In private houses where there is low pressure in the system, fill it with water and then record the pressure readings on the pressure gauge.
The procedure and technological features of performing pressure testing of the heating system
Hydraulic tests of heat supply systems are usually carried out with different pressure tests depending on the purpose of the system and the type of equipment used. For example, a heat input unit into a building is pressurized with a pressure of 16 atmospheres, heat supply systems for ventilation and ITP, as well as heating systems for multi-storey buildings - with a pressure of 10 atmospheres, and heating systems for individual houses - with a pressure from 2 to 6 atm.
Heating systems of newly constructed buildings are pressed with 1.5-2 times greater pressure from the worker, and heating systems of old and dilapidated houses are pressed with lower values in the range of 1.15-1.5. In addition, when crimping systems with cast iron radiators, the pressure range should not exceed 6 atm, but with installed convectors - about 10.
Thus, when choosing pressure testing, you should carefully read the equipment data sheets. It should not be higher than the maximum pressure of the “weakest” link in the system.
First, the heating or heat supply system is filled with water. If the heating system is filled with a low-freezing coolant, then pressure testing is carried out first with water, then with a solution with additives. You should know that due to lower surface tension, coolants based on ethylene glycol or propylene glycol are more fluid than water, so in case of minor leaks on the threaded connections, sometimes they should only be tightened slightly.
When preparing a functioning heating system for the heating season, the working coolant must be drained and refilled with clean water for pressure testing. The heating system is usually filled at the lowest point of the boiler room or heating unit through a drain ball valve. In parallel with filling the heating system, air must be bleed through air vents on risers, the top points of branches or through Mayevsky taps on radiators. To prevent airing of the heating system, the system is filled only from the bottom up.
Then the system pressure is increased to the calculated one, with the pressure drop monitored by measuring pressure gauges. In parallel with pressure monitoring, a visual inspection of the entire system, pipeline assemblies, threaded connections and equipment is carried out for the formation of leaks and the appearance of drops on the seams. If condensation forms on the system after filling with water, the pipelines must be dried and then inspected further.
Heating devices and pipeline sections hidden in building structures are subject to mandatory inspection.
The heating system is kept under pressure for at least 30 minutes, and if no leaks are detected and no pressure drop is recorded, then it is considered that the system has passed pressure testing.
In some cases, the pressure drop is permissible, but within limits not exceeding 0.1 atmospheres, and provided that a visual inspection does not confirm the formation of water leaks and violations of the tightness of welded and threaded connections.
If the result of hydraulic tests is negative, repair work is carried out with further repeated pressure testing.
Upon completion of the testing work, a test certificate is drawn up in the form specified in the main regulatory documents.
How does the crimping process work?
- Preparing the system before pressure testing. If the system is autonomous, then the heat generator is turned off first. If not, then taps are used to close off the area where inspection is required. The coolant must be drained.
- The system circuit is filled with water having a temperature of no higher than 45 C. The air is gradually released.
- The compressor is connected and air begins to flow into the pipes.
- At the beginning of the procedure, the pressure is brought to the working level and the area is visually inspected for violations. Then the pressure is gradually increased to the test level - this is maintained for at least 10 minutes.
- The area or the entire system is inspected for leaks at the connections. It is mandatory to visually inspect fittings, radiators and the entire length of pipe walls for fistulas. If deviations are detected, all defects and shifts are recorded. The operation of taps and valves is checked.
- Using pressure gauge readings, the drop in pressure level is determined. If it has not decreased, the system is in normal operating condition.
- Based on the results of the inspection, a report is drawn up.
Pneumatic testing of heating systems
The main limitation of hydraulic tests is carrying out work in rooms with a positive temperature, which is extremely difficult in a building under construction. Therefore, before the main test work, the heating system is often pressurized with air.
The compressor is connected to the drain valve or to the Mayevsky valve at any point in the system, increased air pressure is pumped in, and the system is maintained for a certain time without a drop in pressure.
How to fix a leak yourself
The listed methods and materials for finding and eliminating leaks are widely used in everyday life; before doing the work yourself, you should turn off the heating (with the exception of installing clamps); if a pipe bursts and the fistula is quite severe, you will have to drain the water from the entire system. You should have large containers on hand if the coolant is expensive antifreeze or purchased distilled water.
Rice. 7 Repair of copper pipe with Bondic plastic
If a pipe is leaking
To eliminate leaks in straight pipes, it is best to use clamps - they can withstand high pressure and temperature, have a long service life and look aesthetically pleasing on the pipeline.
If there is high pressure in a system with an extensive network of radiators and a high number of floors, it is better to use two-component clamps made of thick metal (about 5 mm), which are fastened on both sides with four bolts.
If curved areas and hard-to-reach places are to be repaired, you can use epoxy resin or cold welding, but keep in mind that these materials can only be applied to dry surfaces, and for this in most cases you will have to drain the coolant from the system. To avoid this, it is better to repair the pipes of an operating heating system at any temperature range with a special tape (Siloplast), for this:
- At a distance of about 10 cm from the fistula or crack, clean the pipeline of paint, rust, grease stains and other contaminants.
- Put on rubber gloves from the repair kit, open the package with the repair tape and pour water into it for 20 - 30 seconds.
Rice. 8 Repairing the leak with repair tape
- Clamp the leak site with the acrylic gasket from the kit (for the convenience of further work, you can temporarily secure it with a strong thread) and begin to tightly wrap the pipe in a spiral. Start from the edge of the gasket in such a way as to cover a 10-centimeter section and finish winding in the middle of the fistula. The winding pitch is calculated in such a way as to obtain 5 - 6 turns; if there is high pressure in the system, the number of turns is increased to 8.
- The tape is constantly twisted in the direction of winding and pressed tightly against the pipeline for 6 - 7 minutes (at this time the resin increases in volume and bubbles).
- After polymerization (the time depends on the temperature of the pipeline, if there is cold water in the line, it increases) the tape will become very sticky, the gloves will begin to stick to the surface - contact should be stopped and the work is considered completed.
Flushing heating systems
Hydropneumatic flushing of heating systems is a mandatory measure when preparing the heating system for start-up before the start of the heating season.
Water circulates through a closed circuit of the heating system during the heating period, and when heated and cooled, hardness salts are deposited. And this, together with the processes of corrosion of the internal walls of the pipes, leads to the deposition of scale on them. Scale significantly reduces the internal cross-section of pipelines, increases the hydraulic resistance of the system and reduces the heat transfer of radiators.
In high-temperature heating systems, scale leads to local overheating and further formation of fistulas. Scale deposits one millimeter thick lead to a reduction in heat transfer from the heating system by 15-20%. And on a global scale, this means colossal losses of thermal power and a significant decrease in the energy efficiency of the system with a significant increase in the cost of heating the building.
Flushing heating systems is the same necessary annual event as pressure testing, and is carried out before the start of the heating season or at the time of commissioning.
The main sign of a “clogged” heating system is an increase in coolant consumption, an increase in warm-up time, or uneven heating of the radiators. In these cases, situations often arise when the pipelines are hot, but the radiators are not yet warmed up.
The hydropneumatic method involves filling the system with clean water and connecting an air compressor to it. Excessive air pressure increases the flow rate of the coolant and creates turbulent fluid flows. These flows in places of scale deposits create vortex vibrations, as a result of which contaminant particles are torn off the surface of the walls.
When supplying high pressure air, the valve on the air bleed valves must be closed, and a check valve must be installed to protect the compressor from water entering the system.
Also, for flushing the system, there are special solutions that break down the scale deposited on the walls of pipelines and thereby reduce their hydraulic resistance.
Types of pumps for testing
Test activities are carried out using manual or electric pumps to build up pressure.
Manual models are equipped with pressure control devices, a tap for shutting off incoming water and a shut-off valve for draining water from a rectangular cuvette. A plunger pump is used to pump water under pressure. The main disadvantage of manual equipment is the low download speed and labor-intensive process.
The best choice would be electrical equipment. Its advantage is the high speed of filling the circuits and automatic shutdown when the required pressure is reached.
Hydraulic testing services
If the heating system is installed by a contractor during the construction of a new home, then the responsibility for pressure testing of pipelines lies entirely with the contractor.
In the case when the heating system is already functioning, regardless of whether it is a residential building, a municipal institution, a shopping or office complex, pressure testing is carried out by an organization that services all systems of the building. In housing construction, the law provides for the responsibility of the management company to maintain heating systems in working order, and, consequently, to carry out measures to prepare for the heating season.
For administrative and other complexes, testing of systems is carried out either by the operating organization or by a contractor who has all the necessary permits to carry out a complex of work.