A private residential building without a drainage system is quite difficult to maintain in an up-to-date condition for many years. After all, melt and rainwater significantly worsen the condition of the roof, foundation and facade if they are not drained from the roof surface in time. This is exactly the function that a gutter performs, that is, it is a structure for collecting water from the roofing and draining it into the storm drain. It is recommended to install the drainage system both on small buildings and on massive mansions. In this case, you can always do the installation yourself. To do this, you need to know what elements a drain consists of, as well as how to correctly calculate the dimensions of drainpipes, gutters and other components.
Installation of external drainage
Among the large number of elements of the drainage system, pipes, of course, play an important role. They organize the drainage of water collected in gutters, leading it outside the roof. Thus, representing the most important element of protecting the roof and foundation from premature destruction. The main material used in production is galvanized steel. The relatively light weight of galvanizing allows installation of gutters even on the roof of an old house. And due to the modern polymer coating, the material is resistant to corrosion. The advantage of steel is that it is not subject to deformation due to sudden changes in temperature, so the customer does not have to worry that when it gets colder or warmer, the structure will crack, as happens with plastic gutters. The cross-sectional diameter and dimensions of galvanized drainage systems vary depending on the area and design features of the roof. Let's look at this question in more detail a little further.
The design of an external drainage system includes several components. These are gutters whose task is to direct water flows to the funnel; the pipes and funnels themselves; connectors with a bracket system, as well as contours used on the roof of complex architecture - with niches, columns or projections.
Depending on the cross-sectional shape, pipes are divided into: round or rectangular. Round ones are considered the most practical and easiest to maintain. Due to its originality, the rectangular cross-section is not so common.
Of course, it will not be possible to organize drainage with one drainpipe, so the following are installed together with it:
- Water intake funnel.
- Mounting clamps.
- Knees (allow you to connect the links on the ledges).
- Branches (organize the drainage of water outside the structure).
Elements of the drainage system
A fully assembled communication system for draining storm water from the top of the house includes basic and additional elements. In particular, these:
- Gutters;
- Water intake funnel;
- Straight pipe parts (links);
- Elbows (elements designed to connect sections of the tube at corners, turns and bends. Which ones the master needs can be seen from the finished roof project.);
- Low tides.
Advice: an unreasonably large cross-section of the pipe for the drainage system will, of course, let in a lot of rainwater and drain it all from the roof, but in the end, communication for draining precipitation from the roof will cost the craftsman many times more.
What does the diameter of the drainage system affect and what does it depend on?
Proper calculation of the diameter is a key factor that affects the efficiency of the structure and its ability to perform its assigned functions. The larger d, the better the throughput capacity of the gutter and pipe, but the price also increases.
Such a wide “range” of diameter and its choice depend on the following points:
- Water collection areas
- Schemes for the placement of drain points and their number (loaded and unloaded drain scheme)
Collection area
To calculate this parameter for one gutter, use the formula:
S= L (a+b/2), where
L – length of the roof along the ridge;
a – projection onto the horizontal plane of the roof slope from which precipitation flows;
c – roof height.
Let's give an example. Roof data:
- Height – 2 m.
- Length – 10 m.
- Projection width – 5 m.
Therefore, using the formula, we will perform the calculation: S= 10(5+2/2)=60 m2.
Placement of drain points
With a sufficient number of drain points, i.e. with an unloaded system, you can choose drainage parameters - 125/100 mm with a roof area of 100 sq. m. m.
The exact number of drain points depends on the diameter of the gutter. The data is presented in the table.
| S, sq. m | d gutters, mm | d pipes, mm |
| Up to 79 | 90 | 75 |
| More than 100 | 125 | 100 |
With a loaded scheme (drainage system to one funnel) - 150/120 mm with a roof area of 100 sq. m.
A loaded system requires the use of oversized dimensions. The data is presented in the table.
| Area, sq.m | d gutters, mm | d pipes, mm |
| Up to 42 | 75 | 63 |
| Up to 52 | 100 | 80 |
| Up to 75 | 125 | 100 |
| Up to 100 | 150 | 120 |
When choosing, it is better to choose elements with a larger d, which reduces the risk of contamination or the formation of an ice crust. It is important that all elements are from the same manufacturer, this will help to avoid errors in calculations and installation.
What to look for when choosing
When choosing, we recommend paying attention to:
- Precipitation rates for a specific region.
- Roof area.
- The specifics of the building's architecture.
- Roof slope.
According to the requirements of DIN 18460-1989, the diameter of the drainage system pipe is selected based on the roof area and water throughput. The data is presented in the table.
| Roof area, m2 | Water throughput, l/s | Drainpipe | |
| d, mm | Cross section, cm2 | ||
| 40 | 1,2 | 60 | 28 |
| 60 | 1,8 | 70 | 38 |
| 86 | 2,6 | 80 | 50 |
| 156 | 4,7 | 100 | 79 |
| 253 | 7,6 | 120 | 113 |
| 283 | 8,5 | 125 | 122 |
| 459 | 13,8 | 150 | 177 |
To calculate the number of drainage pipes, use the following option: 1 pipe per 50 m2 of roof slope area, the distance between them should not exceed 10 m. In the case of diameter, there is 1.5 mm2 of pipe cross-sectional area for each square meter of roof area.
Bottom line
As you can see, calculating a drainage system for a private house is not so complicated.
The main thing is to find out in advance all the parameters of your building: the height of the walls, the length of the eaves overhang, the length and width of the slopes.
However, if you are not sure of your calculations or are afraid of forgetting something, you can always test yourself using online calculators on the manufacturers’ websites.
They are good because the system will offer you all the required elements of a drain. When doing manual calculations, it’s easy to forget about some connectors and holders. Here it will be clearly shown: what is installed where and what it is used for.
The system will also calculate the approximate cost of the structure. The only disadvantage of such calculators is that they, as a rule, offer the amount of materials with a reserve. However, this can easily be adjusted to suit your personal requirements.
Current drainage diameters
The sizes offered by Russian manufacturers range from 50 to 200 mm. Previously, only three main parameters were used - 100, 150 and 200 mm. But due to the large assortment from manufacturers and imported products supplied to our market, the diameter of drainpipes has changed significantly. Today there is no single established standard according to GOST in Russia.
Below we present common sizes of downpipes and gutters:
- 80/100;
- 90/125;
- 100/125;
- 120/150;
- 150/200.
Our company offers pipes and gutters that are optimal for many roofs. If the system is needed to drain precipitation from a large roof area, for example, from a warehouse or commercial building, pay attention to a large drainage system made of galvanized steel 120/150 or 150/200 mm. This design can handle high loads without deformation. Large-sized gutters are also suitable for roofs of production and industrial premises.
The thickness of the steel is 0.5 mm, the protective polymer coating is polyester. The homeowner can choose any shade from the RAL catalog so that the drainage system becomes not only protection, but also a decoration for the roof.
Vodostokstroy also offers systems for private construction - “Standard” and Euro “Aquarius” with dimensions of 100/125 mm. The systems have good throughput and affordable cost.
For oversized buildings for household purposes (household buildings, bathhouses, gazebos), we recommend a small drainage system of 80/100 mm.
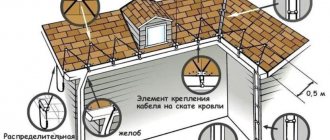
Brackets
The gutter holder and the cornice gutter holder differ from each other in length. They both fix the gutter on the roof, but the regular holder (longer) must be installed BEFORE installing the roofing, and the cornice holder can be attached after the roof is finished.
Conventional chute holders are usually spaced 60 cm apart, sloping towards the outlet funnel. When calculating the slope of the drain, keep in mind that it can range from 3 to 5 mm for each meter of length. For a 10-meter cornice we need 17 gutter holders.
Calculation of drain diameter
For pipes
The primary parameter that must be taken into account when calculating the diameter of external drainage pipes is the roof area. If there are several slopes on the roof, the indicators of individual sections are added up to obtain the total value. The angle of inclination and area of the roof will help determine the volume of all water flowing from the roof.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the maximum level of precipitation characteristic of a particular region. You can use reference books on the Internet that provide data on average and maximum precipitation for a specific area.
To calculate the working section, use the ratio 1 sq. cm section / 0.75-1 sq.m of roof. Next, the results are refined taking into account information about precipitation.
For example, if the pipe has d=100mm, it can be installed for a roof with an area of 75-100 sq.m. And with d=200 mm it can be used on a roof area of 150-200 sq.m.
In addition, the following features must be taken into account:
- To calculate the cross-section of the gutter, the angle of inclination is taken into account, on which the height of the sides of the channel depends. The minimum acceptable value of the parameter is 120 mm.
- The number of gutters depends on the perimeter of the cornice.
- Previously, pipe sizes were fixed by GOST. However, after the introduction of foreign-made products into the Russian market, other standard sizes appeared, so choosing the optimal one will not be difficult.
Kinds
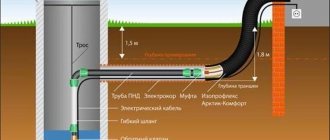
Based on the name of drainage systems, you can understand what their difference is. The external system is installed along the perimeter of the eaves in such a way that water flowing from the roof falls directly into the gutter and then, due to the slope, moves towards the drain pipes through which it descends to the ground.
With this scheme for draining rainwater, drain pipes can be placed almost anywhere along the perimeter of the roof, and the water can be directed by adjusting the angle of the gutters.
The external system is preferable for private houses or multi-storey houses with a gable or hip roof.
Internal gutters are installed inside the building, and, as a rule, only drains are visible from the street; gutters are built into the roof or there may be no gutters at all.
Such systems are used mainly for flat or slightly concave roofs with soft roofing. The design can work on the principle of a sink.
Optimal number of funnels
The number of drainage funnels is calculated taking into account the following requirements:
- if there are no obstacles to the linear expansion of a gutter up to 12 meters long, then one funnel will be sufficient;
- if the gutter length is over 12 meters and there are obstacles to its expansion, then one special compensating funnel will be required at the end of the slope;
- if the gutter encircles the perimeter of the building, then the combined installation of funnels and compensators will be required.
Calculation of drainage funnels must be carried out based on their passport data, which contains information about geometric dimensions, method of fastening and throughput. The number of drainage funnels must correspond to the number of drainpipes in the entire drainage system.