Every homeowner is familiar with the consequences of heavy rainfall and spring snow melt.
And if, at the stage of constructing a private house, you do not take care of the construction of a storm drain on the site, then all this can result in serious problems.
Such measures will help prevent the formation of a swamp in the yard, flooding of the basement and foundation, and at the same time, it will protect the walls of the house from destruction from the outside.
Storm drainage in the house
Norms
Inside the apartment there is practically no way to measure the fluid flows in the sewer system using your own capabilities.
Professionals advise to be sure to take into account the permissible numbers indicated in the regulatory tables. According to SNiP recommendations, the flow speed should be 0.7-1 m/sec. For such a speed, the standard angle of inclination should be for products with a diameter of:
- 5 cm – 30 mm per linear meter;
- 11 cm – 20 mm per linear meter;
- 16 cm – 8 mm per linear meter;
- 20 cm – 7 mm per linear meter.
The regulatory documents that specify these rules are:
- Clause 18 SNiP 2.04.01/85. The structure of internal drainage and sewage systems for buildings is described in detail here. For example, from here you can find out that drainage branches with a cross-section of 4-5 cm should be laid with a slope of 0.03, and with a cross-section of 8.5-10 cm - 0.02.
- Clause 2.41 of SNiP 2.04.03/85 on external sewage drains describes the rules regarding the minimum slope of pipes measuring 15 cm. It should be equal to 0.008 cm, and for pipes measuring 20 cm - 0.007 cm.
- If there is a need to make the network slope smaller, you can be guided by clause 18.2 of SNiP 2.04.01-85. This point takes into account the peculiarities of liquid flow through pipes with different physical characteristics. For example, for plastic pipes the speed coefficient should be 0.5, and for networks made of other materials the coefficient should be 0.6.
A separate explanation in SNiP 2.04.03/85 concerns external sewers with pipe sizes of 15-20 cm. In particular, the rules allow the use of standard indicators for slopes: 0.005 for 20 cm products, 0.007 for 15 cm products.
Clause 18 of SNiP 2.04.01/85 regulates the maximum slope of networks, which should not be more than 0.15. At the same time, branches from plumbing fixtures, the length of which is up to 150 cm, are excluded from the calculations. Thus, on each meter of the sewerage system no more than 15 cm of slope is allowed. If the indicator is exceeded, the highway will silt.
Special tables can help with calculations.
| Plumbing device | Diameter, cm | Slope per meter, cm | Gap between central drain and siphon, m |
| bathroom | 0,4 | 3 | 1-1.3 |
| bath, shower, washing machine | 0,5 | 4.8 | 1.7-2.3 |
| shower room | 0,4 | 4.8 | 1.5-1.7 |
| toilet | 10 | 2 | Until 6 |
| bidet | 0,3, 0,4 | 2 | 0.7-1 |
| washing | 0,3, 0,4 | 3.6 | 1.3-1.5 |
| sink | 0,4 | 1.2 | 0-0.8 |
| main riser | 10 | ||
| branches from the riser | 6,5-7,5 |
In the mathematical system, angles are measured in degrees, so the numbers given in tables often become unclear. And the numbers mean the fractional ratio of the height of the slope to the length of the drainage system. It will be easier to track the value if you convert the numbers to centimeters. For example, 3 cm by 1 meter, 0.8 cm by 1 meter. If the length of the entire sewer is known, you can multiply it by the slope, which will give the total height for the entire designed sewer.
Principles for determining the minimum slope
So, in order to determine the slope of a storm drain according to SNiP, attention is drawn to:
- type of water pipeline;
- diameter of pipes being laid;
- surface coating.
As was said, when using 200 mm pipes, the slope must be at least 0.7 cm, and the slope must be provided for each linear meter.
As for pipes d=150 mm, here the slope is already slightly greater, about 0.8 cm/m.
It is worth noting that the building codes also stipulate that if there is an urgent need, the slope in certain areas can be reduced. For 200 mm pipes the minimum value is 0.5 cm, and for 150 mm it should not be less than 0.07 cm.
The same document also regulates the maximum slope value; it is 1.5 cm/m.
Storm sewer pipe, diameter 200 mm
All rules and regulations must be followed, because otherwise the risk of clogging may increase significantly.
For example, if you make a very large slope, the water will drain too quickly, and accordingly, the sand settling from it will silt up the surface of the pipe from the inside.
Slope of open type storm drain
As for the slope of an open-type storm drain, its value is determined by the type of surface, for example, where the ditches are asphalt - 0.3 cm/m, and where with crushed stone and cobblestones, then 0.04-0.5 cm/m.
Features of the depth of storm drainage according to SNiP
The regulatory document does not provide precise instructions on the depth of pipes. But there are some recommendations. When choosing depth, several important factors are taken into account
They take into account the depth of soil freezing, the occurrence of water, and the personal experience of the specialist.
Recommendations for choosing the depth of storm drains:
- If the dimensions of the pipes are less than 500 mm, then they should be laid 30 cm below the soil freezing level;
- If the diameter exceeds 500 mm, this figure is 50 cm.
The thickness of the sand cushion should be added to the burial depth. This is the indicator that is considered optimal. In any case, there should be at least 70 cm from the surface of the earth to the pipe. But if installation to the required depth is not possible, then you will have to make additional insulation and provide protection from mechanical damage.
Drainage well - concrete or plastic
Drainage wells are classified based on the materials from which they are made. Depending on this, technical, operational and technical characteristics are determined. The most common drainage wells for storm sewers are concrete and plastic. Of course, nowadays plastic wells are more common than concrete ones. They have the following advantages:
- Low weight;
- Easy installation without the use of specialized equipment;
- Huge endurance;
- Ease of operation;
- Impermeability;
- Resistant to adverse weather conditions.
Despite numerous advantages, plastic wells also have significant disadvantages:
- High cost compared to those made of concrete;
- Depth restrictions during installation;
- Fragility of the material.
Drainage wells made of concrete have the following advantages:
- Tightness;
- Low cost;
- Speed of installation;
- Possibility of installation in absolutely any type of soil;
- Unpretentiousness in care.
There are practically no disadvantages to concrete wells. The only drawback is its weight, which requires the use of specialized equipment during installation.
When the question arises about which drainage well to choose, it is impossible to answer unequivocally. Everyone will be guided based on their preferences and financial capabilities.
Important features of laying sewer pipes
- When installing a pipeline system in deep basements or in places with low relief, versions with an extremely low sewer installation depth are provided, in which the installation of a pumping station is provided. The depth of the pressure line must be calculated according to the requirements of regulatory documents.
- Practice has shown that in problem soils (water-saturated, compacted to strong and silty) communications should be laid to a depth of four meters, in dry soils the depth is determined from four to seven meters.
- Communications built with a depth of less than 0.7 meters must necessarily have a sewerage protection zone on the surface of the earth. The security zone is equipped with a system to protect against possible mechanical damage to the pipeline.
- When carrying out projects for laying sewer communications, it is mandatory to take into account the difference in terrain relief lines.
Organization of slope in a private house
The volume of wastewater in a country house is significantly less than in an apartment building. Under these conditions, even with a minimum slope determined from a hydraulic calculation table or formula, the filling level will be insufficient for self-cleaning of the pipe.
It is impossible to reduce the slope even more, since the flow rate will become too slow. Sand with other solid inclusions will settle to the bottom, and the pipe will probably clog. In such a situation, the required angle of inclination of the pipeline is determined by a non-calculation method.
Non-calculation method for determining slope
According to regulatory documents, the non-calculation method is used in cases where, due to the small volume of wastewater, it is impossible to fulfill the condition for the relationship between the optimal and actual filling level.
The old version of SNiP 2.04.01-85 set out the following recommendations on slope for undesigned sections of gravity pipelines:
- Pipe diameter 40 or 50 mm – 0.03
- Pipe diameter 85 or 100 mm – 0.02
The updated version of this SNiP, set out in SP 30.13330.2016, suggests that the minimum slope value for non-calculated sections of the pipeline should be considered equal to 1/d, where d is the outer diameter of the pipe in mm.
Recommendations from specialists for laying a collector from an individual country house to a septic tank:
- A medium-sized house with two bathrooms - 110 mm pipe with a slope of 0.02
- House with three or more bathrooms - 160 mm pipe with a slope of 0.08
Compliance with the proposed parameters preserves the transporting capacity of the liquid flow in the pipeline.
Slope check
The best device for checking the angle of inclination is a level. The device measures the depth of the trench under the pipeline at control points, and the difference is compared with the required value. If there is a deviation from the calculated value, the trench depth is adjusted.
To check the slope without a level, use a simple method using available tools. Two pins are inserted into the bottom of the trench at both ends. The cable is pulled between the pins and the horizontal position is checked using a building level. If necessary, leveling is done.
Then, near both pins, measure the height from the bottom to the cable. After determining the magnitude of the difference, proceed in the same way as in the situation with a level.
In the figure below, the initial depth of the trench is 0.5 m. Based on the recommended slope of 0.02 for a 110 mm pipe, we obtain:
We add the calculated depth difference of 0.6 m to the initial depth of 0.5 m and obtain a trench depth at the end point of the pipeline of 1.1 m.
Solving the problem of a steep slope
If in the direction of laying communications the steepness of the slope exceeds the standard slope, then at some point the more gently located pipeline will come to the surface. The problem can be solved in two ways.
The first option is to make vertical decreasing sections in the pipeline as it approaches the surface. In the second option, a large vertical depression is immediately made, which is enough for the entire length of the collector.
Downgrade scheme according to the first and second options
Example of storm sewer calculation
Some designers do not go into the details of storm sewer calculations, using the recommended pipe diameters specified in SNiP. For non-pressure networks, a pipeline with a diameter of 200-250 mm is usually used as a drainage system. It is this size that guarantees the optimal speed of movement of surface runoff in the event of intense precipitation. At the same time, a correctly performed calculation contributes to more efficient management of the budget, since pipes of a smaller diameter may be suitable for the normal functionality of the storm network.
Calculation of pipe diameter allows you to reduce costs without compromising the functionality of the system
As an example, let’s calculate the parameters of a drainpipe for the roof of a private house with an area of 100 m² (0.01 ha), located in one of the settlements of the Moscow region:
- According to the rain intensity map, the q20 parameter for Moscow and surrounding areas is 80 l/s. The moisture absorption coefficient for the roof is 1. Based on these data, we calculate the flow of rainwater:
Qr =80·0.01 = 0.8 l/s
- Since the roof slope in a private house, as a rule, significantly exceeds 0.03 (3 cm per 1 m), the fill factor of the free tank during pressure mode is taken equal to 1. Thus:
Q = Qr = 0.8 l/s
- Knowing the rainwater flow rate, you can not only calculate the diameter of the storm drain, but also determine the required drainage slope. To do this, we will use the reference book by A.Ya. Dobromyslova “Tables for hydraulic calculations of pipelines made of polymeric materials. Non-pressure pipelines." According to the calculated data presented in the tables, for a flow rate of 0.8 l/s, pipes with the following parameters are suitable:
- diameter 50 mm, slope 0.03;
- diameter 63 mm, slope 0.02;
- diameter 75 mm (and higher), slope 0.01.
The slope of the pipe is inversely proportional to its diameter
- Pipeline material.
SNiP allows the use of pipes made of asbestos cement, steel and plastic (PVC). An asbestos-cement pipeline, although an economical option, is used quite rarely today due to the fragility of the material and its heavy weight (1 meter of a 100 mm pipe weighs 24 kg). Steel pipes are much lighter than asbestos, however, they are prone to corrosion. Therefore, PVC pipes are most often used for storm drains, which combine light weight, ease of installation and long service life.
- The depth of the underground part.
The optimal location of the pipe is below the soil freezing level and above the groundwater level. Since not every location allows this condition to be met, it is permissible to lay the pipeline at a shallow depth, but no closer than 70 cm to the surface.
- Installation of risers.
Rainwater is drained from the roof by means of risers, under which point or linear rainwater inlets are placed. Vertical drainage systems are attached to the wall using clamps. The calculation of the fastening interval for storm sewer risers is carried out taking into account the pipe material. For PVC, clamps are placed at intervals of 2 m, for steel - 1-1.5 m.
- Secured territory.
SNiP provides for the organization of so-called security zones near the location of the stormwater network. At a distance of less than 3 m from the pipeline, it is prohibited to erect construction projects, plant bushes and trees, arrange a garbage dump, or arrange a parking space.
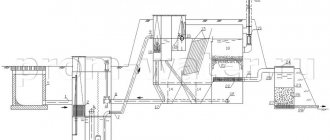
Typical storm drainage scheme for a private house
Designing a rainwater drainage system is an important stage in the construction of a residential building or industrial site. This article provides formulas for a rough calculation of the diameter of a pipeline, since they do not take into account parameters such as friction of water on the inner surface of the pipe, the number of bends and connections in the system, etc. For more accurate calculations of storm sewers, there are special programs that can be found on the Internet . However, the surest method is to entrust the design to specialists who will take into account all the nuances and offer the most effective and cost-effective option.
SP requirements for storm sewer slope
Preliminarily, an accurate calculation is carried out and a pipeline laying diagram is drawn up. All this will help determine the amount of material needed.
The minimum slope of the SP storm drain depends on the diameter of the pipes being laid.
The slope can be calculated using online calculators. Today they are freely available on the Internet. You can search the Internet for tables with ready-made prescribed values of the required slope for pipes with different cross-sections.
According to average indicators, it can be determined that:
- pipe DN 110 should go with a slope of about 20 mm per 1 m;
- DN 150 - this value is reduced to 8–10 mm;
- DN 200 - the required slope is 7 mm per linear meter.
For pipes with a diameter of 50 mm, the difference should be no more than 30 mm/m. This guarantees optimal water drainage speed.
Construction of storm drainage
In general, installation work on the installation of storm drains is carried out in the same way as when laying external pipelines of a conventional sewer system.
Selection of pipes for the underground part of the pipeline
If external storm sewer networks are installed, SNiP allows the use of the following types of pipes:
- Asbestos-cement;
- Steel;
- Plastic.
Asbestos cement is a traditional material used for the construction of external sewerage pipelines, including stormwater. The disadvantages of the material include its high fragility and significant weight (a meter of pipe with a diameter of 100 mm weighs more than 24 kg). Steel pipes have much less weight (a meter of pipe weighs about 10 kg), but they are prone to corrosion, so it is not profitable to use them for the construction of storm drains.
Recently, plastic pipes have been used to construct storm drains. They are light (a meter weighs no more than 5 kg), but durable and resistant to corrosion. In addition, they are easy to connect and do not require welding. Can be used:
- PVC pipes, if external networks are installed, then for their construction you need to use a special type of pipes, they are painted orange;
- Multilayer polymer pipes. Today this is the best option. These pipes have a smooth inner surface, so there is no hydraulic resistance.
Installation of the roofing part
The work goes like this:
- Openings are made in the ceilings for installing rainwater inlets, and all junctions are carefully sealed.
- Drainage pipes are strengthened when constructing a point system or trays when installing a linear storm drain.
- Install drain risers or pipes.
- A unit is assembled for discharging water into a collector or discharging into tray systems.
- All devices are attached to walls and ceilings using clamps. Places for installing clamps are planned in advance, not forgetting to follow the recommended slope values.
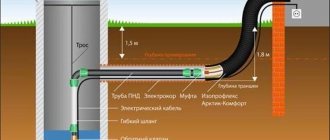
Laying the underground part
- Installation begins with the installation of trenches. When constructing systems such as storm sewers, the depth of installation is most often determined not by the depth of freezing, but by the experience of operating the systems at the construction site.
- Trenches are dug with a slope, that is, their depth should gradually increase.
- At the bottom of the trenches there is a sand cushion, the layer height is 20 cm.
- A pit is being prepared for installing the collector.
- Pipes should be laid in the prepared ditches, the pipes should be connected to each other and connected to the collector using conventional fittings.
- If the sewer network consists of a single branch more than 10 meters long, then it is worth planning to install a manhole in the middle of it. Such wells should be installed at network branch points.
- Sand traps are installed at the junction of water inlet gutters and stormwater pipe systems.
- Now all that remains is to backfill the trenches and cover the open structures (trays) with gratings on top.
Criteria for selecting gratings for storm drainage
One of the main elements of the sewer system is considered to be storm grates, which are oblong plates with identical holes. These grilles perform the following functions:
- Provide protection for gutters from mechanical damage;
- Prevents the system from filling with various types of debris;
- Ensure the safety of the movement of people, animals and vehicles;
- Landscaped areas.
All gratings for storm drains are divided into the following classes:
- A-C - quite durable and resistant to various types of influences. Capable of withstanding loads from 1.5 to 25 tons. Installation of such grilles is carried out in areas of heavy traffic.
- DF – such gratings are used in areas of dense traffic flow with significant loads. Capable of withstanding from 40 to 90 tons.
Also, when choosing gratings, you should take into account the material from which they are made. They come in cast iron, plastic and galvanized. Plastic gratings are mainly used for storm drains in household plots or park areas. They are distinguished by durability, huge throughput, affordable price, low weight and ease of installation. As for metal gratings, they are able to withstand enormous loads, despite their low weight. This is achieved through pressing during the production process. Metal grilles are also easy to install and have an attractive appearance. But they also have a drawback - they are quite expensive.
Cast iron grates are rightfully considered the most reliable gratings for storm drainage. They can be used in absolutely any conditions. They can withstand even the highest loads. In most cases, they are used in industrial areas with heavy traffic, as well as in transport terminals, ports and airports.
When choosing gratings for storm drains, it is quite difficult to give primacy to any type or material, since they are selected individually for each system. When choosing, you should be guided by the following criteria:
- Price;
- Permissible load class;
- Difficulty of installation;
- Length and width of gutters.
Studying the standards
All construction and installation work must be carried out in accordance with current standards, rules and regulations. Such requirements are specified in GOSTs and SNiPs. The same applies to the installation of storm drains. SNiP 2.04.03-85 is in force here, which is called “Sewerage. External structures and networks."
Some paragraphs of this document indicate the recommended depth for laying stormwater pipes. According to them, installation should be carried out:
- for pipes with a cross-section of up to 500 mm, at least 30 cm below the ground freezing level;
- for pipes with a cross-section of more than 500 mm - at least 50 cm.
But all these points regarding the depth of occurrence are rather advisory in nature. Their use lies with the conscience of installers and builders. According to SNiP, installation must be carried out based on the experience of operating sewer systems in each specific region. In general, the minimum depth should be at least 70 cm from the surface.
Pipe immersion depth
A specific feature of storm networks is the depth of the storm sewer. The system operates unevenly, only during heavy precipitation or active snow melting. The rest of the time, the internal volume of the pipelines is empty. Therefore, the depth of the pipes may be small. In the cold season there is no water in them, there is nothing to freeze. This feature facilitates the construction of stormwater networks and reduces the volume of excavation work. The only task that arises when creating a storm drain is to ensure at least a minimum slope of the storm drain. As a rule, it is its value that becomes the main condition for immersing pipelines in the ground. To determine it, the SP has a corresponding table. In addition to the slope, it is also necessary to pay attention to the routes for laying networks. It is recommended to place them away from roads and other busy areas. Mechanical loads can destroy pipes, so you will have to bury them to great depths. The regulatory document that regulates the depth of installation of storm sewers, SNIP, allows for fairly wide limits for systems to be immersed in the ground. They are determined by various factors, mainly of a technical nature.
Formulas for hydraulic calculation of storm networks
In order to calculate the diameter of a storm sewer pipe, it is necessary to determine the average flow of rainwater, which depends on the climatic conditions in a particular area.
The maximum flow rate (intensity) of rainwater is calculated using the formula:
Qr = q20·Ψ·F
Where:
q20 – estimated rain intensity for 20 minutes;
Ψ – coefficient of moisture absorption by a certain type of coating (roofing – 1.0; asphalt – 0.95; concrete – 0.85; crushed stone – 0.4);
F – surface area (in hectares) on which drainage is planned.
Rain intensity map for determining q20 coefficient
For the hydraulic calculation of the storm drainage network, it is necessary to make an adjustment for the filling factor of the free pipeline when a pressure regime occurs (β). Thus, the flow of rainwater is calculated as
Q = Qr·β
Coefficient β is determined from the table:
| Rain duration indicator n | 0,7 | 0,6 | 0,5 | 0,4 |
| β coefficient value | 0,65 | 0,7 | 0,75 | 0,8 |
In turn, the parameter n depends on the geographical location of the object:
| Area | Parameter value n |
| Coast of the Barents and White Seas | 0,4 |
| North of the European part of the Russian Federation | 0,48 |
| Center and west of the European part of the Russian Federation | 0,59 |
| Western slope of the Urals | 0,59 |
| Lower Don and Volga | 0,57 |
| Lower Volga region | 0,66 |
| Central Siberia | 0,47 |
| Eastern Siberia | 0,52 |
| Western Siberia | 0,58 |
| Altai | 0,48 |
| Coast of the Sea of Okhotsk | 0,31 |
If the terrain slope is 1-3 cm per 1 m, then the β coefficient must be increased by 15%. For a larger slope, this parameter is taken equal to 1.
Calculation of pipe filling degree
What pipe diameter should I choose for laying external sewerage? This question should stand alongside other factors when creating a project. Because the rate of water drainage depends on this. The water filling coefficient is measured in centimeters per meter; the degree calculation cannot be used here due to the fact that errors will arise, for example: the length of the pipeline is too large and ultimately even a small discrepancy will lead to the fact that the elements will not converge and will be located in different planes .
The value that will be optimal for the operation of the sewerage system is calculated by the formula, it sounds like this: we divide the sewerage rise level “H” by the diameter of our sewer pipe “D”. The value we should get should vary between 0.5 and 0.6. If we get 0 during the calculation, this will mean that the pipe will be constantly empty. If we have the final number 1, then the pipe will be constantly and completely flooded with water. Which will have a detrimental effect on the system. The formula itself looks like this
Y=H/D
- H – height;
- D – diameter;
- Y – filling values.
If you use PVC pipes, then its filling should be 0.5. The reason for this is its inner surface; it has no roughness. Unlike asbestos or iron pipes, they have the highest degree of roughness, for this value it is 0.6.
The value described above will allow wastewater to pass at an average speed of 0.7 m/s. This will keep solids suspended, preventing them from sticking to the walls of the sewer pipes.
The importance of choosing the correct drainage slope
In most cases, when planning storm drainage systems, preference is given to gravity systems. In such options, the movement of wastewater is carried out by natural gravity. In order for such a system to function properly and without interruptions, care should be taken to lay the pipes at a certain slope. After all, normal operation of the sewer system is possible only if the slope is correctly executed. The slightest mistake in this matter can lead to the failure of waste liquids to pass through and the formation of blockages. But you shouldn’t count on the fact that the greater the slope, the faster the drains will drain. With a fairly strong slope, flooding and breakdown of water locks may occur. Do not forget that the system must be constructed in such a way that the lowest point is at the entrance to the septic tank.
Another significant point is that the slope level is expressed not in degrees, but in centimeters per linear meter. This is due to the significant length of the pipeline and possible errors.
Rainwater drainage via other networks
Private real estate projects traditionally include other communication networks along with storm drainage. Domestic sewerage and drainage systems are also part of household communications. The principle of their operation differs little from the functioning of storm drains, in which owners of private houses often see the possibility of using these networks.
Meanwhile, the combination of storm sewerage with a domestic or drainage drainage scheme is prohibited by SNiP. The ban on combining different types of sewage systems is due to obvious factors. Thus, provided that rainwater is discharged into the domestic sewer system and taking into account the high intensity of precipitation, the normal level of sewerage is increased several times.
Flooding of working wells leads to blockage of household and fecal wastewater. Mud deposits and natural debris flow into the domestic sewage system. As a result, after the next rainstorm, the organizers of the structure will have to clean the system.
Combining a stormwater system with a drainage main threatens to result in even more disastrous results. Overflow of drainage due to violation of design loads leads to flooding of the building foundation. Frequent flooding disrupts the structure of the soil, which causes displacement of foundation blocks, and in the future can lead to the destruction of the building.
Repair of sewer wells
If a storm sewer system is installed, then, of course, it is necessary to think about repairing wells. This applies not only to emergency cases, but also to systematic maintenance and periodic scheduled repairs. If this is not done, then during operation everything will lead to the following unpleasant consequences:
- Subsidence of the well into the ground;
- Destruction of brickwork and asphalt pavement along the perimeter;
- Destruction of the inspection well and tray.
And this is not all the adverse consequences of neglect. To avoid this, you should do the following in time:
- Carry out regular technical inspection and maintenance. This involves removing dirt and debris from the bottom of the wells, which helps prevent the possibility of clogging the entire system. You can clean the wells yourself using a hose and a drainage pump that will supply clean water.
- Perform major cleaning and repairs at least 10 years. It includes diagnosing the system and flushing to remove deposits that have formed.
Only proper operation and timely repair work can extend the life of the entire system to fifty years. Although this is not a chapel. This period is negotiated due to the fact that during this period the wear of polymer materials occurs, but despite this, the operability of the system remains for about twenty years.
Individual slope calculation
Laying sewer pipes with your own hands in a private house is carried out according to the standards that appear in SNiP. But you can calculate the parameters for the arrangement of sewerage and water supply networks yourself. To do this, use the following formula:
V√H/D ≥ K, where:
- K is a special coefficient that takes into account the properties of the material that was used in the manufacture of the pipe;
- V – speed of passage of wastewater;
- H – pipe filling capacity (flow height);
- D – section (diameter) of the pipe.
The slope of sewer pipes can be calculated independently
Explanations:
- coefficient K, for pipes made of smooth materials (polymer or glass), should be equal to 0.5, for a metal pipeline - 0.6;
- indicator V (flow velocity) - for any pipeline is 0.7-1.0 m/s;
- H/D ratio - indicates the filling of the pipe, and should have a value from 0.3 to 0.6.
Internal and external sewer systems
When laying sewer and water supply networks in a private house, you should take into account some features that are determined by the location of their individual sections.
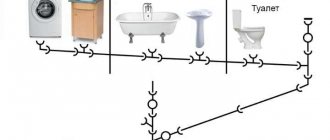
Internal systems
When installing sewer pipes in a private house, two diameters are mainly used - 50 mm and 110 mm. The first is for drainage, the second is for the toilet. The laying of the sewer pipe should be carried out in accordance with the following recommendations:
- turning the pipeline (if it is horizontal) should not be done at an angle of 90 degrees. To change the direction, it is better to install the bends at an angle of 45 degrees, this greatly facilitates the passage of the main flow and reduces the likelihood of accumulation of solid particles;
- in places where the system turns, fittings should be installed for inspection and ease of cleaning or dismantling in case of clogging;
- in short individual sections, it is permissible to increase the slope, exceeding the recommended norm. Such a short sewer branch can be a pipe connecting the toilet to the riser;
- in each individual section, the slope of the pipeline must be uniform, without sudden changes, because their presence can create conditions for the occurrence of a water hammer, the consequences of which will be the repair or dismantling of an already operating system.
External (external) systems
Proper laying and installation of sewer pipes is necessary not only inside, but also outside a private home, from the point of exit of the internal sewerage system to the septic tank.
Therefore, you should pay attention to the following points:
- laying of sewer networks is carried out in trenches with a depth of 0.5 to 0.7 meters. The depth of penetration depends on the characteristics of the soil and is adjusted to specific conditions;
- when preparing trenches, sand should be used at the bottom to be able to establish the correct slope by adding it;
- highlight the pre-calculated slope (per linear meter) as a guide from the cord stretched between the driven pegs. This will avoid unnecessary subsidence or elevation of the sewer system in certain areas;
- After laying the pipes at the bottom of the trench, check again for the correct slope and, if necessary, correct it using a sand cushion.
Professional calculation of slope and other storm drain parameters
It is almost impossible to independently calculate the slope of a storm drain and draw up an installation and commissioning project without special knowledge.
Of course, the site owner can try to design the system at his own risk. But we don't recommend doing this. And that's why.
Even in cases where calculations are required for a small building on urban land or in rural areas, drawing up a project is an obligatory part before starting work. It is important to comply with all established standards (sanitary and construction).
Special organizations with state certification to conduct design and survey work have the right to carry out such activities.
Before contacting the relevant services for calculations, the customer must collect a package of documents that will be used in developing the technical specifications:
- Topographical diagram of the territory where the construction of a storm sewer system is planned.
- Results of geological surveys indicating the quality characteristics of the soil, the level of soil freezing, groundwater level on the building site.
- Layout of a cottage or house.
- When it is possible to discharge water into a centralized sewer system, technical specifications for water utility services for connection will be required.
- Sanitary standards for water purification when discharge to drainage fields or natural sources is expected.
- The customer's wishes regarding the possibility of accumulating collected water.
This is interesting!
Connecting a sewer system in a private house: stages and options Read more
The result of the designers’ activities should be a package of documents containing:
- Detailed storm drainage diagram.
- Comprehensive information about the development area, terrain features and installation of storm drainage systems in these conditions.
- Plan-drawing of each stage of construction. In other words, this is an instruction that indicates the location of each storm drain element.
- Specification of equipment required by technical specifications.
- Preliminary estimate for the purchase of all required building materials, installation, commissioning and commissioning.
The presented version of the project must be agreed upon with the water utility, state technical supervision authorities, the sanitary-epidemiological service, and the environmental control service, which is in charge of the state of water resources.
You can begin construction after receiving a visa from each of these organizations.
Sometimes it is possible to reach an agreement with a design company, and it takes over the process of approval with government agencies.
Drawing up a project is not an easy task; it requires scrupulousness even in small things.
We recommend entrusting the development of the project to a qualified specialist in a trusted organization in order to subsequently protect yourself from fines due to violation of environmental legislation. And, of course, this will ensure the correct calculation of the storm sewer slope and its successful operation for many years.
;
Sewerage
Did you find this article helpful? Share it with your friends: