For many owners of suburban real estate, the problem of removing excess moisture from areas is pressing, to solve which specialized systems are used. The combination of deep drainage and storm sewer allows you to protect buildings from the negative effects of water and prevent waterlogging of the soil. With the help of Uponor specialists, we will look at how to implement similar systems on your site.
This article is part of the FORUMHOUSE Academy course.
- What functions do drainage systems perform?
- Features of drainage systems
- Features of storm drainage
- Nuances of installing drainage systems
Why are drainage and storm sewers needed?
The main task of a “storm drain” (i.e. a storm system) is to collect water from the roof – rain or melt water – using interconnected gutters and pipes. The storm drain consists of two parts - external (gutters under the roof) and underground (receivers and pipes that drain water from the house). The part that is located in the ground receives water from the roof and blind area, and then is discharged from the site.
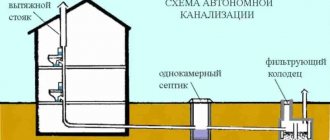
Drainage sewerage is needed to collect excess water from the ground, i.e. drain it. The main task of drainage is to prevent the groundwater level from rising and to prevent flooding of the site.
Since both systems provide for the discharge of water into special storage tanks, the combined scheme of drainage and storm water looks very attractive in terms of functionality and economy. The collected water can be used for technical purposes, such as irrigation.
It is important! “In the same trench” does not mean that the same pipes are used for stormwater and drainage. This scheme is strictly prohibited for the reason that during seasonal increases in the amount of precipitation, the storm drain is systematically overfilled. If the same pipe works as a drainage pipe, then at best the drainage will temporarily cease to function.
Range of polyethylene corrugated pipes FD plast with socket:
- Double-layer HDPE pipe for external sewerage 110 mm
- HDPE double-wall pipe for external sewerage 160 mm
- Double-layer HDPE pipe for external sewerage 200 mm
- Double-layer HDPE pipe for external sewerage 250 mm
- HDPE double-wall pipe for external sewerage 315/271 mm
- Double-layer HDPE pipe for external sewerage 340/300 mm
- Double-layer HDPE pipe for external sewerage 400 mm
- Double-layer HDPE pipe for external sewerage 500 mm
- HDPE double-wall pipe for external sewerage 630/535 mm
- Double-layer HDPE pipe for external sewerage 695/600 mm
- HDPE double-wall pipe for external sewerage 923/800 mm
- Double-layer HDPE pipe for external sewerage 1000/851 mm
Drainage and storm sewerage: types of these systems and their features
The systems have completely different structures, with only pipes and wells having similar elements. At the same time, they differ not only in structure, but also in the method of installation.
Drainage sewer (closed type)
It is located only underground, and therefore belongs to the closed type of sewer systems. The only elements that are partially located above the surface are wells.
Sectional view of a closed drainage system Source domstroim.org
There are several factors that determine whether a site needs a drainage system or not. It is done in the following cases:
- if the aquifer is located high enough on the site;
- the soil is clayey or loamy;
- floods often occur in the area where the site is located;
- a buried foundation is being built;
- The site is located in a lowland.
If one of these conditions is met, then most likely without drainage there will be problems with flooding or increased humidity in the basement and foundation.
The drainage system consists of the following elements:
- Drains (drainage pipes for sewerage, made of geotextile and perforated, through which water enters the drainage).
- Sand traps (prevent pipes from becoming clogged when silt and sand frequently enter).
- Drainage system . Conducts water purified from silt and sand directly into drainage wells.
- Several types of wells .
After the wells, where the water is purified, it enters a common storage tank, and then it is either used for personal needs or discharged into the waste system.
Materials from which drains are made:
- Plastic . Durable, not very expensive, very strong and resistant to low temperatures.
This is what a plastic drainage intermediate well looks like Source kostroma.moydom.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in water supply and sewerage.
- Asbestos cement . Cheap, but very short-lived - after just a few years, growths may appear on asbestos-cement pipes.
- Ceramics . Before the advent of plastic, ceramics were the best option
standards :
- marking SN 2-4 (depth up to 3 meters);
- marking SN 6 and what goes above for depths up to 5 meters.
Plastic products
Polymer products for groundwater drainage are superior in quality to analogues made from other materials. Its advantages:
- long service life;
- sufficient level of strength;
- resistance to aggressive chemical environments;
- low weight, thanks to which pipes are easy to lay, this process is carried out quickly;
- due to the smoothness of the inner walls, deposits do not accumulate on them, so the pipeline does not become clogged for a long time;
- the use of geotextiles during installation prevents siltation of the structure;
- you can bury the system on your own; this does not require special skills or special equipment;
- Plastic drainage is inexpensive.
Products are made from three types of polymer:
- polyvinyl chloride (PVC);
- low-density polyethylene (HDPE);
- polypropylene (PP).
The most popular drains are made of PVC. Polymer products can be:
- one- and two-layer;
- flexible (supplied in coils up to 50 meters long);
- rigid (their length can be 6-12 meters);
- perforated (fully or partially);
- wrapped in filter material.
In addition, plastic products for water drainage are divided into classes based on strength (ring stiffness). They are designated by the letters SN and numbers: 2, 4, 6, 8 and 16.
Video description
An example of arranging a drainage system is shown in the video:
Storm sewer system (open type)
“Storm drain” consists of two parts – upper and lower. The system includes:
- gutters into which water flows from the roof and which lead it further;
- funnels and vertical pipes . Water enters the funnels and then flows through vertical pipes into the lower part of the “storm drain”;
- clamps for strengthening pipes when connecting them;
- tees and swivel elbows that connect horizontal and vertical pipes to each other; a funnel can also be attached there;
- wells.
The system is assembled like a construction kit; you need to draw up a drawing of the system, carefully fasten the parts together and get a finished storm drain.
The most commonly used materials :
- galvanized iron;
- copper;
- ceramics;
- plastic (PVC).
What the storm drain will be made of is selected depending on the structure of the house, its architecture and the material from which the roof is made. You can add mesh and anti-icing cable to the gutters to prevent ice from clogging the water outlet in the spring.
Installation of an anti-icing system on the roof of a house Source rmnt.ru
For the manufacture of intermediate and main wells, the following materials are used:
- PVC (expensive but very effective option);
- Brick and stone (durable, but must be assembled correctly);
- Reinforced concrete rings (difficult to install);
Their design is exactly the same as that of a closed drainage.
Installation features
A storm drain pipe cannot simply be laid in the ground and buried. Special trenches are prepared for it, the bottom of which is filled with sand. This is necessary so that soil subsidence does not damage the pipeline, and in winter, soil heaving does not break the pipe.
The storm drainage route must have a natural slope of at least 2 mm per linear meter. During the installation of the pipeline, you need to ensure that there are no bends in the pipes in which water will stagnate.
As a rule, water conduits are made from pipes with a diameter of at least 100 mm. They are easier to clean and maintain. If an underground highway crosses a road, it is recommended to additionally protect this area with a concrete slab or place a plastic pipe in a steel pipe with a larger diameter.
Since pipes need to be cleaned during sewer operation, inspection wells are made for this purpose in several places of the storm drain.
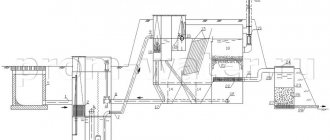
The principle of operation of drainage and storm sewerage
Storm drainage: point drainage. Point elements are necessary for collecting precipitation, be it rain, melted snow, or melted hail. Water can be sent through gutters to the drainage system, and then sent into special ditches with grates, through which water will be removed from the site. It is very important when the building is located on a slope, since if you choose the right angle, you will not need to build additional gutters, but discharge water directly into the ditches.
With linear drainage, water is discharged through gutters and funnels into a special main system consisting of pipes that are suitable for drainage and storm sewerage. Further along this main system, the wastewater enters the collector, and then, depending on the project, the water may go into a storage tank, or maybe beyond the site.
Drainage system with storage tank and site irrigation Source dp32.ru
With deep drainage, water from rising groundwater is gradually, in separate parts, discharged into the well, and from there it is pumped out and removed. This system has 3 types:
- Horizontal;
- Vertical;
- Wall-mounted. If there is a basement or ground floor in the house, groundwater must be drained from it. Wall drainage works most effectively - a moisture collector is installed near the walls, and the wall itself is carefully waterproofed.
Let's sum it up
The presence of storm drainage allows rain and melt water to be drained away from buildings and from the surface in a timely manner, maintaining the foundations and site in optimal condition. Unlike the drainage system, which under certain conditions can dry out the area, the storm drainage system of the house is safe. And an unpresentable ditch can be turned into an element of landscape design.
On the topic, we advise you to study the profile thread on the forum, and consultants and self-builders will always help and advise. Read more about drainage in clay soil in one of the previous materials. In the video - storm drainage quickly and cheaply.
Subscribe to our Telegram channelExclusive posts every week
Care and instructions for use
Both systems require regular inspection and cleaning of silt, sand, clay and other debris. Seasonal inspections are required - in late autumn when the rainy season ends and at the end of winter to ensure that the drainage capacity is not compromised. Despite various filters, sand traps and debris nets, dirt still gets inside. They are found everywhere: in pipes, gutters and wells. If left unattended, the system will simply become clogged and stop functioning.
Timely cleaning of the pipes of the drainage and storm water disposal system at the dacha will avoid many problems Source dp32.ru
To clean the pipe, just turn on the pump at maximum power and run ordinary water from a hose through the pipes; it will collect all the dirt and bring it into the well. You can pour water into the gutters and it will also collect all the dirt and then flow through the vertical pipes. The stronger the pressure, the more dirt and debris will come out.
Already in the pump, all the water is pumped out with an even more powerful pump or suction pump; when all the water runs out, it will be necessary to clean the walls. Most often, this ends with flushing, but if the system has not been looked after for a long time, it happens that you have to manually clean the walls and bottom of the well using a scraper. Therefore, regular cleaning is necessary to ensure that both systems operate reliably.
Types of drainage elements
Based on the material of manufacture, the drainage pipeline can be:
- ceramic;
- reinforced concrete;
- asbestos-cement;
- polymer.
Pipes made from the first three materials are now rarely used, as they have many disadvantages:
- They weigh a lot. Therefore, their transportation and installation are quite expensive. The system must be installed using special equipment.
- Installation of ceramic, concrete and asbestos-cement pipelines is just as difficult. It is produced only by specialists.
- Such network products have low performance characteristics. Its elements in most cases are not equipped with holes. The pipes have to be perforated manually. As a result, they become clogged faster and need to be cleaned regularly.
Rules for installing a dual system
Proper installation of a combined system must be carried out according to a pre-created project, which specifies the nuances regarding connection to the site and synchronization of the operation of wells, so that both drainage and stormwater work properly both in normal mode and during overload.
When installing, the following nuances must be taken into account:
- Arranging a drainage system is quite an expensive pleasure. If something goes wrong and after a few years the drainage stops working, then you will have to spend no less money on its restoration than on installing a new one, especially considering that you will have to “pick apart” the landscape design. As a result, drainage installation should be done by professionals.
- During the flood period, each of the systems will be overloaded. Since they collect moisture from different sources, drains must be laid for each system separately. You can do this in the same trench, but at different depths. A common well can be used to collect water.
- When digging trenches for drains, you should definitely take into account that the bottom of the hole will be covered with crushed stone and sand. This means that if it is necessary to place a drain at a certain depth, the hole must be dug deeper to the thickness of the layers of sand and crushed stone.
The pit for the drainage system well must be deep enough Source besplatka.ua
- Typically, water is collected in a storage tank (pit or reservoir), from where it is used for technical needs or pumped into reservoirs or simply away from the site. If perforated pipes are used for drainage, the outlet pipes are always solid. When combining them vertically in one trench, the perforated ones are laid on the bottom, and the regular ones on top.
- If main and drain pipes are combined horizontally in a trench, then they are laid parallel, at a short distance from each other (so that if the main pipe is damaged, water from there does not enter the drainage system and overload it).