Cast iron pipes are used primarily for the installation of sewer structures. And even after the advent of more modern polymer materials, cast iron parts continue to be used everywhere. This is due to the fact that they have a long service life and are also able to withstand heavy loads when transporting liquids.
Pipes for sewer systems made of cast iron must meet all GOST requirements
2 Normative references
This standard uses references to the following standards:
GOST 164-90 Height gauges. Specifications
GOST 166-89 Calipers. Specifications
GOST 1412-85 Cast iron with flake graphite for castings. Stamps
GOST 9812-74 Petroleum insulating bitumens. Specifications
GOST 11506-73 Petroleum bitumens. Method for determining the softening temperature by ring and ball
GOST 15150-69 Machines, instruments and other technical products. Versions for different climatic regions. Categories, operating, storage and transportation conditions regarding the impact of environmental climatic factors
GOST 18510-87 Writing paper. Specifications
GOST 26358-84 Iron castings. General technical conditions
GOST 26598-85 Containers and packaging means in construction. General technical conditions
GOST 26645-85* Castings from metals and alloys. Dimensional, mass and machining allowances.
________________
* The document is not valid on the territory of the Russian Federation. GOST R 53464-2009 is valid, hereinafter in the text. — Note from the database manufacturer.
Tips for installing and operating cast iron pipes
The main advantage of cast iron pipes over plastic ones is the noise insulation characteristics of the former. Their walls dampen any sounds that appear as a result of the movement of the working medium through the pipes. However, the weight of cast iron products affects the labor costs when installing sewer structures, which in any case affects the speed of all necessary work on their installation.
The specific service life of these products must be at least 50 years, however, in many sources the shelf life can reach 100 years. In any case, in order to extend the service life of cast iron sewer pipes, it is necessary to strictly follow all the rules for their installation.
It is very important to remember that ordinary cast iron is not recommended for use in structures that will transport aggressive chemicals. For such situations, it is better to use pipes with higher resistance to aggressive chemical compounds (for example, ceramic). However, there is also a nuance here - for domestic sewerage, laying steel products will be too expensive.
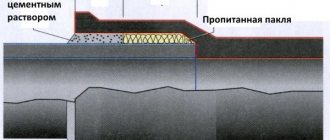
Important! To fill the free spaces at the joints of cast iron pipes, it is recommended to use a special sealant called a cabling. Kabalka is plant fibers impregnated with resin-bitumen mastics, and in some cases with oil solutions. After filling the free spaces with cable, it is necessary to cover the joint with cement mortar.
It is not recommended to fill the joints of cast iron pipes with sulfur, since when heated it emits vapors harmful to human health. In addition, sulfur is highly flammable and cannot be extinguished with water.
3 Assortment
3.1 The range of pipes and fittings must correspond to those indicated in Table 1.
Table 1
| Name | Conditional diameters, mm | Symbol | ||
| graphic | alphabetic | |||
| Pipes | 50 | — | ||
| 100 | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Pipes | 50 | — | ||
| 100 | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Compensation pipes | 100 | — | ||
| 150 | — | |||
| Transition pipes | 50/100 | — | ||
| 100/150 | — | |||
| Knees | 50 | — | ||
| 100 | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Low knees | 100 | — | KN-100 | |
| Bends 110° and 120° | 50 | — | О 110° — or О 120° — | |
| 100 | — | |||
| Bends 135° | 50 | — | About 135° — | |
| 100 | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Bends 150° | 50 | — | About 150° — | |
| 100 | — | |||
| 100D | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Instrument tee bends | 100 | 50 | OTPr-10050 or LOTPr-100 50 | |
| Indentations | 50 | — | OTS- | |
| 100 | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Straight tees | 50 | 50 | ||
| 100 | 50 | |||
| 100 | 100 | |||
| 100 | 100K | |||
| 100 | 100D | |||
| 150 | 50 | |||
| 150 | 100 | |||
| 150 | 150 | |||
| Straight compensation tees | 100 | 50 | ||
| 150 | 50 | |||
| Straight low tees | 100 | 100 | TN-100100 | |
| Straight transition tees | 100/50 | 100 | TPR-100/50100 | |
| Straight transitional low tees | 100/50 | 100 | TPRN-100/50 100 | |
| Tees oblique 45° and 60° | 50 | 50 | TK 45° - and TK 60° - | |
| 100 | 50 | |||
| 100 | 100 | |||
| 150 | 50 | |||
| 150 | 100 | |||
| 150 | 150 | |||
| Crosspieces are straight | 50 | 50 | KP - | |
| 100 | 50 | |||
| 100 | 100 | |||
| 150 | 50 | |||
| 150 | 100 | |||
| Crosspieces are straight with an offset axis of removal | 100 | 50/100 | KPS - | |
| Crosses oblique 45° and 60° | 50 | 50 | KK45° - and KK60° - | |
| 100 | 50 | |||
| 100 | 100 | |||
| 150 | 50 | |||
| 150 | 100 | |||
| Two-plane crosspieces | 100 | 100; 50 | KD - LKD - | |
| 150 | 100; 50 | |||
| Couplings | 50 | — | Mf - | |
| 100 | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Sliding couplings | 50 | — | MfN - | |
| 100 | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Audits | 50 | — | R - | |
| 100 | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Stub | 50 | — | Z - | |
| 100 | — | |||
| 150 | — | |||
| Transitional tees | 100 | 50 | OTP - 10050 | |
| Cleaning | 100 | — | Etc - | |
| 150 | — | |||
Expanders and indents: their parameters
Expanders are used to rotate the pipeline during its installation. No communication system can do without them. GOST distinguishes expanders for 110°, 120°, 135° and 150°. Their parameters are given in the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Instrument tees are made in left and right versions. Their weight according to document 6942-98 is 7 kg.
Cast iron indentation is used in non-pressure sewer networks for the removal of waste and fecal waters. It connects to the pipes thanks to a socket connection.
You need to pay attention! The indentation has good technical and operational parameters, low price and long service life.
Such a connection element as a drain can be found in virtually every sewerage system
The characteristics of cast iron indents standard 6942-98 are shown in the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Table 11
Conditional pass
| Weight without anti-corrosion coating, kg | Bend radius | Length to flare | |
| 5 | 2,1 | 6,0 | 21 |
| 10 | 5,0 | 8,5 | 25 |
| 15 | 8,0 | 9,0 | 25 |
5 Technical requirements
5.1 Cast iron sewer pipes and fittings for them should be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard, according to design and technological documentation approved in the prescribed manner.
5.2 Characteristics
5.2.1 Pipes and fittings for them must not have defects that impair their installation and operational qualities: spills, build-ups, drops of metal, slag deposits on the outer and inner surfaces. It is allowed to eliminate minor defects caused by the production method and which do not impair the quality of the products.
5.2.2 Pipes and fittings for them must not have a chill over the entire outer surface with a depth of more than 1 mm, and at the ends and outer surface of the smooth ends of pipes at a length of 60 mm from the end and in places where molds are separated on fittings - with a depth of more than 2 mm.
5.2.3 Deviations from the nominal dimensions of the internal diameters of the sockets of pipes and fittings and the outer diameters of the smooth ends of pipes and tails of fittings (before applying an anti-corrosion coating to the product) should not exceed ±2 mm. Deviations from the dimensions of construction lengths in products of all types and diameters should not exceed ±0.9%.
5.2.4 It is allowed to thicken by no more than 2 mm the walls of the smooth ends of pipes in a section up to 150 mm long and the shanks of fittings in a section up to 70 mm long from their ends with a corresponding reduction in the internal diameters of the products in these places, as well as rounding on the outside the ends of the smooth ends of pipes and the shanks of fittings.
5.2.5 Maximum deviations from the nominal dimensions of castings of products, with the exception of those regulated in 3.2.3 and 3.2.4, must correspond to the 11 t accuracy class according to GOST 26645.
5.2.6 Deviations from the calculated values of the masses of products established in the design standards, and the dimensions of these products (for the calculation of which the density of cast iron is taken to be 7.1 g/cm) must correspond to the 11 t accuracy class according to GOST 26645.
Castings whose weight exceeds the maximum are considered acceptable provided that in all other quality characteristics they comply with this standard.
5.2.7 Deviations from straightness of 100 and 150 mm pipes should not exceed 2 mm per 1 m length, and 50 mm pipes - 5 mm per 1 m length.
5.2.8 Pipes and fittings assemblies, after applying an anti-corrosion coating to their internal and external surfaces and sealing the sockets, must withstand a hydraulic pressure of at least 0.1 MPa (1.0 kgf/cm).
5.3 Requirements for raw materials, materials and components
5.3.1 Pipes and fittings for them must be made of gray cast iron with flake graphite in accordance with GOST 1412 and in accordance with the requirements for castings in accordance with GOST 26358.
5.3.2 The outer and inner surfaces of pipes and fittings must be coated with an anti-corrosion composition based on bitumen grade BNI IV-3 according to GOST 9812 or other compositions that ensure the softening temperature of the anti-corrosion coating is not lower than 333 K (60 ° C) and operating conditions UHL 4 GOST 15150.
The anti-corrosion coating must be continuous, durable, smooth, without cracks or bubbles, firmly adhered to the metal of the product and should not be sticky.
On the surface of the pipe coating, ring marks from supports for rolling pipes are allowed, and on the surface of the coating of fittings - traces from the hooks of chain conveyor hangers, as well as drips caused by the runoff of the anti-corrosion compound from pipes and fittings, or discontinuities in the coating.
5.4 Completeness
5.4.1 The manufacturer must complete pipes and fittings for delivery in an assortment determined by the customer’s order.
5.5 Labeling and packaging
5.5.1 Pipes and fittings must have markings cast or applied with indelible paint on the end or forming surface of the socket or directly behind the socket and including:
— trademark of the manufacturer;
— symbol of the product;
— designation of this standard.
5.5.2 Pipes are packaged in containers, bags, cassettes or bundles tied with wire.
When packing, pipes are laid with sockets alternately in opposite directions. Shaped parts are placed on box pallets or containers in accordance with GOST 26598, and the carrying capacity of the container must be fully used.
Production of cast iron pipes
Cast iron pipes are made by casting. Today, there are two types of casting for making these sewer parts. Consider these two casting options:
- centrifugal;
- semi-continuous.
The first method involves using a special form. Cast iron is poured into it, after which, due to rotation, it is evenly distributed over the walls of the mold, resulting in the formation of a finished part. The thickness of the wall depends on the amount of liquid cast iron used.
Let's consider the main advantages of this method:
- high speed of pipe production, which affects productivity indicators;
- good quality of cast iron product cast using this method;
- saving raw materials and electricity;
- the possibility of automating this method;
- simplification of the process due to the absence of the need for additional steps (forming and drying);
- This process saves not only time and money, but also space, as it eliminates the need for additional equipment.
Pipe production using centrifugal casting is the most economical
However, centrifugal casting also has its disadvantages. Among the disadvantages of this method are the following:
- the pipe can only be made of a certain shape, in accordance with the shape of the workpiece;
- the need for strict control of the amount of raw materials entering the workpiece (to obtain the required wall thickness).
The semi-continuous casting method involves filling a mold with liquid cast iron. In this form, the cast iron solidifies and the finished product is obtained. After partial hardening, the part is removed from the mold and divided into the required sections. The cooling process is carried out using ordinary water.
Let's look at the main advantages of this method:
- using this method, you can obtain a long product, which is subsequently cut into parts of the required length;
- the accuracy of the geometric parameters of the product is maximum;
- possibility of saving liquid cast iron.
The disadvantages of this method include:
- not very high performance;
- The finished pipe is quite difficult to remove from the workpiece.
Pipes are either pressure or non-pressure, with or without a socket
6 Acceptance rules
6.1 Pipes and fittings are accepted in batches. A batch is considered to be the number of pipes and fittings manufactured during one shift and documented with one quality document.
6.2 To check the compliance of pipes and fittings with the requirements of this standard, the manufacturer carries out acceptance and periodic tests of products.
6.3 During acceptance tests, products are checked for compliance with the requirements:
5.2.2 - 0.5% of products from the batch;
5.2.1 and 5.3.2 regarding the appearance of the anti-corrosion coating - 100% of the products in the batch;
5.2.3-5.2.8, 5.3.2 in terms of the stickiness of the anti-corrosion coating - at least 2% of products from the batch.
6.4 Periodic tests are carried out at least once a quarter.
6.5 Products that have passed acceptance tests are subject to periodic testing.
6.6 During periodic testing, products are checked for compliance with the requirements of 5.2.3; 5.5.1 and 5.3.2 in terms of determining the softening temperature of the anti-corrosion coating and its adhesion strength to metal in the amount of 0.5% of products from the batch.
6.7 The consumer has the right to carry out a control check of pipes and fittings according to any quality indicator, following the procedure for selecting products given in 6.3; 6.6, and applying the control methods specified in section 7.
6.8 If, during inspection, at least one product does not meet the requirements of this standard for any indicator, then a double number of products from that batch are re-tested for this indicator.
If the results of the re-inspection are unsatisfactory, the batch of products is rejected or the products are accepted piece by piece and the indicators for which unsatisfactory results were obtained during the re-inspection are checked.
Advantages and operational scope of cast iron pipes
Like any other product, a cast iron pipe has its advantages. Let's consider the advantages of cast iron parts over modern plastic ones:
- they are distinguished by high strength characteristics;
- cast iron pipes are wear-resistant;
- cast iron has good soundproofing properties;
- parts made of this material are fire resistant;
- are resistant to temperature fluctuations;
- have a low stretch coefficient.
Helpful information! These products are regulated by the relevant state documentation (GOST). According to GOST, cast iron parts for sewer networks are best used for installation inside structures in which the load exceeds economic standards.
Let's consider in what cases it is recommended to lay pipes made of cast iron:
- at industrial enterprises that belong to the food industry;
- in factories;
- on farms;
- in buildings equipped for sanatoriums (if there is access to geothermal sources);
- in buildings equipped for healthcare purposes;
- in educational institutions.
Cast iron pipes are suitable for underground and above-ground drainage systems
Cast iron pipes are heavy, so their installation is quite labor-intensive. Products with large cross-sectional dimensions require the use of special equipment during installation.
7 Control methods
7.1 The depth of bleaching and the dimensions of the bleached layer (5.2.2) are checked on products rejected for other indicators by splitting them and measuring the depth and dimensions of the bleached layer with a ruler or caliper according to GOST 166.
7.2 The appearance and quality of product surfaces (5.2.1) and the appearance of the anti-corrosion coating of products (5.3.2) are checked visually without the use of magnifying devices by comparing the product being tested with the standard.
7.3 Deviations from the dimensions of pipes and fittings (5.2.3-5.2.5) are checked using universal measuring instruments that provide the necessary measurement accuracy. Measurements are carried out in two mutually perpendicular directions. The arithmetic mean of the results of two measurements is considered the outer (inner) diameter. In this case, the result of each measurement must be within the permissible deviations.
7.4 Checking the mass of products and deviations from it (5.2.6) is carried out by weighing the products on scales with an accuracy class of no rougher than 2.
7.5 Determination of the presence and value of pipe non-straightness (5.2.7)
7.5.1 Equipment and tools:
— height gauge according to GOST 164;
— control horizontal plate;
— two steel prismatic supports of the same height.
7.5.2 Carrying out the test
Two prismatic supports are installed parallel to each other at a distance from each other of more than half the length of the pipe being tested on the control plate and the pipe is laid on them with the deflection downwards. Using a height gauge, the distance from the surface of the slab to the bottom point of the pipe at the point of its greatest deflection is measured with an accuracy of 0.1 mm.
7.5.3 Calculation of test results
The deviation from straightness of a pipe per 1 m of its length is calculated using the formula
, (1)
where is the height of the support, mm;
— distance from the horizontal surface of the slab to the bottom point of the pipe, mm;
— distance between prismatic supports, m.
7.6 The softening temperature of the anti-corrosion coating (5.3.2) is checked according to GOST 11506.
7.7 The adhesion strength of the anti-corrosion coating to the metal of the product (5.3.2) is checked by making grid-shaped cuts on the coating with a knife blade with distances between cut lines of at least 40 mm.
The adhesion of the coating is considered strong if the coating does not peel off when making cuts.
7.8 The stickiness of the anti-corrosion coating (5.3.2) is checked at an ambient temperature of 15 to 30 °C by lightly pressing a clean sheet of writing paper to the product coating according to GOST 18510.
A coating is considered non-tacky if, after removing the paper, no traces of the coating remain on it.
The stickiness of the coating is checked no earlier than 24 hours after applying it to the product.
7.9 Checking the tightness of pipes and fittings (5.2.8)
7.9.1 Devices, materials and equipment:
— a stand equipped with a pressure gauge with a division value no rougher than 0.01 MPa (0.1 kgf/cm);
— a pump creating a hydraulic pressure of 0.2 MPa (2 kgf/cm);
— plugs (blind and with pipes).
7.9.2 Carrying out the test
The assembled pipes and fittings are placed on the stand, and a plug with a pipe for connection to the pump is installed on the hole closest to the pump, and a plug with a pipe for draining water is installed on the other hole. If there are other holes, then blind plugs are installed on them. Using a pump, the tested section of the pipeline is filled with water, the water drainage pipe is closed with a valve or other shut-off device, and a pressure of at least 0.1 MPa (1.0 kgf/cm) is created in it. This pressure is maintained for at least 15 s, during which the connections of the pipeline section are inspected.
7.9.3 Test results
A section of the pipeline is considered sealed if, upon inspection, no water leaks through its walls or socket joints, or fogging of the outer surfaces of pipes and fittings is detected.
Cast iron making
Fluxes, ores, and fuel are used to make cast iron .
Iron ores
They are the main type of raw material and contain chemical compounds of oxygen and iron. In addition, they contain empty alumina, oxides of magnesium and calcium. But the latter compounds have little effect on the value of the ore; the sample that has a higher iron content is suitable for processing. A nugget of ore may also contain harmful impurities that reduce the value of the nugget, such as phosphorus and sulfur. Red and brown iron ore are mined in Russia.
Fuel
As a heat source, coke is used, obtained from coking coal by heating in furnaces at a temperature of 1000–1150ºС without the supply of fresh air. Coke is an important component in the smelting of cast iron.
Fluxes
They are used as raw materials in the smelting of cast iron. The role of these mineral substances is to lower the melting temperature of waste rocks and release harmful substances from the alloy in the form of slag.
Fuel, ore and fluxes, combined together in certain quantities, make up the so-called charge. The size of the pieces is required 0t 2 to 4 cm, so large pieces are crushed, and small pieces are pressed to the desired size. Ore nuggets with low iron content are subjected to preliminary preparation for smelting by enrichment. This allows you to lower the melting point, improve the quality of cast iron and reduce fuel consumption.
Blast furnaces
They are a round shaft-type furnace. It is placed in a solid metal case, 2–3 cm thick at the bottom and 3.5–5 cm at the top . The inside of the furnace is lined with clay refractory bricks. The furnace design includes a shaft, a flue, a hearth, shoulders and steam.
The process of processing ore in a blast furnace involves the reduction of iron oxides, which occurs when gases are released from the combustion of coke and the lowering of the charge. The formation of iron occurs from oxides during the removal of moisture and the process of decomposition of carbonates. Under blast furnace conditions, iron is completely reduced and enriched with oxygen.
With the constant combustion of coke in a shaft furnace, manganese, silicon, sulfur and phosphorus are reduced. The carbon increase occurs to a level of 4.5% . This enriched iron alloy is called cast iron. Then it is poured into a receiving ladle and goes to the ingots for filling, or goes to the production workshop to fill molds.
Types of cast iron
According to the intended purpose, the resulting cast iron is divided into foundry, conversion and special. More than 85% of the melted material is white cast iron, which is characterized by increased hardness and brittleness. It is used to produce steel.
Gray (casting) cast iron has a high silicon content and is used for the manufacture of numerous parts. Its variety is alloyed natural cast iron, smelted from ores containing chromium, vanadium, nickel and other components. This type of cast iron is used for structural purposes . Cast iron pipes for sewer pipelines are made from this type of alloy.
Special cast irons are used for alloying steels. They contain large amounts of two minor components.
Pipe manufacturing
The production of cast iron products involves the use of one of the proposed methods: casting using the method of pouring into a sand mold; method of centrifugal continuous casting in molds and casting intermittently; de Lavaux centrifugal casting method.
Modern cast iron pipes for laying communications have a gradation of diameters, ranging from 50 mm to 1200 mm . The smallest wall thickness is 1 cm. The length of pipes ready for sale starts from 2 m and ends at 7 m, depending on the diameter of the product.
The dimensions of cast iron pipes are determined using the value of the nominal (internal) diameter of the product. The inner diameter is called Dy, and the outer diameter is called Dout. A very large number of pipes with internal diameters from 5 to 40 cm are characterized by a high strength index. They are produced with smooth edges and a length of 3m. Detachable shaped elements are produced in lengths from 150 cm to 3 m .
Despite the emergence of modern new materials for sewer lines, cast iron pipes are still in demand due to their strength and long service life. A cast iron pipeline can serve for many years; an indispensable condition for this is compliance with installation technology and choosing the right products.
About socketless products
For more than three decades, the international group of companies Saint-Gobain has been producing SML cast iron pipes with a diameter of 100 mm. Throughout this time, these socketless devices have successfully competed with socket-type collectors.
A significant advantage of such products is that they are connected to each other using the “joint to joint” method, using clamps that are resistant to various types of chemical influences. The presence of such stainless steel clamps makes it possible to easily tolerate increased external loads.
Modern SML systems are widely used in external and internal drainage systems of airports, high-rise buildings, offices, warehouses, supermarkets, underground parking lots, hospitals, train stations, and other facilities that are subject to increased requirements in terms of noise and fire protection.
By the way, if you want to replace or repair cast iron pipes of sewer or water supply systems yourself, then for reliable clamping we recommend using the Yato YT-6513 folding vice. Buying a reliable clamp for cast iron pipes 100 mm in diameter means getting rid of possible rotation of the pipe while working with it.
How much does it weigh? What is the mass?
The weight of a pipe is significantly influenced by its class. The table shows the weight of one meter of class A cast iron pipe. Class B is heavier, and class LA is 10% lighter. (approximate for quick weight estimate)
Table of parameters of cast iron sewer pipes with internal diameters of 50 mm, 65 mm, 100 mm, 110 mm, 150 mm, 300 mm.
| Bore diameter, mm | outer diameter, mm | wall thickness, mm | weight of cast iron pipe 1 m | number of meters per ton |
| 50 | 65 | 6.9 | 8.6 | 110 |
| 65 | 81 | 7.4 | 12.4 | 80.6 |
| 100 | 118 | 8.3 | 20.8 | 48 |
| 110 | 130 | 8.5 | 22.5 | 43 |
| 150 | 170 | 9.2 | 33.7 | 29.6 |
| 300 | 326 | 11.9 | 85.2 | 11.7 |
Characteristics of crosses
When installing communication systems, the main thing is not to forget to take into account the pipe branching factor. Using a cross for these purposes allows you to save space and make the best use of the material. Branching occurs in two planes. Document 6942 has the characteristics of crosses. The angle between the key and secondary axis is 87° 30? with a possible deviation of 1° 30?.
You need to pay attention! The mass of straight crosses with an offset axis of removal is 7.6 kg. The axis shifts by 25 mm.
Characteristics of oblique crosses at 60° with a possible deviation of 1° 30? are given in the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Table 13
Symbolic passage: key/bends 10/5.0
15/5Distance from the branching point to the expansion89.2Distance from the branching point to the shank9.58Distance from the branching point to the branch expansion912.0Weight without anti-corrosion coating, kg5.87.05/510/1015/109.01518.010118.59.01518.84.010.510 ,5Two-plane crosses according to GOST 6942 are available in left and right versions.
Why do you need to determine the weight of the pipeline?
The weight of 1 meter of cast iron pipe products needs to be known when you plan to purchase them in bulk. Then the pipes are sold in tons. In this case, the mass of one product does not matter, since the footage is calculated the other way around, based on data on the number of meters per ton. For retail purchases, the weight of the pipe is not taken into account. The dimensions of cast iron pipes are of key importance in this case. It is also necessary to look for the weight of products in order to:
- determine the carrying capacity of the vehicle for transportation;
- find out the cost of transportation;
- calculate labor costs for each shift;
- Determine the lifting capacity of a crane or loader.
Important! Incorrect calculations can lead to accidents when transporting cast iron pipe products or during work with them. For example, beams will bend, hangers will break, crane slings will break.
Without preliminary calculations, it is impossible to be sure that the work will be 100% successful.
Dimensions
GOST 9583-75, which replaced the previously existing 9583-61, regulates the sizes and diameters of water pipes; The table below shows all the features of products of different classes.
| Conditional bore, mm | Outer diameter, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Length standards, m |
| 65 | 81 | 6,7 | 7,4 | 8 | 2;3. |
| 80 | 98 | 7,2 | 7,9 | 8,6 | 3;4. |
| 100 | 118 | 7,5 | 8,3 | 9 | 3;4;5;6. |
| 125 | 144 | 7,9 | 8,7 | 9,5 | 3;4;5;6. |
| 150 | 170 | 8,3 | 9,2 | 10 | 3;4;5;6. |
| 200 | 222 | 9,2 | 10,1 | 11 | 4;5;6. |
| 250 | 274 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 4;5;6. |
| 300 | 326 | 10,8 | 11,9 | 13 | 4;5;6. |
| 350 | 378 | 11,7 | 12,8 | 14 | 4;5;6. |
| 400 | 429 | 12,5 | 13,8 | 15 | 4;5;6;7;8;9;10. |
| 500 | 532 | 14,2 | 15,6 | 17 | 4;5;6;7;8;9;10. |
| 600 | 635 | 15,8 | 17,4 | 19 | 4;5;6;7;8;9;10. |
| 700 | 738 | 17,5 | 19,3 | 21 | 4;5;6. |
| 800 | 842 | 19,2 | 21,1 | 23 | 4;5;6. |
| 900 | 945 | 20,6 | 22,3 | 25 | 4;5;6. |
| 1000 | 1048 | 22,5 | 24,8 | 27 | 4;5;6. |
Designations in the markings:
|
Application area
The assembly of a drainage system is most often carried out using products made from modern polymer materials. Cast iron sewer pipes GOST 6942-98 are more often found at industrial enterprises, where discharged water may contain a large amount of aggressive substances. This includes the following objects:
- Enterprises where livestock are kept and slaughtered.
- Enterprises where food is produced.
- Factories and plants.
Cast iron is used in the assembly of the following systems:
- Water pipes.
- Drainage.
- Heat supply.
- Pipeline.
- Ventilation.
On what indicators does the mass of the pipeline depend?
As you can see from the tables, the weight of pipe products is primarily determined by the thickness of the walls. The higher the last indicator, the greater the mass. Almost nothing depends on other factors: for example, if class A, B and LA pipelines have a nominal bore of 100 millimeters, a type B pipe will still weigh more compared to other types of products.
The weight of a meter of pipe may increase if the product is equipped with additional parts. The type of connections also plays an important role: for example, pipes with a diameter of 100 millimeters with sockets will differ in weight from exactly the same products with threads.
And although the differences between the weight of two individual tubular products are insignificant, the difference in weight will become noticeable if you buy products in bulk.
If you take a responsible approach to the choice of pipe products, there will be no problems with assembling the system, and the sewerage or water supply system will properly perform its functions for a long time.