Standards governing steel pipe wall thickness and other characteristics
When choosing appropriate products and analyzing suitable characteristics, keep in mind that there are several standards.
First of all, they are designed for different production technologies:
- GOST 10704-91 regulates the requirements for the production of electric-welded straight-seam pipes;
- GOST 3262-75 describes steel water and gas pipelines;
- GOST 8732 – seamless hot-deformed.
Straight-seam electric welded pipes
The range of each of the listed types implies requirements for wall thickness, which also depends on the nature of the technology used for production (reflected in the tables in the appendices to each standard). For example, seamless hot-formed products have higher tensile strength than others. These products are designed for a specific type of work that dictates durability and performance requirements. Strength will depend on wall thickness, steel grade (in some cases), and production technology.
Steel water and gas pipes
In general, the diameter and wall thickness of steel pipes made using casting technology (standard 8732) implies a wall from 2 to 45 mm with sizes ranging from 20 mm to 550 mm, respectively; conventionally, the wall thickness is approximately 1/10 of the size. The parameters can be analyzed in more detail using the appropriate regulatory standard.
Seamless steel hot-formed pipes
What is the nominal pipe size?
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) is a North American set of standard sizes for pipes used for high or low pressures and temperatures.
The name NPS is based on the earlier Iron Pipe Sizing (IPS) system. This IPS system was created to indicate pipe size. The size is the approximate internal diameter of the pipe in inches. IPS 6" pipe is pipe that has an internal diameter of approximately 6 inches. Users started referring to the pipe as 2-inch pipe, 4-inch pipe, 6-inch pipe, etc. To begin with, each pipe size was manufactured to have one thickness, which was later named as standard (STD) or standard weight (STD. WT.). The outer diameter of the pipe was standardized.
To meet industrial requirements for higher pressure fluids, pipes were manufactured with thicker walls, which became known as extra strong (XS) or extra heavy (XH). Higher pressure requirements increased with thicker walls. Accordingly, the pipes were manufactured with extra-strong (XXS) or extra-heavy (XXH) walls, while the standardized outer diameters remained unchanged. Please note that this site only uses the terms XS and XXS.
Steel electric-welded straight-seam
In straight-seam welded products, the metal thickness increases in increments of 0.2 mm. According to the standard, the wall thickness of electric welded steel pipe is from 1 mm to 32 mm. This is the only technology that produces products with a 1 mm wall.
Dimensions of steel electric-welded longitudinal pipes
When choosing straight-wood ones based on size and required metal strength, keep in mind that the seam is made with reinforcement. It is this gain that affects the total weight of the product and is approximately 1%. These products are suitable for a number of jobs and are made of sheet steel. The wall also depends on the passage opening of the product. More detailed information on the relationship between thickness and size, as well as the weight of the product, can be found in the corresponding section of the standard.
Solid and reinforced polypropylene pipes
In addition to classification according to the composition of polypropylene pipes, products differ in structure and number of layers. This affects their strength and coefficient of linear expansion when heated. The type of reinforcing material also varies, as does the technology for its application. In this case, the copolymer base can be one of the four types described above. Let's take a closer look.
Solid polypropylene pipes (single-layer)
Single-layer pipes are made of polypropylene and do not have any solid inclusions inside their structure. They are easily cut to size and are one of the most affordable on the market. Products are produced with a longitudinal blue or red stripe, indicating the temperature intended for the product.
Polypropylene pipes with red stripe.
Polypropylene pipes with blue stripe.
Pipes with a red stripe are used for hot water supply and heating systems. They, unlike versions with a blue stripe, have stabilizing additives that reduce linear expansion when the walls are heated. Practice shows that even such cheap pipes serve in plumbing and heating systems for decades.
White polypropylene pipes.
Gray polypropylene pipes.
Reinforced polypropylene pipes
Reinforced pipes have additional inserts inside that inhibit linear expansion as the temperature rises. Such pipes are more expensive, but are more durable and bend less when the coolant heats up. Products differ in material and reinforcement technology. Such pipes are used mainly in individual and centralized heating systems.
Glass fiber reinforcement
To make such pipes, polypropylene is poured into a mold into which fiberglass fibers are laid. Because of this, the pipes are called fiberglass. The result is a homogeneous structure (polypropylene passes through the fibers, enveloping them on all sides).
Polypropylene pipes reinforced with glass fiber device.
1. Polypropylene.
2. Stereo fiber.
3. Polypropylene.
This provides the following benefits:
- the rigidity of the pipes increases, since fiberglass does not stretch as much as plastic;
- soldering is carried out without preliminary preparation - simply the ends are placed on the soldering iron and aligned after heating;
- installation time is reduced;
- the system does not oxidize from the inside;
- fiberglass melts easily and provides a durable seam;
- Due to the homogeneous structure, the pipes do not delaminate.
But fiberglass pipes lose as much as 6% in terms of expansion when comparing their performance with pipes with aluminum reinforcement.
Aluminum reinforcement (double-layer pipes)
When making such pipes, thin aluminum is added to increase the rigidity of polypropylene. It is located inside the circle and is in direct contact with water.
The outer shell of plastic only complements the thickness of the case, and the main restraining role in resisting linear expansion is played by metal. As a result, the pipes are two-layer. One of the disadvantages is that before soldering you will have to clean the metal layer (from the part that fits onto the outer coupling) in order to melt the ends well.
Aluminum reinforcement (three-layer pipes)
Another type of reinforced pipes is a three-layer structure. A layer of plastic is used inside to ensure accelerated flow of coolant and protection against corrosion. There is aluminum foil in the middle, and another layer of polymer on the outside.
Three-layer pipes are more expensive than others, but they are of the highest quality, since the metal in them does not come into contact with water. There is no need to clean anything before soldering. But cases of delamination still occur due to poor-quality glue used by the manufacturer. You should buy pipes only from trusted companies. There are several varieties of this design.
Continuous reinforcement
The inner layer of foil is attached to polypropylene using a special glue. This technology is slightly cheaper than the next one because it is easier to implement.
Construction of a polypropylene pipe reinforced with solid aluminum.
Perforated reinforcement
A more advanced option is reinforcement using a perforated sheet of foil. Due to the holes in the metal, the use of glue is not required. Polypropylene in liquid form perfectly penetrates through perforations and bonds with aluminum. Such pipes resist linear expansion well and do not delaminate, but are more expensive. The downside is the same cleaning before soldering, which slows down the installation process.
Construction of a polypropylene pipe reinforced with perforated aluminum.
1. Polypropylene.
2. Perforated aluminum.
3. Polypropylene.
Steel water and gas pipelines
Steel water and gas pipes are made in different assortments, characteristic of the category.
The standard specifies the following types of pipe products (see photo):
- light;
- ordinary;
- reinforced.
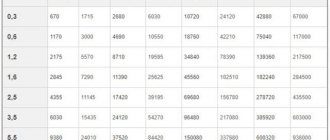
For example, for an outer size of 10.2 mm, the parameter will vary in the following values: 1.8, 2.0, 2.5, respectively. The same dependence is typical for standard pipe products with an internal diameter of 20 mm, the metal thickness is 2.5, 2.8, 3.2 mm, respectively.
Size chart for thick-walled pipes
When purchasing, specify what kind of pipe you are interested in - light, ordinary or reinforced, and not just the standard internal diameter of 20mm. When this parameter changes, the strength of the metal of the water and gas pipe will change at the same diameter.
For what purposes is the mass of steel pipes determined?
Steel pipes are widely used in the construction industry. In any project you can find information about the mass of the water supply system laid in the building. The same applies to other pipeline systems and structures made from rolled profiles. The weight of water and gas steel pipes is calculated in several ways. Why else is it necessary to calculate this parameter?
The weight of metal pipes is calculated before transporting the products.
The theoretical weight is necessary for sale, since the sale of pipes is carried out taking into account weight, not length. Thus, determining this indicator makes it possible to calculate the cost of a single batch.
Calculation of the mass of these products is used in construction to determine the strength of the future structure. This parameter allows you to find out what loads a frame made of pipes can bear.
On a note! Finding the specific gravity helps to increase the accuracy of calculations, since real values often do not coincide with GOST standards.
And finally, the weight of metal pipes is calculated before transporting the products. Transportation must be carried out using special cargo equipment, taking into account the possible load. When concluding a contract that specifies the number of products and their weight, you should be sure that transportation will be carried out in one trip.
Knowing the weight of pipes is necessary for sale, since the sale of material is carried out taking into account weight, not length.
Thus, knowledge of the weight of steel pipes is a necessary condition when purchasing them. Of course, when purchasing these parts individually, there is no need for such a calculation. Determining the weight in such a situation may be required only in order to calculate the real cost of the products.
Seamless hot-deformed steel
This type of pipe is the most expensive to manufacture and sell. By analogy with the previous category, some craftsmen want to find several options for carrying out work. This is one of the options for installing engineering systems. In this case, pipes are also divided into especially thick-walled, thick-walled and thin-walled. Depending on this parameter, the final weight is calculated, and the parameters include the maximum possible pressure in the system. Minimum – from 3 mm.
Differences in pipes depending on the type of polypropylene and area of application
Polymerization technology using a Ziegler-Natta catalyst was discovered in 1957. Since then, the production of polypropylene has begun, which differs from other types of plastics in its strong crystal lattice, increased heat resistance and high strength. Pipes made of this material perfectly tolerate alkalis, saline solutions and acid, as well as all types of inorganic substances (household chemicals, antifreeze). The material belongs to the dielectric group and does not absorb water.
Using polypropylene as a base, environmentally friendly products are obtained. Disposal is carried out by processing the material using a crusher or extruder into granules. They are used for re-melting and producing new types of plastics, so polypropylene is actively displacing other types of plastic on the market.
Polypropylene pipes are used for laying hot and cold water supply communications and organizing heating systems. Other types of polypropylene are used for external and internal sewerage. Let's consider their classification to make it easier to select a product for a specific purpose.
Propylene homopolymer (marking: type-1, TYPE-1, PP-N or PP-1)
Description
The material is very hard compared to ordinary polyethylene, and, reaching a temperature of less than +5 degrees, is capable of cracking under mechanical stress. During installation, care is required and a minimum of deformation, otherwise microcracks and leaks are possible.
For a short time, such pipes are capable of transmitting temperatures up to +93 degrees, but this is allowed for 2-3 minutes. The total operating temperature of regularly flowing liquids should not exceed 40º C.
Application
Homopolymer pipes are suitable for the manufacture of ventilation channels and free-flow sewerage inside a building. They should not be placed outside due to their increased fragility at low temperatures. They will withstand not only domestic use, but also use in commercial laundries or catering establishments where there are short-term hot water discharges.
Air ducts made of polypropylene.
Polypropylene homopolymer (marking: type-2, TYPE-2, PP-B, PP-S, PP-2)
Description
The second type of homopolymer has about 30% ethylene units in its structure, which increases the flexibility of the pipe walls. As a result, the material is more durable and elastic even at an ambient temperature of -20 degrees. It is more difficult to break, because low hardness eliminates the tendency to crack. The pipes can withstand constant exposure to temperatures of flowing liquids up to +90 degrees.
Application
Due to the preservation of softness at low temperatures, the pipe is in high demand for the organization of external non-pressure sewerage. It perfectly withstands pressure from the ground and cars passing on top. Internal sewage systems made of such material also last for decades. In other areas, the second type of homopolymer is not used.
Pipe for external sewerage made of polypropylene.
Polypropylene block copolymer (marking: type-3, TYPE-3, PP-R, PP-3, PPRC)
Description
Block copolymers can withstand heat up to +176 degrees. This characteristic means that even boiling coolant or antifreeze in the heating system will not cause harm to the pipe walls. In addition to thermal stability, the material demonstrates excellent strength when exposed to pressure from the inside.
The operating indicator of the system is 10 bar (the pressure in open heating circuits often does not exceed 2 bar, and in closed ones - 6 bar). In this case, the coolant temperature can reach 95 degrees (most often, for comfortable heating in winter, the coolant is heated to 70-80 degrees). All this gives a large margin of safety.
Another advantage of PPR polypropylene is its long service life of up to 50 years. This implies regular operation at a temperature of +95 degrees and periodic increases to 100º C.
Application
Based on the above properties, the most optimal application for polypropylene PPR pipes is the organization of a water heated floor, distribution of a centralized heating system, or laying communications for hot water supply (supply from the secondary circuit of a boiler, boiler, gas water heater). This is the most common material for the manufacture of hot and cold water supply pipelines.
Polypropylene random copolymer with increased heat resistance (marking: type 4, TYPE-4, PPRCT)
Description
This is another modified type of polypropylene, characterized by increased thermal stability. The fourth type serves without destruction or deformation, constantly passing through liquids with a temperature of 95º C.
Application
A type of thermally stable polypropylene has found active use in heating systems, hot water supply and other circuits with high temperature flowing liquids.
Next, we will take a closer look at the last two types of pipes: PPRC and PPRCT.
Where to find information
Comprehensive information about the dependencies between parameters and operating features is in the standard. It contains tables that allow you to calculate the weight of the pipe, as well as familiarize yourself with the available range of pipes. Keep in mind that the standard regulates what a manufacturer can produce, but not the units and volume of products. You can usually find the most popular pipe options on sale.
For example, straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes with wall thickness are indicated in the standard tables, from which data on the weight of the pipe can be obtained. If you are not satisfied with the weight, use pipe products made from lighter materials. Please note that lightweight materials may not withstand water pressure. A pipe with 1 mm metal is available only in the electric welding production method.
Selection of pipes for communications
Steel pipes are mainly used for heating and water supply systems. To independently determine the most suitable diameter of a particular pipeline, you need to know the technical characteristics of the pipeline and the formula for calculation.
Selection of pipe parameters for water supply
The diameter of pipes for water supply or sewerage is determined taking into account the following parameters:
- pipeline length;
- bandwidth;
- presence of turns in the system.
The determining factor is the throughput, which can be calculated using the following mathematical formula:
Rules for calculating throughput
Having determined the throughput, the diameter can be calculated using the formula or selected from the table below.
Selection of diameter according to pipeline capacity
To avoid the complexity of mathematical calculations, you can use the recommendations of experts:
- installation of the system riser must be equipped with pipes with a diameter of at least 25 mm;
- Water pipes can be laid using pipes with a diameter of 15 mm.
Additionally, when determining the diameter of the pipeline, you can focus on the relationship between the length of the pipeline and the diameter of the pipes, which is expressed by the following characteristics:
- if the total length of the water supply system is less than 10 m, then pipes with a diameter of 20 mm are suitable;
- if the length of the pipeline is between 10 and 30 m, then it is more advisable to use pipes with a diameter of 25 mm;
- for a total length of more than 30 m, it is recommended to use pipes with a diameter of 32 mm.
You can more accurately calculate the diameter of pipes for a water supply system using various online programs presented on specialized websites or in special organizations.
Techniques for making simple and original potholders
Any idea should be implemented by a home craftswoman using diagrams and sketches, which greatly simplifies the work process. Original and unusual products, along with traditional models, can be made using different techniques:
- Crocheting is an original and uncomplicated technique used for making potholders of various shapes and differing in aesthetic appearance;
- simple stitching, the technique allows you to make products that are not complex in design, used to decorate the kitchen and protect your hands from hot surfaces;
- patchwork and patchwork techniques are used to create real works of art, with minimal expenditure of materials and your own time.
The easiest way to make a potholder is to sew several layers of fabric and be sure to use insulation. Crochet products look festive and original; they use strong and dense threads that do not ignite easily (smolder, but do not burn).
Pipe weight: how to calculate weight when purchasing
Most often, manufacturers who produce various types of metal pipes sell their products in wholesale quantities. Individual parts are also sold, but the percentage is much lower compared to large orders placed by developers and individuals.
On a note! Measuring the length of products that make up one batch is not a convenient solution. In order to simplify implementation, the cost is calculated taking into account the mass of the batch, which is determined based on the mass of the part. To calculate it, you need to know the weight of 1 meter of pipe. This is the fastest calculation method, but it is not the best for the customer. This is due to the fact that after using steel pipes, as a rule, a certain percentage of surplus remains.
To determine the mass of a batch in production, two methods are used. The first of them takes into account the use of an online calculator. This program allows you to quickly calculate the weight of steel parts. Often, an online calculator is posted on the website of a company that produces steel products. Thus, each buyer can determine the required batch weight in a matter of minutes and immediately place an order.
To determine the mass of a batch of pipes in production, you can use several different methods.
The second method to calculate the weight of steel pipe for purchase is weighing. It is produced using special cargo equipment. This operation is performed in 2 stages. First of all, the car (or trailer) is placed on the scales, which allows you to determine its weight. Next, a batch of metal parts is loaded into it. The initial weight of the vehicle is subtracted from the resulting figure to obtain the total mass of the batch.
Each buyer can come to production if it is necessary to determine other characteristics of the batch. For example, you may need to calculate the number of pipes in one order. It is also very often necessary to know the length of products. As a result, carrying out such calculations will allow you to place an order not by weight, but by the number of packages.
Read the continuation of the article on the next page. To move to the next part of the article, use the page navigation numbers.