On this site you can buy crushed stone with fast delivery!
An excellent alternative to metal products used in the maintenance and arrangement of private houses, as well as personal buildings, is a 32 mm HDPE pipe. Its characteristics are determined by several parameters that make it possible to judge the quality of the material and the throughput capacity of the future highway.
Unlike those manufactured under high pressure, HDPE collectors have a higher density, hardness, and strength.
They are less susceptible to deformation when heated. The maximum temperature that HDPE fabricates can withstand is 120⁰, and for materials transported along the highway - no more than 40⁰.
In addition, polyethylene products are absolutely insensitive to substances containing oils and fats.
The main property, and most likely disadvantage, of such collectors is gas permeability. This means that PE collectors are ideal for supplying drinking water. But not suitable for transporting volatile materials.
Is it possible to use plastic pipes to supply gas? You can, but not any kind, you need to look at the markings.
All these characteristics provide a wide range of applications for 32 mm pipes, the price of which varies between 15-45 rubles per 1 meter long section.
All collectors with this size, by the way, are suitable for construction:
- Non-pressure water pipes for technical purposes.
- Water supply lines for agricultural projects.
- Irrigation systems.
- Non-pressure sewer networks (when laid underground).
A 32 mm HDPE pipe is ideal (the fittings ensure the tightness of the connected sections) for protecting wires and power cables. Collectors of this size have performed well as waterproofing products.
Why do you need a heating cable?
It is reasonable to argue that you can easily do without heating the water supply. It is enough to find out the level of soil freezing in the area, and then, based on the indicators, dig a trench of the required depth. Usually this is 1.5-1.7 m for the middle strip, depending on the type of soil.
Pipes buried at such a depth and insulated do not freeze, since the surrounding soil has a positive temperature (let's say + 2-4 ° C).
However, not all so simple. In wetlands or areas close to water bodies, high groundwater levels are a common occurrence. This means that during floods or snow melting, communications will be flooded, which will negatively affect their functional properties.
If you bury the pipes only half a meter, but at the same time connect the electrical cable and provide proper thermal insulation, then you will not have to dig deep ditches.
It happens that in severe winters even deep-rooted areas freeze. Living in a house without automatic water supply from a well becomes less comfortable and sometimes even impossible. We have to carry out emergency repair work
Let's not forget about the critical areas that are most susceptible to the effects of cold - the places where the pipeline enters the house. If the building is built on a pile-screw foundation, then underneath there is an open section of the pipeline, which is easiest to insulate with a heating cable.
Conclusion: if it is technically possible to install a heating system for a water supply system, you should definitely use it, at least for the sake of insurance against freezing.
When contacting a specialized company, you may encounter some variety of offers. Let's look at the assortment.
Making your own cable
Using some materials you can make your own heating cable. A telephone wire number P274-M is suitable for this. It is quite strong, rigid, has a suitable diameter, and due to its good insulation, it can be used in damp environments. It will not have self-regulation, but if it is laid outside the pipeline and rarely connected, for example, in a country house, then this will be enough.
The telephone cable is divided into several separate wires, one of which is folded in half and then twisted back. Using a sealing gasket from a water hose, a sealed entry is created from the open end of the wire. It is fixed by a connecting pipe with wires running inside.
Fill the connecting fitting with epoxy glue and press it down a little. Then tighten it with a union nut, so the connection will be much tighter.
How to choose a cable according to power?
To put it simply, for each degree below 0, 1 W of power is taken. That is, if a sewer pipe must operate at a temperature of -10°C, then the cable power must be at least 10 W/m (meaning that the pipe temperature will not be 0°C, but positive, for example, +3 - +5° WITH). However, these are fairly average indicators and for a more accurate calculation you need to use special calculators that take into account the heat loss of the pipe material (metal or plastic), the length of the pipeline, whether there is additional thermal insulation, the installation of the wire and the temperature it generates. Cables from different manufacturers with the same output power can produce different temperatures. For example, one wire at a power of 10 W/m produces a maximum operating temperature of 65°C, and the other at the same power produces 75°C.
The product data sheet usually indicates the rated output power of the cable, as well as the maximum heating (exposure) temperature. Above you can see a clipping of the characteristics of self-regulating cables from one of the manufacturers. From it you can find out which wire can be used for what purposes. Almost every manufacturer provides similar data.
What are they used for?
As materials for water supply systems and gas supply, 32 mm pipes are produced in two types:
- Smooth are single-layer collectors with a smooth surface and holes of different sizes.
- Corrugated - 1 or 2-layer with a smooth wall on the inside and a textured wall on the outside.
All these products are designed for use in water supply systems for drinking and technical purposes, as well as for the supply of other substances in liquid or gaseous states. They are marked with the index PE 100 SDR 17 (high quality materials) or PE 80 (lower class products).
However, when laying hot water supply lines, such collectors are not used due to operating temperature limitations.
What pressure can a HDPE pipe withstand? Collectors produced for water supply needs can withstand up to 10 atmospheres. The manufacturer supplies them in reels (100 or 200 m per coil).
A characteristic feature of such pipes is a blue (blue) stripe applied along their entire length.
Design and scope of application
Depending on the type and technical characteristics, heating cables are used to heat drains, water and sewer pipes, and tanks. The main purpose is to protect liquids from freezing by increasing the temperature.
Heating systems are relevant for external communications, that is, for use in the ground or in the open air.
The basis of its operation is the ability of the cable to convert electricity into heat. The wire itself cannot transmit energy, as power analogues do. He only accepts it, and then gives off heat to the pipe (tray, gutter, tank, etc.)
Heating systems have one useful ability - zonal application. This means that you can take a set of elements and assemble a mini-system from it for heating a separate area, without connecting to the entire network.
This results in savings in materials and energy. In practice, you can find miniature “heaters” of 15-20 cm, and 200-meter windings.
The main components of the heating cable are the following elements:
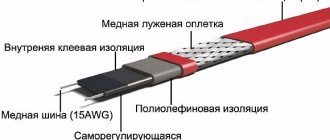
- Inner core - one or more. It is made using alloys with high electrical resistance. The higher it is, the greater the specific heat release value.
- Polymer protective shell. Together with plastic insulation, an aluminum screen or copper wire mesh is used.
- Durable PVC outer shell covering all internal elements.
Offers from different manufacturers may differ in nuances - the alloy of the core or the method of protection.
Shielded types are considered more reliable, equipped with foil protection and containing 2-3 cores instead of one. Single-core products are a budget option, which is good for assembling systems for short sections of water supply (+)
To improve the characteristics, the copper braid is nickel-plated, and the thickness of the outer layer is increased. In addition, the PVC material must be moisture resistant and not susceptible to ultraviolet radiation.
Device and types
Let's look at the design and types of heating cables.
In appearance, the heating cable is no different from a regular one, only instead of a conductor, it has a resistive element - that is, one with high electrical resistance - an element.
When connected to electricity, it heats up, just like a heating element in an electric kettle or a coil in an electric stove.
The main characteristic of such a cable is the specific thermal power, that is, per 1 m of length (unit of measurement - W/m). Other characteristics are mainly related to the quality of the outer shell: resistance to abrasion, impact and chemicals, moisture resistance and dielectric strength.
Heating cables come in the following types:
- unregulated;
- self-regulating;
- inductive.
Unregulated (fixed resistance)
This is the cheapest option, which today is often called obsolete.
The resistive element of such a cable is one or more cores made of nichrome, steel, copper or a special alloy.
All this is placed in a shielding shell (copper mesh or aluminum foil) and then in protective insulation made of PVC or modified polyolefin.
Often, a second layer of insulation is placed under the shielding shell - made of fluoropolymer or the same polyolefin.
The multi-core version is preferable because it does not generate as powerful electromagnetic radiation as the single-core version. In addition, a cable with several cores is connected to the mains only on one side (type A), while for a single-core heater both ends have to be connected to the mains (type E). In view of this circumstance, they usually try to make the trajectory of a single-core cable closed.
The resistance of this type of cable cannot be adjusted, so it always operates at full power. If heat dissipation in any area is insufficient, the resistive element may overheat and melt. Sensitivity to overheating must be taken into account during installation and operation; moreover, it requires more accurate calculations when selecting power.
Unregulated cables (often simply called resistive) are divided into two types:
- Linear: this is the most common option, consisting of one or more cores. This cable cannot be cut; it is used only in its entirety.
- Zonal: have a more complex structure. Inside there are two ordinary (non-resistive) conductors, between which insulation is laid with holes made through every meter. The conductors are wrapped in a spiral of high-resistance wire (resistive element), which is connected to them through holes in the insulation. Thus, it turns out that the resistive element consists of several fragments powered in a parallel circuit. This allows you to cut the heating cable anywhere.
In industry, mineral insulated heating cables are used. They have a flexible, corrosion-resistant metal shell (ALLOY 825), which makes them very durable and allows the heater to be used in very high temperature environments. Between the outer shell and the resistive element there is a protective insulation of magnesium oxide. Typically, such cables are made very powerful and are used to solve specific problems.
If you decide to organize your own water supply from PP pipes, then you cannot do without a soldering iron. Soldering iron for polypropylene pipes: how to choose the right model? Read on.
Read about tools for installing metal-plastic pipes here.
And here https://aquacomm.ru/cancliz/zagorodnyie-doma/avtonomnaya/stoki/uklon-kanalizacionnoj-truby.html information on methods for measuring the slope of sewer pipes. What should the slope be and what are the consequences of deviation from the norm.
Variable resistance (self-regulating)
Discoveries in the field of materials science have made it possible to create a new generation of heating cables. Inside it there are two conductive wires connected to each other by a matrix or threads made of a special polymer with semiconductor properties. It is this that is the resistive element.
The peculiarity of this polymer is that its resistance depends on temperature, and if it turns out to be too high, the matrix will simply stop passing current and the cable will turn off. And not all of it, but only that part of it where there was a danger of overheating.
Self-regulating heating cable for pipes
The rest of the line will operate normally. Thus, the self-regulating cable is absolutely reliable, because even under the most unfavorable circumstances it simply cannot physically burn out.
Another advantage of such a heater is its efficiency. If a conventional unregulated cable, regardless of temperature, always consumes the maximum amount of electrical energy, then a self-regulating cable in warm weather will reduce its consumption to a minimum.
This type of cable can be cut into fragments.
Inductive
A cable of this type is a highly elongated flexible electric coil with a ferromagnetic core.
When current is passed through the winding, the latter generates an alternating magnetic flux in the core, leading to the formation of eddy currents.
As a result, the core begins to heat up. The conductive winding also heats up, releasing approximately 20% of the total thermal energy.
Using the principle of inductance, the water pipe itself can be turned into a heating cable, if, of course, it is made of steel or other metal alloy. The pipe is wrapped with wire, which is connected to a source of high-frequency alternating current. As in a ferromagnetic core, eddy currents will arise in it, leading to heating.
For full operation of the heating system, in addition to the cable, a temperature sensor is required, which will turn it on as soon as the temperature drops to a certain point specified by the user.
What characteristics are important for choosing a warm cable?
Before choosing a heating wire, you need to pay attention to the following factors:
- on the diameter of the main line and the length of the area that needs heating;
- to the minimum soil temperature at the depth of the water main.
To correctly calculate the cable power, study the video materials:
When selecting a cable, the type of external insulation and the temperature class of the product are taken into account. For example, to heat sewer drains, a wire with a polyolefin insulator is used. When arranging external protection for water pipes, a cord coated with materials based on fluoropolymer (resistant to ultraviolet radiation) is used.
The heating cable inside the pipe is covered with fluoroplastic protection. It is also recommended to pay attention to the power consumption and the name of the company that manufactured the product.
Advantages of self-regulating cables
A self-regulating cable for heating a water pipe has a rather higher price than a resistive cable. But, thanks to their advantages in operation, they pay for themselves in a fairly short period. The main advantages of a self-regulating product include:
- Reliability. The thermal cable is highly resistant to voltage surges and voltage increases for a long period. Therefore, in the event of a power failure, users should not worry that the product may malfunction.
- Self-regulation. The pipe heating cable itself distributes the temperature throughout all sections of the pipeline. It is also capable of independently increasing power when cooling the coolant.
- Ease of installation. Unlike its analogues, due to the continuous heating of the matrix, the thermal wire can be cut into pieces of different sizes according to the indicated markings. And also, without fear for its functional qualities, overlap can be allowed when used for shut-off and control equipment.
- Economy. According to experts, despite the fact that the heating cable for pipes has a high cost, its operating costs are lower than those of similar products. Therefore, when using it you can save up to 20%.
- Versatility. The thermal cable can be used both underground and in open areas .
- Lifetime. If secured correctly, the heating system can last up to 13 - 15 years.
Having considered all the positive qualities, it is also worth noting that this pipe cable can be used not only for the water supply pipeline, but also for the sewer system. Therefore, before purchasing it, you should pay attention to its division class.
Types of heating cable
All heating systems are divided into 2 large categories: resistive and self-regulating. Each type has its own area of application.
Suppose resistive cables are good for heating short sections of pipes with a small cross-section - up to 40 mm, and for long sections of water supply it is better to use a self-regulating cable (in other words, self-regulating, “samreg”).
Type #1 – resistive
The principle of operation of the cable is simple: a current passes through one or two cores located in the insulating winding, heating it. Maximum current and high resistance add up to a high heat dissipation coefficient.
Pieces of resistive cable of a certain length that have a constant resistance are available for sale. During operation, they give off the same amount of heat along their entire length.
A single-core cable, as the name suggests, has one core, double insulation and external protection. The single core acts as a heating element
When installing the system, you must remember that a single-core cable is connected at both ends, as in the following diagram: Schematically, a single-core connection resembles a loop: first it is connected to an energy source, then it is pulled (wound) along the entire length of the pipe and returns back
Closed heating circuits are more often used for heating roof drainage systems or for installing “warm floors”, but an option applicable to plumbing also exists.
A special feature of installing a single-core cable on a water pipe is that it is laid on both sides. In this case, only the external connection type is used
For internal installation, one core is not suitable, since laying the “loop” will take up a lot of internal space, and accidental crossing of wires can lead to overheating.
A two-core cable is distinguished by the separation of the functions of the cores: one is responsible for heating, the second is for supplying energy.
The connection diagram is also different. In “loop-shaped” installation there is no need: as a result, the cable is connected at one end to the power source, the other is pulled along the pipe
Two-core resistive cables are used for plumbing systems as actively as samregs. They can be mounted inside pipes using tees and seals.
The main advantage of a resistive cable is its low cost. Many note reliability, long service life (up to 10-15 years), and ease of installation.
But there are also disadvantages:
- high probability of overheating at the intersection or close location of two cables;
- fixed length – can neither be increased nor shortened;
- the impossibility of replacing a burnt-out section - it will have to be completely replaced;
- no power adjustment - it is always the same along the entire length.
In order not to spend money on constantly connecting the cable (which is impractical), install a thermostat with sensors. As soon as the temperature drops to + 2-3°C, it automatically starts heating; when the temperature rises to + 6-7°C, the energy is turned off.
Type #2 – self-regulating
This type of cable is universal and can be used for various applications: heating roofing elements and water supply systems, sewer lines and liquid containers.
Its feature is independent regulation of power and intensity of heat supply. As soon as the temperature drops below the control point (assuming +3°C), the cable begins to heat up without outside intervention.
Self-regulating cable diagram. The main difference from its resistive counterpart is the conductive heating matrix, which is responsible for regulating the heating temperature. The insulating layers are no different
The principle of operation of the samreg is based on the property of the conductor to reduce/increase the current depending on the resistance. As the resistance increases, the current decreases, which leads to a decrease in power.
What happens to the cable during cooling? The resistance drops - the current increases - the heating process begins.
The advantage of self-regulating models is the “zoning” of work. The cable itself distributes its “labor power”: it carefully warms up the cooling areas and maintains an optimal temperature where strong heating is not needed.
The self-regulating cable works constantly, and this is welcome in the cold season. However, during a thaw or in the spring, when frosts stop, it is irrational to keep it on (+)
To fully automate the process of turning the cable on/off, you can equip the system with a thermostat that is “linked” to the outside temperature.
Installation methods for water supply
There are two ways to install a heating cable - external and internal. In the first case, it is attached along the pipe (or wound around it), in the second, it is wound inside. Both options have active practical applications, so let’s take a closer look at them.
Option #1 – external
Linear installation of cable along a water pipe is easy. The wire is fixed on one side using heat-resistant plastic clamps or fiberglass self-adhesive.
The holders are fastened at intervals of 0.3 m. Metal fasteners cannot be used. It is not difficult to calculate the length of the cable - it is equal to the length of the pipe that needs to be heated.
Line installation instructions:
For pipes buried in the ground, the cable is not placed strictly at the bottom or at the top, but slightly offset, which can be called the “8 (4) o’clock position.”
In addition to linear installation, spiral installation is used - the cable is wound along the entire length of the pipe with a uniform pitch. Plus – maximum contact with the pipe surface, minus – increased material consumption.
The pitch between turns can be changed depending on conditions. For example, for areas subject to severe freezing, it is reduced - thus, the entire surface of the pipe will be heated to the maximum
The wound method is relevant for pipes of medium and large diameter - sewer, drainage, but is also used for heating water pipes.
Option #2 – internal
The internal installation method is not suitable for all pipes, but only for water pipes with a cross-section of more than 40 mm. In pipelines with a smaller diameter, the cable will partially block the flow of water. It is difficult to equip a long pipe with internal heating, but for sections several meters long this is one of the best ways.
It is easiest to pull the cable in vertical sections - from top to bottom. The procedure takes place using a tee and a sealing coupling, which prevents the cord from slipping.
In some cases, internal cable installation is more rational than external installation - for example, for repairs or replacement of elements. It is not difficult to insert and connect a finished system; it is much more difficult to assemble it.
You can learn how to properly prepare the wires for insertion into the pipe from the following instructions.
Thermal insulation of heating cables
Regardless of the type of cable, it is necessary to carry out insulation. Thermal insulation is mounted on top of the heating system and water pipe. If the water supply along with the heating cable is not placed in a sealed “cocoon”, the heating will go in all directions, that is, mostly into the air.
The thickness of the thermal insulation layer is selected depending on external factors. Let’s assume that for installation in the ground, a 20-30 mm layer is sufficient, while for above-ground installation, insulation of at least 50 mm in thickness will be required
Expanded polystyrene or foamed polyethylene act as reliable and effective insulation materials. They are moisture resistant and provide some protective cushioning for the pipe, but also need protection.
For this reason, the “pipe-in-pipe” design is often used, when water pipes located in the ground or in the air, together with insulation, are placed inside another pipe of a larger diameter.
Thermal insulation of pipelines
According to the recommendations of experts, in order for the heating cable for pipes to have a longer service life, after installation work, it is necessary to apply a thermal insulation layer to the pipeline. Due to inexperience, many people use fiber wool or compressed insulation for insulation, thereby making mistakes. Mineral wool, under the influence of condensation, loses its thermal insulation properties. In winter, it freezes and crumbles under the influence of high temperatures. Compressed insulation materials, under the pressure of gravity, lose their thermal insulation. Therefore, the best option for insulation would be foam rubber and polyethylene foam. Foam rubber will well insulate the pipeline in the constructed sewer system, and foamed polyethylene will insulate pipes under the ground.
Food and non-food - 3 differences
Self-regulating cables are divided into food-grade cables, which can be laid directly into the pipe, and non-food-grade cables, which can be laid on top.
How do they differ from each other structurally? Firstly, the size.
Food grades, with fairly similar characteristics, have a smaller cross-section so as not to occupy useful space inside the water supply. Compare, the most common dimensions for external ones are 7*14mm, 7*15mm, and for internal ones – 5*7mm.
Mistake No. 4 If you get the size wrong, such a cable can actually reduce the water pressure.
At the same time, do not forget about the end coupling, which has a cross-section 1.5-2 times larger than the wire itself.
The second difference is the mandatory presence of a screen. External ones may not have it.
And thirdly, and most importantly, the external insulation material.
Here, for example, is a food option.
On the outside we have:
- fluoropolymer shell
This shell is chemically inert to aggressive environments and does not decompose inside the water supply.
Next come:
- armored, protective screen or braid
Error No. 5 Without such a grounding screen, the cable cannot be used inside the pipe.
- insulation layer
- two copper strands with a polymer between them
For the non-food model, the shell consists of ultraviolet-resistant polyolefin.
Determining the power of a heating self-regulating cable
The use of heating cables for heating water pipes is associated with the following circumstances:
- When laying the system outdoors. This method is used very rarely today and requires careful thermal insulation even when heaters are used.
- Heating is necessary at the area where the pipeline enters the house.
- If the pipelines are located in an unheated and uninsulated attic or basement.
Internal self-regulating cables are installed in cases where an external heater was not used when laying the network. At the same time, the size of the pipes is limited; such insulation is used up to a size of 32 millimeters. This is due to the limited power of such devices - 9-13 W/m. The pipe is heated only in the area where the conductor is located.
External heating cables come in higher power ratings - 17, 23 and 30 W/m in resistive or self-regulating versions.
Some caution should be exercised when installing heaters on plastic water pipes. The limitation here is the properties of the pipe material itself.
IMPORTANT! The maximum permissible temperature for most plastics is a maximum of 95 degrees, which corresponds to a maximum heating cable power of 17 W/m.
This must be taken into account when planning water supply works. It should be noted that plastic pipes do not defrost when frozen and emergency measures do not need to be taken in winter.
The level of heat transfer and energy consumption directly depends on such indicators as cable power. The higher it is, the stronger the heating and the amount of electricity consumed. The power of the wires has a wide range, the minimum is 5, and the average maximum is 150 W/m. Therefore, it is difficult for a specialist who is poorly versed in thermal wires to select a product with the required characteristics.
To facilitate the process of calculating power, there are special tables that take into account all operating features that may affect efficiency:
- application area;
- ambient temperature level;
- material of the heating object, its size, diameter;
- placement features;
- length of cable.
| Purpose of heating wire | Installation conditions | Material of manufacture | Power | |
| For heating the water supply system | In layers of soil | Inside the pipe | plastic | 5 – 10 |
| metal | 10 – 15 | |||
| Outside the pipe | plastic | 10 – 20 | ||
| metal | 15 – 25 | |||
| By air | Inside the pipe | plastic | 20 – 25 | |
| metal | 25 – 30 | |||
| Outside | plastic | 25 – 30 | ||
| metal | 30 – 25 | |||
| For roofing and drainage structures | Roof heating | Roof with insulation | — | 30 – 40 |
| Cold roof | — | 40 – 50 | ||
| Heating of a separate section of the roof around the perimeter | — | 300 – 400 | ||
| Gutters and drains | — | 30 – 60 | ||
| For self-regulating heating | Wooden floor on joists | — | 8 – 10 | |
| Floor with concrete screed | — | 18 – 20 |
For your information! The use of a cable heating system together with a programming thermostat will significantly reduce power consumption, thereby saving the family budget.
When purchasing a self-regulating cable, its power should be given special attention, since:
- excessive power will lead to overheating of the cable, and this in turn will cause damage and premature failure of the heating system;
- the use of a cable with a reduced value will contribute to freezing of the structure, since the system will not provide the necessary heating.
Correctly calculated power - efficiency, economy, safety and durability of your heating system.
Life time
The standard service life declared by manufacturers for self-regulating heating cables ranges from 10 to 40 years. They are made on the basis of semiconductor matrices, which is precisely due to the mistrust of users in the possibility of such long-term operation.
It is worth saying that this is not unreasonable, since the matrix can wear out up to 15% over a year of operation. Experts recommend several options to solve this problem:
- if the installation is underground, then a 100% reserve should be made, that is, laying a rubber thread of the heating cable;
- use a cable channel and place the heating wire in it; in case of a malfunction, you will not need to open the entire pipe, but only the area where the junction box is located;
- install the cable inside the pipe - an industrial certified product for food-grade water supply is suitable;
- laying the pipeline on the ground, with an increase in the thickness of the thermal insulation, this will reduce heat loss.
In addition, there are several rules that should be followed to extend the life of the self-regulating cable:
- When purchasing a thermal cable, you need to focus on well-known manufacturers. Naturally, the cost of such products is much higher, but repairing or redoing the entire structure will be much more expensive.
- In terms of type and power, the selected cable must correspond to the load that will be placed on it during operation.
- A thermoregulation system and protective automation should be installed.
- It is necessary to ring the self-heating system before installing it.
- Strictly follow the conditions of the technological process during installation and the operating instructions.
Important! The key condition under which a warranty replacement of a product is made is if the temperature conditions during use are observed.
Since manufacturers conduct an examination to evaluate the wire remaining in the outer sheath of the stabilizer. This study makes it possible to establish the temperature at which the thermal cable operated.
Self-regulating heating cable - do-it-yourself installation inside a pipe
Watch the video
How to install a self-regulating heating cable inside a water pipe
Above we have already paid attention to the circumstances under which the internal device is installed. It should also be noted that such heaters are manufactured specifically for this installation method. They must meet certain requirements:
- The outer sheath of a self-regulating cable should not emit harmful substances. Such heaters are used on small pipes through which drinking water is supplied.
- Due to the use of electricity in an aquatic environment, the degree of electrical protection must be at least IP.
- The end coupling must be sealed, therefore, before installing a self-regulating cable, you must carefully study the technical documentation and fully follow the recommendations.
To ensure the cable is inserted into the pipe at its end, you need to install a tee with the required outlet angle and then proceed as follows:
- Shut off the water supply to the water supply system.
- Measure the required cable length, having previously made the necessary measurements on the pipeline.
- Cut a piece of the heater at the nearest mark on the cable sheath.
- Install the end coupling.
- Place the heater inside the pipe.
- Place the sealing sleeve, rubber washer, conical metal clamping washer and clamping sleeve onto it.
- Assemble the oil seal in the order listed and carefully tighten the connection.
- Connect a coupling with an installation wire and a Euro plug to the rear end of the heating cable.
If tapping is necessary, heaters can be installed in several places in the water supply network.
DIY installation on the outer surface of the pipeline
When installing such a device on an external surface, the main condition for success is its tight fit. Therefore, before installing the coolant, the surface of the pipe (especially metal) must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt and traces of corrosion. This can be done efficiently using a wire brush in the form of an attachment to an electric drill.
Watch the video
Heating cable on a pipe. Installation rules
The heating element is laid in the direction of the pipe axis. Every 30 centimeters it should be secured using construction plastic clamps or metallized tape. The second option is preferable, since the heat transfer area increases significantly and the system will work more efficiently.
If several heating elements are installed, they should be located at the bottom of the pipe, where the coldest water is located.
You can run the heater in a spiral while simultaneously fastening it with metallized tape; in this case, the contact surface between the cable and the pipe increases and heating is more intense.
If it is necessary to heat plastic pipes, it is advisable to wrap a layer of metallized adhesive tape under the coolant. Having good thermal conductivity, it will distribute heat more evenly throughout the pipe, eliminating local heating at contact points. In this case, local overheating is eliminated, which can cause a breakdown of the water supply system.
During the operation of the water supply system in winter conditions, the fittings are subject to greater cooling. Therefore, when laying the heater along these elements, it must be placed like a snake, while simultaneously controlling the permissible bending radius so that there are no creases.
Electrical connection
Regardless of installation, for the functioning of the heating self-regulating cable for heating pipes, a power supply of 220 Volts will be required. There are several ways to connect to the network, which depend on the following nuances:
Linear method
- If the wire does not have a braid, it can simply be powered from the mains.
- If there is a grounded shield, the product can be connected to ground; if this is not possible, it can be removed.
- The cable can simply be plugged into a power outlet.
As you can see, you can connect the heating system yourself, without the help of a specialist. But before you connect everything to the electrical network, you need to make sure that there is no contact between the wires and that the other end of the wire is reliably insulated.
Self-regulating heater
There is no exaggeration in this name. Engineers have actually managed to create products that do not require external control.
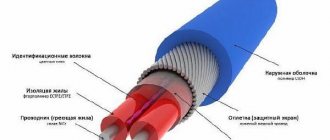
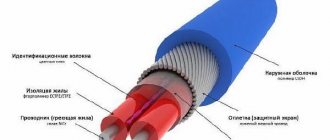
Design of self-regulating heating cable for water supply
The diagram shows the usual elements: copper conductors, shielding, fluoroplastic insulation resistant to high temperatures. But here the main useful function is performed by a special matrix. Its conductivity changes with increasing/decreasing temperature. At the same time, the heating decreases/increases.
These products are more expensive than their resistive counterparts. However, they are much more economical to operate. When using them, the temperature will increase only where it is really needed.
Self-regulating and resistive heaters
Creation of a heating system
The implementation of plans will be easier if you divide the entire project into stages:
- Preparation of drawings and list of components, tools, consumables.
- Connecting heating elements to power wires.
- Installation inside (outside) of the pipeline.
- Additional activities.
Connecting the heater and power cable: instructions
Below is an algorithm of actions and features that will be useful in practice:
| Drawing | Instructions |
| Purchase a special kit designed for termination of self-regulating cables. It includes metal sleeves that create electrical connections. Heat-shrinkable tubes with adhesive inside will come in handy. When heated, they contract and provide the necessary insulation and tightness. | |
| The cable is cut to the required size. Protective sheaths are removed from the connected end at a length of 40-50 mm. The semiconductor matrix is carefully separated along the center line. | |
| Different tubes are placed on these areas and heated with a hairdryer. This will allow you to subsequently space the joints to improve insulation parameters. | |
| The conductors are removed from the outer layers by 9-11 mm. | |
| They are inserted into the sleeves and rigidly fixed using wire cutters. | |
| The preparation of this part of the structure is completed by putting on tubes of larger diameter (there is no need to heat them yet). | |
| Prepare the power cable in the same way. Remove insulation. Apply heat shrink tubing of suitable sizes. | |
| The wires are inserted into the sleeves one by one, taking into account different lengths, and secured with a clamp. | |
| The tubes are successively shifted and heated to obtain multi-layer reliable protection. | |
| Next we proceed to insulating the other end. Remember that the conductors in it are not connected, since the current only passes through the matrix. To completely eliminate the possibility of contact, the cable is cut with a “step”. | |
| A heat shrink sleeve is placed on top and heated. As a result, something like this will be created. |
Using the same technology, working devices are created using other types of self-regulating cables
Installation outside the pipe
With this option for placing the heater, the following table is used to approximately calculate the required power:
| Metal pipe diameter, inch | Power per 1 m length, W |
| up to ¾ | 16-17 |
| from ¾ to 1½ | 23-27 |
| over 1½ | 30-31 |
For more precise actions, you can use free calculator programs that are offered on the official websites of cable product sellers. In this case, specific operating conditions, liquid temperature, and installation features are taken into account. Experts do not recommend installing heaters with a power of more than 17 W per 1 m length on plastic pipes. But in reality, it is necessary to take into account the heat resistance of a certain type of polymer. Such restrictions do not apply to metal products.
Flat cables are better suited for this option. They adhere well to the surface and are easier to fix.
Typical installation of a cable for heating an outdoor water pipe
The cable is secured with clamps that are resistant to high temperatures. The pitch is chosen in such a way as to eliminate sagging. A protective casing is installed on top of the thermal insulation layer made of porous material to prevent mechanical damage.
If necessary, increase the heating by adding the required number of cables. It is advisable to place them in the lower part of the pipe, since this is where unwanted icing processes begin.
In this option, the insulation and heating element are protected by special metal shells
Attaching heating wires to water pipes with metalized tape reduces heat loss
Spiral installation
For your information! In some places you can reduce the winding pitch and make a reverse turn to increase the heating area.
During installation, special allowances are made around flanges, valves and fastening points.
Installing a heating cable inside a water pipe
This option looks preferable. Inside the pipe, the product is well protected from mechanical influences. The heater is located inside the liquid, so it performs its functions with maximum efficiency. The numbers confirm this. To maintain a positive temperature, 8-10 W per 1 m of route is sufficient. This figure is almost two times less than the previous (external) installation method.
But this technology can only be used on straight sections where there are no shut-off valves.
You can purchase a ready-made kit, or connect the heater and power cable according to the above algorithm src=»https://ventkam.ru/images/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/26-1.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width =»800″ height=»644″[/img] Manufacturers include bushings and sealing elements in such kits
When designing the pipeline, allow for a 90° turn and install a tee with the appropriate dimensions to accommodate the gland assembly.
Temperature control
A thermostat is used to automate work processes. The device itself is installed in an electrical panel. The temperature sensor is fixed to the pipe at the control point. It should be remembered that this element may fail over time, so it is installed in a place convenient for maintenance. The thermostat of a self-regulating heating cable for heating pipes is used in accordance with the instructions src=»https://ventkam.ru/images/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/28-1.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=»850 ″ height=”286″[/img] Different electrical circuits are used to connect single- and double-core cables
In separate sets, a compact thermostat (with temperature sensor) is installed in the power supply circuit
Important! The disadvantage of compact thermostats is the lack of adjustment and remoteness from the work area.
Connecting pipeline heating to the electrical network using a heating cable
The total power of the heating system can be significant. Therefore, it is connected to a 220 V network through a separate machine. It is also recommended to install a specialized protection device (RCD) in this circuit. It constantly measures the current. When losses caused by insulation breakdown or touching a bare wire are detected, the heater quickly turns off.
Connecting the heater to the electrical network
Thermal insulation
This operation is required. It will prevent heat loss and prevent cold penetration. The best insulator is air, so porous materials that are resistant to humidity are used.
Special split tubes made of foamed polymers
The water supply is installed in a special channel, which is formed by Penoplex slabs.
Manufacturers
The modern consumer market offers a wide variety of types of thermal cables for heating water pipes at low temperatures. According to user reviews, the following companies produce quality products:
- "SST" is a Russian company that produces high quality products. Their self-regulating cables of different lengths are capable of maintaining the required temperature in all sections of the pipeline. The products of this company have passed testing and received the appropriate certificates. provides its customers with quality guarantees and reasonable prices.
- "Lavita" is one of the best South Korean companies that produces thermal cables for heating pipes. All of their products, without loss of performance, can withstand high voltage in the electrical network for a long time.
- Raychem - this American company provides the most innovative products made using new technologies. Their thermal cables, due to their fibrous structure, are able to provide high-quality heating of water pipes for more than 15 years.
- Nelson is a German company that, due to its quality products, occupies a leading position in the consumer market. The cables of this company are made from new high-strength materials that allow them to be used in aggressive environments, with a service life of at least 15 years.
Having examined the types of self-regulating heating cables, as well as their installation, it is clear that there are no difficulties in installation. Therefore, after studying the instructions that come with the product, installation can be carried out without the services of a specialist. However, according to general recommendations, in order to reduce energy costs to a minimum, you will first need to purchase a thermostat.
AdminAuthor of the article
Did you like the article?
Share with your friends:
Self-regulating cable - operating principle
Self-regulating, there is no closed loop or loop.
Error No. 2 There is no need to short the cores together at the end of the cable!
Between them, along the entire length, there is a cunning polymer, which, when cooled to a certain temperature, forms different conductivity bridges.
That is, at the cooling point, the loop of two wires closes on its own, current begins to flow between them and the cable heats up. In this case, you will have different temperatures along the entire length of the cable.
The hottest point will be in the coldest place. But at no point will the temperature exceed 85C. The nominal heating is 65 degrees.
This cable is completely fireproof. Even if it is overlapped on itself, it will still not burn.
Error No. 3 Make no mistake, when the weather is warm enough outside, it does not completely turn off on its own.
He simply reduces his consumption several times. There is no such option for its consumption to be zero when switched on.
Self-regs from different manufacturers differ in the quality of the so-called matrix. This is the same miracle polymer that transmits electricity through itself.
The vast majority of specialists use self-regulating types of cable to heat pipes. This is explained by their simpler operation and simplified installation.
You don't have to buy and connect a thermostat.
All you have to do is plug it into a power outlet, and it will immediately start working as it should.
What kind of outer insulation should the wire have?
Internal insulation of conductors is not as important as external insulation. The external conditions determine the conditions in which the product can be used. For example, if it is necessary to run a wire inside a water pipe, then the insulation should be made of food-grade fluoroplastic, which will not affect the taste of the water or change its chemical composition. Moreover, dust and moisture protection must be according to the IP68 standard.
For roof or gutter installations, it is important that the insulation can withstand prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays. It is usually made from fluoropolymer. The product may not indicate the shell material, but only the phrase “protection from UF rays.” But for sewerage, a cable with a polyolefin sheath is intended. Although this information is usually written in the specifications for each product, it is better to check with the seller so as not to make a mistake and buy the right wire.
Sources
- https://sovet-ingenera.com/santeh/trubodel/greyushhij-kabel-dlya-vodoprovoda.html
- https://ichip.ru/sovety/pokupka/kakoj-greyushchij-kabel-luchshe-vzyat-dlya-vodoprovoda-711692
- https://vodatyt.ru/uteplenie-truby/vybiraem-greyuschiy-kabel.html
- https://domikelectrica.ru/montazh-greyushhego-kabelya-dlya-obogreva-trub/
- https://TrubaNet.ru/kanalizacionnye-truby/greyushhijj-samoreguliruyushhijjsya-kabel-dlya-obogreva-trub.html
- https://HouseChief.ru/kabel-dlya-obogreva-vodoprovodnojj-truby.html
[collapse]