Nowadays, polyethylene (PE) pipes are used to install good and cheap water supply and sewerage systems. These products are easily replacing iron, asbestos-cement and other analogues. Regulates the production of polyethylene pipes GOST 18599 2001. This regulatory document also contains technical standards and requirements that apply to the final product. By the way, if you are interested in a compression flange for HDPE pipes, go to the website ingplast.ru. Flange-type pipe connections are used for organizing irrigation systems and drip irrigation systems, for indoor water supply systems, and for free-flow sewers.
In most cases, polyethylene pipes become an excellent alternative to heavy metal products
Characteristics of polyethylene pipes
All polypropylene pipes are characterized by general operational and technical characteristics. But, not paying attention to this, some types of products of this type have their own characteristics. The characteristic features of PE products include: the warranty period for the operation of polyethylene pipes GOST 18599 2001 is 50 years and the improvement of the parameters for transporting the operating environment over a certain period of time.
The throughput of a polyethylene pipeline increases for two main reasons:
- The boundary layer of the polymer material increases over a certain time. Thanks to this, a peculiar effect of upper flexibility appears, thanks to it, the resistance to movement is reduced, and the conditions for flow around the pipe walls are constantly improved.
- Corrosive growth of a metal pipe leads to a decrease in its internal diameter. In addition, due to the characteristic creep property of polymer ethylene, the flow area of a product made from this material increases during operation without compromising its performance. In numbers, the increase looks like this: about 10% during the first 10 years and about 3% during the entire service life of the pipeline.
The wide operating temperature range is another major advantage. The polyethylene pipe, which meets the requirements of GOST 18599 2001, does not lose its characteristics in operation at a significant low temperature (-70? C) and maintains its strength at +60? C. When this mark is exceeded, the strength of the PE decreases and it loses the ability to withstand high pressure.
Resistance to high pressure and low temperatures makes it possible to use polyethylene pipes for laying underground networks without any insulation
The decrease in the value of this indicator for pipes made of polymer ethylene, depending on the temperature of the operating environment, is presented in Table No. 1.
Table 1
| Liquid temperature, ? C | Pressure reduction coefficient, Ct. | ||
| PE 100, PE 80 | PE 63 | PE 32 | |
| 36-40 | 0,74 | 0,62 | 0,3 |
| 31-35 | 0,8 | 0,72 | 0,47 |
| 26-30 | 0,87 | 0,81 | 0,65 |
| 21-25 | 0,93 | 0,9 | 0,82 |
| Less than 20 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 |
The plasticity of pipes, in addition to ease of installation, has a good effect on the transportation of such products. It is allowed to deliver pipes with a diameter of no more than 160 mm to the consumer in coils longer than 200 meters. You can cut them with an ordinary hacksaw. Utility networks are assembled from such pipes using specialized couplings, connectors and other parts.
Important! Exposure to direct sunlight causes aging of polymer ethylene. Due to this, pipes made of polymer material stabilized with soot should be used in external communications.
Classification of HDPE material
High-density polyethylene can be of different types depending on changes in manufacturing technology. At the same time, it may contain in its mass all kinds of impurities, which are both products of the reaction and residues of related substances: Suspension PVP may contain various chemical stabilizers that form a suspension mass from granules during cold polymerization of ethylene. These can be non-aggressive acids, light metal oxides, polymer alcohols and even some types of clay. This plastic is of the highest quality, homogeneous, without structural damage or weak areas. Solution polyethylene often contains proportions of catalysts present in the "hot" polymerization reaction. Gas-phase contains residues of gases and essential substances. Of all three types, it has the weakest structure, since it is relatively heterogeneous and includes the presence of areas less resistant to wear.
ATTENTION! Due to the presence of foreign elements and substances in HDPE (especially catalysts), it is most often used for industrial purposes, where strength is a more important factor than environmental friendliness and non-toxicity.
State regulations and their requirements
The technical specifications of polyethylene pipes are regulated by the standards listed below:
- GOST 18599 2001. It contains requirements for PE pressure pipes used for transporting water (including domestic and drinking water supply) with a temperature of 0? T? 40? C. This GOST does not apply to polymer pipe products prepared for the movement of flammable gases and for electrical installation work.
- GOST 22689 89 describes the characteristics of pipes and fittings for them, made of LDPE and HDPE (these abbreviations denote, based on this, polymer ethylene of high and low pressure). This standard covers only those products that are used in internal sewage systems of buildings with the highest stable drain temperature of +60 degrees and short-term (up to 1 minute) +95? C.
Pipes with thick walls and large diameters are not rolled into coils, but are supplied only in straight pieces of standard length
The melt fluidity, determined from the material of the finished product, should be no more than 2 g/10 min. The surface of the pipes must be flat and smooth. On the surface from the outside, traces of no more than 0.5 mm in size from the calibrating and shaping tool are allowed. Pipes of this type cannot be rolled into coils. GOST 22689 89 does not regulate deviations from straightness.
After heating the pipes, the change in their dimensions in the longitudinal direction should not be more than 3%. These products should not crack in a 20 percent solution of the additional substance OP-10, established in GOST 8433 81, within 24 hours after heating to 80±3 degrees. The connection of PE pipes GOST 18599 2001 with fittings will be considered impermeable if it successfully passes testing with an internal hydrostatic pressure of 1 kgf/m 2 (0.1 MPa) at a temperature of +15 ± 10 degrees. Pipes, as well as shaped parts, should be produced from HDPE melt with a fluidity criterion determined by GOST 16338. If LDPE is the raw material, then the value of this parameter is regulated by GOST 16337. In general, the range of values of the fluidity indicator is: 0.25? PT ?1.5. Measurement unit – g/10 min.
GOST R 50838 of 1995 takes into account the production of polyethylene gas pipeline pipes in coils, straight sections and on reels. But with one clarification: products with a diameter of 225 and 200 mm are produced exclusively in sections, their length fluctuates in the range of 5?L?24 meters with a step ratio of adjacent values of 0.5 m. The possible deviation of the length from the nominal value is no more than 1 percent.
On a note! In one batch, GOST 18599 2001 allows the presence of pipes with a length of 5 3 ? L ? 5 meters at least 5% of the total volume.
With regard to manufacturing in coils and on coils, the maximum deviation criterion looks like this:
- pipe length up to 500 mm – no more than 3 percent;
- pipe length from 500 mm - no more than 1.5 percent.
The length of pipes supplied in coils differs from the standard length as agreed with the customer
The production of polyethylene pipe products of other lengths and with other maximum deviations is permitted solely by agreement with the customer. The criterion for low long-term strength depends on the type of product and is used when calculating the operating pressure of the pipeline. Its designation has 3 Latin letters MRS, followed by numbers. Polymer ethylene grade PE 100 is marked MRS 10.0 MPa, PE 80 - MRS 8.0 MPa and PE 63 - MRS 6.3 MPa.
Briefly about the main thing
HDPE pipes are made from ethylene at low pressure. This can be primary or secondary raw materials.
Products are marked using letters, numbers and pigment indication. The exception is technical products, which are solid black.
The wide range of sizes is due to the applicability of HDPE pipes for transporting liquids and gases indoors and outdoors.
The technical characteristics allow for the installation of water supply, gas supply, sewerage, and insulation channels for electrical networks.
Read later
We will send the material by email
Brand differences
For the first time, PE 63 was used for the manufacture of polypropylene pipes. Its very high temporary strength is not able to overcome its low crack resistance. Also, with long-term use, the strength characteristics of the material decrease significantly. Thanks to this, in our time the production of pressure pipes made of PE 63 according to GOST 18599 2001 has sharply decreased. Today, consumers hold products made from PE 80 and 100 in high esteem, with the latter being the most popular. This is caused by the following factors:
- The density, which is quite higher than that of PE 80, makes it possible to produce pipes with a smaller wall thickness, without compromising the ability to maintain the set operating pressure.
- Capacity is 20 percent higher and pressure loss is 30 percent lower than in a PE 80 pipe of the same nominal diameter.
- The weight of one linear meter is twenty percent less than that of a PE 80 pipe that can withstand the same pressure. This point ensures a reduction in the costs of transportation and installation of pipelines.
- The criteria for resistance to fast and slow cracking are several times higher than those of similar products made from PE 80.
- Quite high resistance to frost and resistance to a wide variety of damage caused by mechanical means are excellent features of PE 100 pipes.
- During the production of large-section pipes from PE 100, a large reduction in material consumption is achieved due to a reduction in the outer diameter without loss of throughput.
- Most pipes of small diameter are made from PE 80.
Pipes of very high strength are made from polymer ethylene grade PE 100
Advantages over steel pipes
As mentioned above, a polyethylene pipe is guaranteed to last about fifty years. Such an operational period is possible due to the following features of PE/pipes:
- there is no need for electrochemical protection against corrosion, which is why such products require almost no maintenance;
- High chemical and rust resistance. Polyethylene pipes are not afraid of contact with an aggressive environment;
- the possibility of scale formation on the surface inside is excluded;
- low thermal conductivity reduces the level of heat loss and reduces the formation of condensation on the surface on the outside;
- Even if the liquid in the polyethylene pipeline freezes, it will not break. The pipe will simply increase in size, and after thawing the working environment it will return to its previous size;
- low elastic modulus reduces the risk of hydraulic shocks;
- welded seams of connections maintain their strength throughout the entire operational period of polyethylene pipes (GOST 18599 2001);
- butt welding is easier, requires less time and is much cheaper;
- multiple secondary installation is possible;
- polyethylene pipe is a reliable shield against bacteria and microorganisms. The construction and reconstruction of utility networks using pipe products of this type will not be very expensive - 40% compared to conventional methods.
Important! Polyethylene pipes weigh 5-7 times less than steel pipes. Thanks to this, the small movements necessary during their installation are made without the use of lifting mechanisms.
The most important advantage of PE pipes is their ease of installation both in domestic conditions and in industry.
Areas of application
Pipelines made of low-density polyethylene are used in all areas of our lives:
- infrastructure of cities and towns;
- construction;
- technological industrial communications;
- agricultural engineering communications;
- oil and gas complex;
- communications of railways, airfields.
HDPE pipes of various sizes are used for water and gas pipelines, sewer systems, drainage, storm drains, laying electrical power, telephone, and information networks.
The spread of polyethylene pipelines is limited only by its instability to ultraviolet radiation, elevated temperatures and lower strength compared to steel: plastic still does not reach the strength of metals.
SDR criterion for polyethylene pipes
When purchasing these products, great attention should be paid to the markings applied to them. It has the following information about a specific pipe:
- information about the manufacturer;
- The standards in accordance with the requirements of which it was manufactured;
- brand of polymer ethylene, for example, PE 100;
- thickness of the material of the walls of the product and its diameter;
- the abbreviation SDR followed by a certain index. This is a strength criterion that provides the most accurate information about the capabilities of tubular products
The abbreviation SDR comes from the English term Standard Dimension Ratio, which in Russian translation sounds like this: Normal Dimensional Indicator. Its value is calculated by dividing the outer diameter by the wall thickness of the polyethylene pipe GOST 18599 2001.
SDR = Outside Diameter/Wall Thickness.
A simple analysis of this formula shows that products with a small SDR index have much thicker walls, and, conversely, a thin-walled pipe corresponds to a large value of this index. The differences in “pressure classes” of such products depending on the SDR are presented in Table No. 2.
table 2
| SDR 41 | SDR 33 | SDR | ||||||||
| 4 atm. | 4 atm. | 5 atm. | 6 atm. | 7 atm. | 8 atm. | 10 atm. | 12 atm. | 16 atm. | 20 atm. | 25 atm. |
In general, this indicator, along with the thickness of the polyethylene layer, indicates what level of load or pressure (internal and external) a polyethylene pipe GOST 18599 2001 can withstand.
Pressure networks require the use of pipes with an SDR rating of 6-9
This standard dimensional coefficient is recommended to be used when determining the suitability of a pipe for the implementation of a specific system - free-flow and pressure, namely:
- pipes with SDR 6-9, in addition to supplying water, are suitable for arranging pressure sewer collectors and even gas pipelines;
- products indexed from 11 to 17 can be used to create low-pressure water supply and irrigation systems;
- polyethylene pipe products with SDR ratings of 21-26 can be used to organize low-pressure intra-house water supply for multi-storey buildings. And, for example, PE 100 pipes with SDR 26 have found application in the food industry: they transport juice, milk, beer or wine;
- pipes with SDR 26-41 are used for gravity (free-flow) sewer outlets.
Important! Taking into account the grade of polyethylene is one of the most important conditions for the correct selection of pipes made from it. Even with the same SDR, a product whose marking contains a larger number, for example, PE 100 rather than PE 80, will be more resistant to various mechanical influences.
Below are some examples regarding the use of PE 80 pipes.
- PE 80 pipes with SDR 21 are characterized by low internal pressure and compressive strength. Therefore, it is not recommended to use them for installing a gas pipeline, burying them in the ground, or for pressure systems.
- PE 80 products with an SDR index of 17 are recommended for installing water supply systems in low-rise buildings. For this, their level of strength is quite sufficient. And the low weight and low cost will allow you to save on installation.
- PE 80 pipe with an SDR of 13.6 is very durable and can be used to build a long-term water supply system.
A pipe with a low strength index is suitable only for use in networks with low pressure, for example, in a watering system for a summer cottage
The basic standards for pipes made of low-density polyethylene are described in GOST 18599 2001.
Manufacturing technologies. According to this regulatory document, for the production of these products it is necessary to use not any polyethylene, but only those obtained during a polymerization reaction under low pressure. Its production is carried out in special chambers in which a constant value of this parameter is maintained over a range of atmospheres. A characteristic feature of the manufacturing process is also the stabilization of the temperature around 150? C, and not only the control of constant pressure.
Today, two methods of producing HDPE pipes according to GOST 18599 2001 are used:
- Rotary casting technology. The tubular configuration is obtained due to the distribution of the molten polymer under the influence of centrifugal force - it sticks to the surface of the walls of the casting mold.
- Extrusion. The product is produced by extruding from molten granules. In this case, the tubular structure is formed by the extruder head: a screw press pushes the superheated polymer through it. This process is simpler than casting. However, in the first case, the dimensions of HDPE pipes according to GOST 18599 2001 are more accurate and with minimal deviations from ovality.
As for the weight characteristics, their numerical value does not depend on the manufacturing technology. This is due to the absolute compliance of the dimensions of the final product with the figures specified in GOST 18599 2001. After all, the specific gravity of the raw materials is the same in any case.
Most HDPE pipes are produced by extrusion method
To get an idea of the weight of HDPE pipes depending on the diameter and SDR index, check out the data presented in Table No. 3.
Table 3
| Diameter, millimeters | SDR 26 | SDR 21 | SDR 17.6 | SDR 17 | SDR 13.6 | SDR 11 |
| 630 | 46 | 56,50 | 66,60 | 69,60 | 84,80 | 103,0 |
| 560 | 36,30 | 44,80 | 52,60 | 55,0 | 67,10 | 81,0 |
| 500 | 29,0 | 35,80 | 42,0 | 43,90 | 53,50 | 64,70 |
| 450 | 23,50 | 29,0 | 34,0 | 35,50 | 43,30 | 52,40 |
| 400 | 18,60 | 22,90 | 26,90 | 28,0 | 34,20 | 41,40 |
| 355 | 14,60 | 18,0 | 21,20 | 22,20 | 27,0 | 32,60 |
| 315 | 11,06 | 14,2 | 16,70 | 17,4 | 21,30 | 25,70 |
| 280 | 9,09 | 11,30 | 13,20 | 13,80 | 16,80 | 20,30 |
| 250 | 7,29 | 8,92 | 10,6 | 11 | 13,4 | 16,2 |
| 225 | 5,880 | 7,290 | 8,550 | 8,940 | 10,90 | 13,20 |
| 200 | 4,680 | 5,770 | 6,780 | 7,040 | 8,560 | 10,40 |
| 180 | 3,780 | 4.660 | 5,470 | 5,710 | 6,980 | 8,430 |
| 160 | 3,03 | 3,710 | 4,35 | 4,510 | 5,5 | 6,670 |
| 140 | 2,31 | 2,8 | 3,35 | 3,5 | 4,22 | 5,1 |
| 125 | 1,83 | 2,3 | 2,66 | 2.8 | 3,37 | 4,1 |
| 110 | 1,42 | 1,8 | 2,1 | 2,16 | 2,6 | 3,14 |
| 90 | 0,969 | 1,2 | 1,4 | 1,5 | 1,8 | 2,12 |
| 75 | 0,668 | 0,82 | 0,97 | 1,01 | 1,230 | 1,46 |
| 63 | 0,488 | 0,573 | 0,682 | 0,72 | 0.87 | 1,05 |
| 50 | 0,308 | 0,37 | 0,44 | 0,449 | 0,55 | 0,663 |
| 40 | — | 0,24 | 0,281 | 0,293 | 0,353 | 0,43 |
| 32 | — | — | — | 0,193 | 0,228 | 0,277 |
| 25 | — | — | — | — | 0,147 | 0,168 |
| 20 | — | — | — | — | — | 0,116 |
Advice! If you intend to use products of this type for hot water supply, pay attention to their labeling when purchasing. It should contain the following sequence of letters: PE-RT.
GOST 16338-85 for low-density polyethylene (HDPE)
The production, supply and storage of HDPE low-density polyethylene is fully regulated by specially created rules, in accordance with which it receives specific markings. This is done in order to clarify for the consumer the characteristics of the product, methods of its transportation and the possibility of using it for specific purposes. Such rules are spelled out in a document adopted in the Russian Federation - GOST 16338-85 standards.
Download free GOST 16338-85
HDPE according to GOST
The standards describe low-density polyethylene made using two different technologies:
- Suspension, which is obtained during the polymerization of a granular mixture (suspension). For it, GOST standards describe the characteristics of 10 basic brands that do not yet contain additives in the form of dyes, stabilizers, etc. Its modifications are selected at the discretion of the manufacturer, in the form of compositions with additives proposed in a separate paragraph.
- Gas-phase HDPE, obtained by reaction with catalysts, comonomers and other substances in a gas reactor, is described by standards and is produced with the addition of various stabilizers. GOST gives standards for 20 brands of this type of HDPE with a description of composition recipes.
ATTENTION! The labeling of suspension HDPE contains information only about a specific base type, but for gas-phase HDPE, the index of the additive formulation is written through a dash from the three-digit number of the base.
What can be found in the GOST rules
The standard itself can always be found in the databases of legal portals or downloaded on the same page. To make it easier to navigate all the rules describing HDPE polyethylene in it, you should immediately refer to the contents of this document.
Document structure
In the list of contents you will find:
- Relevance of the prescribed rules (dates of adoption and amendments),
- Links to additionally necessary legislative acts,
- Explanation of markings with an explanation of the meaning of each position from the 8-digit code,
- A complete description of HDPE of existing brands with standards for all technical indicators for each grade - in relation to the chemical composition and physical and mechanical properties,
- List of permitted additives with their individual properties, separately for gas-phase and suspension types,
- Safety requirements for both the polyethylene composition itself and the rules for working with the finished product,
- Rules for acceptance of finished batches of HDPE with a description of the tests carried out and determination of grades,
- Issues of proper packaging, safe transportation and storage that does not violate the quality of products,
- Guarantees that a polyethylene manufacturer can provide for its product.
Useful applications
At the end of the document, you will find as many as 5 appendices that describe not only the physical and mechanical properties of polyethylene, but also provide recommendations for its production and further use:
- The first appendix gives markings for the first and second grades of each base brand.
- The second will help you choose the appropriate (and permitted) additive formula for the manufacture of products for various purposes:
- for those in contact with food,
- intended for children,
- for the production of packaging,
- pipelines and fittings,
- medical devices and even prosthetic products.
- The next page (Appendix No. 3) provides instructions for the use of polyethylene of each of the brands described - both a complete description of the scope of application and processing methods.
- The fourth sheet will be necessary for those who need to color low-density polyethylene in any color: here is a table matching the color and the substance that will color HDPE products.
- The latest appendix describes all the physical and mechanical characteristics of the grades, from melting points to a list of dielectric properties.
IMPORTANT! GOST is not only instructions for action for manufacturers, but also useful information for consumers. Knowing the standards, you can choose products that fully meet your needs and safety regulations.
propolyethylene.ru
Cross-linked polyethylene and the advantages of pipes made from it
In recent years, low-temperature heating systems have become especially popular. This phenomenon is due to the appearance on the market of relatively cheap and reliable cross-linked polyethylene pipes.
Cross-linked polyethylene is one of the most reliable materials for heating installations
This material is the densest modification of the ethylene polymerization product, characterized by a network molecular structure strengthened by additional intermolecular bonds. It is designated by the following Latin letters: PEX. The first two, as you might guess, denote polyethylene, and the last one - X - just says that it is cross-linked.
Ordinary polyethylene is a collection of large polymer molecules with numerous side branches, most of which “float freely” in intermolecular space. “Crosslinking” forms additional bonds, which, in turn, create a particularly strong structure - an intermolecular network, similar to the crystal lattice of solids. The use of various cross-linking technologies makes it possible to obtain a substance with fewer or more such bonds and, accordingly, with lower or greater strength characteristics.
- PEXa – characterized by the highest percentage of cross-linking. The number of cross-linked molecules can reach 85%. This peroxide polyethylene is obtained in the presence of hydrogen peroxide molecules.
- PEXb – the volume of the bound structure is 70%. This silane polymer is most widely used and is used in a wide range of product items sold on the modern market.
- PEXc – up to 60 percent of molecules are cross-linked. Manufactured by radiation.
- PEXd – cross-linking reaches 70%. It is created in the presence of nitrogen molecules, and the reaction conditions are highly complex.
In terms of technical characteristics, cross-linked polyethylene is comparable to many solid substances. And in terms of parameters such as long service life and resistance to various destroyers, it even surpasses some of them. Of course, not all brands of cross-linked polyethylene can compete on equal terms with materials traditionally used for the manufacture of heating and water supply pipes. We are primarily talking about the PEX-a product. It is characterized by the greatest impact resistance, crack resistance and the highest melting point.
The strength and high flexibility of PEX pipes make them one of the best options for underfloor heating systems.
Helpful information ! High-percentage cross-linking produces less plastic and harder products. This factor does not mean that she is the best. Simply, with its help, you can obtain materials of different quality for the production of products for various purposes.
Taking into account the above, cross-linked polyethylene pipes have the following advantages:
- shape stability. If such products are not exposed to external load, they will not deform even at a temperature of +200? C;
- high fatigue strength. This property is preserved when transporting the working environment at a temperature of +95? C;
- crack resistance. High impact strength and the same impact strength in the places of cuts is recorded even at significant negative temperatures (-50? C);
- optimal ratio of flexibility and strength;
- absence of heavy metal ions and halogens;
- corrosion resistance;
- ability to withstand the effects of chemically active compounds;
- excellent shrinkage properties of the material;
- high wear resistance: the surface of the cross-linked polyethylene pipe is subject to abrasion to a small extent.
Tips on how to choose
HDPE is the optimal choice for installation in the ground or basements without ultraviolet rays, sudden temperature changes and mechanical vibrations. When choosing the type and size of pipes, they are guided by the purpose and operating conditions. First, the purpose of the pipelines is determined - pressure and non-pressure, sealed or not. Power, telephone or Internet networks are laid in casings made of larger tubes; often these pipelines are not sealed.
The second important factor is the working pressure in the water supply or soil pressure on free-flow networks. The choice of pipe design (smooth-walled, corrugated, double-layer corrugated, bell-shaped) depends on these factors. In addition, the temperature regime is taken into account - overheating of the ground in summer, freezing in winter.
The choice of pipe parameters for sewerage depends on the weight of the overlying soil layer. If the depth is more than 5–6 m or the sewage system is located under a platform for cars, use corrugated two-layer pipes with high ring rigidity. Corrugation is also used for deep laying of water pipes and a large layer of screed over a heated floor system.
When choosing materials in a store, it is better to choose products from well-known brands. Corrugation is definitely better than imported ones. Smooth-walled pipes can also be selected from domestic manufacturers.
In any case, the pipes must be inspected when purchasing to see if there are any cracks, chips, sagging, if they are too soft and if the wall is thin. Receipts and certificates are required for purchase.
Approximate price and best manufacturers
The best domestic ones, “Kazanorgsintez”, “TekhStroyPolymer”, “PolyPlastik”, “BaltEnergosystems”. There are many imported manufacturers, but the quality of imported HDPE pipes is not much higher than domestic ones, but the price is significantly different. The availability and prices of pipes from foreign manufacturers must be determined separately for each region: the range and prices are very different!
Price of popular domestically produced products:
- 1 m of smooth-walled water pipe Ø 32 mm costs from 50 mm, Ø 40 mm - from 70 rubles;
- 1 m of single-layer corrugated pipe Ø 50 mm costs approximately 60 rubles; Ø 63 mm – 90 rubles; Ø 110 mm – 150 rubles;
- bell-shaped HDPE design with a running size of 110 mm and a length of 2 m costs about 300 rubles; corrugated - about 400 rubles.
Welding of polyethylene pipes
Welding is considered the most reliable way to connect elements of polyethylene pipelines. Knowing how to carry it out will allow you to choose the most suitable equipment.
Butt welding. This method is applicable when the pipe walls are thicker than 5 mm, and the diameter of the products themselves exceeds 5 cm. The ends of the products are heated to the required viscosity due to contact with the heating element - the plate. After their docking, a very reliable fixation is obtained because the process of forming the connection itself occurs at the molecular level. Butt welding technology cannot be called complex. Any home craftsman can implement it with his own hands. However, you cannot do without a special unit for welding polyethylene pipes. If you do not plan to lay pipelines from such a polymer regularly, you can simply rent the device rather than buy it.
Butt welding provides a reliable and durable connection, but it requires a special unit
The sequence of steps is as follows:
- we place the ends of the pipes in the appropriate welding machine;
- we install the above-mentioned heating plate between them;
- press the ends against it under slight pressure;
- we wait until they melt to the required level;
- reduce the pressure and let the elements finally warm up;
- take out the stove;
- we connect both pipes under pressure;
- We wait for the joint to cool and the joint to completely harden.
Important! Manipulate the stove as smoothly and accurately as possible. Otherwise, you risk disturbing the places where molecular bonds are formed between heated elements.
Today in construction stores you can purchase the following types of welding equipment for welding polyethylene pipes:
- automatic welding machine with mechanical drive. Involves carrying out all actions manually;
- units with hydraulic drive. Thanks to hydraulics, less effort is required;
- modern software-controlled devices. Being fully automated, these devices will significantly speed up and, most importantly, facilitate the process. Of course, their cost is very high.
Experts note the following advantages of butt technology:
- errors due to inexperience and the human factor are generally excluded. As a result, the connection is of very high quality;
- process automation (this applies to hydraulic and software-controlled equipment for welding polyethylene pipes);
- control is possible during the execution of work.
Butt welding of polyethylene pipes will be of high quality and reliable if all stages are performed correctly. Data from experiments conducted by independent organizations indicate that the strength of a correctly formed weld is 8 (!) times higher than the similar characteristics of the pipes themselves.
One of the options for welding polyethylene pipes is connection using electric couplings
The rules that must be followed when butt welding are very simple.
- Work should only be carried out on flat and hard surfaces, for example, on a reinforced concrete base, asphalt or boards. An important point is maintaining the alignment of the pipes. The deviation of the axes should not exceed 10 percent of the thickness of their walls.
- Plugs must be inserted at the reverse ends. This ensures the absence of a draft in the pipe cavity and the constancy of the specified butt welding temperature.
- Before securing the ends in the clamps, wipe them inside and out with a lint-free cloth. Carry out a similar procedure with the clamps of the centralizer.
- Fix the pipes in the chassis so that their markings are located along the same line and are on top.
- Before you begin, wipe down your welding equipment. Carrying out a test joint will remove dust and microparticles from the heater. When working with pipes whose diameter exceeds 180 mm, make two test joints.
- Before welding pipes of a different diameter, allow the heater to cool and then make an additional test joint.
- You should start a new connection only when you are sure of the alignment of the already connected pipeline segments.
- Grinding of joints is necessarily preceded by the procedure of cleaning the grinding discs from polyethylene particles previously adhering to their surface.
Important! Use a non-metallic stick to remove chips from the ends and chassis. Doing this with your hands is strictly prohibited.
Electrofusion welding. This method involves the use of a welding unit and special electric couplings. It is relevant when installing long pipelines, when butt welding is impossible.
The work must be carried out in the following sequence:
- workplace preparation;
- selection of a suitable fitting;
- cleaning the connected parts from contamination;
- trimming the ends of pipes with subsequent removal of the oxidized layer;
- securing polyethylene pipes and fittings in the positioner device;
- turning on the welding unit and waiting for the end of the operation;
- Upon completion, you must turn off the equipment and check the quality of the seam.
During a visual inspection, pay special attention to the following points:
- the edge of the seam should protrude above the outer and inner surfaces of the pipes in the form of a roller;
- the optimal height of these rollers is about 2.5 mm with a wall thickness not exceeding 5 mm. This indicator for more massive samples is no more than the same 5 mm;
- the displacement of the pipes should not be more than 0.1 percent of the wall thickness.
The design and dimensions of the welding machine required for installation work depend on the diameter of the PE pipes
If these conditions are met, the connection will last for decades.
Installation features
To avoid blockages along the wastewater route, pipe laying begins from the main riser in the direction of the well. Pipes should initially be taken larger than the calculated diameter - this is for safety net - in case of installing new plumbing or building a bathhouse with a swimming pool.
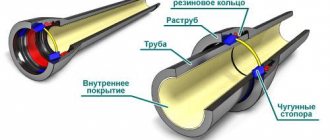
There are two connection options:
- Detachable when couplings or flanges are used. Tightness is ensured by rubber gaskets. The method is convenient because, if necessary, the water supply or sewerage system can be disassembled by simply removing the couplings.
- One-piece - in a socket, using welding or glue. The glue is selected depending on the materials. For polymers, this is epoxy resin.
Not all methods are available to beginners, so it is better to turn to professional workers, or choose the easiest connection method.
Advantages and disadvantages
The easiest way is to connect the pipes into a socket. It is important to place a rubber ring for tightness, and the socket itself should be directed in the direction from which the water flows. This reduces the risk of blockages. To make the pipes easily dock, use lubricant or regular detergent.
Welding is a complex method. Without skills, connecting pipes will not be easy. For non-pressure sewerage, welded seams are quite reliable.
The use of epoxy glue allows you to connect pipe parts at the molecular level. Before starting work, the joints are degreased. You need to act quickly, as the resin dries quickly in air.
The fittings are installed on O-rings to avoid leakage at the joints.