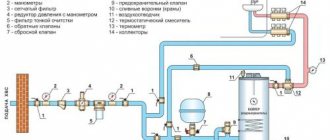
A compensator is a device designed to compensate for temperature expansion, vibration effects, pressure drops, and displacements. Allows you to avoid, stabilize or minimize undesirable consequences resulting from the action of these factors. It is used in main pipelines for various purposes.
Modern heating networks are very long, and in our climate, they require great effort to maintain their working condition.
Therefore, increasing the performance of heating networks, as well as their reliability, is an urgent problem. One of the ways to solve this problem is compensators for heating pipelines. Such compensators are used not only on main pipes and distribution networks, but also inside house heating (and not only) wiring.
Types of compensators
Structurally, such devices are of the following types:
- Oil seal compensators. These types of expansion joints for pipelines are capable of smoothing out temperature expansion along long-distance heating and water supply lines. They are the oldest type of heating main fixtures. Although it is still used successfully.
If we compare these types of elements for the heating and water supply network with bellows compensators, they have more important disadvantages.
These include the need for constant monitoring of leaks. They also do not tolerate the angular stresses of the system. The listed disadvantages are complemented by rather difficult repairs and large financial costs for maintenance. Any inexperienced master will logically raise the question of why it is necessary to install these mechanisms in heating and water supply, if they have so many shortcomings, is such a thing necessary? compensation? The thing is that stuffing box compensators have a very high compensating ability, and this becomes a priority when choosing them. They are made of steel. It includes two shells of different volumes. One shell was inserted into the other and a special gasket was installed between them. Without it, it is impossible to seal the stuffing box and move two parts relative to one another. The pressure on a pipeline with such an element can rise to 2.5 MPa, and the maximum temperature to + 300 degrees Celsius. Stuffing box compensations, in turn, are divided into single-sided and double-sided . The double-sided type differs in that it consists of three main parts (two internal and one external). It has already been said that these devices have a high compensation capability, and it increases in proportion to the increase in network volume.Important! The stuffing box type of the mechanisms can withstand temperature conditions well, but they are not allowed to be used in a network where an aggressive chemical environment passes through. The fact is that their padding does not withstand such influence well. In such conditions, the use of bellows or rubber types is recommended.
- Rubber compensation elements. These anti-vibration inserts are also a type of compensator that protects polypropylene or any other pipeline. Its difference is the presence of a working element made of rubber, which exhibits special physical properties. The estimated service life for these pipeline elements is twenty years, and during this period no maintenance or repairs will be required.
The advantages in this case include the fact that the compensation is U-shaped. in a heating system is not as resistant to cyclic displacements relative to the initial installation. Also, rubber types better tolerate short-term axial deformations (compression or tension). Compared to U-shaped devices, rubber devices are better able to withstand sudden stops in circulation and the formation of a vacuum. After the flow movement is restored, they continue to function. These mechanisms can be installed in a structure that pumps an aggressive chemical medium. They also do not change their abilities when the temperature rises to 200 degrees. The preference for installing this type of device, in contrast to U-shaped compensators, is a network with low pressure, where vacuum formation is possible. The working element in such mechanisms is located between steel flanges, and the inner layer is a rubber shell. This element, in fact, has a protective function inside. The maximum pressure in the heating system that these types of compensating elements can withstand is 2.5 MPa. - Fabric expansion joints. This is a special type of compensator that can be used to smooth out thermal expansion on gas pipelines operating under low pressure.
When manufacturing these elements, special attention is paid to the strength of the base material. Typically, such material is characterized by high frost resistance and resistance to ultraviolet radiation. The insulating coating on such elements can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to mechanical damage to the heating network. In addition to such parts, a thermal protective casing is installed. Fabric mechanisms are of the following types: devices for working with aggressive chemical environments ; devices for installation in a high-temperature pipeline; mechanisms for working in low-temperature conditions; multilayer devices with internal insulation. - Lens type devices. Lens expansion joints for pipelines are distinguished by their effective operation in smoothing axial or angular movements of the heating network caused by temperature effects. This mechanism is made up of lenses. Each is a circumferentially welded pressed steel half-lens. Thanks to their design, these devices stretch and compress, thereby smoothing out the elongation. If we compare this type of device with bellows, then the advantages are on the side of the first type. The thing is that lens devices for heating or water supply lines withstand high temperatures better and exhibit higher rigidity. But they cannot function at a very high level on a heating main. This type of mechanism is widely used in industry. Lens mechanisms according to GOST are of the following types: axial KLO; corner mechanism; rectangular PGVU; round PGVU. Lens compensator can be seen in boiler rooms, in small sections of polyethylene and other mains where high thermal compensation is not required. In addition, they are found on purge lines and near pumping equipment.
- Flange options. These compensators, as the name implies, are connected to the main line via flanges. The main advantage of these devices is their fairly simple installation. The bolts are tightened with freely rotating flanges.
But when using these mechanisms, it is necessary to take into account that these products cannot be repaired. In case of breakdown (loss of tightness), they must be replaced with new ones. Such devices will also require regular checking and tightening of the bolts. It is not recommended to paint these types of compensating mechanisms due to possible damage to the surface. - Radial options for thermal compensation on pipelines. These types of smoothing elements for heating networks work effectively on heating and water supply lines laid in a zigzag, snake, or slightly curved compensating sections. In most cases, these types of compensating elements for heating networks are considered the most appropriate because they allow cleaning devices (such as pistons) to pass through without difficulty. This type of compensator is advantageous in that it can be installed on heating and water supply lines of any configuration. But experts recommend installing it only after it is not possible to compensate with natural options.
- P - shaped. Can be horizontal, vertical or inclined. Their main purpose is to compensate for thermal linear expansion, as well as dampen vibration through the pipeline system.
Installation of compensating systems is highly desirable on pipelines of heating systems and hot water supply distributions of intra-house heating networks of a private house.
Installation of expansion joints is mandatory regardless of the pipeline material;
- Bellows devices are structures in the form of a corrugated two-layer pipe with a thin wall, the inner part is made of sheet steel grade 12x18n10t, the outer part is made similarly from St.20. This composite solution makes it possible to give the product sufficient strength while maintaining the specified safety properties.
Such inserts respond almost perfectly to lengthening or shortening of the pipe under the influence of temperatures and significantly reduce vibration phenomena. Can be used with pre-tension to increase the vibration amplitude. The advantage of such mechanisms is the ability to withstand increased loads and compactness, which significantly reduces the volume of excavation work; - stuffing box fuses - are a combination of two pipes of different diameters, integrated into each other through the stuffing box and the ground box. The inner part has the ability to move in the outer part, leaks are contained by the seal. Structurally, this is the simplest type of compensator for heating systems, but it quite reliably performs its assigned function.
When using such devices, there is a need for constant monitoring of their operation with periodic tightening of the ground axle, which is done during preventive examinations. Thus, there is a need to install inspection wells, as well as rooms in the heating main for maintenance; - lens compensators – installed on hot water supply pipelines (in particular) to compensate for thermal linear expansion
Structurally, these products are made of half-lenses made by stamping from a steel sheet, welded along the ridge. There are one-, two-, three-, and four-lens compensators. Fastening to the pipe is carried out by welding or on flanges. Dimensions of compensators according to pipe diameter in the range of 100 – 2021 mm. Installed on fixed sections of the heating pipeline. Both angular and straight versions are available. The same square and rectangular devices are used for air ducts with high temperatures; - safety rubber structures - used as vibration-damping inserts in various pipelines to dampen vibrations from pumping equipment when pumping various media, as well as mildly aggressive solutions at temperatures from -10°C to +110 at a pressure of 1.0 - 1.6 MPa.
In addition to the main function of vibration damping, it successfully works against thermal deformations of heating pipelines, as well as in the event of radial displacements and angular deformations.
Compensator SKU PPU
The compensator is made of special grades of rubber with the addition of polypropylene rubber. Reinforcement with synthetic threads is used, which increases the service life of the product.
This type of compensator is the most common for use on water supply systems, since, despite its reliability and simplicity, it has the lowest cost.
Selection rules
The choice of compensator for a pipeline for any purpose is based on an analysis of the specific characteristics of different types of models. Basic parameters (starting points of the search) - pressure in the system, temperature range, flow of the working fluid, pipe material. In addition, before making a decision, you should consider the following:
- the longest life cycle is for stuffing box options, this is one of the reasons that made stuffing box devices popular for overhauls of complex systems and repairs of heating supply networks;
- there is a direct connection between the smoothness of the mirror and the service life of the filling (models with a smoother mirror have a longer service life of the filling);
- in networks where there is a high probability of minor equipment damage, you should not use multi-layer expansion joints (with minimal deformation they lose the tightness of the chambers/channels);
- One of the weak points of the structure is the corrugation; it is easily damaged during loading/unloading and transportation, therefore its integrity must be checked before acceptance.
Why are these devices needed?
Compensation elements for a heating main are its very important components. Not everyone has an accurate idea of the load under which a heating main or pipeline operates. And their functioning is constantly influenced by temperature and pressure.
High loads from pressure, water hammer, and temperature cause compression and elongation of the material from which the network is made. All these factors lead to deformation changes and damage to the system. If all this is not taken into account and a protective element is not installed, the system will quickly fail.
It is better to select a special mechanism at the system planning stage, after first calculating the possible overload of the heating or water supply system. After this, you can install an elastic structure that has the ability to compensate.
It is recommended to use load smoothing parts for all highways. At the same time, it is necessary to clearly understand that the trouble-free operation and reliability of a heating pipeline made of steel or plastic directly depends on the correctly resolved issue of compensation.
Compensation mechanisms, in turn, are also made from various materials. Therefore, the choice of a device for a given situation must be approached with all responsibility, because this is the only way to extend the life of the heating or water supply network, and therefore save on expensive repairs.
Installation requirements and cost of installation of U-shaped devices
Despite the relative simplicity of the device, the installation of a U-shaped expansion joint is not always lower in cost, compared, for example, with the cost of a bellows expansion joint. Now we are talking about large-diameter pipelines. In this case, the cost of additional elements and their installation exceeds the cost of the bellows device, and if we take into account the need to build supports, the difference in price will be very noticeable.
If the compensator is made by bending a straight pipe, it must be taken into account that the radius of this bend must be equal to eight radii of the pipe itself. If there are seams, the structure is made so that these seams fall on straight sections. When creating steep bends, naturally, you have to deviate from these rules.
Compensators for polypropylene pipelines
Composite materials and plastics are increasingly coming into use in pipelines. Although the coefficient of linear thermal expansion of plastics is noticeably lower than that of metal, it is no less important to compensate for thermal deformations. Vibration loads for pipelines made of such materials are also extremely undesirable.
A safety device in the form of a loop for polypropylene pipelines appears to have an extremely simple design, which makes it easy to install in a heating network. Such products are widely used for their intended purpose for pipelines of all types.
By using such fuses, they eliminate the negative impact of water hammer, as well as a sharp increase in temperature (of the heating system). Thus, they can be considered as safety devices that ensure the integrity of the heating or hot water supply system.
Installation of supports
Particularly worth mentioning is the installation of supports for P-compensators. They must be mounted so that the pipeline moves only along the longitudinal axis and nothing else. In this case, the compensator will absorb all the resulting longitudinal vibrations.
Today, for one P-compensator it is necessary to install at least three high-quality supports. Two of them should be located under those sections of the compensator that are connected to the main pipeline (that is, under two vertical sticks of the letter “P”). It is also permissible to install supports on the pipeline itself near the compensator. Moreover, there should be at least half a meter between the edge of the support and the welded joint. Another support is created under the back of the compensator (a horizontal stick in the letter “P”), usually on a special suspension.
If the heating main has a slope, then the side parts of the U-shaped elements must be located strictly level (that is, the slope must be observed). In most cases, U-shaped expansion joints are installed horizontally. If the compensator is installed in a vertical position at the bottom, an appropriate drainage system must be organized.
Purpose of compensators for heating
Devices of this type perform specific but extremely important functions:
- Damping vibration of pipes that occurs along the network from the operation of pumps. Even if this phenomenon is not felt tactilely or visually, it is definitely present. Particularly dangerous is the coincidence of the vibration frequency from the pump with the natural frequency of the pipeline. In this case, resonance may occur, which can increase the amplitude of vibrations many times over, quickly destroying the pipeline system.
- Compensation for linear thermal expansion in networks that occurs when the coolant temperature changes. The ongoing lengthening or shortening of pipes causes additional stress on welded or coupling joints, reducing their service life up to the destruction of the latter.
Kozlov compensator - an elegant solution for heating and water supply
The use of such fuses on pipes of heating systems significantly increases their service life and increases the time between repairs on heating mains.
The installation of compensators is currently a mandatory step in the construction of heating networks.
Installation of compensators on pipelines of heating systems
The installation of compensators on the heating and water supply system of a residential building must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of the design documentation. The method of its fastening is by welding the pipes of the product to the pipeline.
Compensators are installed in the absence of pressure and pumped products in the pipeline. It is necessary to control the alignment of the pipe with the compensator body, which will avoid the occurrence of radial loads on the system during operation. The occurrence of such loads is fraught with jamming and breakage of the moving parts of the device.
Work on the installation of these structures on pipelines of heating systems must begin after securing its section in fixed supports and only on straight sections. In vertical areas, pressure from the weight of the system on the compensator should be avoided.
In addition to fixed ones, sliding supports must be installed on the pipeline to prevent its deformation under load during thermal expansion.
The amount of friction at these nodes is taken into account when calculating the maximum length of the section with a compensator during design. If bellows-type devices are installed, suspended supports cannot be used in this area.
When designing fixed supports, the following must be taken into account:
- The force created by the expansion joint.
- Device rigidity force.
- Frictional force in sliding bearings.
Lens compensator
Installation of protective structures is allowed on both horizontal and vertical sections of the pipeline. In this case, the arrow on the product body should be directed in the direction of the coolant flow, and in vertical sections - always downwards, regardless of the direction of movement of the coolant.
Compensators are not serviced; if a malfunction occurs, they must be replaced with a new one.
Manufacturers
The market for these products is filled, as a rule, by domestic manufacturers. Their products are characterized by quite tolerable quality and stable performance. Rubber vibration inserts are successfully produced; their own products are small in size and easy to install.
The production of bellows expansion joints is actively developing, which are also presented by “Kompenz” with fairly decent quality.
Bellows expansion joints
However, today it is not possible to cover the entire size and standard range in demand on the market. Therefore, a number of sizes of expansion joints have to be imported from abroad, which Apel also successfully does, closing the deficit gap through imports and at the same time producing its own products.
Self-compensation of heating mains and additional compensating elements
In the field of heat supply there is such a phenomenon as self-compensation. This means the ability of the pipeline to independently, without the help of special devices and devices, compensate for those dimensional changes that occur as a result of thermal effects due to the elasticity of the metal and geometric shape. Self-compensation is only possible if there are bends or turns in the pipeline system. But it is not always possible during design and installation to create a large number of such “natural” compensatory mechanisms. In such cases, it is important to think about the creation and installation of additional compensators. They are of the following types:
• U-shaped;
• lens;
• stuffing box;
• wavy.
Technical characteristics of stuffing box expansion joints, mm, for pipes with nominal pressure up to 2.5 MPa
| DУ | General dimensions | Compensating capacity, mm | Design friction force, t | Compensator dimensions, mm | |||||||
| D0 | D | D1 | L1 | L2 | one third party | two- outsider | |||||
| D2 | L | L | L5 | ||||||||
| 100 | 108 | 133 | 190 | 360 | 65 | 250 | 1,5 | 98 | 830 | 1540 | 820 |
| 125 | 133 | 159 | 220 | 360 | 65 | 250 | 1,8 | 124 | 630 | 1540 | 820 |
| 150 | 159 | 194 | 255 | 370 | 75 | 250 | 2,6 | 148 | 895 | 1590 | 850 |
| 175 | 194 | 219 | 280 | 370 | 75 | 250 | 3,1 | 182 | 920 | 1590 | 850 |
| 200 | 212 | 273 | 345 | 370 | 120 | 200 | 6 | 206 | 970 | 1670 | 980 |
| 200 | 219 | 273 | 345 | 370 | 120 | 400 | 6, | 206 | 1370 | 2470 | 1330 |
| 250 | 273 | 325 | 395 | 370 | 120 | 200 | 7,5 | 257 | 970 | 1640 | 930 |
| 250 | 273 | 325 | 395 | 570 | 120 | 400 | 7,5 | 257 | 1370 | 2470 | 1330 |
| 300 | 325 | 377 | 450 | 370 | 120 | 200 | 9 | 308 | 990 | 1670 | 930 |
| 300 | 325 | 377 | 450 | 570 | 120 | 400 | 9 | 308 | 1390 | 2470 | 1330 |
| 350 | 377 | 426 | 500 | 370 | 120 | 200 | 10,5 | 355 | 1990 | 1740 | 1000 |
| 350 | 377 | 426 | 500 | 570 | 120 | 400 | 10,5 | 355 | 1390 | 2450 | 1400 |
| 400 | 426B | 480 | 550 | 480 | 120 | 300 | 12 | 411 | 1150 | 2140 | 1180 |
| 400 | 426B | 480 | 580 | 680 | 120 | 500 | 12 | 411 | 1550 | 2840 | 1480 |
| 450 | 480 | 530 | 600 | 40 | 120 | 300 | 13,5 | 465 | 1150 | 2140 | 1180 |
| 450 | 480 | 530 | 600 | 680 | 120 | 500 | 13,5 | 465 | .1550 | 2840 | 1480 |
| 500 | 530 | 578 | 690 | 490 | 131 | 500 | 15 | 514 | 1165 | 2260 | 1280 |
| 5000 | 530 | 578 | 690 | 134 | 134 | 500 | 15 | 514 | 1656 | 3060 | 1680 |
| 600 | 630 | 682 | 790 | 490 | 134 | 300 | 18 | 610 | 1180 | 2280 | 1300 |
| 600 | 630 | 682 | 790 | 690 | 134 | 500 | 18 | 610 | 1580 | 3080 | 1700 |
| 700 | 720 | 774 | 885 | 490 | 134 | 300 | 20,5 | 698 | 11B2 | 2280 | 1300 |
| 700 | 720 | 774 | 885 | 690 | 134 | 500 | 20,5 | 698 | 1582 | 3080 | 1700 |
| 800 | 820 | 876 | 990 | 490 | 134 | 300 | 23 | 796 | 1186 | 2280 | 1300 |
| 800 | 820 | 876 | 990 | 690 | 134 | 500 | 23 | 796 | 1586 | 3080 | 1700 |
| 900 | 920 | 978 | 1090 | 540 | 134 | 350 | 26 | 894 | 1290 | — | — |
| 900 | 920 | 978 | 1090 | 790 | 134 | 600 | 26 | 894 | 1790 | — | — |
| 1000 | 1020 | 1082 | 1200 | 540 | 134 | 350 | 29 | 990 | 1800 | — | —. |
| 1000 | 1020 | 1082 | 1200 | 790 | 134 | 600 | 29 | 990 | 1800 | — | — |
| 1200 | 1220 | 1286 | 1400 | 565 | 154 | 350 | 35 | 1186 | 1865 | — | — |
| 12D0 | 1220 | 1286 | 1400 | 815 | 154 | 600 | 35 | 1186 | 1864 | — | — |
| 1400 | 1420 | 1490 | 1610 | 565 | 154 | 350 | 40 | 1382 | 1375 | — | — |
| 1400 | 1420 | 1490 | 1610 | 815 | 154 | 600 | 40 | 1382 | 1875 | — | — |
Axial unbalanced bellows (wavy) expansion joints are designed for pipelines with a diameter of 50 to 1000 mm. Bellows expansion joints can be used for all methods of laying heating networks.
Manufacturers
The domestic market mainly offers products from Russian enterprises, which are distinguished by their affordable prices and relatively good performance qualities. For example, it specializes in rubber vibration inserts - these are compensators that are small in size and versatile in laying. Quite a few manufacturers are actively developing the bellows model segment. Compensators of this type are produced with good quality by the companies “Kompenz” and “Metalkomp”. If the compensator for a pipeline needs to be supplemented with other fittings and, in particular, metal hoses, then you should turn to the Vladimirsky assortment. Of course, domestic producers are not able to fully cover all demand. Especially in advanced developments and technical innovations, Russian enterprises lag behind their foreign colleagues. In this regard, it is worth mentioning “ANT”, which not only produces, but also supplies from Europe high-quality compensators of famous brands, as well as the official distributor of the HELS brand.
Lens models
In this case, the lens refers to a welded structure that uses two thin-walled metal components. It is thanks to them that harmless deformation compression occurs. As a rule, lens pipeline compensators are used not in the singular, but in series. This can be a number of elements installed in series, each of which takes its own compensating load. There are special glasses inside the element, through which the resistance to water movement can be weakened. To ensure the release of condensate, drainage fittings are also provided in the lower parts of such lenses. Such models are effective in the sense that they make it possible to rationally use both the potential of the compensator itself and the pipeline resource by selecting the optimal number of elements.
Principle of operation
To understand the functions that the compensator performs, it should be said about the natural processes occurring in the pipeline during its operation. The fact is that under the influence of high temperatures the pipe lengthens. And vice versa, when cooling it returns to its normal state. If the line is securely fixed at two points, then there is a very real risk of mechanical deformation of the material. To prevent this from happening, a compensator for the pipeline is introduced into the design, which takes on all the loads from natural deforming processes. We can say that there is a local concentration of elongation and contraction in specific areas where compensating devices are installed. What happens to this element? It is acted upon by several forces at once, including transverse and longitudinal. In this case, the compensator can bend and take different shapes. But in any case, it must be a reliable element capable of performing responsible service while maintaining the tightness of the pipes.
Rubber models
Models of this type are made of elastomers and are distinguished by cord reinforcement. Typically, rubber expansion joints are used to work in liquid media. Actually, based on the characteristics of the coolant, an elastomer should be selected. For example, the most popular are rubber based on ethylene propylene or butadiene nitrile. In the first case, the device is supposed to be used in an aquatic environment, and the second option is intended to work with petroleum products. Not all pipeline expansion joints can handle acids and alkalis. Rubber models designed for aggressive environments are made of a special material called hypalon. To enhance resistance to chemical attack, manufacturers provide compensator material and Teflon coatings. Technologists also take care of the structural functionality of rubber products, providing them with all kinds of connecting rods and corner stops.