A fairly simple question, how the height of a ventilation pipe above the roof is determined according to SNiP, often confuses even self-confident designers, what can we say about amateur builders who have planned a refurbishment or major reconstruction of their home. The question, meanwhile, is far from idle, since a fundamental characteristic—its performance in terms of the volume of air moved—depends on the height of the ventilation pipe above the roof.
The height of ventilation ducts above the roof: 5 factors influencing the calculation
For efficient operation of the ventilation system, it is important to correctly calculate the height of the ventilation ducts above the roof through which the exhaust air exits. An error in the calculations, when the pipe is located too low relative to the roof, will lead to exhaust air flowing back into the room, as a backdraft will occur.
If the pipe is located too high, then the operation of heating devices in the room will not be effective: warm air quickly goes out into the street, and the room heats up weakly. Consequently, fuel consumption and the atmosphere in the room depend on the height of the ventilation duct pipe.
Wind pressure zone
Even with correct calculations, traction can be poor. It can be influenced by taller buildings nearby and even tall trees. It is defined this way. It is necessary to draw a conditional line through the lower edge of the roof and the upper point of the taller building at an angle of 45˚. If the chimney is below this level, then increased pressure is created there, which can lead to backdraft. In this case, it is necessary to raise the pipe at least 500 mm above the imaginary line.
Calculations and standards
The outer pipe connects all parts of the ventilation system, through which exhaust air leaves the room.
Note! Properly functioning ventilation ensures a favorable atmosphere in the room, the absence of foreign odors and an optimal level of humidity.
The efficiency of ventilation depends on the height of the pipe and the values of other related parameters. In addition, the arrangement of ventilation is regulated by SNIP 41-01-2003 - this is a standard that must be observed when installing ventilation ducts.
Five factors that affect calculations
Calculation of the required height of the ventilation duct depends on five key factors:
- Distances from the highest point - the ridge to the ventilation pipe;
- Roof design features;
- Prescribed fire protection requirements;
- Ventilation duct diameter;
- Organization of ventilation and smoke removal.
What is a skate?
The ridge is the top edge of the roof structure. This element connects the roof slopes, the planes of which converge on it in one line. Since the ridge is the top point of the roof, the height of the roof is determined by its location .
This element performs the functions of protection and ventilation . It closes the joints of the slopes, preventing moisture and dirt from entering the interior of the roofing pie. In this case, circulating air masses exit through the ridge.
Determining the height of the roof is important not only for the purposes of ensuring wind and snow resistance. Most roofing materials have clear ranges of possible pitch angles for their installation . When installing heavy materials, it is necessary to minimize the load per unit area of the roof base; for this, the slope angle (and, accordingly, the height of the ridge) increases.
If it is planned to equip an attic space in a house, then the range of possible slope angles is limited by the requirements for the maintenance capabilities of the room and its fire safety. For residential attics, requirements for ease of movement around the room are added, depending on the height of the residents.
Pipe location relative to the ridge
If the ventilation pipe exits onto the roof at a distance of less than 1.5 m from the ridge of the roof, then above the level of the ridge, it is raised another 50 cm.
The pipe should be located no lower than the ridge of the roof of the adjacent house.
When removed from the ridge by more than 1.5, but less than 3 m, the height of the ventilation duct should not be lower than the ridge of the roof.
If the ventilation duct is located at a distance of more than 3 m from the highest point of the roof, then the top of the pipe should be located at the intersection of the line indicating an angle of inclination of 100.
Distance of the chimney from the ridge
To ensure sufficient draft, it is necessary to correctly calculate where to install the chimney duct. This takes into account the type of roof and the surrounding buildings. The flow of wind passing over the roof is of great importance.
Technological regulations
All rules and requirements for heating are specified in building codes. In particular, specialists are required to:
- The total length of the pipe was at least 5 meters from the grate to the outlet, with the exception of houses with a roofless structure. Otherwise, sufficient traction will not be provided.
- The height of the chimney above the flat roof was at least half a meter.
- The chimney outlet must be located no lower than the line of the top point of the ridge. In this case, it is necessary to maintain an inclination of 10 degrees relative to the horizon.
Graphic and mathematical methods
The most complex calculation option involves the use of this technique. It is usually used when the distance from the pipe to the ridge exceeds 3 m, although other situations also occur.
Height of the ventilation duct and roof structure
The height of the ventilation pipe depends on the roof slope. The roof can be single-pitch, gable or combined.
- For single- and double-pitched roofs, the height of the ventilation duct is calculated according to standards, i.e. this value is determined in accordance with the distance of the pipe from the highest point of the roof.
- The pipe installed on a flat roof should be at least half a meter.
- For combined roofs, this parameter is calculated taking into account the height difference, with the roof ridge taken as the starting point.
It is important! It is better to entrust the design of a ventilation system for roofs of complex design to specialists.
Fire safety and ventilation duct height
In addition to properly insulating the structures adjacent to the vent pipe, it is important to consider what materials were used for construction. If the roof is made of flammable materials and there are holes on the pipe, then the height of the pipe must be increased by another 50 cm to prevent fire from a spark that could get on the coating.
The distance of the pipe from the skylights should be 2 m or more.
Tall buildings and treetops should be 6 m or more away from the pipe.
Correspondence between the diameter of the pipe and its height
The section size is determined according to SNIPs as the ratio of the width of the product (first column) and its height (top line):
Ventilation pipe and smoke exhaust duct
The height of the ventilation pipe and chimney should be the same, provided that they are located at a distance of no more than 3 m from each other. Otherwise, gases from the chimney pipe will enter the room through the ventilation duct.
Note! A ventilation duct pipe that is positioned incorrectly relative to the ridge can cause gas attenuation in the heating device, which has serious consequences.
The volume of air flowing from the ventilation duct into the room, which is heated by the boiler, in accordance with SNIP, must correspond to 3 m³/hour for each m2 of living space, and 180 m³/hour in utility rooms.
The cross-sectional area of the ventilation duct is determined by the formula:
L= V x N,
L is the section size, V is the volume of the room, N is the existing standard for a certain type of room.
Note! According to the regulations, it is strictly prohibited to use the ventilation duct to remove combustion products from the room.
Features of the chimney
Removal of gases through the channel will occur effectively only if the pipe is constructed according to standard dimensions and made of the correct material. These pipe characteristics are selected depending on the type of fuel; the material for the chimney is:
- refractory ceramic bricks;
- asbestos pipes;
- stainless steel;
- sandwich pipes with an inner layer of insulation.
Brick channels are made in the case of a stationary chimney , which ensures the removal of gases when heating with wood and coal. To determine the diameter and internal size, the boiler power and the dimensions of the firebox are taken into account. If the calculation is incorrect, reverse draft results or the useful effect of the furnace is significantly reduced.
For gas boilers, it is effective to use pipes with two walls , between which insulation is laid. The problem with a chimney for a gas fuel boiler is internal condensation, so insulation will help avoid significant temperature differences.
It is allowed to install one chimney for two operating heating units , if the internal size of the chimney, raised to the required height above the roof ridge, allows combustion products to be easily removed from both stoves. The cutting section pipe is about 0.8 m high.
A feature of the functioning of the chimney is that all overall, internal dimensions and height must be made with maximum accuracy. A wide and tall chimney, folded to a large height, with a low power of the heating unit, will reduce the efficiency. Insufficient dimensions will lead to smoke being sucked into the room, creating backdraft, and leaking dangerous carbon monoxide.
The warmth in the house depends on a well-designed heating system. But not a single stove or boiler will be able to cope with the task of supplying heat unless a technically competent chimney is made, raised to the required height above the roof ridge.
Dependence of draft on pipe height
The importance of the chimney in the heating system cannot be overestimated. Attempts to save on an extra meter of pipe will lead to cold walls during the heating season and excessive waste of fuel. The danger of carbon monoxide is that it is invisible and undetectable, but can be fatal.
Thrust occurs when heated smoke and gas with low density, in accordance with the laws of physics, rises upward. The result is a pressure difference at the beginning and end of the channel, that is, draft occurs. To ensure that the process is constantly repeated, cold oxygen is supplied through the blower. The greater the temperature difference, the stronger the thrust will be.
A narrow chimney of great height relative to the ridge will accelerate the smoke masses, thus reducing heat transfer. To maintain the desired temperature in the room, you will have to add fuel in excess of the norm. A wide channel of small height will allow smoke and gases to rotate arbitrarily in the pipe, their movement will slow down, and most likely a reverse flow of gases will result. Most often this happens in autumn or spring, when the temperature difference between outside and inside decreases and smoke, without overcoming resistance, is drawn into the room through the firebox.
Chimney location and height
To correctly select the height of the chimney relative to the roof ridge, you need to take into account the location of nearby structures. For an outdoor home, the draft indicators will be good, since there is constant blowing and pick-up of smoke masses. If we talk about a small building surrounded by high-rise buildings, then the length of the pipe should be increased. The height of the chimney depends on several factors:
- slope of the roof plane;
- location of the channel on the roof plan relative to the ridge;
- the location of surrounding buildings and trees;
- estimated thickness of snow cover in a specific area.
When installing a chimney, you should determine:
- elevation of the pipe relative to the roof ridge;
- the total length of the smoke channel from the stove;
- type and dimensions of the head;
- the height of the chimney relative to ventilation and windows of neighboring buildings.
The norms and rules for the construction of a chimney are prescribed in documents SNiP 41.01.03 and in building regulations under number 7.13130.09.
How to correctly calculate the height of ventilation ducts above the roof according to SNIPs?
Not only the comfort of living in a house, but also its service life largely depends on well-equipped ventilation. Excessive dampness can destroy a structure in a matter of years. One of the main indicators of exhaust systems is the height of the ventilation ducts above the roof. Its calculation is carried out in accordance with building codes and regulations. Deviation from them leads to disruption of air exchange, which can be a precedent for creating an unhealthy microclimate in rooms and causing dangerous diseases in people.
The worst case scenario is that carbon monoxide enters the premises from the chimney. Let's consider the main aspects regarding determining the height of the ventilation pipe above the roof, depending on the type of structure, roof configuration and other nuances.
The best for the entire life of the house. Ceramic chimney systems
In addition to the height of the chimney and its correct location on the roof, the choice of the optimal material and design of the chimney is important.
The reliability, service life and efficiency of the heating system and the minimum cost of repair and operation depend on this.
Previously, the chimney was made of brick. The time it takes to lay a high-quality brick pipe is significant. Today, single-layer construction is being replaced by modern multi-layer chimneys based on a stone shell made of expanded clay concrete, thermal insulation made of stone wool and a liner/sleeve - a ceramic pipe. Their installation is not only 3 times faster, but also meets modern harsh operating conditions.
To understand the advantages of a well-insulated ceramic chimney, let’s compare its internal channel with a regular brick pipe.
Modern chimney system made of ceramics.
AND
Standard brick chimney.
Uneven masonry and protruding mortar inside a brick chimney create additional resistance in the path of flue gases. This will lead to the formation of unnecessary turbulence and poor traction. In addition, uneven internal channels quickly become overgrown with soot.
The ceramic chimney has smooth walls. Smoke streams move without resistance.
The round shape of the ceramic chimney promotes optimal movement of hot gases.
Yuri KozakSchiedel specialist
Multilayer chimneys with internal ventilation began to be made for several reasons:
1. The movable sleeve inside the shaft eliminates the load on the supporting structure of the pipe (outer shell) due to thermal expansion. This chimney is characterized by increased gas density. A modern chimney operates in a cyclic mode, and a single-layer brick shaft cracks and collapses faster. In places where there is possible severe pinching (in ceilings and roofs), cracks form. This leads to a high fire hazard of the structure.
2. In a multi-layer insulated structure, the inner pipe warms up faster and the chimney melts faster (comes to draft). This is especially important during cyclical – episodic operation of the chimney, for example, near fireplaces. With constant stove heating, the pipe usually does not have time to cool down.
Another advantage of a ceramic chimney compared to a brick one is its resistance to condensation.
Changing the types of fuel and operating mode of the heating system leads to an increase in the volume of condensate, which destroys the brick over several heating seasons.
Advice. If brick smoke ducts are already being built in the house, then the ducts for the stove, fireplace and gas pipe are best made in the form of an equilateral, level shaft with an internal size of at least 26x26 cm (“six-shaped”, i.e., made of 6 bricks in a row).
Then in the future you can “sleeve” it.
Uneven-sided shafts worsen the flow movement in the pipe due to reverse countercurrents (resistance), which stimulates increased soot formation in the pipe.
The internal cross-section of the smoke channel is selected depending on the power of the heat generator.
Why does a private house need ventilation?
Structurally, residential buildings are enclosed spaces, reliably isolated from the external environment. Walls, doors and windows protect premises from precipitation, warm and cold air, dust, animals and insects.
However, such isolation from the outside world has the following side effects:
- When people breathe, carbon dioxide is produced, which in high concentrations is harmful to health. If you don’t get rid of it, then feeling unwell is the least of the possible troubles.
- Constant dampness. Human activity (washing, wet cleaning, water procedures, cooking) is inextricably linked with the formation of high humidity.
- Accumulation of carbon monoxide from the operation of heating boilers. And this is a real threat to life.
Incorrect calculation of the removal of waste air masses from a room leads to complex and sometimes insoluble issues.
What happens if you do it poorly?
Without delving into the essence of ventilation technology, many believe that it is enough to install an air conditioner and the problem will be solved. However, this unit circulates the air inside the room without refreshing it at all.
The absence or incorrect calculation of the length of the air duct is fraught with the following consequences:
- In the absence of an influx of oxygen-rich fresh air, residents of the house will suffer from headaches. Their sleep will be disturbed, their immunity will be weakened, and their performance will decrease.
- Due to constant dampness, fungus and mold will develop on walls, furniture, things and products. Pathogenic microflora is extremely dangerous to health and destroys interior elements.
- The aesthetic component suffers. Excess moisture settles on walls and windows. Perspiration forms on the glass, constantly flowing onto the window sills.
According to current codes of practice, it is recommended to install ventilation in rooms that do not have windows. These include bathrooms, toilets, storage rooms and kitchens, regardless of their architecture.
Types of ventilation
According to fire safety requirements, air conditioning systems must be installed in all houses equipped with boilers operating on any type of fuel.
Ventilation can be natural or forced. Let's briefly look at the features of each.
Natural
As a rule, it is installed in tall buildings, where the difference in height of the inlet (windows) to the final point of the ventilation outlet (pipe cut) is quite significant. The outflow of air occurs due to the difference in atmospheric pressure at different levels of the building. The flow speed depends on the wind strength and is adjusted by changing the parameters of the inlet and outlet openings.
Mechanical
Involves the installation of one or more fans. Used for arranging interior spaces where there is no natural air flow to create sufficient draft. In some cases, mechanical air conditioning is done when there is a slight difference in air temperature inside and outside the building.
To create a comfortable microclimate, forced pumping is organized using window or wall fans.
The power of the products is selected individually.
How to correctly determine the height of the pipe
This factor is decisive when designing a ventilation system. It is necessary to carry out the necessary calculations at the stage of drawing up drawings of utility lines for the future home. During construction or after its completion, it will be extremely difficult or impossible to make adjustments and changes.
What influences
The overall height of the exhaust duct is influenced by several factors.
The most significant of them are the following:
- temperature changes indoors and outside;
- the presence of a chimney pipe from a heating boiler nearby;
- the prevailing direction of the wind and its strength;
- the degree of air friction resistance against the walls of the pipeline;
- exhaust system configuration, presence and number of corners.
So, in the summer, the draft is significantly reduced, since the temperature inside and outside the house is almost the same. However, an excessively tall pipe may pose a risk of falling due to strong gusts of wind.
Roof structure
The roofs of residential buildings have different shapes. In snowless regions of the country with little rainfall, houses are covered with a flat roof, as it is easier, faster and cheaper. The height of the ventilation duct is not particularly important here. The main thing is that sufficient traction is provided; this requires 50-60 cm of elevation when the pipe is located next to the roof ridge or parapet.
In cases of arranging buildings with pitched roofs, it is necessary to take into account the relationship between their highest point and the cut of the ventilation duct.
If the distance to the ridge is less than 150 cm, then the pipe must be raised above the roof by 40-50 cm. If the distance is greater, it must be raised above the ridge by at least 100 cm. This will ensure that the outgoing air is captured by the wind and creates good traction.
Fire safety rules
Since not only combustion products, but also sparks enter the chimney, the heating system requires increased attention from a fire safety point of view.
In order to minimize the likelihood of a fire, you must adhere to the following rules:
- there must be at least 3 meters between the chimney of exhaust pipes and the ventilation duct to prevent sparks and carbon monoxide from entering;
- the height of the ventilation and chimney pipes must be the same level;
- heating of the external route must be made safe in terms of the possibility of ignition.
If the hood and chimney pass outside the building, then they should be separated by thermal insulation material to avoid burning out the ventilation duct.
When designing an exhaust system in a private house, you must initially decide on the configuration of the pipeline. This issue needs to be approached differentiatedly, without choosing aesthetics at the expense of practicality and vice versa.
There are the following options for choosing the cross-section of pipes for arranging the main line:
- Round. Air moves best through such channels, without creating turbulence or reverse flows.
- Rectangular. Looks good both inside and outside the house. but the aerodynamic qualities of such ventilation ducts are somewhat worse.
The optimal solution is to lay rectangular channels indoors, and round ones in technical rooms and on the rear walls of the house.
Type: natural or mechanical
As for the choice of the type of exhaust system, in most buildings it is combined. Living rooms use a natural way to remove polluted air due to differences in temperature and pressure. Ventilation ducts are masked with ducts, paint or wallpaper. Decorative grilles are selected to match the tone of the interior.
As for rooms with a limited volume of supply air, inlet valves and openings for exhaust fans are made in their walls. The air from such rooms is removed directly to the street or supplied to a common pipeline.
Correct calculation of air flows
How is the height of the chimney relative to the roof ridge correctly determined? Bumping into the outer part of the chimney, the wind changes direction. The horizontal flow, encountering the pipe wall, simply tries to go around it and turns upward. Due to this change in course, a rarefied atmosphere is formed in the wall area, due to which smoke is drawn out of the chimney.
To create good traction, the influence of wind is required. If force majeure obstacles interfere with the normal movement of air flows, smoke removal will not occur correctly. A ridge rib can become such an obstacle. For this reason, it is very important to maintain the correct relationship between the distance to the ridge and the size of the pipe.
Calculation of duct diameter and duct height
To correctly calculate the diameter of the air duct, you can use the help of a specialist, study regulatory documents or use an electronic calculator.
The rules for arranging ventilation ducts are set out in SNiP 2.04.05–86.
The main ones are the following:
- ventilation ducts from the kitchen and heating boiler should be the last to be inserted into the ventilation system;
- the strength and height of the pipes must correspond to the wind load;
- The air duct passing through the walls and roof of the cottage must be sealed and resistant to corrosion.
To reduce the flow rate in the channels, it is necessary to install ventilation grilles.
The inflow must be at least 3 m³/h, regardless of the number of people in the room.
According to the table
Calculation according to the table is used in cases where the owner of the house has a wide selection of building materials and has accurate data regarding the parameters of the future structure. You just need to compare the diameter or area of the air duct with the volume of the room. More complex calculations take into account the shape of the line, its roughness and temperature indicators. You can use the table:
Calculator
The electronic calculator on the website https://ventkam.ru is a real find for craftsmen who arrange ventilation in the house with their own hands. Data counting is done quickly and accurately. All you need to do is take measurements and enter the resulting numbers into the cells.
The calculation accuracy of the calculator varies between 80-90%.
Even properly and well-built ventilation needs regular maintenance. This is necessary to restore the geometry and cross-sectional area of the ventilation ducts.
Regular cleaning of ventilation is carried out to remove objects from it that can cause a fire and the spread of infection. This should be done at least once a year.
Recommendations
It happens that in addition to heating equipment, a house has a fireplace or a gas heater, and each of them requires its own smoke exhaust channel. Naturally, no one will build a chimney for every appliance. In this case, a combined chimney with several channels is made, taking into account the power of each device, the type of fuel and the amount of combustion products produced.
Such structures have several advantages:
- stable operation of all devices;
- saving living space;
- saving money and labor costs.
The calculation of such a structure must be entrusted to professionals.
Steel chimney
It happens that in addition to heating equipment, a house has a fireplace or a gas heater, and each of them requires its own smoke exhaust channel. Naturally, no one will build a chimney for every appliance. In this case, a combined chimney with several channels is made, taking into account the power of each device, the type of fuel and the amount of combustion products produced.
We calculate the height of the pipe above the roof according to standards and SNiPs
To create the right microclimate in the house, you need to equip it with an air circulation system. To ensure its effective operation, it is necessary to correctly calculate the length and diameter of the pipe that removes air from the house. Calculations are performed using different methods, depending on what type of ventilation system is installed in the house.
An incorrect pipe height above the roof contributes to oxygen deficiency in the house and excess humidity. If an error was made in the design of the hood, carbon deposits and fungus will appear on the walls and furniture, and the windows will be constantly covered with perspiration.
Volume of incoming air
As a rule, residential buildings are equipped with natural air circulation. The flow of outside air can be through a window or a special valve. The outflow occurs through the ventilation duct. It can be located inside the wall or designed as an extension. A ventilation duct cannot be installed in an external wall, since in this case condensation may form on the surface, which will lead to damage to the structure. Also, due to cooling, the speed of air movement may decrease.
The values for ventilation pipes in residential buildings are determined by the established requirements, which are regulated by SNiP. The frequency of exchange, which reflects the quality of operation of the ventilation system, is also important. So, the volume of air flowing into the room should have the following values:
- in a residential building - 3 m³ per hour per square meter of area. Moreover, this indicator does not depend on how many people are in the room. Sanitary standards establish that for temporarily staying people in a building, 20 m³ per hour of supply air is sufficient, and permanent residents require 60 m³;
- in a utility building (for example, in a garage) - at least 180 m³ of air per hour.
To calculate the diameter of the ventilation pipe, use a system in which there is only natural air flow, without installed forced devices. The simplest method of calculation is the ratio of the area of the room to the cross-section of the ventilation duct opening.
For a living space, 5.4 m² of air duct cross-section is required per square meter, and for a utility room - 17.6 m². With a diameter of 15 m², sufficient air circulation will not be ensured. To obtain more accurate figures it is necessary to use complex calculations.
Advantages of insulation
According to SNiP, insulation makes it possible to create a microclimate in rooms in which people can live and work comfortably. With high-quality insulation:
- heat transfer decreases;
- the formation of condensation, which causes corrosion and mold on the surface of the structure, is prevented;
- the risk of fire is reduced;
- vibration and noise that occur during operation of the air exchange system are weakened;
- heat transfer to the external environment is reduced.
The thickness of the thermal insulation layer depends on such parameters as:
- presence of dew point,
- shape, dimensions of the air vent,
- thermal conductivity of insulation,
- temperature difference between the ventilation system and the room.
The optimal solution is considered to be technical insulation, which has high vapor permeability and low thermal conductivity.
In systems with natural air exchange, as well as with forced air exchange for a certain category of buildings, the presence of insulation is mandatory. For brick ventilation shafts, unlike metal ones, the problem of condensation does not arise, so the issue of thermal insulation loses its relevance.
As for industrial buildings, the forced air exchange shafts here are made of construction steel, which heats up quite quickly. Since a sufficiently large volume of air passes through them, when cooling the structure does not have time to reach the dew point, that is, the problem of water vapor condensation in this case does not arise. The only possibility of condensate formation occurs when the ventilation equipment is stopped, so for such systems, condensate drainage that may form during this period is organized.
How to insulate
Thermal insulation is carried out using two methods: internal insulation and external.
The second is today considered the most economical and efficient. Issues of noise insulation and fire are resolved much easier in this case. For example, noise suppressors are installed directly at the sound source. The likelihood of fire spreading is practically reduced to a minimum. Another valuable advantage of this technology is the ability to periodically carry out measures to prevent the formation of bacteria and microbes, which lead to the delamination of thermal insulation materials, and, therefore, to the loss of their performance characteristics.
Pipe length
All the channels in the building are connected to the ventilation pipe, through which air flows, exiting through the pipe to the street.
To calculate the height of this pipe, you need to know its diameter and have a special table. The cells in the tables contain the values of the cross-sections of the air ducts, and the left column indicates the width of the pipes. The top line shows how high the pipe should be for a certain diameter in millimeters.
The following SNiP standards must also be taken into account:
- If the chimney and ventilation pipes are located next to each other, their height should be the same. If this requirement is not observed, smoke from the heating unit may enter the room.
- If the air duct is located no more than 1.5 m from the ridge, then its height should not exceed 0.5 m. If the pipe is 1.5-3 m from the ridge, it should not be located below it.
- If the roof is flat, then the pipe should be at least half a meter.
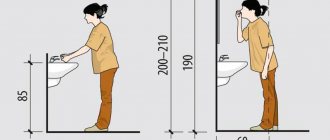
When choosing a ventilation pipe and determining its location, you should also take into account the fact that it must have sufficient resistance to wind. So, the pipe must withstand a force 10 storm, and for this its weight must be about 50 kg per 1 square meter of surface. The picture shows how the height of the ventilation pipe above the roof is calculated.
Special programs can also be used to determine natural ventilation. In this case, the calculation process is greatly simplified. To do this, it is necessary to determine the optimal amount of air supplied to the living or utility room, respectively. The program also determines the following data:
- average temperature indoors and outdoors;
- air duct shape;
- the degree of roughness of the walls inside the air duct;
- resistance that is formed when air moves.
As a result, the program determines how long the ventilation pipe should be to ensure optimal air movement under the given conditions.
When calculating the values for the air duct, it is also necessary to take into account the resistance indicators when moving air flows. The occurrence of resistance is affected by meshes, gratings and other structural details.
Pipe diameter
To calculate the values of ventilation pipes based on the air exchange rate, the SNiP table is used. The air exchange rate is an indicator that determines how many times the air in the room changes in one hour. Before calculating the diameter of the ventilation pipe, you must perform the following steps:
- Calculate the volume of each of the available rooms.
- Determine the volume of air that is necessary for normal circulation. The formula used for this is:
Using the above formula, the volume is calculated separately for each room.
- As a rule, rationing of exhaust or inflow is used for premises. Sometimes in rooms it is necessary to organize not only the flow of air, but also its effective outflow.
- When making calculations, keep in mind that the L value should be rounded up. After rounding, the resulting value must be divisible by 5.
- After determining the required air volume for the entire housing area, a special diagram is used to calculate the diameter of the pipe. In this case, you should know that in the central ventilation pipe the speed should be no more than 5 m/s, and in its branches - no more than 3 m/s.
Choosing a pipe section for the furnace
Experts do not recommend tapping ceramic bricks additionally to get them into place. During the tapping process, an air space is formed, which affects the draft of the flue gas. If it is necessary to lay 4-6 rows of bricks from the inside of the pipe, then the brickwork of the chimney is wiped with a damp cloth, and all seams are rubbed down. The masonry seam is usually 0.5 cm horizontally and 1 cm vertically.
The shape of a brick chimney for a metal stove or fireplace affects the level of hydraulic resistance in the pipe, so its cross-section can be in the form of a rectangle or square. The best option is a round chimney, but it is quite difficult to lay it out of brick with your own hands.
The chimney should not have turns or slopes, since these types of elements lead to the creation of additional air resistance. If you cannot do without a turn, it is easy to equip it at an angle of 60 °. Laying a pipe involves arranging a head, made of 1 brick. The upper part is laid out on a cement-sand mortar.
The level of heat transfer of the stove or fireplace should depend on the choice of cross-section. The cross-section can be within the range of 260x260 mm. For example, if the selected cross-section is 130x130 mm, then the heat transfer is 3.5 kW, and with a cross-section of 130x250 mm - more than 3.5 kW. You should not choose a very large pipe cross-section for a boiler, stove or fireplace, since this will result in a loss of heating efficiency, which leads to a decrease in heat transfer.
SNiP requirements for air ducts
SNiP requirements provide for checking and cleaning the chimney and ventilation pipes:
- before the start of the heating season;
- at least once every 3 months (for combined and brick channels);
- at least once every 12 months (for asbestos-cement ducts and chimneys, as well as for pottery pipes and pipes made of heat-resistant concrete).
During the initial inspection of ventilation ducts and chimneys, the materials from which they were made, the presence of blockages in the ducts, and the presence of separate smoke and ventilation ducts are checked. SNiP standards categorically prohibit the removal of waste combustion products through the ventilation duct.
The homeowner has the right to clean the ventilation ducts only after undergoing training and with the appropriate document confirming the training. When starting the construction of a ventilation pipe, the owner is obliged to notify the operating organization that owns the house about this. Upon completion of the work, the same organization must check and give permission to operate the air duct.
Building a high-quality system that allows you to control moisture levels and provide the best living conditions is a completely feasible task. To do this, you just need to correctly calculate the parameters of the ventilation pipe.