Operating principle of bellows compensator
The compensator is installed on the pipes to prevent thermal expansion.
Stresses arise in the pipeline; the heating compensator counteracts deformation due to the elastic shell. Circuits fail due to axial shear and rotation loads, depending on which certain types of relief inserts are used.
Devices must be installed in systems:
- heating lines under pressure;
- closed supply and return circuits;
- pipelines for pumping gases and liquids.
Bellows installations reliably connect sections of the heating main if they are correctly selected and installed. The structures dampen vibration with small and large amplitudes, and the range of vibrations should not be more than 10% of the total displacement of the compensator.
Universal or balanced inserts are used if standard devices do not meet the requirements or there is a risk of a pressure surge in the network above the permissible values.
What is water hammer
Water hammer (water hammer) is a short-term, but sharp and strong increase (decrease) in pressure in a pipeline (in a water supply system) due to sudden braking (acceleration) of the fluid flow moving through it.
In simple words, water hammer is a sharp increase in pressure in pipes
Water hammer occurs:
- Positive - when the pressure in the pipeline increases very sharply. This can happen when a tap (valve, valve) is quickly closed or a pump is turned on.
- Negative - when, on the contrary, there is a decrease in pressure in the water supply due to the fact that the tap was opened or the circulation pump was turned off.
The greatest danger to the water supply system is positive water hammer. Let's say you turned on the tap and washed the dishes. Finished washing, you don’t need water, turn off the tap.
In this case, the following happens in the water supply. The water flow for some time, by inertia, flows at the same speed. Then he encounters an obstacle (the tap was closed). And “hitting” against this barrier, a reverse wave is formed. And since the entire water supply system is sealed. This backward wave collides with the water flow coming towards it. The result is water hammer.
The very first signs of water hammer are dull knocks and clicks heard when opening or closing a tap. The appearance of leaks at the junction of water pipes or leaking taps.
Causes of water hammer
The main reasons for the occurrence of water hammer in the water supply system are:
- Abrupt closure of shut-off valves (taps, valves, gate valves.
- Breakdown or shutdown of the circulation pump or pumping station.
- Air locks in the water supply system.
- Variations in the cross-section of water pipes.
Basically, water hammer occurs when the shut-off valves are suddenly closed. Water passes through pipes with constant pressure, but when the water flow suddenly stops. The water pressure on the pipe walls increases several times.
As a result, pipes may burst or seals of threaded connections and locking elements may become unusable.
Of course, a sharply closed tap is not the only cause of water hammer. A similar situation occurs when air remains in the system. The moment the tap opens, the water encounters a plug of air.
And this air plug in a confined space acts as a shock absorber. As a result, the water is pushed out with enormous force and an impact occurs.
Also, the appearance of water hammer can be caused by pipes of different diameters. Pressure drops, if the pipes are not reduced to a common denominator, are guaranteed
Consequences of water hammer
Pressure above the permissible limit is critical for pipes and their connections. Shut-off valves can also fail.
The first water hammer usually does not cause damage to the water supply system. After all, water supply products are manufactured with reserves in case of increased pressure. But subsequent water hammers will hit the same weak spot. And at some point the pipe or shut-off valve will fail.
If a water pipe breaks in an apartment in an apartment building, flooding will occur and the property of your apartment and the neighbors below will be damaged.
If the central water supply is damaged, several houses or an area may be cut off. This is already a state of emergency. Since residents of apartment buildings will be left not only without drinking water, but also without sewerage.
Well, what if a hot water supply pipe is damaged as a result of a water hammer? This can lead to serious burns.
Read about the temperature of hot water in the apartment here
Specifications
Bellows compensator in action
Bellows are produced using rolled steel with a thickness of 0.3 - 0.5 mm. The output batch is tested for resistance to corrosion from chlorine at a temperature of +150°C. Tightness is tested by hydrostatic compression using nitrogen, air or helium bubbles. Expansion joints, leakage of the control substance and reduction in pressure are not allowed in expansion joints.
Devices are tested for resistance to heating by raising the temperature to +270°C and holding them under these conditions for at least 1 hour. Internal ruptures, swelling and peeling are checked. The rigidity test is carried out by compression and tension of the sample, the value must correspond to GOST 286. 1997.
During manufacturing, the longitudinal seams of the shells are made by welding at the same distance from one another. Metal bellows are produced by molding with calibrated corrugations. Small-diameter devices are made by hydraulic pressing.
Main Dimensions
Compensators are also installed on polypropylene pipes.
Visual and instrumental inspection is used to determine the appearance. The presence of a corrosion coating on the pipes and bellows and markings are visually established. There should be no damage, dents, or drops of frozen metal on the body. The compensator for polypropylene heating pipes should not have delaminations of different sizes at the ends of the pipe.
Using measurements, the following parameters are checked:
- flow area size;
- working length of the device;
- wall thickness and internal diameter of flange preparation for welding;
- perpendicularity of the pipe axis to the cut end.
The diameters and lengths of bellows inserts are determined depending on the installation location, operating parameters of the heating main and the power of the heating equipment. Engineers carry out technical calculations and select the dimensions of the device in accordance with the standard.
Criterias of choice
You need to select compensation parts depending on the conditions of use:
- Axial - suitable for heating systems, hot water supply pipelines. To connect them to the pipe, you need to use a special coupling.
- Shear products that have two corrugations. They dampen thermal expansion in two directions.
- Flanged - used to dampen water hammer that occurs in water pipelines. There is no need to use welding equipment during installation.
- Universal - suitable for installation in places where it is impossible to install other compensation parts.
When choosing, you need to pay attention to the wall thickness of the expansion joints. They must match the wall thickness of the pipes on which they will be installed.
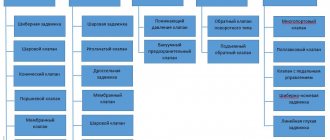
Types of compensators
Products are produced in different diameters and lengths.
The design solution of the compensator determines the purpose of the product and its displacement during operation. Devices are produced without thermal and waterproofing, or preliminary protection is provided on the housing, depending on the type of heating main (air or underground).
The manufacturer produces types of expansion inserts:
- axial;
- flanged;
- angular;
- gimbal;
- shear;
- starting.
Unloaded compensators are used in heating mains to prevent thrust loads; seismic types are used in areas of expected earthquakes. External pressure devices are installed in pipelines when there is a high pressure of liquid or gas in the environment or when there is a lack of it.
The designs differ in length and diameter, number of bellows and type of steel, size and grade of metal of the pipes. Products work for rotation, tension, bending, compression, and are available with or without connecting flanges.
Axial
The axial expansion joint is designed for installation on a straight section of a pipe.
KSO expansion joints for pipelines reduce the axial displacement of the pipeline, reduce vibration and prevent destruction from expansion when heated. The efficiency of operation depends on the number of bellows and rings. The difference from other types is the threaded connection to the main pipes.
Axial compensators have the following characteristics:
- passage size 15 – 100 mm;
- withstands pressure 16 bar;
- length dimension – 260 mm;
- allows movement along the axis for compression up to 30 mm, for expansion - 20 mm;
- axial stiffness parameter – 30 – 89 kg/mm.
The motion limiter and pipe are made of galvanized metal, the bellows and internal screen are made of stainless steel. Steel is used for the protective housing; the device is produced in one section and is designed for energy carrier temperatures up to +90°C.
Flanged
Flange expansion joint made of rubber
This type of bellows is made of rubber or rubber; for flanges, the raw material is heat-resistant metal, and the cord is made of durable fabric. Installation using the flange method greatly simplifies the installation of products. Compensators are used in chemically active environments, used in heating and air conditioning, and installed during the reconstruction and repair of boiler equipment.
Flange structures reduce vibration, reduce temperature shifts along the length, and compensate for deviation from the central axis of the pipeline.
Main parameters:
- nominal diameter – 32 – 800 mm;
- withstands energy carrier temperatures -10 - +135°C;
- operate with a pressure of 16 bar.
Flanges are loose and solid in structure; they are attached to pipe elements with studs, bolts using washers and nuts. Paronite gaskets are used, sometimes steel ones, made of thermally expanding granite or fluoroplastic are used.
Angular
angular compensator
KSP (rotary) is installed in cases of limited space, when it is possible to compensate only for an axis shift and a contour rotation without a change in plane. Contains a bellows, a guide element and fasteners. The device provides for shifting the pipe along a selected angle; for this purpose, there are hinged or cardan stops.
Characteristics of rotary (angular) compensators:
- nominal bore diameter – 15 – 1600 mm;
- maximum pressure – 1.6 – 4 MPa;
- axis movement – 24 – 200 mm;
- steel screen and protective box;
- bellows material – stainless steel;
- Available with one or two sections;
- works with energy carrier heated to +85 - +150°C.
Angle structures are used as part of heating mains and for pumping oil and gas, and are used in the chemical industry.
Cardan
Cardan compensator
Bellows pipeline compensators balance the movement of the circuit in different planes, thanks to the hinge elements, they bend in the direction of the central axis. The displacement of the line is compensated along the X, Y, Z axes and in terms of rotation due to shrinkage and vibration. The flexible design allows for deformation in rigid contours.
Specifications:
- are designed, calculated and manufactured in accordance with the EJMA standard;
- contain 2 bellows with cardan-type joints;
- shifted sideways by a distance multiple of 100 mm (100, 200, 300, 400), other sizes of shifts must be ordered separately;
- nominal bore diameter – 25 – 1000 mm;
- works with energy carrier temperatures -190 – +850°C.
The bellows is made of stainless steel, connectors and pipes are made of chrome steel. Placed in the design position by welding or using a rotating flange. Can be used in any pipeline system.
Shear
Shear compensators
KSSO compensators balance the shift due to longitudinal compression or elongation of the contour under the influence of temperature, eliminating the consequences of misalignment. The design includes a corrugated capsule, a guide piece and fasteners. The longitudinal displacement is coordinated using guide pins.
Parameters of shear compensating devices:
- nominal passage diameter – 32 – 500 mm;
- maximum pressure 0.6 – 4 MPa;
- the bellows, couplers and pipe are made of stainless steel;
- The material of the protective screen is selected by the customer;
- withstands energy carrier temperatures up to +850°C.
Shift devices are made in one or two sections and are used to compensate for stress in oil, water, steam, and gas pipelines. They are used in various industrial sectors and in energy complexes.
Starting
The starting compensator is used one-time when starting a hot water supply system.
The SKK compensator is used temporarily as a one-time device when starting a heating main or hot water pipeline.
Technical specifications:
- nominal diameter DN - 50 - 100 mm;
- shift along the central axis – 80 – 175 mm;
- device rigidity is 430 – 2300 N/mm;
- transports water at temperatures up to +150°C, steam – 250°C;
- allows water flow speed up to 5 m/s, steam – 65 m/s;
- the normalized pressure when starting the line should not exceed 1.5 MPa.
The starting compensator is used when laying the circuit using the channelless method. The material of the body, pipes and bellows is selected by the customer.
For pipelines of heat and water supply systems.
In the wide range of pipeline fittings of the Genebre SA company, expansion joints occupy far from the last place. Genebre bellows-type pipeline expansion joints, designed specifically for heat supply systems and which are quite common at similar facilities in many European countries, are also presented on the Russian market. The design of Genebre bellows expansion joints has some features that ensure high quality and excellent performance characteristics.
Compensators (vibration inserts): welded, flanged, coupling.
In an effort to reduce the cost of their products, some expansion joint manufacturers make the inner layer of the bellows from a lower quality material (while the upper layer is made from a higher quality material). It is clear that when choosing, it is impossible to determine such a substitution; it makes itself felt already during operation, when an emergency situation and its elimination can cost much more than the initial savings. Minor damage to the outer layer or a poor-quality weld can allow water or other substances to enter the siphon, which will eventually lead to its destruction. All layers of the Genebre bellows expansion joint are made of high quality stainless steel, which guarantees maximum service life.
| Metal bellows for welding |
| Metal flange |
| Rubber coupling |
| Rubber flange |
Compensators (vibration inserts): welded, flanged, coupling. Inside each Genebre compensator there is a special protective pipe that protects the inner layer of the bellows from abrasive substances contained in the coolant. Also, the protective pipe prevents the accumulation of sand on the bellows lenses and reduces the level of resistance to the working flow. Another advantage of Genebre compensators is convenient installation. Each of them is completely ready for installation in the heating system: a special clamp eliminates the need to stretch the compensator and additional heating of the heating main section immediately before installation, and also protects the bellows during installation (from twisting) and limits the degree of compression during operation. All these advantages of Genebre bellows expansion joints allow guarantee trouble-free long-term operation of the device in the pipeline. Rubber expansion joints for process water.
Application:
Compensation for thermal elongation of pipelines, misalignment of pipelines, elimination or reduction of vibration levels and absorption of noise produced by the operation of pipelines, pumps and other mechanisms. Working environment:
Hot water, cooling water, saline water, chlorine solutions, esters and ketones.
Installation of bellows compensator
The expansion joint should be located here.
The reference points for inserting expansion joints are the locations of the supports when the highway is divided into sections and the position is predetermined. Supporting elements are aligned using a level in three axes to ensure proper operation of the heating main. The pipes on the supports must slide without additional friction; for this purpose, clamps with fluoroplastic gaskets are used.
Suggested installation points:
- behind the thermal support;
- behind supports from bends and deflections;
- between sliding supports.
The course of movement of the energy carrier is taken into account when installing compensators with protective internal sleeves. Guide elements prevent pipes from moving along a tangential straight line. The diameter DN in millimeters, working pressure and the ability to balance shifts are taken into account. The diameter must correspond to a similar parameter of the heating main.
Pipe distance
Compensators are installed in parallel on sections of the main line
. The main line is divided into sections if one bellows structure is not enough to balance the shifts or there are branches on the heating main. The length of the segment should not be greater than what one expansion joint can cover. The device on site is selected in accordance with operating conditions and technical characteristics. A description of the compensator model is given in the working documentation for installing the heating system.
Typically, the bellows device is embedded at a distance of two nominal diameters from the supporting part. If it is placed between supports, the distance to the supporting elements is 4 DN. These dimensions prevent bending of the pipeline and reduce it to a minimum.
If several polypropylene circuits are installed in parallel, it is taken into account that the diameter of the compensator is slightly larger than the diameter of the pipe. In this case, the bellows structures are placed in a checkerboard pattern, and the distance between the pipes does not increase and is done according to the standards of the technical passport of the heating main.
Valtec polypropylene pipes. general information
Technical characteristics of PP pipes
Since its founding, Valtek has gained a significant place in the global market. Its specification is large plumbing devices for water supply, heating and wastewater networks. In 2010 they started producing PP pipes.
There are single-layer and multi-layer PP pipelines.
Aluminum is used to reinforce multilayer pipes. Thanks to the reinforcement, complete protection against air penetration is ensured, thereby reducing the risk of corrosive formations in the internal system of heating devices.
For the production of PP pipes, very durable polypropylene class PPR-100 is used. Such products are used in heating and plumbing systems and in industrial enterprises. They are capable of operating at temperatures up to +90C. The company produces products in accordance with GOST. Thanks to the use of a modified type 3 PP-R polymer, the products are significantly resistant to temperature fluctuations and network pressure.
These pipes are durable, their service life reaches fifty years. Valtek provides a 7-year warranty period for its products.
The assortment includes solid products used for cold water supply and low-temperature systems. Installation is carried out by resistance welding using connecting elements (fittings) special for pipes produced by Valtek, because the quality of any system can only be achieved by matching all elements.
Valtec PP pipes are marketed in special four-meter tubes. On which all technical characteristics are indicated.
pros
The numerous advantages of polypropylene products include:
• As stated above, these pipes are durable; • Resistance to aggressive environments and chemicals, corrosion; • Polypropylene is resistant to fungal growths, mold, and ultraviolet radiation; • Smoothness of the internal walls, which prevents the formation of various types of deposits; • Polypropylene is an environmentally friendly material, does not change the properties of water, which makes it an ideal option for installing drinking water supply; • Light weight, which is a big advantage during transportation and installation; • Multifunctional use.
Minuses
One of the disadvantages of polypropylene material is the presence of a large coefficient of thermal expansion.
So if the permissible temperature value is exceeded even by one degree, the pipes begin to increase in length.
Although today this problem is solved by reinforcement. To avoid deformation changes, the design of polypropylene products is reinforced with a frame, which imparts rigidity and prevents the pipe from bending.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=BsKzDC0kpvE
Correct operation
When laying pipes underground, expansion joints are insulated with polyurethane foam.
Compensating inserts are thermally insulated with polyurethane foam if the line is protected from heat loss. Mandatory isolation from leaks is carried out.
Materials for waterproofing:
- polyethylene - for closed installation in underground conditions;
- galvanization – for thermal communications arranged in an open way.
The insulation is installed taking into account the possible displacement of the casing during expansion or contraction of the pipeline. Thermal protection is checked and repaired from time to time along with the line insulation.
Criterias of choice
You need to select compensation parts depending on the conditions of use:
- Axial - suitable for heating systems, hot water supply pipelines. To connect them to the pipe, you need to use a special coupling.
- Shear products that have two corrugations. They dampen thermal expansion in two directions.
- Flanged - used to dampen water hammer that occurs in water pipelines. There is no need to use welding equipment during installation.
- Universal - suitable for installation in places where it is impossible to install other compensation parts.
When choosing, you need to pay attention to the wall thickness of the expansion joints. They must match the wall thickness of the pipes on which they will be installed.
Safety standards
The compensator may burst if the load exceeds the permissible norms.
The service life of compensators is expected to be 30 years, while the devices can be stored in a warehouse for no more than 5 years before starting work.
Within the service life, the following loads are allowed:
- compression-extension from minimum to maximum – 10 cycles;
- reduction or extension by 70% of the maximum and minimum limits - 150 cycles;
- shifts within 20% of the working stroke - 10 thousand cycles.
Bellows expansion joints must have manufacturer certificates certifying compliance with regulations. Certified materials are used for welding, and installation is performed by certified workers. It is prohibited to use structures in conditions exceeding the permissible ones. Compensators cannot be used as supports when installing heating mains.
How to choose a device?
When choosing a compensator for heating and water supply pipelines (and in general, all compensators for any purpose), you must remember the following nuances:
- There should not be any damage to the corrugation - before purchasing, you should carefully inspect it from all sides; perhaps it could have been damaged during transportation or unloading.
- When choosing, you need to focus on certain characteristics (flow, pressure, temperature) of the transported medium - they are different for one or another type of compensator, as a rule, this can be found out from the description.
- The tightness of chambers and channels is of great importance - multilayer compensators often lose it even with slight damage.
- Stuffing box compensators have the longest service life.
- The service life of the packing directly depends on the smoothness of the compensator mirror: the smoother it is, the longer the service life.
- Stuffing box expansion joints have proven themselves best during major repairs of complex structures in heating mains.
The price of compensating devices depends on the manufacturer, as well as the specifics of the varieties and is:
- bellows expansion joints from 2 to 8 $;
- axial (stuffing box) linear expansion – $25-50;
- U-shaped compensators – $10-15.
Typically, expansion joint bellows are made of brass, beryllium or phosphorus bronze. Stainless steel is also used. During changes in temperature and pressure, materials undergo some deformation, expansion or contraction during sudden cooling. If the installation of such a device is not used in the pipeline, the pipes will not be able to cope with compensation and will fail quite quickly.