Why gasify your house?
The main reason is cheapness and convenience.
The difficult economic situation in the country is forcing owners of private houses to look for the most affordable option for heating the building. Therefore, it is not at all surprising that over time, cottage owners come to the conclusion that the building needs to be gasified. Yes, of course, you can heat your home with electricity. But such a solution is quite expensive, especially if you need to heat several hundred square meters. And the vagaries of nature in the form of strong winds or hurricanes can break the cables and you will have to sit for who knows how long without heating, food or hot water.
Another alternative to gas is the old and proven method - heating using a fireplace or brick oven. The main disadvantage of this solution is that storing firewood or coal will lead to dirt.
In addition, it will be necessary to allocate additional square meters for their storage. Therefore, blue fuel will occupy a leading position for many years to come, and the issue of designing a gas pipeline to connect the private sector will be relevant for a very long time.
Overview of hydraulic calculation programs
Example program for heating calculations
In fact, any hydraulic calculation of water heating systems is a complex engineering task. To solve this problem, a number of software packages have been developed that simplify this procedure.
You can try to make a hydraulic calculation of the heating system in Excel using ready-made formulas. However, the following problems may arise:
- Large error. In most cases, one-pipe or two-pipe schemes are taken as an example of the hydraulic calculation of a heating system. Finding similar calculations for a collector is problematic;
- To correctly account for the hydraulic resistance of the pipeline, reference data is required, which is not included in the form. They need to be searched for and entered additionally.
Considering these factors, experts recommend using calculation programs. Most of them are paid, but some have a demo version with limited features.
Oventrop CO
Hydraulic calculation program
The simplest and most understandable program for hydraulic calculations of a heating system. An intuitive interface and flexible settings will help you quickly understand the nuances of data entry. Minor problems may arise during the initial setup of the complex. It will be necessary to enter all the system parameters, from the pipe material to the location of the heating elements.
It is characterized by flexibility of settings, the ability to make simplified hydraulic heating calculations both for a new heating system and for modernizing an old one. It differs from analogues in its convenient graphical interface.
Instal-Therm HCR
The software package is designed for professional hydraulic resistance of a heating system. The free version has many limitations. Area of application: heating design in large public and industrial buildings.
In practice, for autonomous heat supply of private houses and apartments, hydraulic calculations are not always performed. However, this can lead to deterioration of the heating system and rapid failure of its elements - radiators, pipes and boiler. To avoid this, you need to timely calculate the system parameters and compare them with the actual ones to further optimize the heating operation.
Example of hydraulic calculation of a heating system:
Why gasify your house?
The main reason is cheapness and convenience. The difficult economic situation in the country is forcing owners of private houses to look for the most affordable option for heating the building. Therefore, it is not at all surprising that over time, cottage owners come to the conclusion that the building needs to be gasified.
Yes, of course, you can heat your home with electricity. But such a solution is quite expensive, especially if you need to heat several hundred square meters.
And the vagaries of nature in the form of strong winds or hurricanes can break the cables and you will have to sit for who knows how long without heating, food or hot water.
Modern gas pipelines are laid using durable and high-quality pipes and parts. Therefore, natural disasters are unlikely to harm such a structure
Another alternative to gas is an old and proven method - heating with a fireplace or stove. The main disadvantage of this solution is that storing firewood or coal will lead to dirt.
In addition, it will be necessary to allocate additional square meters for their storage. Therefore, blue fuel will occupy a leading position for many years to come.
Calculation of gas pipeline diameter online
When designing pipelines, the choice of pipe sizes is carried out on the basis of a hydraulic calculation that determines the internal diameter of the pipes to pass the required amount of gas with acceptable pressure losses or, conversely, the pressure loss when transporting the required amount of gas through log houses of a given diameter.
Resistance to gas movement in pipelines is composed of linear friction resistances and local resistances: friction resistances “work” along the entire length of pipelines, and local ones are created only at points of change in the speed and direction of gas movement (corners, tees, etc.). Detailed online hydraulic calculations of gas pipelines are carried out using the formulas given in SP 42-101–2003, which take into account both the mode of gas movement and the hydraulic resistance coefficients of gas pipelines. A shortened version is provided here.
The internal diameter of the gas pipeline is taken from the standard range of internal diameters of pipelines: the nearest larger one is for steel gas pipelines and the nearest smaller one is for polyethylene ones.
The calculated total gas pressure loss in low-pressure gas pipelines (from the gas supply source to the most remote device) is accepted to be no more than 1.80 kPa (including in gas distribution pipelines - 1.20 kPa), in gas inlet pipelines and internal gas pipelines - 0.60 kPa. To calculate the pressure drop, it is necessary to determine such parameters as the Reynolds number, which depends on the nature of the gas movement, and the coefficient of hydraulic friction λ. The Reynolds number is a dimensionless ratio that reflects the mode in which a liquid or gas moves: laminar or turbulent.
The transition from laminar to turbulent regime occurs upon reaching the so-called critical Reynolds number Rekp. At Re Reкp, turbulence may occur. The critical value of the Reynolds number depends on the specific type of flow. Programs for calculating gas flow by restriction devices (diaphragms). The calculation is performed on the basis of data obtained from traditional measuring systems (a restriction device equipped with recorders for pressure drop, pressure and temperature or a gas meter equipped with recorders for pressure and temperature).
Impact on gas consumption
Gas consumption is affected by the boiler power and the quality of the mixture.
Gas consumption depends on various factors. In large houses, boilers are installed that consume more fuel mixture than units in small buildings or apartments.
Fuel consumption is affected by:
- boiler power;
- outside temperature;
- quality of the gas mixture.
Some gas distribution companies supply undrained gas mixtures into the pipeline, which contain moisture and impurities. Calorie content decreases and volume consumed increases.
Installation methods and their features
A gas pipeline can be laid using various methods. This is underground, onshore or underwater installation. In buildings, network installation can be done hidden or open.
Each variety has its own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, before giving preference to any of the varieties, it is necessary to understand in detail all its features.
Advantages and disadvantages of the underground method
Until recently, the underground method was predominantly used when installing a gas pipeline. In this case, the pipes are laid in pre-dug trenches. Moreover, their depth must correspond exactly to the value specified in the project. Today this solution is used less and less.
The drop in demand is due to the high cost of this type of gasket. In addition, digging holes where the pipes will be laid will take quite a lot of time. Currently, engineers prefer the trenchless method. Its peculiarity lies in the use of equipment that can perform horizontal directional drilling.
Thanks to this, the cost of laying is reduced threefold, and the time required to organize the highway is reduced by at least two times.
The underground drilling method using HDD equipment eliminates the need to restore green spaces. Therefore, this kind of solution can be called as environmentally friendly as possible. Installation using this method involves drilling a pilot well, which is subsequently expanded to the required dimensions.
Next, the walls are strengthened using a special solution. To protect the pipeline from underground water flows and excessive mechanical loads, it is placed in a protective case. The final stage is pulling the pipes through the well.
External organization of the gas pipeline
The external method is used most often. In this case, the gas pipeline is usually stretched across the cottage yard. In this case, the structure must be protected from unauthorized persons. For this purpose, the pipes are located at a considerable height.
Particular attention should be paid to fixation. Fastenings must be as strong and reliable as possible to minimize the risk of falling and, as a result, damage to the gas pipe
Ground and overhead installation
Compared to the underground installation method, the above-ground installation will cost almost half as much
But in this case, special attention must be paid to protecting the structure from environmental influences and mechanical damage.
For example, the pipe must be insulated so that precipitation does not fall on it and temperature changes are not noticeable. Moreover, the type of protection is selected depending on the climatic conditions of the region.
To prevent unauthorized connection to the highway, it is necessary to take care of security. After all, due to the fact that the pipe lies on special supports on the ground, third parties can easily access it. Therefore, unlike underground installation, this solution is less reliable.
Which method of installing a gas pipeline is better?
It is necessary to give preference to one or another solution depending on the climate of the region where the work will be carried out, building density and soil characteristics. Accordingly, there is simply no clear answer.
To decide which installation method is best to choose, you should consider the following recommendations:
- If the soil on the site is highly corrosive, then the most correct solution would be to install the gas pipeline using the ground method.
- When the pipeline crosses a road, a combined option is economically viable. That is, in the area of the roadbed the pipe should be located above the ground, and in a suburban area it should be laid in trenches.
- In the case of laying a pipeline through adjacent areas, it is recommended to choose the above-ground (open) method.
- When a gas pipeline passes through an area with an extensive power transmission line system, a hidden installation of the pipeline would be a reasonable solution.
The installation method directly affects the material from which the pipeline should be made. The question related to which pipe and fittings to use in this or that case will be discussed further.
Water pipe capacity
Water pipes are the most commonly used pipes in a home. And since they are subject to a large load, calculating the throughput of the water main becomes an important condition for reliable operation.
Pipe patency depending on diameter
Diameter is not the most important parameter when calculating the patency of a pipe, but it also affects its value. The larger the internal diameter of the pipe, the higher the permeability, and also the lower the chance of blockages and plugs. However, in addition to the diameter, it is necessary to take into account the coefficient of friction of water on the pipe walls (tabular value for each material), the length of the line and the difference in liquid pressure at the inlet and outlet. In addition, the number of elbows and fittings in the pipeline will greatly influence the flow rate.
Table of pipe capacity by coolant temperature
The higher the temperature in the pipe, the lower its throughput, as the water expands and thereby creates additional friction.
For plumbing this is not important, but in heating systems it is a key parameter
There is a table for calculations of heat and coolant.
Table 5. Pipe throughput depending on the coolant and heat output
| Pipe diameter, mm | Bandwidth | |||
| By warmth | By coolant | |||
| Water | Steam | Water | Steam | |
| Gcal/h | t/h | |||
| 15 | 0,011 | 0,005 | 0,182 | 0,009 |
| 25 | 0,039 | 0,018 | 0,650 | 0,033 |
| 38 | 0,11 | 0,05 | 1,82 | 0,091 |
| 50 | 0,24 | 0,11 | 4,00 | 0,20 |
| 75 | 0,72 | 0,33 | 12,0 | 0,60 |
| 100 | 1,51 | 0,69 | 25,0 | 1,25 |
| 125 | 2,70 | 1,24 | 45,0 | 2,25 |
| 150 | 4,36 | 2,00 | 72,8 | 3,64 |
| 200 | 9,23 | 4,24 | 154 | 7,70 |
| 250 | 16,6 | 7,60 | 276 | 13,8 |
| 300 | 26,6 | 12,2 | 444 | 22,2 |
| 350 | 40,3 | 18,5 | 672 | 33,6 |
| 400 | 56,5 | 26,0 | 940 | 47,0 |
| 450 | 68,3 | 36,0 | 1310 | 65,5 |
| 500 | 103 | 47,4 | 1730 | 86,5 |
| 600 | 167 | 76,5 | 2780 | 139 |
| 700 | 250 | 115 | 4160 | 208 |
| 800 | 354 | 162 | 5900 | 295 |
| 900 | 633 | 291 | 10500 | 525 |
| 1000 | 1020 | 470 | 17100 | 855 |
Table of pipe capacity depending on coolant pressure
There is a table describing the capacity of pipes depending on pressure.
Table 6. Pipe capacity depending on the pressure of the transported liquid
| Consumption | Bandwidth | ||||||||
| Du pipe | 15 mm | 20 mm | 25 mm | 32 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm | 65 mm | 80 mm | 100 mm |
| Pa/m – mbar/m | less than 0.15 m/s | 0.15 m/s | 0.3 m/s | ||||||
| 90,0 – 0,900 | 173 | 403 | 745 | 1627 | 2488 | 4716 | 9612 | 14940 | 30240 |
| 92,5 – 0,925 | 176 | 407 | 756 | 1652 | 2524 | 4788 | 9756 | 15156 | 30672 |
| 95,0 – 0,950 | 176 | 414 | 767 | 1678 | 2560 | 4860 | 9900 | 15372 | 31104 |
| 97,5 – 0,975 | 180 | 421 | 778 | 1699 | 2596 | 4932 | 10044 | 15552 | 31500 |
| 100,0 – 1,000 | 184 | 425 | 788 | 1724 | 2632 | 5004 | 10152 | 15768 | 31932 |
| 120,0 – 1,200 | 202 | 472 | 871 | 1897 | 2898 | 5508 | 11196 | 17352 | 35100 |
| 140,0 – 1,400 | 220 | 511 | 943 | 2059 | 3143 | 5976 | 12132 | 18792 | 38160 |
| 160,0 – 1,600 | 234 | 547 | 1015 | 2210 | 3373 | 6408 | 12996 | 20160 | 40680 |
| 180,0 – 1,800 | 252 | 583 | 1080 | 2354 | 3589 | 6804 | 13824 | 21420 | 43200 |
| 200,0 – 2,000 | 266 | 619 | 1151 | 2486 | 3780 | 7200 | 14580 | 22644 | 45720 |
| 220,0 – 2,200 | 281 | 652 | 1202 | 2617 | 3996 | 7560 | 15336 | 23760 | 47880 |
| 240,0 – 2,400 | 288 | 680 | 1256 | 2740 | 4176 | 7920 | 16056 | 24876 | 50400 |
| 260,0 – 2,600 | 306 | 713 | 1310 | 2855 | 4356 | 8244 | 16740 | 25920 | 52200 |
| 280,0 – 2,800 | 317 | 742 | 1364 | 2970 | 4356 | 8566 | 17338 | 26928 | 54360 |
| 300,0 – 3,000 | 331 | 767 | 1415 | 3076 | 4680 | 8892 | 18000 | 27900 | 56160 |
Procedure for laying a gas pipeline
Despite the fact that pipe installation should be carried out exclusively by professionals with the necessary qualifications, every owner of a private house should familiarize himself in detail with the procedure for carrying out the work. This will avoid troubles and unplanned financial expenses.
Installation of the riser and preparation of the premises
If a private house is gasified for the purpose of organizing heating, then you need to take care of the arrangement of the premises. The room with all the equipment should be separate and have fairly good ventilation. After all, natural gas is not only explosive, but also toxic to the human body.
As for the dimensions, the ceiling height in the room should be at least 2.2 m. For a kitchen where a stove with two burners will be installed, an area of 8 m2 will be sufficient, and for a four-burner model - 15 m2.
If equipment with a power of more than 30 kW will be used to heat the house, then the boiler room must be moved outside the house and be a separate building.
Gas is supplied to the cottage through an input device, which is a hole above the foundation. It is equipped with a special case through which the pipe passes. One end of it is connected to the riser, and the other is part of the internal gas supply system.
The riser is installed exactly vertically and the structure must be removed from the wall at a distance of at least 15 cm. The reinforcement can be secured using special hooks.
Subtleties of internal system construction
When installing a pipeline in a wall, all its parts must be passed through sleeves. In this case, the entire structure must be coated with oil paint. The free space present between the pipe and the sleeve is filled with tarred tow and bitumen.
Each of the units is assembled at the bottom, and at the height only the fastening of the preparatory components is carried out. If the diameter of the pipes does not exceed 4 cm, then they can be secured using clamps or hooks. For all others, it is recommended to use brackets or hangers.
Welding, assembly and acceptance rules
The following article, which examines in detail the options for heating units, will introduce you to the specifics of organizing autonomous gas heating. Independent craftsmen will find the boiler piping diagrams given in the material we recommend useful.
All components of the pipeline are connected to each other by welding. In this case, the seam must be of high quality and reliable. To achieve this, you must first align the end of the pipe and strip about 1 cm from each side.
As for assembling threaded connections, you need to use a special technique for this. First, the joint is processed using whitewash. The next step is to wind long-fiber flax or special tape. Only after this can the threaded connection be tightened.
As soon as the craftsmen finish the work, a commission should come to the house. She carries out pressure testing of the gas pipeline and checks the quality of installation. Moreover, the owner is required to be instructed on the rules for using the gas pipeline. Employees will also tell you how to properly operate equipment that consumes blue fuel.
What documents will be needed?
Before proceeding directly with the installation, you will have to start collecting the necessary papers. To do this as quickly as possible, you must immediately prepare a passport, as well as documentation that confirms ownership of the plot and the house located on it.
The next step is to submit an application to the appropriate service. It expresses a desire to gasify the house. Employees will issue a form listing all technical conditions.
The document issued by the gas service is filled out by the specialist involved in drawing up the project. Choose a qualified designer. After all, the result of work and the safety of residents depend on his competence.
According to the project, a gas network is being installed. Sometimes pipes are laid through neighbors' properties. In this case, it is necessary to request written permission from them to carry out this type of work.
In addition to the papers listed above, you will also need to obtain the following documents:
- act of putting gas-powered equipment into operation;
- agreement on the preparation of technical documentation and work;
- permission to supply natural gas and pay for this service;
- document on installation of equipment and gasification of the house.
A chimney inspection will also be required. After this, specialists will issue a corresponding certificate. The last document - permission to gasify a private house - is issued by a local architectural and planning company.
Selection of pipes and fasteners
Since the pipeline with blue fuel is an object of increased danger, all fittings used must have the necessary quality certificates. Otherwise, the commission conducting the final inspection will not allow the house with such pipes to be gasified.
Nuances of choosing material
The pipe material is selected depending on the method of laying the pipeline. Products made of polyethylene and steel are in greatest demand. The main advantage of the latter variety is its versatility. After all, steel pipes can be used for both underground and external installation. But such a solution will cost more.
The polymer pipeline can only be used for hidden installation. This is due to the fact that under the influence of the sun the material decomposes and quickly loses its properties.
As for the fastening elements, for installation you will need angles, couplings, tees, crosses, plugs and adapters. As a rule, they are made of cast iron, steel or polyethylene.
Also, do not hesitate to install the meter. After all, it will significantly reduce costs.
Advantages of polyethylene pipes
First of all, such fittings do not rust over time. Therefore, it allows you to save on pipeline maintenance and repair. Thanks to a special production technology, polyethylene products have an absolutely smooth inner surface. As a result, the fuel flow rate is not slowed down in any way.
One of the main advantages of polymer pipes is their safety. There will be no stray currents in them that could cause the gas to explode. So in case of underground installation there is no need to use a special expensive case.
If we compare the weight of a steel pipe and a polymer pipe, the latter type is as much as 7 times lighter. This property makes it possible to significantly reduce the cost of construction, because there is no need to involve equipment with increased load capacity.
If all standards are met, a polyethylene pipeline will last at least half a century. Moreover, over time, its performance characteristics will not deteriorate in any way.
Pipes made of polyethylene, due to their flexibility, have earned the respect of specialists. Due to this, installation using the horizontal directional drilling method will not cause any difficulties or problems. This solution is especially relevant when the well has an uneven shape or any obstacles were discovered during its creation.
When should you stop using polymer?
In some cases, polyethylene products will be a poor choice. Limiting conditions include a situation where the ground temperature in winter can drop below -15 degrees.
Plastic pipelines should be abandoned in regions where there is a risk of an earthquake with a magnitude greater than 7 on the Richter scale
The use of polymer reinforcement is also prohibited in the following situations:
- the pipeline will supply liquefied hydrocarbons;
- an open installation method was chosen;
- if the gas pipeline passes over any obstacles (railway or highway).
After all the necessary products have been purchased and the documents have been collected, you can understand the features of laying a line with blue fuel.
PS for sewerage
PS for sewerage depends on the wastewater disposal system used: pressure or gravity.
The basis for determining the PS involves the laws of hydraulic science. To calculate the PS of a sewer system, you will need not only complex formulas for calculation, but also tabular information. To determine the volumetric flow rate of liquid, a formula of the following form is taken:
q=a*v;
where, a – flow area, m2;
v—movement speed, m/s.
The flow area a is the cross section perpendicular at each point to the particle velocity of the fluid flow. This value is also known as the live flow cross section. To determine the specified value, the formula is used: a = π*R2. The value of π is constant and equals 3.14. R is the radius of the pipe squared. To find out the speed at which the flow moves, you will need to use the following formula:
v = C√R*i;
where, R – hydraulic radius;
C – wetting coefficient;
I – slope angle.
To calculate the slope angle you will need to calculate I=v2/C2*R. To determine the wetting coefficient, you need to use the following formula: C=(1/n)*R1/6. The n value is the pipe roughness coefficient, equal to 0.012-0.015. To determine R, the formula is used:
R=A/P;
where, A – cross-sectional area of the pipeline;
P – wetted perimeter.
The wetted perimeter is the line along which the flow in cross section comes into contact with the solid walls of the channel. To determine the value of the wetted perimeter in a round pipe, you will need to use the following formula: λ=π*D.
The table below presents the parameters for calculating the PS of wastewater sewer pipelines using a gravity or free-flow method. The information is selected depending on the diameter of the pipe, and then substituted into the appropriate formula.
If you need to calculate the PS of the sewer system for pressure systems, then the data is taken from the table below.
Methods for hydraulic calculation of gas pipelines
When designing pipelines, the choice of pipe sizes is carried out on the basis of a hydraulic calculation that determines the internal diameter of the pipes to pass the required amount of gas with acceptable pressure losses or, conversely, the pressure loss when transporting the required amount of gas through log houses of a given diameter.
Resistance to gas movement in pipelines is composed of linear friction resistances and local resistances: friction resistances “work” along the entire length of pipelines, and local ones are created only at points of change in the speed and direction of gas movement (corners, tees, etc.). Detailed hydraulic calculations of gas pipelines are carried out according to the formulas given in SP 42-101-2003, which take into account both the mode of gas movement and the hydraulic resistance coefficients of gas pipelines. A shortened version is provided here.
To calculate the internal diameter of the gas pipeline, use the formula:
where dp is the design diameter, cm; A, t, t1 - coefficients depending on the category of the network (pressure) and the material of the gas pipeline; Q0—calculated gas flow, m3/h, under normal conditions; йРу - specific pressure loss (Pa/m for low pressure networks
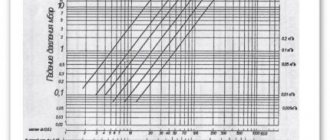
Here ARdop is the permissible pressure loss (Pa); L - distance to the most distant point, m. Coefficients A, t, t1 are determined from the table below.
The internal diameter of the gas pipeline is taken from the standard range of internal diameters of pipelines: the nearest larger one is for steel gas pipelines and the nearest smaller one is for polyethylene ones.
The calculated total gas pressure loss in low-pressure gas pipelines (from the gas supply source to the most remote device) is accepted to be no more than 1.80 kPa (including in distribution gas pipelines - 1.20 kPa), in gas inlet pipelines and internal gas pipelines - 0.60 kPa.
To calculate the pressure drop, it is necessary to determine such parameters as the Reynolds number, which depends on the nature of the gas movement, and the coefficient of hydraulic friction A. The Reynolds number is a dimensionless ratio that reflects the mode in which the liquid or gas moves: laminar or turbulent.
The transition from laminar to turbulent regime occurs upon reaching the so-called critical Reynolds number ReKp. At Re ReKp, turbulence may occur. The critical value of the Reynolds number depends on the specific type of flow. The Reynolds number as a criterion for the transition from laminar to turbulent flow regimes and vice versa works relatively well for pressure flows. When transitioning to free-flow flows, the transition zone between laminar and turbulent regimes increases, and the use of the Reynolds number as a criterion is not always valid.
Table 5.1. Coefficient values depending on the gas pipeline material
Comments
| What did you like?: Thank you so much for such a rare program!) What needs to be changed?: I would like to download a portable program in case there is no network access What didn’t you like?: no mobile app |
Mass flow of gas Length of gas pipeline Number of pipes (looping) Gas temperature Permissible pressure drop Coefficient of kinematic viscosity To calculate the internal diameter of a low-pressure gas pipeline, enter the necessary parameters for calculation and click the “Calculate” button Internal diameter of the SPBT gas pipeline (Propane-Butane)
Why gasify your house?
The main reason is cheapness and convenience. The difficult economic situation in the country is forcing owners of private houses to look for the most affordable option for heating the building. Therefore, it is not at all surprising that over time, cottage owners come to the conclusion that the building needs to be gasified.
Yes, of course, you can heat your home with electricity. But such a solution is quite expensive, especially if you need to heat several hundred square meters. And the vagaries of nature in the form of strong winds or hurricanes can break the cables and you will have to sit for who knows how long without heating, food or hot water.
Another alternative to gas is the old and proven method - heating using a fireplace or brick oven. The main disadvantage of this solution is that storing firewood or coal will lead to dirt.
In addition, it will be necessary to allocate additional square meters for their storage. Therefore, blue fuel will occupy a leading position for many years to come, and the issue of designing a gas pipeline to connect the private sector will be relevant for a very long time.
Selection of pipes and fasteners
Since the pipeline with blue fuel is an object of increased danger, all fittings used must have the necessary quality certificates. Otherwise, the commission conducting the final inspection will not allow the house with such pipes to be gasified.
Nuances of choosing material
The pipe material is selected depending on the method of laying the pipeline. Products made of polyethylene and steel are in greatest demand. The main advantage of the latter variety is its versatility. After all, steel pipes can be used for both underground and external installation. But such a solution will cost more.
As for the fastening elements, for installation you will need angles, couplings, tees, crosses, plugs and adapters. As a rule, they are made of cast iron, steel or polyethylene.
Also, do not hesitate to install the meter. After all, it will significantly reduce costs.
Advantages of polyethylene pipes
First of all, such fittings do not rust over time. Therefore, it allows you to save on pipeline maintenance and repair. Thanks to a special production technology, polyethylene products have an absolutely smooth inner surface. As a result, the fuel flow rate is not slowed down in any way.
One of the main advantages of polymer pipes is their safety. There will be no stray currents in them that could cause the gas to explode. So in case of underground installation there is no need to use a special expensive case.
If we compare the weight of a steel pipe and a polymer pipe, the latter type is as much as 7 times lighter. This property makes it possible to significantly reduce the cost of construction, because there is no need to involve equipment with increased load capacity.
Pipes made of polyethylene, due to their flexibility, have earned the respect of specialists. Due to this, installation using the horizontal directional drilling method will not cause any difficulties or problems. This solution is especially relevant when the well has an uneven shape or any obstacles were discovered during its creation.
When should you stop using polymer?
In some cases, polyethylene products will be a poor choice. Limiting conditions include a situation where the ground temperature in winter can drop below -15 degrees.
The use of polymer reinforcement is also prohibited in the following situations:
- the pipeline will supply liquefied hydrocarbons;
- an open installation method was chosen;
- if the gas pipeline passes over any obstacles (railway or highway).
After all the necessary products have been purchased and the documents have been collected, you can understand the features of laying a line with blue fuel.
Reducing gas consumption
Saving gas is directly related to reducing heat loss. Enclosing structures such as walls, ceilings, and floors in the house must be protected from the influence of cold air or soil. Automatic adjustment of the operation of heating equipment is used for the effective interaction of the external climate and the operating intensity of the gas boiler.
Insulation of walls, roofs, ceilings
You can reduce gas consumption by insulating walls
The outer heat-protective layer creates a barrier to cooling surfaces in order to consume the least amount of fuel.
Statistics show that part of the heated air escapes through structures:
- roof - 35 - 45%;
- non-insulated window openings - 10 - 30%;
- thin walls - 25 - 45%;
- entrance doors - 5 - 15%.
Floors are protected with a material that has acceptable moisture permeability according to the norm, since when wet, the thermal insulation characteristics are lost. It is better to insulate the walls from the outside; the ceiling is insulated from the attic side.
Window replacement
Plastic windows let in less heat in winter
Modern metal-plastic frames with double- and triple-glazed windows do not allow air flow to pass through and prevent drafts. This leads to a reduction in losses through the gaps that existed in old wooden frames. For ventilation, tilt-and-turn mechanisms are provided for the doors, which contribute to the economical consumption of internal heat.
The glass in the structures is covered with a special energy-saving film, which allows ultraviolet and infrared rays to pass through, but prevents their reverse penetration. The glass is equipped with a network of elements that heat the area to thaw snow and ice. Existing frame structures are additionally insulated with plastic film on the outside or thick curtains are used.
other methods
It is beneficial to use modern gas-fuelled condensing boilers and install an automated coordination system. Thermal heads are installed on all radiators, and a hydraulic arrow is mounted on the unit’s piping, which saves 15–20% of heat.
Detectors and temperature regulators are installed in the heating system, which regulate the boiler power depending on the state of the external climate. If the weather is warm outside, it is more efficient and economical to switch to heating with air conditioners.
Source
Why is it necessary to calculate a gas pipeline?
Throughout all sections of the gas pipeline, calculations are carried out to identify places where possible resistance is likely to appear in the pipes, changing the fuel supply rate.
If all the calculations are done correctly, then you can select the most suitable equipment and create an economical and efficient design for the entire gas system design.
This will eliminate unnecessary, inflated indicators during operation and costs in construction, which could occur when planning and installing the system without hydraulic calculations of the gas pipeline.
There is a better opportunity to select the required cross-sectional size and pipe materials for a more efficient, fast and stable supply of blue fuel to the planned points of the gas pipeline system.
The optimal operating mode of the entire gas pipeline is ensured.
Developers receive financial benefits by saving on the purchase of technical equipment and building materials.
The gas pipeline is correctly calculated taking into account the maximum levels of fuel consumption during periods of mass consumption. All industrial, municipal, individual and household needs are taken into account.
Calculation of liquefied gas consumption
Calculating gas using propane or butane has its own characteristics, but is not particularly difficult. What matters is the density of the flammable substance, which changes with increasing or decreasing temperature and depends on the composition of the gas mixture. Only the weight of the liquefied fuel remains constant.
The volume of gas used differs in winter and summer, so it makes no sense to use m³ units to determine the consumption of liquefied gas per 1 kW of heat; kilograms are taken for designation, which do not change with the change of seasons.
Calculation for 1 kW of heat
The amount is calculated for heating the house and heating the water in the system. If you cook food using gas, this needs to be taken into account additionally.
The formula used is Q = (169.95 / 12.88) F, where:
- Q—fuel mass;
- 169.95 - annual amount of kW for heating 1 m² of a house;
- 12.88 - calorific value of propane;
- F is the quadrature of the structure.
The resulting value is multiplied by the cost of 1 kg of liquefied mixture to calculate the cost of purchasing the required quantity. The price is usually given per 1 kg and not per 1 m³, which should be taken into account.
How to calculate the diameter of a gas pipeline?
When drawing up a project, special attention is paid to the diameter of the pipe. This will be done by the designer using complex formulas or a program
In order not to bother yourself with various formulas, a good choice would be to use one of the specialized programs. Fortunately, the Internet is full of such software. Using calculators is as easy as pie—you just need to fill in the fields with the appropriate information.
Standard prices for connecting a private household to main gas are given here. Owners of suburban areas should know “how much” gasification will cost.
Main types of gas pipelines
There are three types of highways. The first is a low pressure gas pipeline. For such a system, the maximum permissible pressure is 5 kPa. Most often, this type is laid in small settlements. It is also used for gas supply to medical institutions, residential buildings, children's and public buildings.
For the second type - medium pressure line - the fuel flow can be supplied with a force of up to 0.3 MPa. The scope of application of this type is limited to the provision of gas to quarterly and regional regulatory stations.
As for the high-pressure line, it is intended for supplying fuel to large industrial enterprises. For owners of private houses, such a solution is irrelevant. After all, gas is supplied to the cottage using a pipe, the pressure in which does not exceed 5 kPa.
Details about pressure parameters and the classification of gas pipeline networks according to their value are written in the article, the contents of which we recommend that you familiarize yourself with.
Classification of gas pipes
Different pipes are used for different class systems. The state standards for them are:
- For gas pipelines with low or medium pressure, electric-welded straight-seam general-purpose pipes are used;
- For systems with high levels, electric-welded straight-seam and seamless hot-rolled are allowed.
The choice of material is also influenced by the installation method.
- For underground utilities, both steel and polyethylene products are the norm.
- For overhead structures, only steel ones are allowed.
- In the house, both private and multi-story, steel and copper pipelines are used. The connection is assumed to be welded. Flange or threaded is permitted only in areas where shut-off valves and devices are installed. The copper pipeline allows connection to press fittings.
The photo shows an example.
Dimensions
GOST allows two types of gas pipes in an apartment. The products belong to general-purpose products, since complete gas tightness and mechanical strength are important here, while resistance to pressure is of little significance: 0.05 kgf/cm2 is a modest value.
- The parameters of the steel pipeline are as follows.
- The outer diameter of the steel pipe can range from 21.3 to 42.3 mm.
- The nominal bore ranges from 15 to 32 mm.
- The choice is made depending on the volume of supply: a gas appliance in an apartment or a riser in a house.
- The diameter of the copper pipeline is selected in the same way. The advantage of this option is simpler installation - with press fittings, anti-corrosion material and attractive appearance. According to the standard, copper products must comply with GOST R 50838-95, other materials are not permitted.
- The diameter of gas pipes for mains with pressure from 3 to 6 kgf/cm2 varies in a much larger range - from 30 to 426 mm. The thickness of the walls depends on the diameter: from 3 mm for small sizes, to 12 mm for diameters over 300 mm.
- When constructing an underground gas pipeline, GOST allows the use of gas pipelines made of low-density polyethylene. The material is designed for pressure up to 6 kgf/cm2. The diameter of the plastic pipe varies from 20 to 225 mm. The photo shows a gas pipeline made of HDPE.
The pipeline is laid in the trench only in ready-made sections, so installing the pipeline is an expensive and time-consuming job. When turning, steel gas pipes are cut and connected through special elements. Polyethylene allows bends: for systems with pressure from 3 to 6 kgf/cm2 up to 25 outer diameters, with values up to 0.05 kgf/cm2 - up to 3. Together with greater lightness and high corrosion resistance, this makes the option with a plastic pipeline increasingly attractive .
Norms and standards for pipe laying
Gas enters residential buildings through inlets coming from fuel distribution stations. As a rule, they are installed on the ground floor and then laid along the staircases. The pipe that is supplied to a residential building must be manufactured using a seamless method, and its wall thickness is at least 3.5 mm.
When connecting the main line to a private house, it must be located at a distance of at least 15 cm from the water supply and heating pipes. In the case of telephone or electrical cables, this value increases to half a meter.
The gas pipeline is predominantly made of steel. Therefore, to prevent pipe corrosion, it is coated with a special insulating material. Thanks to this, the structure does not come into contact with wet soil.
Laying methods
The technical characteristics of the gas pipeline are regulated by the relevant GOST. The material is selected based on the category of the system, that is, the value of the supply pressure, and the installation method: underground, above-ground or installation inside the building.
- Underground is the safest, especially when it comes to high-pressure lines. Depending on the class of the gas mixture being transferred, installation is carried out either below the ground freezing level - wet gas, or from 0.8 m to ground level - dry gas.
- Aboveground - implemented in case of unavoidable obstacles: residential buildings, ravines, rivers, canals, and so on. This installation method is allowed on factory premises.
- Gas pipeline in the house - installation of the riser, as well as the gas pipe in the apartment, is carried out only in the open way. It is allowed to place communications in grooves, but only if they are interrupted by easily removable shields. Simple and quick access to any part of the system is an indispensable condition for security.
Main types of gas pipelines
There are three types of highways. The first is a low pressure gas pipeline. For such a system, the maximum permissible pressure is 5 kPa. Most often, this type is laid in small settlements. It is also used for gas supply to medical institutions, residential buildings, children's and public buildings.
For the second type - medium pressure line - the fuel flow can be supplied with a force of up to 0.3 MPa. The scope of application of this type is limited to the provision of gas to quarterly and regional regulatory stations.
As for the high-pressure line, it is intended for supplying fuel to large industrial enterprises. For owners of private houses, such a solution is irrelevant. After all, gas is supplied to the cottage using a pipe, the pressure in which does not exceed 5 kPa.
Details about pressure parameters and the classification of gas pipeline networks according to their value are written in the article, the contents of which we recommend that you familiarize yourself with.
On the classification of gas pipelines
The need to classify gas pipelines came into our lives with the widespread spread of technologies for using gas for the needs of the population. Heating of residential, administrative, and industrial buildings, the use of gas both in cooking and in production has long become an everyday thing for us.
Main gas pipeline
The classification of gas pipelines is the necessary measures and rules for systematizing the laying of gas pipelines. Gas communications can differ both in their purpose and in a number of indicators, such as: pressure, the material from which it is made, location, volumes of transported gas and others.