How does a roof heating system work?
Let's figure out what basic elements are part of the system and how they should be located.
Approximate diagram of the installation of a heating system on the roofSource dom-electro.ru
The entire complex of heating equipment usually consists of three main components.
The heating unit includes a network of single or double heating wires. Also at this point it is worth pointing out that a special film can be used as a heating element
It is important that the heating elements meet certain requirements. They must be adapted to sudden temperature changes, as well as power surges
The system must also be resistant to excess moisture. If you plan to walk on the roof, then resistance to mechanical damage is a mandatory requirement for the heating unit. The information and distribution unit is designed to control the transfer of electricity from the network to the heaters. This part of the system provides information in the form of sensor readings and powers all components of the anti-icing complex. It is better to install all sensors and elements of this unit in places where moisture does not enter. For example, in the attic or under the roof overhang. The control unit includes thermostats, weather sensors, as well as devices that allow you to manually change the roof temperature and power supply. An option with a self-regulating control system is possible. Here there is no need to constantly regulate the operation of the heating complex, and the necessary changes are introduced automatically. In this case, the mini-computer makes decisions based on weather sensor readings.
The icing cable is also laid in the drainage channelSource eximtec-plus.com.ua
Operation of electric heating systems
If installed correctly, operation of the system does not cause any problems.
Automation ensures switching on and off when the temperature changes, which eliminates icing of the roof and drains.
In cases where the need arises, you can switch to manual mode.
Expert advice
To keep the system in working order, experts give the following advice:
- Before the start of the winter season, it is necessary to thoroughly clean all problem areas and drains from dirt and fallen leaves. When cleaning cables, use a soft brush.
- It is necessary to carry out a preventive examination. All connections must be checked, as well as the condition of the cables, especially for the presence of sheath melts.
- The condition of the sensors is carefully monitored. Any contamination leads to loss of sensitivity.
When using an anti-icing system, safety is the most important thing. Installation and operation must be carried out taking into account the specifics of servicing electrical installations. It is necessary to completely prevent people from being exposed to electrical voltage.
Why is this necessary?
The obvious goal is to get rid of ice buildup, prevent narrowing of gutters and making gutters heavier. The accumulated ice is quite capable of completely blocking the outflow of melt water from the roof. The consequences are quite unpleasant: the roof overhang will be decorated with massive icicles, the fall of which will not bode well for either pedestrians or vehicles.
Why do gutters and gutters become filled with ice?
There are two reasons:
- During thaws and the off-season, temperatures often fluctuate around zero during the day. A very typical situation is when snow melts in the sun and immediately freezes in the form of ice on the inner wall of a pipe hung in the shade.
- In addition, so-called “warm” roofs with residential attics or exploitable attics underneath can cause accumulated snow to melt at temperatures down to -10C. It is clear that a significant part of the melt water will not have time to escape down.
The roof of a house with a residential attic on a thermal imager.
Calculation of the required amount of cable.
The total length for anti-icing systems is determined by the total number of roof components that need to be heated. Table 1 below will help determine the required cable length for roof heating. Table 1
| Design element | Required quantity of cable m per m structure | Note |
| Overhanging roof edge | See Table. 2 | In table 2 Based on weight and length, calculate the required number of cables. |
| Gutter | 1 | One strand of cable for every 10 cm of width |
| Drainpipe up to 100 mm. | 2 | |
| Drainpipe more than 100 mm. | 4 | |
| Endova | 2 | * Laying on the bottom is allowed 2/3 length. For large quantities precipitation may increase to 6 cable threads. |
| Dormer window | 1 | 1 meter of cable per meter of window perimeter. |
* For complex roof structures or large areas, it is possible to use a more powerful cable.
Attention! These recommendations are not absolute. The amount of cable may vary depending on the roof structure. Table
2
| Visor (see) | Heating cable loop height | Meters of cable per meter of soft roof * | Meters of cable per meter of metal roofing** |
| 30 | 45 | 1,9 | 2,5 |
| 60 | 75 | 2,7 | 3,5 |
| 90 | 105 | 3,6 | 4,5 |
| 120 | 135 | 4,6 | 5,5 |
* Standard soft roof design. ** Metal roof with laying pitch of 60 cm.
Installation procedure
- The cable should be warmed to room temperature before installation.
- Clear all gutters and gutters of debris.
- Remove sharp edges that could damage the heating cable.
- Mount a moisture-resistant junction box in a protected area.
- Start cable installation from the junction box. Leave a small loop where the cable exits the junction box.
- After installation, test the cable with a megger for a resistance of 10 MΩ.
- A thermostat can be used to turn the cable on/off. An automatic ice and snow detector can be additionally used to switch cable modes.
ATTENTION!
- To minimize the risk of fire if the cable is damaged or improperly installed, use a safety circuit breaker (fuse) to ground the circuit. On circuits longer than 30 meters, it is recommended to use a 30mA switch to prevent abnormal shutdown. The braid must be connected to ground, providing protection through the circuit switches. All electrical connections must be made by a qualified electrician.
- Do not twist the wires relative to each other. This may cause a short circuit and damage the cable.
- Live electrical elements must be protected from moisture, otherwise an accident may occur.
- A damaged cable must be replaced.
- Avoid installing ladders on top of heating cables.
Flat roof
Heating system installation technology
Heating cable laying areas
The heating cable should be laid in places where melt water drains and in areas where ice forms:
One or more threads are pulled along the entire length of the gutters. The linear power of the cable, depending on the diameters of the elements of the drainage system, is selected from 200 to 300 W per square meter.
Layout diagram for cable heating system for gutters and roofs
- In drainpipes. Heating of funnels and pipe outlets requires additional reinforcement. Typically, two cable lines with a power of 20-30 W per linear meter are laid in pipes, depending on the diameter of the pipes.
- In roof valleys the cable is laid up and down. The laying length is chosen to be at least 1 m from the beginning of the overhang, but it is better to be 2/3 of the entire length of the valley. The estimated power is 250-300 W per square meter of valley.
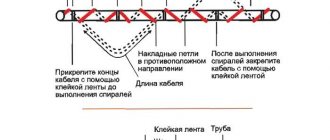
- To prevent the formation of ice on the roof eaves, a “snake” cable laying pattern is chosen. This heating scheme involves laying the cable along the edge of the eaves. In this case, the snake pitch on hard roofs is selected as a multiple of the pattern, and on soft ones - depending on the power consumption per square meter (35-40 cm). The height of the “snake” triangle is chosen so that the heated surface does not have cold zones on which ice can form.
- Along the drip line on the water separation line. 1-3 strands of cable depending on the drip design.
Step-by-step instructions for installing a cable heating system for gutters and roofs
Installation of heating gutters and roof eaves is carried out according to the following rules:
- It is recommended to fasten the cable in gutters using a special mounting tape across the gutter in strips. The greater the thickness of the mounting tape, the longer its service life. The installation pitch of the tape strips is 0.25 m for a resistive cable and 0.5 m for a self-regulating one. It is most often fixed to the gutter with rivets, after which the installation sites are treated with sealant.
- In drainpipes, the cable is secured using heat-shrinkable tubing or mounting tape. If the height of the pipes exceeds 6 m, it is better to additionally attach the cable to a metal cable in an insulating sheath to transfer the load-bearing load to it.
- In the pipe mark and funnel, the heating cable is secured with mounting tape with rivets.
- The cable is secured to the roof using mounting tape and sealant.
Rules for installing a self-regulating heating cable with braid (if the cable is without braid, points 2 and 6 should be excluded)
Pro Tip: It is highly recommended to avoid drilling into the roofing to install fasteners to avoid leaks.
- The procedure for installing a cable heating system involves inspecting the installation site, which should not have sharp edges or third-party objects that could damage the cable.
- Cable sections are checked to ensure their length matches the heating zones.
- If necessary, sections are cut to the required size, coupled, laid out and secured.
- Install the mounting boxes, ring and measure the insulation resistance of the sections.
- Thermostat sensors are installed, signal and power cables are laid.
- Install the control panel.
- Resistance is measured and power and signal cables are rung.
- Testing the residual current device.
- Adjust the thermostat.
- Perform commissioning work.
So, we looked in detail at how you can organize cable heating of a drainage system with your own hands, we figured out the structure of the system and the rules for choosing its components. We hope that our tips and recommendations will be useful to you and you will be able to put them into practice.
Calculation of the length of the heating cable for gutters
The calculations take into account the length of all heated drainpipes and drainage trays, as well as the presence of additional elements (funnels, drips, water jets, and so on). Based on the principles given above, the total length of the cable required for the heating system is calculated.
For example, there is:
the total length of plastic gutters with a diameter of 150mm is 54m, the total length of 4 plastic drainpipes with a height of 6m and a diameter of 150 is 36m. We lay the cable in the drainage trays in 2 threads, and in 1 thread in the drainpipes - we get 108m+36m=144m of heating cable with a power of 30W/m.
In addition, we add additional length to strengthen the lower part of the drainpipe, adding 1-1.5 m of heating cable to each drainpipe.
When calculating the system, it is necessary to take into account the maximum length of the heating cable section.
For a 30 W/m heating cable with a screen, the maximum section length is 75 m. For a 40 W/m heating cable with a screen, the maximum section length is 55 m.
Based on the maximum length, the number of cable sections is calculated, and then components are selected (junction boxes, coupling kits, fasteners and controls).
Why does ice form on the roof?
There are two main reasons:
- If the day is warm, the snow begins to melt. The resulting water flows down the gutters. At night, when the temperature drops, the remaining water turns into ice. Such a difference in temperature in winter and spring is observed within the city. When a large number of houses are clustered, the air is always warmer. Metal gutters are sometimes covered with a thick crust of ice, which is very difficult to remove from the gutter without breaking it.
- The reason for the formation of ice is the roofs themselves, especially if the roof is of the attic type. The snow melts from the heat emanating from the house. Water flowing onto the cornice cools and freezes again. Unreliable or poorly designed thermal insulation can trigger snow melting. Through cracks and unreliable joints in the thermal insulation material, internal heat comes out, warming up the snow. It turns into water and then into ice.
To get rid of this problem once and for all and protect the drainage system, it is necessary to install heating for the drainpipes. There are a number of anti-icing systems.
Causes of ice formation
Those that restrain snow from falling off the roofing and heat cables that serve to heat gutters. Their main function is to free the roof from the ice crust and prevent dangerous icicles from forming.
Modern storm drainage systems must be equipped with an anti-icing system for the roof surface. What is she like?
Cabling
Although the system itself is simple, it needs to be laid where a lot of snow accumulates and then ice forms. For each square when installing the cable on the roof surface there should be 250-300 W of power. Laying on the edge of the roof will be effective; this should be done in the form of a twisting strip. The estimated length of the fastening is from 30 to 45 cm; on hard roofs you can make longer snakes.
The cable is also mounted inside gutters; two strands can be laid here; the power will be sufficient, but the diameter must also be taken into account. If it is large, then you can add a third for effective heating
Also, attention should be paid to the outlets of pipes and funnels, since additional heating may be required here
How the system works
A private house is heated by a boiler, from which hot liquid flows into radiators, which release heat into the air inside the room. But for heating gutters, a fundamentally different approach is used. Storm drains are heated using a heating cable. It maintains the temperature at a constant level. This system is used not only for roofing, but also for drainage pipes, water supply and drainage systems, etc.
The drainage heating system is installed in all areas of the storm drain. Heating occurs due to electricity. For proper and adequate functioning there are many auxiliary elements. Among the main ones there are devices that automatically turn on or off heating elements, measure the outside temperature, and act as fuses. The electricity heats the cord, producing heat. There are two main types of wires with which you can insulate a storm drain - resistive and self-regulating. They are very different from each other, but both successfully fulfill their task.
This heating is installed over the entire drainage area
Resistive looks like an ordinary wire with protective insulation, inside which a metal core runs. He has constant resistance. This allows you to maintain the same temperature in all areas if the wire has no mechanical damage. It heats itself using a closed circuit. There are single-core and double-core cord types on sale.
They also install a heating system for gutters and drains with a self-regulating cable. It works differently. This is a pretty high tech device. The current flows through copper conductors, and the insulation is made of thermoplastic material. The top of the cable is covered with a main insulating layer. This heating element is based on a self-regulating matrix that independently changes the resistance of the wires in the cable when interacting with the outside temperature. Due to this, the degree of heating in different areas differs.
Heating cable for roofing and gutters: types and features
Any anti-icing system requires a heating cable to heat gutters and downpipes, which provides heat to the gutters and prevents water from crystallizing into ice.
There are two types of electrical cable:
- resistive;
- self-regulating.
Resistive type
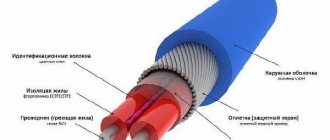
Self-heating cable consists of multilayer insulating material. In the cable cavity there are two heating cores that are connected to an electrical source.
NOTE!
Current resistance and power are constant. It heats up to a certain fixed temperature, which cannot be adjusted.
This type is a conventional cable in a multilayer winding, which consists of:
- outer polymer shell;
- underneath there is a protective screen made of tinned copper wire;
- then the inner polymer shell;
- conductor or heating wire inserted into fluoropolymer insulating cores.
The principle of operation is similar to that of an ordinary household heating element.
Such a heating wire has a constant resistance and power, unregulated by the heating temperature.
In demand, having the following positive qualities:
- low price;
- Easy to mount on the roof.
This type of cable heats up equally along its entire length, which reduces its efficiency. To defrost severe ice conditions, a lot of power is required. The cable may overheat and break.
Resistive type
Using a self-heating cable with increased power is irrational from the point of view of energy consumption. If the power is reduced, then ice areas in the gutters and on the roof remain unfrozen.
The flexibility of the cable allows it to be placed in any configuration. If bending waves are made more often and placed one to the other at a short distance, the heating power can be increased . But if the core overheats, the damaged cable cannot be repaired.
To prevent this, you need to clean the roof from dirt and fallen leaves more often. Its short service life and high power consumption make it unpopular. And it is used more often on roofs with a large area.
Self-regulating heating cable for drains
The manufacturing technology of a self-regulating cable is more complex.
The heating capabilities depend on the matrix, the action of which is to spontaneously regulate heating depending on the air temperature.
The matrix is located between two conductor cores.
When there is a large volume of snow and heavy icing of the roof, the power increases; when it warms up, the heating decreases.
This functional feature allows you to save on energy consumption . When an ice crust forms, the heating element installed in the gutters automatically turns on.
When not needed, it retains its linear power. Always works in optimal mode. Self-regulation of heating, leading to savings, is the most important advantage of the heating wire.
Especially if the weather in winter is unstable and the temperature regime changes frequently. If part of the cable burns out, it is cut out and the working parts are reconnected . There is no need to install a temperature sensor or an on/off system.
Self-regulating heating cable
The thermal cable consists of an external protective sheath and internal thermoplastic insulation. At the end there is the semiconducting matrix itself and conductive cores. This is a special technology for self-regulation of heating power.
Means for heating gutters and roof overhangs
To prevent the formation of ice, various systems for heating gutters and roofs are currently used, but almost all of them are based on the use of a special heating cable and automation equipment.
Let's take a closer look at what types of heating cables and control equipment exist, and which ones would be preferable for selection.
Which heating cable to choose
There are two main types of heating cables for roofs and gutters:
Resistive cable. In practice, it is a regular cable consisting of a metal core and insulation. A resistive cable has constant resistance, constant heating temperature during operation and constant power. Heating of the cable occurs from a closed circuit connected to electricity.
Design (diagram) of a resistive heating cable
Self-regulating cable for heating gutters and roof overhangs is more technologically advanced. It consists of a heating self-regulating element (matrix) that reacts to the temperature of the environment (drainpipe) and changes its resistance and, accordingly, the degree of heating depending on this, as well as an insulating shell, braid and outer shell.
Each type of heating cable is capable of providing equally effective heating of the roof and gutters. However, each of them has its own unique advantages. Thus, the main advantage of a resistive cable is its much lower price compared to a self-regulating one. At the same time, the second type is more efficient in terms of energy consumption and is unpretentious to installation conditions.
As the outside temperature rises, the number of current-carrying paths in the cable matrix decreases, due to which the power and amount of electricity consumed decreases. The temperature of the self-regulating cable also decreases. All this avoids the need to use a temperature sensor that automatically regulates the cable.
Advice from a professional: The most effective in terms of cost and quality ratio is considered to be a combined heating cable system. Typically, inexpensive resistive cables are used in the roofing portion of the system, while heating of gutters and gutters is provided by self-regulating cables.
Design (diagram) of the self-regulating heating cable Devi
As for calculating energy consumption and choosing the power of heating cables, the norm for resistive-type products is a cable with a power in the range of 18-22 W per linear meter, for self-regulating ones - 15-30 W per meter. However, it should be taken into account that if there is a drainage system made of polymer materials, the cable power should not exceed 17 W per linear meter, otherwise there is a risk of damage to the drainage due to excessively high heating temperatures.
Composition of a heating system for drainage and roofing
In addition to the heating cables themselves, heating systems also consist of the following main components:
- Fastening elements.
- Control panel, usually consisting of:
- input three-phase circuit breaker;
- residual current devices, usually 30mA sensitivity;
- four-pole contactor;
- single-pole circuit breakers for each phase;
- thermostat control circuit protection circuit breaker;
- signal lamp.
Distribution network components:
- power cables used to power heating cables;
- signal cables connecting thermostat sensors to the control unit;
- mounting boxes;
- couplings that ensure tightness of connections and ends of all types of cables.
Heating cable connection diagram
Thermostat. The operation of the cable heating system can be adjusted using two types of devices:
- Actually, the thermostat. This device is designed to operate the heating system in a given temperature range. Typically the operating range is set within -8..+3 degrees.
- Weather stations. In addition to a certain temperature range, the weather station is capable of monitoring the presence of precipitation and its melting on the roof. The station includes not only a temperature sensor, but also a humidity sensor, and some weather stations are equipped with both a precipitation sensor and a melting (humidity) sensor.
When using a conventional thermostat in a cable system, the user will need to independently turn the system on in the presence of precipitation and turn it off in the absence of it. The weather station allows you to fully automate the process of system operation and even program time delays for its shutdown. However, in terms of cost, conventional thermostats are significantly more profitable.
Features of heating gutters at home
Heating of the roof and gutters depends on many factors, which include:
- type of electrical cable;
- roof type;
- climatic conditions of the region.
We will talk about the types of heating cables a little later; now we will determine what main types of roofs exist and how this can affect the installation of an anti-icing system.
Cable structure for heating a drain.
A warm roof is characterized by a lack of insulation, which causes the formation of ice build-up. Such roofs melt snow even at sub-zero temperatures, after which the water flows onto the cold edge and freezes. That is why for this type of roof it is necessary to additionally lay the heating sections along the very edge with loops. The width of such loops ranges from thirty to fifty centimeters, the specific power of the system varies from two hundred to two hundred and fifty watts per square meter.
Heating a cold roof and gutters is somewhat different. Such roofs are well insulated and often have a well-ventilated attic space. For such roofs, only heating of gutters is installed with a linear power of twenty to thirty watts per meter, while the power should gradually increase to sixty to seventy watts in parallel with the increase in the length of the gutter. All cables must be equipped with a special protective device for disconnection.
Another feature of heating drainage systems and roofs is careful planning of the length and location of cables, and the ability to install the system yourself. This takes into account the length of the valley, all parts of the system, linear footage of drainpipes, and their required number. One hundred to one hundred and fifty millimeters of gutter requires approximately thirty to sixty watts of power per linear meter; for a gutter one hundred and fifty millimeters wide, the estimated power under standard weather conditions is two hundred watts per square meter.
Types of cable for gutters
To heat the roof, various types of cable are used, which you can lay with your own hands after calculating the system and sections. Two types of cable are used: resistive and self-regulating.
A resistive cable is characterized by lower cost and availability; its operating principle is as follows: a conductive metal core is heated due to the internal resistance supplied to the electric current. Heating gutters using this method is quite simple; operating the system is not complicated or expensive. Among the advantages it should be noted:
- low cost;
- absence of starting currents during startup;
- availability of constant power.
Although the latter characteristic can also become a serious disadvantage, since the heat needs of different areas are specific, some of them may overheat, while others simply do not have enough heat.
Installing a do-it-yourself system with resistive cables is simple; the cable can be laid along gutters and pipes or wrapped around them.
A more preferable option is to lay a zonal resistive cable, which has a special nichrome heating filament. Moreover, the linear power of the cable does not depend on the length; it can even be cut if necessary.
Heating gutters using a self-regulating electric cable is more reliable, but the price of the system is much higher, and the cable itself has a limited shelf life due to the gradual aging of a special heating self-regulating matrix. The advantage of such a system for heating gutters is that the cable being laid can change its resistance, that is, the heat generated corresponds to exactly the level that is needed at the moment.
It is believed that the installation of self-regulating systems is more economical to use, simple and reliable. Therefore, you can look at the cost of similar systems from different manufacturers and choose the option that best suits your budget.
Share a useful article:
Installation of a cable system for heating the roof covering
The most important point in the process of assembling a cable system is to correctly distribute them in the required areas. Therefore, installation involves bundling several sections of cable into one assembly. This ligament is called a knot.
Which areas are connected to each other:
- Part of the roof is closer to the eaves. Here the width of the area is determined as needed, most often from the snow guards to the edge. The heating cable is secured to the plane of the roofing material with special strips and clamps or rivets. Installation is carried out in a zigzag manner.
- Gutters of the drainage system.
- Vertical drainage pipes.
Look at the photo above, it shows how you can install one heating cable that would immediately cover both the roof plane and the gutters of the drainage system. And this is one of the options that can be called economical in terms of material consumption.
After the heating cable for heating the roof and drains has been completely installed and secured, it can be connected to the power network through a switchgear. Therefore, even before installation begins, you need to decide on the installation location of the two components. The best option is to install it under the roof structure in the attic; there should be easy access to this place.
If all installation processes have been completed, it is necessary to proceed to commissioning work.
Please note that this work is a mandatory condition, which is fixed by the UE Rules in Chapter 1.8. what needs to be done:
- Carry out a resistance test on all installed cable systems. That is, the resistance value of each core is measured and this value is checked with the passport data of the heating cable itself.
- The entire system must be grounded.
- A check is being carried out to ensure that it is turned off in emergency situations.
- Each cable is called, where the phase and zero are checked.
- The automation is also tested to ensure proper operation.
- An acceptance certificate for the entire heating system must be drawn up.
So, everything is ready, you can start the process of heating the roof and gutters. The simplest scheme is a start-up on a relay, which removes the blocking of the power cable. More complex circuits include a time relay. That is, the starting relay is turned on for a certain time, which is set by the operating temperature of the entire heating system. As soon as the time relay turns off, the precipitation and water sensors turn on. They control the amount of precipitation that falls on the roof of the house.
If there is a lot of precipitation, the roof heating system works; as soon as the precipitation stops, all cables are turned off simultaneously. At the same time, the drain heating system continues to operate until the water sensor (meaning melt water) signals. That is, there will be no water in the trays and pipes of the drainage system, and the system will not work either. It turns out that automation controls the entire process and regulates which unit should work and which should not. Typically, a gutter heating system lasts longer because the meltwater running through the gutters and pipes cannot be allowed to freeze.
In principle, there is nothing complicated in the process of laying a cable system. The main thing, as mentioned above, is to correctly distribute the sections and nodes, and also securely fasten the cable. The photos above show several mounting methods, although this is not the only option. Melting snow and water flow are quite serious loads at low temperatures outside. So the fastening must be carried out in accordance with all the rules, taking into account the requirements of the operating conditions.
Let us add that, having understood the layout of the heating wires and taking into account some technical aspects, you can carry out the installation yourself.
Do-it-yourself heating of the drainage system and roof
In winter and early spring, you can often see huge, menacing-looking icicles hanging on the roof eaves of houses, ice-covered or, even worse, gutters rendered inoperable by the mass of ice. Properly organized heating of gutters can prevent such phenomena - protect residents of the house from falling ice from the roof, and protect the drainage pipe system from the need for annual repairs.
In our article, we will analyze the factors influencing the appearance of ice on roof overhangs and gutters, and also describe in detail how to choose a suitable heating cable, its installation scheme, and organize heating of the roof and gutters on your own.
The most effective scheme is considered to be one in which the cable simultaneously heats the valleys, roof overhang and drainage system
Means for heating gutters and roof overhangs
To prevent the formation of ice, various systems for heating gutters and roofs are currently used, but almost all of them are based on the use of a special heating cable and automation equipment.
Let's take a closer look at what types of heating cables and control equipment exist, and which ones would be preferable for selection.
Which heating cable to choose
There are two main types of heating cables for roofs and gutters:
Resistive cable. In practice, it is a regular cable consisting of a metal core and insulation. A resistive cable has constant resistance, constant heating temperature during operation and constant power. Heating of the cable occurs from a closed circuit connected to electricity.
Design (diagram) of a resistive heating cable
Self-regulating cable for heating gutters and roof overhangs is more technologically advanced. It consists of a heating self-regulating element (matrix) that reacts to the temperature of the environment (drainpipe) and changes its resistance and, accordingly, the degree of heating depending on this, as well as an insulating shell, braid and outer shell.
Each type of heating cable is capable of providing equally effective heating of the roof and gutters. However, each of them has its own unique advantages. Thus, the main advantage of a resistive cable is its much lower price compared to a self-regulating one. At the same time, the second type is more efficient in terms of energy consumption and is unpretentious to installation conditions.
As the outside temperature rises, the number of current-carrying paths in the cable matrix decreases, due to which the power and amount of electricity consumed decreases. The temperature of the self-regulating cable also decreases. All this avoids the need to use a temperature sensor that automatically regulates the cable.
Advice from a professional: The most effective in terms of cost and quality ratio is considered to be a combined heating cable system. Typically, inexpensive resistive cables are used in the roofing portion of the system, while heating of gutters and gutters is provided by self-regulating cables.
Design (diagram) of the self-regulating heating cable Devi
As for calculating energy consumption and choosing the power of heating cables, the norm for resistive-type products is a cable with a power in the range of 18-22 W per linear meter, for self-regulating ones - 15-30 W per meter. However, it should be taken into account that if there is a drainage system made of polymer materials, the cable power should not exceed 17 W per linear meter, otherwise there is a risk of damage to the drainage due to excessively high heating temperatures.
Composition of a heating system for drainage and roofing
In addition to the heating cables themselves, heating systems also consist of the following main components:
- Fastening elements.
- Control panel, usually consisting of:
- input three-phase circuit breaker;
- residual current devices, usually 30mA sensitivity;
- four-pole contactor;
- single-pole circuit breakers for each phase;
- thermostat control circuit protection circuit breaker;
- signal lamp.
Distribution network components:
- power cables used to power heating cables;
- signal cables connecting thermostat sensors to the control unit;
- mounting boxes;
- couplings that ensure tightness of connections and ends of all types of cables.
Heating cable connection diagram
Thermostat. The operation of the cable heating system can be adjusted using two types of devices:
- Actually, the thermostat. This device is designed to operate the heating system in a given temperature range. Typically the operating range is set within -8..+3 degrees.
- Weather stations. In addition to a certain temperature range, the weather station is capable of monitoring the presence of precipitation and its melting on the roof. The station includes not only a temperature sensor, but also a humidity sensor, and some weather stations are equipped with both a precipitation sensor and a melting (humidity) sensor.
When using a conventional thermostat in a cable system, the user will need to independently turn the system on in the presence of precipitation and turn it off in the absence of it. The weather station allows you to fully automate the process of system operation and even program time delays for its shutdown. However, in terms of cost, conventional thermostats are significantly more profitable.
Types of heating
There are several types of insulation of gutters. They are classified according to the type of materials used. This:
- Natural;
- Electrical;
- Vodyanoe.
Natural insulation of drainpipes involves enveloping communications with special coatings. Most often this is geotextile - it is lightweight, has good thermal insulation and waterproofing. With its help, you can ensure regular operation of the system regardless of the time of year. At the same time, it does not weigh down the facade and is known for its affordable cost.
The most popular is electrical insulation. Its installation is easy to do independently. For heating purposes, a self-regulating wire is installed along the pipe drains. Power heating cables and special cords can be used as it. To regulate and connect the wires, special power supplies are used, which in turn are connected to the building's power supply system. Thermostats allow you to set electric heating to a specific temperature in order to use energy efficiently. But such a system is rarely allowed to be used for heating plastic drainpipes of apartments and houses.
Photo: Roof heating
Unlike electrical wires, water heating hose is completely safe for plastic. A small diameter pipe is installed along the cavity of the pipelines, through which hot water flows all the time. It is most often connected to a heating boiler. This is an economical way to heat gutters, but it is only used in regions with a central European climate. In the northern regions, it simply will not be able to heat the drain to the required level.
The anti-icing system is “on guard” – the roof is in order!
The anti-icing system for roofs and gutters is a complex of elements that prevent the formation of crust, ice and snow debris on the roof in any weather. The system includes heating devices for the roof gutter and eaves, a temperature control subsystem, a current distribution box and a set of fastening parts:
The main element of the system is the heating cable. Its structure is similar to a conventional electrically conductive wire, with a fundamental difference - the cable core (or one of the cores) converts electricity into heat. Warm wire prevents snow and ice from accumulating on eaves and in drainage systems. Thus, your roof receives guaranteed protection from icicles, ice crust, snow and the corresponding destructive consequences, and you and all household members have the opportunity to safely walk near the roof of your house.
Which heating cable to choose?
In order for the roof anti-icing system to work effectively and for as long as possible, experts advise paying attention to the following points when purchasing it:
- Reliable moisture resistance and UV resistance of the main cable;
- Integrity and tightness of the outer layer of the cable and electrical box;
- Thermal resistance of all materials from which the system elements are made;
- Mechanical stability of the cable and fasteners.
You can purchase cables in ready-made sections or coils. Ready-made sections are the best option for standard roofing structures. Adaptation systems formed from coils of cable to match the shape and texture of the roof will help equip the eaves of complex roofs.
There are two main types of heating cables: resistive and self-regulating. Which one is right for you? To answer this question, let's look at each type separately.
I. Resistive cable for drain heating
This is the traditional and most affordable heating cable option. Heating is evenly distributed along its entire length.
Resistive cables can be series or zone. The first are a copper core (or wires) covered with a layer of insulation. They are easy to operate, easy to install and affordable. A zone cable is an improved version of a serial cable. It has two cores, connected in places by a spiral wire, which forms independent zones. The “plus” of this structure is that when one zone burns out, the others continue to work. Once a serial cable burns out, it cannot be repaired.
Serial cables:
Zone cables:
It is better to use resistive cable on a homogeneous surface (eaves, gutter, pipe) without overlaps. An important point that should be taken into account when purchasing it is that the high energy consumption is ultimately not justified by the low price.
II. Self-regulating cable in a roof anti-icing system
The more complex structure of this wire determines its increased efficiency and reliability. The cable has two cores, between which a semiconductor matrix is laid. It is this layer that allows the system to adapt heat to different sections of the cable, changing resistance under the influence of ambient temperature. The internal and external layers of the cable are made of modern high-tech materials and are resistant to mechanical, thermal and other influences:
This self-regulating ability helps save a significant amount of energy and makes the system practical and durable. These advantages can be considered as compensation for the high price of a self-regulating anti-ice system.
Types of heating cables
The range of heating cables is small; there are only two types:
- resistive – heating evenly along the entire length;
- self-regulating – responsive to changes in ambient temperature.
Resistive cables
When the electrical circuit is closed, such a cable heats up evenly due to the homogeneous composition of the heating core.
Types of resistive cables:
- Single-core serial - has a primitive design: a wire covered with a shielding braid and a polymer sheath. The braid acts as grounding and reduces the level of electromagnetic radiation. The outer sheath protects the wire from mechanical stress and serves as insulation.
- Two-core series - consists of two insulated cores conducting current in opposite directions, a shielding braid and an insulating sheath. This cable structure makes it possible to neutralize electromagnetic radiation.
- Zonal - consists of two insulated parallel cores and a nichrome spiral, braid and external insulation. The insulation of the current-carrying conductors has windows through which the heating coil closes either on the first or on the second conductor, forming independent heat release zones.
We recommend that you read: How to hide the ventilation pipe from the hood in the kitchen?
Serial cables cannot be cut, as this changes the resistance of the heating wires and the heating level. These cables are cheap, simple and easy to install, as due to their simplicity of design they are flexible. In operation, the heating circuit is ineffective and susceptible to overheating, since it heats up equally everywhere. A failed cable cannot be restored.
A zone cable is slightly more expensive than a series cable, but overheating of one zone does not threaten a shutdown - the current flows through a parallel zone. It is convenient to install; it can be cut into pieces, but taking into account that the length of the segments is a multiple of the length of the heat-generating zone. Otherwise, the heat-generating zone will be open and the cable will not heat up.
How to mount the system
In order to be fully equipped to begin installing the system, let’s look at a clear example of a heating scheme for a roof and gutters and adhere to a certain sequence.
First, we select the location for installing the automation and control system indoors. Often the main controller and protection devices must be located near the electrical distribution panel. This is done for ease of installation, and allows you to reduce the length of cable and wire routes and increase the reliability of the circuit. Connecting the controller will not be difficult, since all its pins and terminals are signed and marked. A person who is familiar with the basics of electrical wiring and knows how to handle tools will quickly find his bearings and do such work with his own hands.
The installation of a heating conductor in gutters should be considered based on the fact that it is divided into four component parts (gutter, waste pipe, funnel and water inlet), each of which must be heated. First, you need to feed a loop of wire into the drainpipe and screw it into the water inlet using steel clamps. Then we attach the cable to the bottom of the drain pipe as high as possible, placing it at a distance of 5 cm from each other in the part of the pipe located closer to the house (melt water usually flows through it). In the same way we attach the conductor at the top near the bottom of the funnel
It is important that if the pipe consists of several collapsible parts, then in each of them it is necessary to organize an intermediate fastening of the heating system. In the funnel, the cable is laid in the shape of a ring and screwed with clamps in this position. Moving on to the gutter
In it, the wires need to be placed on opposite side surfaces. Next, the ends are connected in the distribution junction box to the terminals
Let's move on to the gutter. In it, the wires need to be placed on opposite side surfaces. Next, the ends are connected to the terminals in the distribution junction box.
Advice! The self-regulating conductor does not have to be laid in a loop. Installation into one core is suitable, the end of which is insulated with a special plug.
As an example of installing a heating element, let's take a flat roof. The cable is laid in the lower part along the perimeter of the water drainage line and laid in the internal funnel of the drain at a distance of 400 mm, if the drain pipe is located in the building. If the pipe is installed outside, then a “dripping loop” scheme is used. Where the parapet and roof touch, the laid conductor should have a power of about 60-70 W/m2. It is also necessary that a wire be laid around the heated funnel at a distance of 2 m as shown in the figure below:
The sequence of cutting the heating wire is shown in the photo:
Finally, when the previous steps are completed, the control system for heating the gutters and roof is connected to the heating elements using power cables through adapter junction boxes. Also, all the necessary sensors and protection equipment are connected.
You can clearly see the installation process of the anti-icing system in the video:
That's all I wanted to tell you about how to heat the roof and gutters with your own hands. We hope that the instructions provided were useful and interesting for you!
How to secure cable to roof and gutter
After this, screw the fastening clips or tape onto the roof.
To prevent leaks, do not forget to treat the entry points of the screws with sealant.
The step between the top and bottom rows of clips is 60cm.
Mistake #5
To install the heating cable on the roof, use only specialized fasteners.
Forget about the cable ties that are often used to run cables along the walls of the house.
For certain types of roofing, special petals with latches are produced. You don't even have to make holes with them.
There is also a fastening method using self-adhesive sealing tape on an aluminum base.
According to the manufacturer, the tape has a high level of adhesion, is heat-resistant and durable. But still, the majority prefer through cable fastening, considering it more pragmatic and reliable.
Before installing the heating cable, be sure to check its resistance and integrity of the wires with a multimeter.
Resistance data must be indicated in the product passport.
If everything is in order, lay the cable in waves according to the fixed clips on the roof slope.
After which, the cold end is inserted into the installation box under the ridge.
Sections for drainage are also called. Both between the working conductors and with the protective conductor.
Between the grounding protective conductor and the working conductors, the insulation should reach several megohms.
This check is no longer carried out with a multimeter, but with a megger.
Be sure to write down all the data in your passport so that you have something to compare with later. Suddenly, in a few years you will need to find the reason for the system's inoperability.
After all checks, the gutter is thoroughly cleaned of dirt and debris.
A mounting tape is secured inside it. Most often this is done on rivets.
But there is also a rivetless fastening.
It is best to use a combined option. Every 1.0-1.5 m you rivet the tape, and in the middle of these sections you place plastic spacers that simply push the cable apart.
The horizontal section of the cable is laid in the gutter, and the vertical section is lowered down the drain using a cable.
Please note that if you have pets at home, they love to chew on such a cable, provocatively peeking out of the pipe.
Mistake #6
In this situation, you cannot release it outside, and it is better to hide the noose inside.
The cable of the vertical section of the cable is suspended on a hook.
This cable is required for pipe heights over 4 m. By the way, when laying cables in the valley, a support cable is also often used.
It absorbs all mechanical load, protecting the shell from damage.
Instead of a cable, you can use a chain in the drain. It must be galvanized so that it does not rust from constant contact with water.
The cable is simply put on individual links through special spacers.
The last link from above is suspended on a spacer rod or pin.
The pin itself should not just lie across the hole in the drain, it is advisable to secure it.
For example, for the same mounting tape.
Mistake #7
Do not skimp and do not lower the cable into the pipe without such a chain or cable.
They perform a protective function. If the system fails, ice very quickly sticks to the cable in the drain, increasing its weight several times.
And so that it does not break from such a load, an additional load-bearing element is required.
After installation, all cold ends of the cables are inserted into the installation box.
The whole process is repeated on all roof slopes.
If you have an extension without gutters (garage), the cable is also placed on it, but in such a way that its loops hang down a few centimeters (5-8cm).
This is the so-called “drip loop” scheme.