To ensure the safe operation of objects with welded joints, the seams, regardless of how long ago they were made, must be regularly inspected. Flaw detection of welded joints is carried out using different methods. A universal testing method is ultrasonic testing. The method was discovered in 1930 and is now used everywhere. The effectiveness of ultrasonic testing is determined by the fact that diagnostics are able to detect even small defects, which over time lead to loss of strength and destruction of the structure.
Advantages and disadvantages of ultrasonic testing
The main advantages of ultrasound diagnostics include:
- High accuracy and speed combined with an affordable price.
- Absolute safety. Ultrasonic testing is a non-destructive testing method. It does not harm the structure and the health of people who are present during the procedure.
- Possibility of implementation in field conditions. For this purpose, special portable ultrasonic flaw detectors are used.
- Ease of implementation. Application of the method does not require decommissioning of the facility.
But there are no perfect diagnostic methods. Ultrasonic testing also has a number of disadvantages:
- Limited information obtained about the defect: it is impossible to determine the exact shape of the crack due to the presence of air or slag, and also to unambiguously identify the nature of the slag inclusions.
- When using ultrasonic testing, it is difficult to inspect metals with a coarse-grained structure due to the strong scattering and attenuation of ultrasound.
- The need to prepare for diagnostics: it is important to clean the surface of the seam from dirt and rust.
Basic ultrasonic testing methods
- Shadow method. This technique consists of controlling the reduction in the amplitude of oscillations of reflected and transmitted pulses.
- Mirror-shadow method. With this method, seam defects are detected by the attenuation coefficient of the reflected ultrasonic vibration.
- Echo-mirror method. This method, which is also called “Tandem”, consists of using two ultrasonic devices. They work simultaneously and are installed on one side of the object. The generated oscillations are reflected to the receiver
- Delta method. It is based on the control of ultrasonic energy that is reflected from the defect.
- Echo method. This technique is based on recording an ultrasonic signal that is reflected from a defect.
Note that there are other methods of conducting examination. But the ones listed above are the most popular. They have proven themselves due to their ease of implementation and high efficiency.
The essence of ultrasonic flaw detection
The human ear does not perceive ultrasonic waves, however, it is the basis of many diagnostic techniques. The ability of ultrasonic waves to reflect and penetrate is used in various industries, incl. and in medicine. This method is important for areas where the main requirement is not to harm the object being examined.
Ultrasonic flaw detection is a non-destructive method for monitoring and determining the locations where defects of various types are localized. The quality of the procedure depends on a number of factors. This is the correctness of the setup and calibration of the device, the sensitivity of the instruments, and the experience of the operator. Therefore, ultrasonic flaw detection should be performed by professionals.
This method is used to diagnose various welded joints. Using ultrasonic testing, it is possible to identify the chemically heterogeneous composition of a material (for example, the presence of slag deposits in the metal, the presence of non-metallic elements), air voids, hidden and internal mechanical defects.
Please note that the facility will be allowed for operation only after the quality of the connections has been determined and even the slightest defects have been eliminated.
Ultrasonic testing of welded joints is a method based on the ability of high-frequency vibrations (approximately 20,000 Hz) to penetrate the metal structure and be reflected from the surface of irregularities, voids, and scratches. The wave that penetrates the weld, when a defect is detected, deviates from the standard propagation. This deviation is reflected on instrument monitors. An experienced operator characterizes the detected defect using specific parameters. For example, the distance to it is calculated from the wave propagation time, and the size of the defect is calculated from the amplitude of the reflection pulse.
Results Evaluation Options
The quality of the work performed is directly affected by the sensitivity of the device, which allows you to accurately recognize the parameters of the defect. First of all, using an ultrasonic flaw detector, the number of flaws that can lead to destruction of the weld and the entire metal structure as a whole is determined. The assessment of defects located in the weld is carried out according to the following criteria:
- acoustic wave amplitude;
- conditional wave length;
- size of the defect and its shape.
To determine the length of the wave and the width of the defect, it is necessary to carefully move the emitter along the weld joint. To determine the height of an internal crack or cavity, it is necessary to take into account the time intervals between the reflected and emitted waves. It is worth noting that the process of identifying the form of a defect requires a highly qualified operator, so it is better to entrust this work to specialists who have undergone appropriate training.
Ultrasonic testing: types
There are several types of ultrasonic testing. The main methods of ultrasonic testing include:
- Shadowy. The method is based on the use of two converters. They are installed on different sides of the object. The first converter is the emitter. The second is the receiver. Install them strictly perpendicular to the weld. The flow of ultrasonic waves from the emitter is directed to the seam, and on the other side they are received by the receiver. If a blind zone appears in this flow, it means that there is a section with a defect not in the path of the waves.
- Pulse echo. An ultrasonic flaw detector is used, which both emits and receives waves. The method is based on the technology of ultrasound reflection from the surface of areas with a defect. That is, if the waves pass through the metal and are not reflected at the receiver, there are no defects. If they are reflected, then there is a flaw.
- Echo-mirror. An ultrasonic testing method similar to that described above. Two devices are used: a receiver and an emitter, but they are installed on one side of the object. The waves emanate from the emitter at an angle, and when they hit defects, they are reflected. The reflected waves are received by the receiver. In this way, vertical defects - cracks - are often detected.
- Mirror-shadow. It is a combination of mirror and shadow methods. The emitter and receiver are placed on one side of the object. Oblique waves emanate from the emitter, which reflect the walls of the metal, and are then received by the receiver. If there are no defects in the path of the reflected ultrasonic waves, then the changes will not be registered. If a blind zone is reflected, you need to look for a flaw.
- Delta method. Ultrasonic testing of this type is rarely used, as it requires fine calibration of equipment and complex interpretation of the results. The method is based on the re-emission of directed acoustic waves into the weld by the defect. That is, reflected waves are divided into mirror waves, which are transformed longitudinally, and re-emitted ones. The receiver does not pick up all waves, almost only those that are reflected or moving directly towards it. The configuration and size of the defect depends on how many waves are received.
When diagnosing transverse and longitudinal seams, experts often use shadow and echo-pulse methods. Basically, inspection of welded joints of pipelines is carried out using such methods. Other methods are used much less frequently, depending on the situation.
What is ultrasonic testing of pipeline welds
The method is based on the physical capabilities of ultrasound. Its peculiarity is that it is reflected from the boundary between media with different compositions. By its nature, ultrasound is an elastic mechanical vibration, which is generated by various methods. Its sound range is beyond the reach of the human ear. The emitters do not have a harmful effect on the human body.
Ultrasound diagnostics are performed in a wide frequency range: from 20 kHz to 500 MHz. Waves directed from the emitter in any direction propagate at the same speed, provided the medium is homogeneous. When the environment changes, they are refracted or reflected, like a ray of light. The speed of a longitudinal wave is almost twice that of a transverse wave.
The sensitivity of devices depends on its design features and varies greatly. The wide range is explained by the fact that the generated waves can only be reflected from those defects that are equal to or greater than the wavelength. Ultrasound perfectly detects small defects in a welded joint, namely: voids, cavities, various types of inclusions, slag, grains and other impurities that reduce the strength of the seam.
Ultrasonic testing equipment: operating principle
Devices used for ultrasonic testing of pipes and metal structures operate on a similar principle. The main working element is a piezoelectric sensor plate made of barium titanite or quartz. The piezoelectric sensor is located in the probe - it is placed along the connections and smoothly moved in a reciprocating motion. While the probe is moving, a high-frequency current flows to the plate, which is why it emits ultrasonic vibrations perpendicular to its length.
The reflected waves are received by the same plate with a receiving probe. It converts the oscillations into alternating current, which immediately rejects the wave on the oscilloscope monitor. As a result, an intermediate peak appears. During ultrasound diagnostics, the sensor sends short alternating pulses of elastic vibrations with different durations, which are separated by pauses. Due to this, the presence and depth of the defect is determined.
Theory of technology
Ultrasonic flaw detection technology. (On the left there is no defect, on the right there is a defect)
Ultrasonic vibrations are based on ordinary acoustic waves, which have a vibration frequency above 20 kHz. The person does not hear them. Penetrating into the metal, the waves fall between its particles, which are in equilibrium, that is, they oscillate in the same phase. The distance between them is equal to the ultrasonic wavelength. This indicator depends on the speed of passage through the metal seam and the frequency of the vibrations themselves. The dependence is determined by the formula:
L=c/f, where
- L is the wavelength;
- c is the speed of its movement;
- f – oscillation frequency.
The speed depends on the density of the material. For example, ultrasonic waves move faster in the longitudinal direction than in the transverse direction. That is, if there are voids (another medium) in the path of the wave, then its speed also changes. At the same time, encountering various defects along the way, waves are reflected from the walls of shells, cracks and voids. And, accordingly, deviation from the directional flow. The operator sees the change in movement on the monitor of the ultrasonic instrument and, based on certain characteristics, determines which defect stands in the way of the movement of acoustic waves.
For example, attention is paid to the amplitude of the reflected wave, thereby determining the size of the defect in the weld. Or by the time of propagation of an ultrasonic wave in the metal, which determines the distance to the defect.
How is ultrasonic testing carried out?
The procedure is performed in several stages, namely:
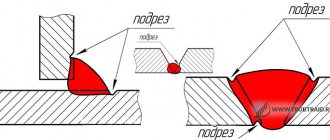
- Removing paint and rust from seams and on both sides of welded joints at a distance of 5-10 cm (the exact dimensions of the heat-affected zone are regulated by the technological documentation for the control object in accordance with GOST R 55724-2013).
- Treatment of the metal surface near the seam and the seam itself with machine oil, turbine oil, glycerin, grease or silicone gel with corrosion inhibitors. The surface is treated with oil to create a contact zone between the sensor and the surface of the test object and improve the penetration of ultrasonic vibrations.
- Setting up the device with calibration. Thickness, ARD, AVG or DGS diagrams are configured.
- Moving the finder probe. Performed along the seam, in a zigzag manner. In this case, the finder is rotated around its axis by about 10-15 degrees.
- As soon as a stable signal appears on the device screen, the finder is deployed. The search is carried out until a signal with the greatest amplitude appears on the screen.
- They clarify where the oscillation originated from, whether it is associated with the reflection of the wave from the connections, which happens during ultrasonic testing.
- If the reflection occurs due to a defect, it is recorded, and the coordinates of the location are recorded.
The flaw detection results are entered into a table. Using it, in the future, the defect can be re-identified and then eliminated. Inspection is carried out according to GOST in one or two passes. If ultrasonic testing is not enough to determine the exact nature of the defect, gamma flaw detection or X-ray flaw detection are additionally used.
The basis for safe operation
Flaw detection of welded joints must be carried out in a timely manner. Only in this case will you be able to prevent emergency situations from occurring.
Unfortunately, many people remember the need to use ultrasonic testing only at the final stage of production. However, this is unacceptable.
The assessment of welds should be carried out not before the commissioning of a pipeline or the commissioning of a construction project, but immediately after the preparation of structures and their individual elements. Only in this case can the correct operation of the facility be guaranteed.
You should not take risks and completely abandon the examination of welds. An irresponsible approach can cause an increase in accidents and even a real man-made disaster.
Also, you should not trust the examination to non-specialists. They are capable of making mistakes and missing a serious defect. At the same time, they often do not bear any responsibility for the work done.
Contact the specialists of the MICRO testing laboratory! They are true professionals in ultrasonic testing. All operations are carried out by experienced craftsmen in accordance with established standards and requirements.
What defects does ultrasound diagnostics reveal?
Using ultrasonic testing of pipes and structures, a number of different defects are determined, for example:
- cracks in the heat-affected area;
- pores in joints;
- lack of penetration;
- delamination of deposited metal;
- lack of fusion of the seam;
- fistulous defects;
- metal sagging that occurs in the lower section of the welded joint;
- corrosion damage;
- material mismatch in chemical composition;
- zones with distorted geometric dimensions.
Diagnostics can be carried out in metals such as copper, cast iron, alloy and austenitic steels. At the same time, there are certain geometric frameworks for applying the method, in particular:
- Seam depth (max) – 10 meters;
- Depth (min) – 3-4 mm.
- Seam thickness (min) – 8-10 mm.
- Metal thickness (max) – 500-800 mm.
Using ultrasonic testing of pipes and structures, various types of seams are checked: longitudinal, flat, circular, T-joints, as well as welded joints.
Features and essence of the methodology used
Ultrasonic testing of welded joints (flaw detection, ultrasonic testing) is a popular non-destructive testing method. It is mandatory.
Ultrasonic testing is an examination that can quickly identify:
- wear and tear of products
- surface or internal defects of metals and alloys,
- quality of the product or individual weld.
The essence of the technique is to treat the object with ultrasound. When testing welded joints, vibrations are sequentially radiated into the product. After this, they are perceived as a reflected wave by special equipment (flaw detector).
The results obtained are analyzed.
As a result, the specialist can:
- Detail the size of the defect.
- Determine the type of damage, classifying it as extended or point.
- Determine the shape of the defect (volumetric or planar).
- Find out the depth of the deformation and solve other problems.
The key parameters of the flaw are determined during the ultrasonic technique by the time of propagation of ultrasound inside the material from which the product is made.
Traditionally, ultrasonic testing of welded joints is carried out in the range from 0.5 to 10 MHz. Specialists can identify a large number of different defects in metal products and entire building structures. In some cases, ultrasonic testing of welds is performed with pulses with a frequency of up to 20 MHz. Using this technique, even the most minor flaws can be detected.
Low-frequency testing is carried out to check objects with significant thickness (casting, forging, etc.), as well as to evaluate metals with a coarse-grained structure (copper, austenitic steel, cast iron) and poor conductivity of ultrasonic pulses.
Using ultrasonic examination, you can easily identify such defects in a welded joint as:
- cracks in the area next to the seam,
- pores,
- lack of penetration,
- metal delamination,
- poor seam quality,
- fistulas,
- corrosion,
- areas with size distortion and chemical composition inconsistency,
- sagging of the metal in the lower zone of the seam.
The study of a welded joint can be carried out in such metals as:
- copper,
- alloyed and austenitic steels,
- cast iron, etc.
The following types of seams are tested:
- T-joints,
- welded joints,
- welded pipes.
Scope of application of ultrasonic testing
This control method is used in the industrial sector, as well as in the reconstruction and construction of houses. Ultrasonic testing is often used:
- For analytical diagnostics of units and components.
- To determine the wear of pipes in the main pipeline.
- In nuclear or thermal energy.
- In the field of mechanical engineering, oil and gas, chemical industries.
- When checking welds of structures with complex configurations.
- When diagnosing metal compounds with a coarse-grained structure.
- When welding joints of units and boilers of equipment that are under the influence of pressure, high temperature, and aggressive environment.
The technique is used both in field and laboratory conditions.
A seam checked for defects is a guarantee that the structure is safe for use, reliable and can be used for its intended purpose. Without monitoring for compliance with standards, putting the structure into operation is impossible. The accredited construction laboratory IRONCON is ready to carry out ultrasonic diagnostics of welded joints at the customer’s site in full compliance with current control standards.
Inspection of welded joints using ultrasound
The technology for detecting defects is regulated by GOST provisions. Operators allowed to work have the appropriate certificates. Before starting a set of work, they undergo safety training. Ultrasonic testing of welds is often required in inconvenient or hard-to-reach places. Grounding of the device is mandatory. The results are assessed according to several criteria. The log records the main indicators:
- length of the welded joint being tested;
- parameters of detected defects – size and shape;
- range of the emitted wave.
Before diagnosis, the area being examined is cleaned. In order for ultrasound to pass better, an oily film should be formed on the metal surface. Depending on the accuracy requirements, the procedure is carried out once or twice.
Design and principle of operation
Ultrasonic flaw detector
The device consists of a pulse generator, the signals generated by it are transmitted to the receiver. After the wave is reflected from the surface of the defect, the signal is received by the transducer, after which it is converted into electrical and displayed on the signal recording and display device (screen).
The principle of operation of the flaw detector is to move the probe along the weld seams. The finder is moved over the sample under study until a stable, clear signal appears.
Preparation and properties of ultrasonic vibrations
Acoustic waves or ultrasonic vibrations are generated at a frequency exceeding the 20 kHz parameter. Mechanical vibrations that can be dissipated by elastic, solid media, the range is usually 0.5 - 10 MHz. The propagation of waves through the metal structure occurs by acoustic ultrasonic waves affecting the equilibrium of the central point.
Ultrasonic method technique
There are several methods of ultrasonic non-destructive testing, the most common of which is piezoelectric. The plate, charged with electricity at a certain frequency, vibrates, mechanical vibrations are transmitted to the environment in a wave state. Electric wave generators are used regardless of the purpose, the size of the equipment, and can produce different parameters.
The speed of ultrasonic testing directly depends on the properties and type of physical medium. The speed of propagation of a longitudinal wave is twice as high as that of a transverse wave. Information is received by a plate made of a piezoelectric element, which converts energy into pulsed energy. The process uses short alternating pulses of various types of vibrations, which makes it possible to determine the depth and properties of the defect.
Angles of direction of ultrasonic vibrations
At the boundary between two media, the result of the incidence of a longitudinal acoustic wave in an inclined type is the appearance of reflection and transformation of ultrasonic waves. There are main types of control:
- reflected;
- refracted;
- shear transverse;
- longitudinal waves.
The process occurs by dividing the wave incident at an angle into transverse and longitudinal, the propagation of which is carried out directly by the material.
Angles of direction of ultrasonic vibrations
There is a certain value of the feed angle, the direction of ultrasonic vibrations, if violated, ultrasonic testing will not spread deep into the metal, but will remain on its surface. This method is used for certain parameters and tasks; the wave moves only along the surface of the material, which allows you to control the quality of the weld.