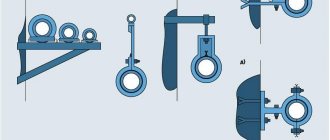
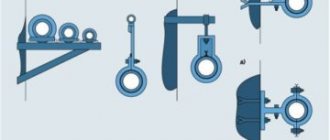
Varieties
Clamps are presented on the construction market in a wide range.
Models are produced in a wide variety of standard sizes and are divided according to such characteristics as the method of fixation, the presence of a seal, shape, material of manufacture and purpose. Based on the material used, products are divided into plastic and steel. Moreover, steel elements can be made either with or without galvanization. Compared to plastic models, steel clamps are considered more in demand and popular. This is due to the low cost of the products, good tensile strength of the metal and high strength. The disadvantage of metal clamps is the low resistance of non-galvanized models to corrosion processes. Therefore, in cases where the installation of clamps is planned in extremely humid rooms, you should choose models made of stainless steel or clamps coated with zinc.
Plastic options are characterized by increased elasticity, high resistance to vibration and the ability to create movable fixation. Models can be used for fastening pipelines with a diameter of no more than 10 cm.
Depending on the tasks assigned to them, clamps are divided into spiral, power, wire, worm, pipe and mortise options.
A spiral clamp is a fairly common device and is intended for rigid fixation of pipes in the system.
The power one has the shape of a tape with holes for bolts and is indispensable when working on lines with increased operating pressure, at pumping stations, pneumatic and hydraulic systems.
Wire clamps are presented in the form of one or several steel rings equipped with tightening fasteners. The model is designed for corrugated pipes and is indispensable for fixing them during strong movements.
The worm model is a steel strip with a track, equipped with teeth and screws for tightening. The model is used in the construction of heating systems, as well as as a fixing mechanism for pipelines exposed to severe vibrations.
Pipe clamps are presented in the form of rings with brackets and are installed to secure the pipeline in cases where it is necessary to reduce the internal stress in the system during repairs.
The spring clamp has a fairly narrow specialization and is used on pipes subject to linear expansion.
A mortise, or saddle, clamp with a branch is a more complex mechanism and is designed for installation in places where the pipeline branches. Its main difference from traditional models is the presence of a coupling equipped with threaded pipes, which allows you to insert the clamp into the system and quickly connect an additional branch. The tightness of such a connection is ensured by a gasket located inside the clamp and made of profiled rubber.
Pivot models, also known as hinge locks, are used to install scaffolding and are used when attaching diagonal type braces. Thanks to the rotary clamps, all elements can be fixed at any angle, which gives additional strength to the structure and ensures its stability.
According to the type of fixation, all clamps are divided into two types:
- The first include models that form a rigid type of fastening, in which the pipe becomes completely motionless. The crimping brackets of such products are securely tightened with bolts, and the clamp itself is firmly attached to the wall. This type of fastening is used in areas where the pipeline bends and in the presence of branches.
- The second type includes models with movable fastenings, used for fixing heating and hot water pipes. The specificity of the fastening does not create obstacles to the elongation and compression of the pipeline and ensures its longitudinal mobility. As a result, an optimal line voltage is created, significantly extending the life of the networks.
Structurally, clamps are available in several types:
- a split ring, formed in the form of a circle and having one fastening mechanism, fixed with a bolt;
- a ring consisting of two semicircular plates and having fastening ears on both sides;
- a tape folded into a ring and having several positions for fixation;
- A U-shaped model, often made of plastic, equipped with a locking latch and capable of being attached in a rigid and movable manner at the same time.
Fasteners for profile pipes
Fasteners for profile pipes can be either stationary or mobile. The most common variation of the latter is the crab system.
The crab type fastener is the optimal solution for laying not only square, but also rectangular pipes. Its advantages are:
- in a wide range of applications;
- in high strength and reliability;
- at a relatively low weight;
- at low cost;
- there is no need for welding work;
- in the simplicity of the design;
- in high quality of the final result.
Speaking about the types of crab systems, there are designs in the form of the letters “T”, “G”, “X”.
Pipe installation methods
The key stage in creating a sewer system is fastening the sewer pipes. Fixation in a certain position ensures the strength of the system and allows you to disguise the pipes with lining materials. Hidden installation requires tightness and reliability of connections. Leaks that occur under finishing materials will not be immediately noticeable. They are often reported by downstairs neighbors when the problem is already large enough.
There are two ways to install the system. They differ from each other in the position of the pipelines relative to the plane of the floor, wall or ceiling. Let's take a closer look at these methods:
Closed
Closed installation involves laying sewer lines into a recess made in the supporting plane. Before starting installation work, markings are made, along which gating is carried out. The depth of the groove is chosen so that the pipe is completely hidden in the surface of the support. This method allows you to hide the elements of the system and eliminate the formation of unnecessary ledges or boxes. In addition, fastenings for sewer pipes become optional. The disadvantages of this option are:
- The thickness of the walls should allow making a recess of the required size. In typical apartments this method is not always suitable. Most often, this option is used in private houses or apartments of old construction, with brick walls;
- Making a groove requires a lot of labor. As a rule, water communications are hidden in the wall at the same time as the sewer system. This increases the amount of work and requires more preparation time.
The advantage of closed installation is a neat and smooth wall surface. After laying the tiles, no elements of the system remain visible. This allows the use of wall mounted plumbing fixtures.
Open
Open pipe installation is much faster. A special fastening of sewer pipes to the wall is used, which reliably fixes the pipes in the desired position. The specified slope is ensured, the position of the system elements remains unchanged. The disadvantage of this method is the open arrangement of the pipes. When finishing, they have to be hidden under the cladding, for which a box is first built. This takes up space in a room that is already not very large. However, in apartments with concrete walls this method has practically no alternative.
Plastic pipe fasteners
The second position in the ranking of fixing elements is occupied by plastic clips. This is the most common type of plastic pipe fastening. The advantages of this polystyrene device:
- long service life;
- strength;
- resistance to external factors;
- versatility;
- variety of configurations and sizes.
Clips for fastening PP pipes can be of two types:
- Simple. Self-tapping screws are required to secure them.
- With built-in locking element. They are one-piece parts. Plus - ease of use.
Another fastening structure is a clamp. It is used if there is a need to secure pipes more firmly.
The difference between a clamp and a clip is that it has a latch. It is this element that allows you to securely fix the pipe in any direction.
Types of fastening structures
Load-bearing fastening structures are divided into the following types:
- Fixed supports. When using this fastener, angular or linear movement of the fixed areas is not allowed.
- Guide supports. The use of this design allows displacement in only one direction. As a rule, only along the horizontal axis.
- Hard pendants. Movements are permissible, but only in the horizontal plane.
- Spring suspensions and supports. Movements are possible both in the vertical and horizontal planes.
Types of fastening pipelines to the wall
Requirements for supports and suspensions
If fixation occurs between two fixed supports, movements that may occur as a result of changes in temperature conditions, installation stretches or displacement of supports must be self-compensating. But such compensating ability, as calculations show, is sometimes not enough. In this case, special compensators must be installed.
The pipe clamp is equipped with a screw/bolt
They are made from pipes of the same type and diameter as the structure as a whole. Most often they are made in the form of the letters “P” or “G”.
If the structure is fixedly fixed, the fastenings must withstand the weight of the pipeline itself, the liquid that moves along it, as well as axial loads generated by thermal deformation, vibrations and hydraulic shocks. When installing polymer products, movable supports are most often used.
If the installation is carried out in fixed supports, restrictive rings or segments 10-20 mm wide, which are made from pieces of pipes of the same plastic, are welded to the pipes. These segments or rings should be located on both sides of the support.
Selection of fastening elements
Suitable fastenings are selected taking into account many factors. The choice depends on the location of the installation site, the purpose of the specific system, and so on.
Fastening a plastic pipe
Sometimes the pipe must be insulated from the source of cold or heat. If you use a simple clamp that fixes the area, then it will not provide the gap from the adjacent surface necessary to solve the problem. But, for example, a ring support, which has a threaded extension and a plate for fastening to the supporting surface, will completely eliminate the problem.
If you have to fasten heavy cast iron pipes, then use special fasteners that can withstand heavy loads. For vertically located systems it is installed on the floors. Horizontally oriented systems are fixed not even one at a time, but in groups of pipes laid on a console.
A competent approach to the selection and placement of fasteners allows you to operate the pipeline for a long time and efficiently, without fear of emergency situations. But we should not forget about the economic component of this problem. After all, exceeding the required and sufficient number of elements can lead to an unjustified increase in the cost of the structure and complication of installation work.
Selection of the type and size of fasteners for pipeline structures
The choice of fasteners for pipeline installation is based on several simple rules:
- the most reliable way to complete the project is to study the design documentation and specifications, which are necessarily present in any high-quality project;
- If there is no project, it is recommended to turn to professionals. Engaging in independent selection of fasteners is an activity that requires studying regulatory documentation, standards, and technical regulations;
- fulfillment of the conditions listed in the previous paragraph as preparation for completing the facility on its own;
- basic criteria are strength, reliability, suitable area of use and service life corresponding to a similar parameter of the pipeline itself.
Following these rules guarantees a smart choice. If you follow the installation technology at the outlet, you will be able to get a pipeline that will last a long time and without problems.
Pipeline attachment points
There are several options for piping placement:
- to Wall;
- semi;
- to the ceiling.
The most commonly used method is to attach pipes to the wall. This way, less material is wasted and unnecessary bends are eliminated. Reduces the risk of blockages. However, in older houses, pipes are often recessed into the floor. This option is even more effective, since the level of placement of the system is guaranteed to be lower than the plumbing drain sets. Sometimes sewerage is attached to the ceiling. This is a convenient option if the riser goes into the basement of a private house. The pipes do not get in the way underfoot and do not take up space along the walls. In addition, the pipes can be fixed under a suspended ceiling. To do this, they must be lowered to the floor below, or a pump for waste liquids must be used.
Types of fasteners
The standard fastening for sewer pipes to a wall or other support is a special clamp. This is a universal element capable of holding any round pipelines. There are different types of fasteners:
- crimping Capable of simultaneously performing two functions - holding the pipeline and sealing the connection;
- guides. Used only to indicate the position of the pipe relative to the supporting structure;
- supporting They can fix pipes to vertical and horizontal planes - to walls, floors or ceiling slabs;
- safety. These elements are installed as additional support for complex system components.
To assemble PVC sewer systems, fasteners for sewer pipes of 110 or 50 mm are used. These are the most common sizes for vertical and horizontal pipelines.
Two types of installation are used:
- hard. The pipeline is tightly clamped with a clamp and fixed in a stationary state. This method is used for vertical pipelines (risers) that require complete immobility;
- mobile. The pipeline has the ability to move inside the clamp. This method is used for horizontal pipelines (beds), which do not need to be rigidly attached to supports. Mobility allows you to compensate for thermal expansion of the plastic.
In order to ensure free movement of the pipe, fasteners of a larger diameter are chosen. Any sewer clamp is manufactured in accordance with pipeline standards. Before starting assembly, you need to count the number of clamps
It is important to consider which areas will be rigidly fixed and which will be movable
Plastic clamps
These are fasteners made of PVC of the same brand as the pipelines. There are clamps for all available diameters of system parts. The design of fasteners varies according to the assembly method:
- an element of two halves connected with screws. It is attached to the supporting planes using a pin screwed into a dowel. Provides a strong and rigid connection;
- clamp equipped with a movable latch. The pipe is inserted into the bracket, and the latch wraps around it from above and is fixed on a special protruding tooth.
The first type of clamps allows you to adjust the distance from the wall to the pipe. This is provided by a pin, which can be immersed deeper into the wall or slightly unscrewed from the fastener itself. The second type is convenient for assembly, as it does not require the use of additional tools. In this case, clamps with a latch are tightly attached to the support at a fixed distance from it.
Metal clamps
Metal fasteners are load-resistant. They usually consist of two halves that are connected with screws. Both parts have rubber gaskets that seal the connection and cut off the metal from the pipeline. Before fixing the sewer pipe to the wall, you only need to mark the axis and place the clamp installation points on it
It is important to remember the need to create a slope, for which the axis is immediately placed at an angle. For a diameter of 50 mm it is 30 mm for each meter of length
Let's look at how to attach sewer pipes to the wall using metal clamps. The studs for such fasteners have two types of cutting. At one end there is a thread for attaching the lower half of the clamp, at the other there is a standard thread, like a screw. When installing, first drill a hole for the dowel. Then install the stud using a wrench or pliers. The gap between the two types of cutting is shaped like a hexagon. This section is used to install the element into the dowel. The last step is to screw the clamp half onto the stud. Then all that remains is to install part of the system and screw the upper part of the fastener.
Production material
With some degree of convention, fasteners are divided into two categories. The first includes metal products, and the second - plastic. The pros and cons of each need to be studied separately. Do not forget: in addition to the two listed, for the manufacture of a number of fasteners, for example, gaskets, rubber or other materials with similar characteristics are used.
Metal
The advantages of metal fasteners include the following:
- strength. The main alternative option - plastic - is noticeably inferior in this parameter. High-strength steel fasteners, which are distinguished by their increased service life and resistance to aggressive environments, are in noticeable demand;
- versatility. Metal fasteners are used when laying all types of pipelines;
- diversity. A variety of types of fasteners are made from metal - clamps, staples, brackets, studs, anchors, embedded parts, bolts, screws and even nails. An additional plus is the use of several metals and alloys, including regular and stainless steel, brass, etc.;
- durability. High-quality metal fasteners are guaranteed to last a long time - comparable to the standard service life of the pipeline;
- maintainability. Most structures can be easily repaired by replacing one or more parts;
- testing in practice. It has long been used in real construction and has repeatedly proven its effectiveness.
Among the disadvantages of metal fasteners are:
- significant weight, which increases the load on the load-bearing surface and increases the requirements for the strength and load-bearing capacity of fasteners;
- not always high resistance to corrosion and aggressive external factors;
- technological complexity of installation;
- the need for periodic maintenance, tightening, updating the anti-corrosion coating and other similar work.
It is also worth remembering another common disadvantage - the usually higher cost of manufacturing fasteners. This applies, first of all, to stainless steel hardware, the most reliable, durable, and valuable.
Plastic
No less in demand are fasteners made of plastics - PVC, polystyrene, propylene or other material with similar characteristics. Some of its advantages overlap with those listed for metal, others are noticeably different. The advantages of practical use of plastic fasteners are:
- versatility. In terms of this parameter, the type of fastener under consideration is slightly inferior to those made of metal;
- low weight and, as a result, absence or minimal additional load on supporting structures;
- resistance to various influences, including corrosion, aggressive environments, pressure and temperature changes, climatic conditions;
- durability. The service life of PVC/propylene fasteners is comparable to that of plastic pipelines and often exceeds metal ones;
- diversity. Plastics are used to produce several varieties, including clamps, brackets, dowels, staples, and, in recent years, studs and pins;
- convenience and simplicity of installation technology, as well as storage and transportation of products.
The main disadvantage of plastic fasteners compared to metal ones is their strength characteristics. It is compensated by the constant improvement of products, the emergence of new types of plastics, and affordable and constantly decreasing manufacturing costs.
Distances between pipeline supports according to the SNIP table
A correctly selected distance between the support fasteners is one of the operating conditions for the system. The supports allow you to distribute the load, minimize stress, and in certain cases - when arranging heating mains, for example, distribute the temperature load.
SNiP standards include requirements for the distance between supports for pipelines with different diameters, wall thicknesses and purposes. Such data is entered into special tables, which greatly facilitates calculations. It is worth remembering that the table does not contain recommended data, but an exact indication, corresponding to SNiP, how many and what structures are needed.
The table of distances between pipeline supports given in the article concerns sliding structures for steel pipes.
| Outer diameter, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Maximum distance between supports, m | Accepted distance for above-ground and underground installation, m | Accepted distance for underground installation in impassable channels, m |
| 25 | 2,5 | 2.5 | 1,9 | 1,9 |
| 32 | 2,5 | 3,2 | 2,7 | 2,7 |
| 40 | 2,5 | 3,9 | 3,0 | 3,0 |
| 57 | 2,5 | 4,9 | 3,8 | 3,8 |
| 76 | 3,0 | 6,4 | 4,9 | 3,8 |
| 89 | 3,0 | 6,9 | 5,3 | 4,1 |
| 108 | 3,5 | 8,3 | 6,4 | 4,9 |
| 133 | 4,0 | 9,6 | 7,4 | 5,6 |
| 159 | 4,0 | 10,4 | 8,0 | 6,1 |
| 219 | 4,0 | 12,8 | 9,8 | 6,4 |
| 273 | 4,5 | 14,7 | 11,3 | 7,9 |
| 325 | 5,0 | 16,6 | 12,8 | 8,3 |
| 377 | 5,5 | 18,3 | 14,1 | 9,2 |
| 426 | 6,0 | 19,8 | 15,2 | 9,9 |
| 530 | 7,0 | 22,7 | 17,5 | 11,4 |
| 630 | 8,0 | 25,6 | 19,7 | 12,8 |
| 720 | 8,5 | 27,7 | 21,3 | 13,9 |
| 820 | 9,5 | 30,3 | 23,3 | 15,2 |
| 920 | 10,0 | 31,9 | 24,5 | 16,0 |
| 1020 | 11,0 | 33,6 | 25,8 | 16,8 |
The distances between the supports of steel pipelines with equal wall sizes are determined by the diameter. The characteristics of the soil during underground installation also influence. In addition, when installing thermal routes in accordance with SNiP, the distance is affected by temperature deformation. For heating mains, only movable supports are used in order to create an installation offset to compensate for thermal expansion.
Some tips
When choosing consoles and fasteners, remember these instructions:
- Choose with a margin of safety, taking into account the load.
- The product must be certified and with a warranty card or receipt indicating the replacement period.
- Check the factory packaging against the list of components and parts. Instructions are required.
Fastening rules and technology
Installation of sewer pipeline holders requires compliance with certain fastener installation rules and technological conditions.
- The attachment points are determined directly near the socket connections and branches in order to increase the rigidity of the pipeline (pictured).
- The installation of fixed fasteners is alternated with floating ones. At the same time, it is taken into account that between rigid fastening units the rules allow the placement of no more than two movable compensating connections.
- The distance and distance between rigid and movable holders must also comply with the standards. Thus, rigid supports on polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 110 mm are attached at a distance of no more than 2 m, floating ones - at a distance of no more than 10 branch diameters.
- On horizontal sections of the sewer system, the slope should be 20 mm for each meter of communication.
To Wall
Installation of fasteners is carried out in the following sequence.
- Using the wiring diagram, mark fixation points on the wall taking into account technological requirements.
- Installation begins from the bottom of the riser, where a fixed support is installed. Subsequent fasteners are made in such a way as to ensure alignment and verticality of all segments.
- When the riser is installed correctly, its deviation from the vertical axis should not be more than 2 mm per meter of pipe.
- Further fixation of the pipeline to the wall surface is done with clamps or clips (if the cross-section of the bends does not exceed 50 mm).
- Plastic and metal clamps are fastened using a self-tapping screw or metal pin with a fastening pitch for polypropylene bends - 2 m, metal-plastic - 1.5 m, steel - 1 m.
- In critical places where heavy elements of the system are located, rigid supports are used.
- Brackets are used to provide distances from the wall of waste pipes.
To the ceiling
Installation of sewer outlets along the ceiling is carried out in the basement and is carried out using the same methods.
Features are:
- Fixing clamps with anchors.
- The use is mainly of floating supports.
- Use of hanging fastener with strap.
- Minimum distance between holders.
To the floor
As a rule, cast iron sewer pipes are not attached directly to the floor. Polymer ones, in contrast, can become deformed and sag, which will affect the slope. If it is not possible to attach them to the wall, they are attached to the floor using plastic clips and galvanized screws.
According to building codes, laying sewer outlets in the floors of residential and administrative premises is not allowed. In other places, it is possible to carry it along the floor using hidden wiring in the concrete screed.
Installing waste pipes along the floor is practiced in bathhouses, where they discharge wastewater into drainage pits.
In the basement
The basement is an unheated room. There is a high temperature difference here and the problem of thermal expansion requires resolution. Fixed supports in basements and technical undergrounds of buildings alternate with floating fasteners.
Fastenings often have to be made along the floor and to the ceiling; for this, various types are used: clamps with studs, hangers with punched tape, plastic holders with galvanized screws.
Why do we need supports for pipelines?
In an ordinary nine-story residential building, if you connect the pipelines in one line, they will stretch for more than one kilometer. This is a lot of weight, and it must be securely fastened to the erected structures so that they can be accessed for repair or replacement, and so that they do not break off the brackets or rupture under their own weight.
Therefore, special fasteners are required to install the pipeline on external systems. Previously, steel pipe brackets, especially those with larger diameters, were used for industrial wiring. Galvanized ones are suitable for apartment wiring; they are laid in basements on U-shaped racks.
The lighter ones were hung on duralumin brackets nailed to strong metal parts of the building or on dowels driven into the concrete walls of basements. If this is a production facility with vibration, then choose a pipe bracket with a rubber seal.
Modern and not very heavy PVC piping material requires both simple and lightweight, but equally durable plastic pipe brackets.
The market for fastening materials is filled with numerous products in an assortment from domestic and foreign companies. And there is still more demand for brackets. At the same time, they became much lighter without losing the strength of the metal. It has become more resistant to the humid environment of hot and cold water pipelines and central heating.
They did not lose strength characteristics, and acquired some new ones. For example, their coating (galvanization, painting with moisture-resistant paints) makes their service life much longer than previously simply made of black unalloyed metal. You can see what they look like in the photo of pipe brackets - both old and new designs.
For central coolant supply pipelines to apartments, there are brackets for heating pipes. The fasteners on them have a thermal break so that the pipes do not warp at 75 degrees.
Kinds
Depending on the design, the following types of brackets for chimneys are distinguished:
Starting
This is the most durable and powerful type - the entire chimney rests on it. Usually it is made of two cantilever triangles made of a durable metal profile with a wall thickness of 1-3 mm. From the wall side and from the street side they are connected by jumpers, giving additional rigidity to the structure. A support platform with a cutout for inspection and a tap for draining condensate is attached to the top. Sometimes, instead of a platform, another jumper is used, and the lower edge of the pipe rests on a square contour.
Chimney support bracket
Wall (wall)
These are lighter structures, they do not carry a weight load, their function is limited to fixing the vertical position of the pipe. They are a split ring and a lightweight cantilever structure connecting the clamp and the wall mounting panel.
Manufactured by stamping and welding from stainless steel, galvanized or painted ferrous metal.
At a small distance from the wall (up to 100 mm), a metal plate located perpendicular to the wall can be used to connect the ring to the mount. Part of the split ring is welded to a semicircular cutout in this plate, and the other end of the plate is bent and attached to the wall.
At a large distance, the ring is attached to the plate with two consoles made of metal profiles.
Wall bracket for chimney
Telescopic
In such designs, you can change the distance from the ring to the wall; one square profile tube can move inside another. Such brackets are very convenient for installing a chimney on a wall made of solid logs and on other uneven surfaces. After adjusting the extension of the tube, they are fixed with a bolt and nut. A telescopic pipe mount is less reliable than an all-welded one, so they have to be made from a profile of a larger cross-section.
Telescopic pipe mount
Heels
Lightweight budget mount. It uses a standard pipe clamp welded to a threaded rod. The pin is wrapped into a wooden wall or into a dowel. Due to the single point of attachment to the wall, rigidity and ability to withstand wind loads are reduced.
Bracket with studs
Console
This mounting option does not use crimp rings or clamps; the chimney is attached to a pair of cantilever guides. With this method of fixation, the ability to withstand lateral wind loads is reduced. Recommended for budget-friendly starting fastening of indoor chimneys. fastenings
Features of use
Pipes of medium diameter are placed on the brackets. They are equipped with clamps and other products that stabilize the position of pipes on shelves.
The brackets have several advantages. For example, the simplicity of both their installation and the pipelines on them. Even a person installing such installations for the first time can cope with this. Further, consoles for pipelines are for long-term use. Increasingly, they are sold with nickel plating or phosphating of the surface - against corrosion of low-alloy steel.
Convenient methods for attaching brackets to a brick or concrete wall have also been developed. A strong bolt is screwed into it to a depth of three centimeters or dowels are driven in with a pistol. Pipes are fastened to the horizontal either with clamps on bolts or by holding them with rivets.
The size of the console shelf is set either by the project or, with additional pipe laying, depending on their purpose, the thickness of the heat-insulating layer.
The principle of attaching pipes to the wall
Now let's look at how to attach heating pipes to the wall. There are two ways to accomplish this task: hard and floating. The first is intended for sewers, heating systems and other pipelines through which hot or cold water will be transported. In this case, the fastenings completely fix the movement of communication elements. The fitting here is a rigid support.
Floating mounts most often use clamps that are not tightened all the way. In this case, slight mobility of the system elements is maintained. This fastening option is only possible if the inner diameter of the clamp is larger than the outer diameter of the pipe.
The movable option is used in case of possible temperature changes. After all, then it is possible to expand or narrow the pipes. And loose clamps give them the ability to change sizes while remaining in place. As has already become clear, the choice of fastening option depends on the purpose of the pipeline, as well as possible temperature fluctuations.
Advantages of steel clamps
The steel pipe clamp for the water supply system is characterized by the following advantages:
- Versatility. Using rings and brackets, you can fix different types of pipelines.
- Easy installation.
- Low cost.
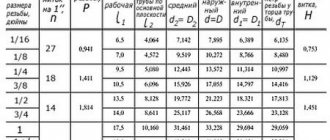
All products have an anti-corrosion coating, which makes the external surface more attractive and extends the service life of the part. Clamps are produced according to a certain standard. In this document you can familiarize yourself with the main characteristics of the products:
- The greatest load that the fastener can withstand.
- Maximum tightening value.
- Optimal indicators of the width and thickness of the tape.
- Product diameter.
- Composition of the material from which the clamp is made.
Clamps can be not only of the fastening type; repair plumbing clamps with rubber seals are in great demand. These parts help to quickly troubleshoot the system without stopping the flow of the working fluid or draining it.